Mycotoxin colorimetric sensing method based on fluorescent metal-organic framework material
A metal-organic framework and mycotoxin technology, applied in the field of agricultural product and food quality testing, can solve the problems of poor water stability and unfavorable rapid detection of mycotoxins, and achieve the effects of good dispersion, improved sensitivity and uniform particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
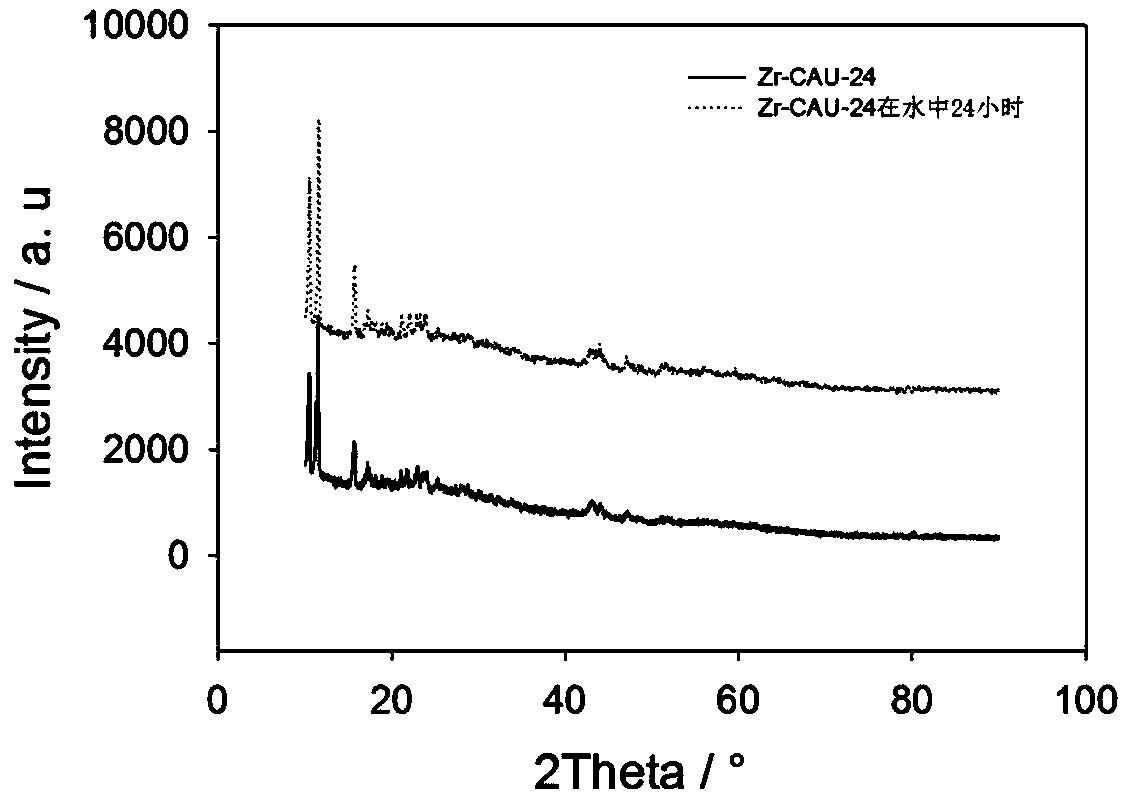
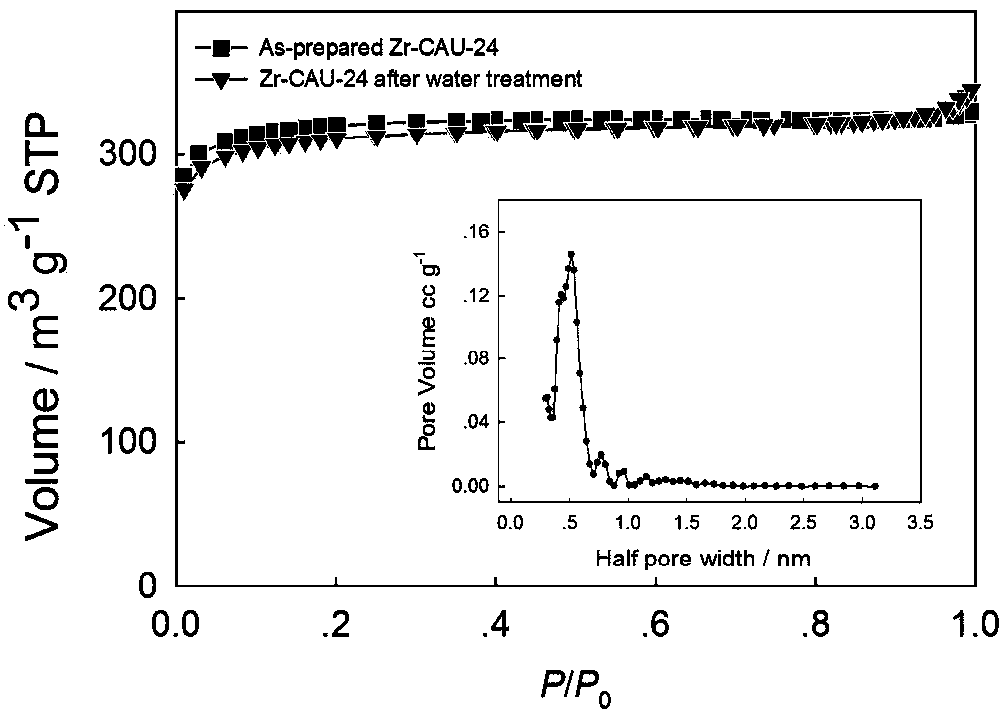
[0048] 175mg ZrCl 4 , 125mg H 4 TCPB ligand and 6.3g structure regulator benzoic acid were dissolved in 40mL DMF solution. The mixed solution was ultrasonicated for 15 min to mix the solution thoroughly. The dispersion liquid was packaged in a 100 mL quartz reactor, and a cloudy liquid containing Zr-TCPB was obtained after continuous heating at 120° C. for 24 hours. After natural cooling at room temperature, wash with methanol centrifugation three times at a centrifugation speed of 6000 rpm. Place the washed product in CH 2 Cl 2 for 24 hours to replace the remaining DMF molecules in the pores. After centrifuging again, the product was dried in an oven at 60° C. for 24 hours to obtain a white powder, which was the activated fluorescent Zr-TCPB material. Appearance: as figure 1 As shown, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy can be used to see that the prepared nanomaterials are rod-like structures with a size of 1 μm. Further observations show...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Add AFB to walnut dew sold on the market 1 , to verify the application of this colorimetric method in actual detection. Add 100uL 1mM AFB to 10mL walnut dew 1 Methanol solution to make 10μM AFB 1 walnut dew, and then serially diluted to 10 μM, 1 μM and 0.1 μM spiked samples. Adopt embodiment 1 to prove the detection method in 1 to the AFB in the standard sample 1 to test. As shown in Table 1, by demonstrating with Example 1 that AFB in 1 1 Comparing the standard response curves, the calculated concentrations of the 0.1 μM, 1 μM and 10 μm spiked samples were 0.0975, 0.079 and 9.73 μM, respectively. By comparing with the standard detection method high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) ( Figure 9 ), Figure 9 (a), (b), and (c) are the detection results of 0.1 μM, 1 μM, and 10 μM aflatoxin B1 in walnut milk, respectively; (d), (e), and (f) are 0.1 μM, 1 μM in almond milk, respectively , 10μM aflatoxin B1 detection results.
[0091] Figure 9 It can be seen...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Add AFB to almond milk sold in the market 1 , to verify the application of this method in practical detection. Add 100uL 1mM AFB to 10mL almond milk 1 Methanol solution to make 10μM AFB 1 walnut dew, and then serially diluted to 10 μM, 1 μM and 0.1 μM spiked samples. Adopt embodiment 1 to prove the detection method in 1 to the AFB in the standard sample 1 to test. As shown in Table 1, by demonstrating with Example 1 that AFB in 1 1 Comparing the standard response curves, the calculated concentrations of 0.1 μM, 1 μM and 10 μM spiked samples were 0.0966, 1.041, and 9.06, respectively. By comparing with the standard detection method high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) ( Figure 9), it was found that the reproducibility rates of the standard sample added by this method were 102.1, 108.8 and 93.3 respectively, which had a high reproducibility rate and could meet the requirements of rapid and sensitive detection in practical applications.
[0096] In summary...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com