One-pot bioconversion method of lignocellulose
A lignocellulose and biotransformation technology, applied in the field of lignocellulose biotransformation and lignocellulose saccharification field, can solve the problems of high cost, poor technical matching, serious pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
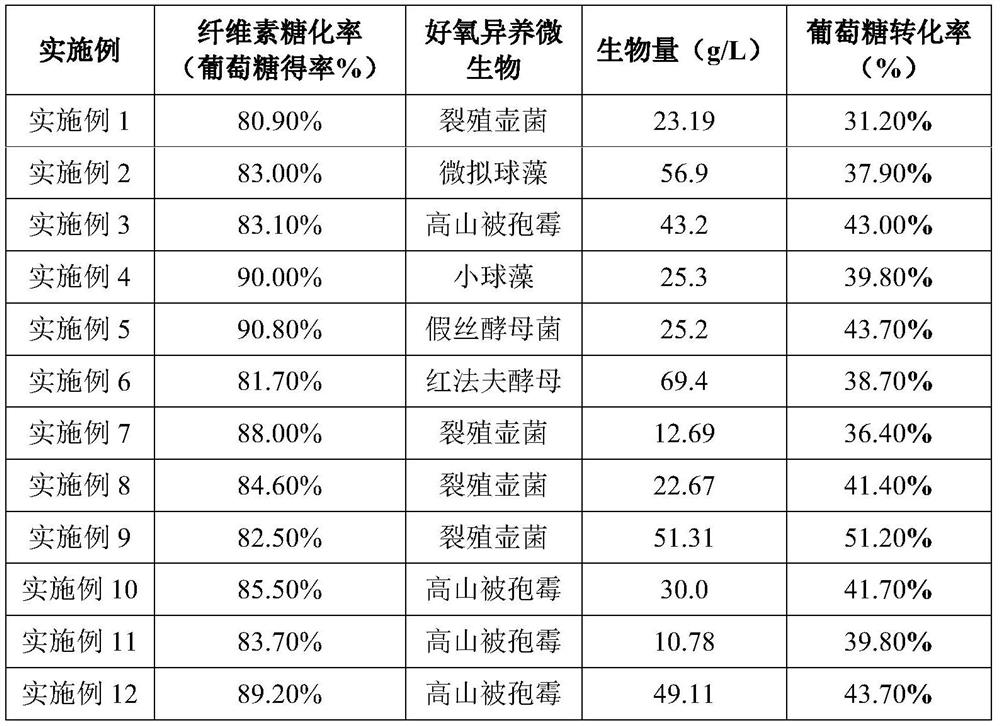
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Lignocellulose one-pot bioconversion method
[0030] A method for one-pot biotransformation of lignocellulose, comprising the following steps:
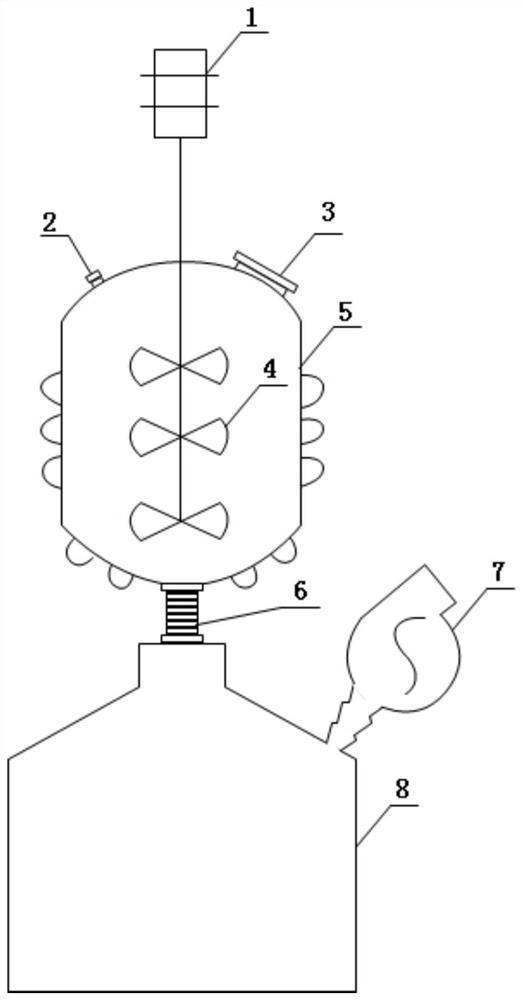
[0031] (1) Mechanical treatment: mechanically pulverize the corn stalks until the particle size of the fragments does not exceed 2cm; wash with water, then put it into the closed reactor from the feeding port above the closed reactor, and add it according to the solid-liquid weight volume ratio of 1:2 water, mix evenly, and soak for 4 hours.
[0032] (2) Chemical treatment: Ammonium sulfite was added into the closed reactor until its final concentration was 11% (w / v), and sulfonation treatment was carried out at 175° C. for 3.5 hours. After the reaction is completed, the discharge port at the bottom of the closed reactor is opened to allow the black liquor to flow out into the storage tank through the filter device equipped at the discharge port; the storage tank is connected to the closed reactor through a pipel...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: Lignocellulose one-pot bioconversion method
[0040] Different from Example 1, the method for one-pot bioconversion of lignocellulose comprises the following steps:
[0041] (1) Mechanical treatment: Mechanically pulverize the wheat straw until the particle size of the fragments does not exceed 2cm; wash with water, then put it into the closed reactor from the feeding port above the closed reactor, and add water according to the solid-liquid weight volume ratio of 1:3 , mix evenly, soak for 2-4h.
[0042] (2) Chemical treatment: Ammonium sulfite was added into the closed reactor until its final concentration was 12% (w / v), and sulfonation treatment was carried out at 180° C. for 4 hours. After the reaction is completed, the black liquor is flowed into the storage tank until the water content of the material in the closed reactor reaches 30%-50%, and the discharge port is closed.
[0043] (3) Material cleaning: add water of 1 times the material volume in ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3: Lignocellulose one-pot bioconversion method
[0050] Different from Example 1, the method for one-pot bioconversion of lignocellulose comprises the following steps:
[0051] (1) Mechanical treatment: Mechanically crush the shrub branches until the particle size of the fragments does not exceed 2cm; wash with water, and then put it into the closed reactor from the feeding port above the closed reactor, according to the solid-liquid weight volume ratio of 1:4 Add water, mix well, soak for 2-4h.
[0052] (2) Chemical treatment: Ammonium sulfite was added into the closed reactor until its final concentration was 13% (w / v), and sulfonation treatment was carried out at a temperature of 185° C. for 1 hour. After the reaction is completed, the black liquor is flowed into the storage tank until the water content of the material in the closed reactor reaches 30%-50%, and the discharge port is closed.
[0053] (3) Material cleaning: add water of 1.5 times the mater...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com