Phosphating process for phosphating layer on neodymium-iron-boron surface
A NdFeB technology, applied in the field of phosphating process, can solve the problems of low porosity, corrosion resistance and insufficient corrosion resistance of phosphating film layer, so as to achieve low porosity, avoid magnetic performance decline, and process stability controllable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] In this implementation case, the composition of the phosphating solution is: magnesium oxide 4g / L, phosphoric acid 28mL / L, sodium borate 4g / L, and NaOH is used to adjust the pH of the phosphating solution to 4.8.
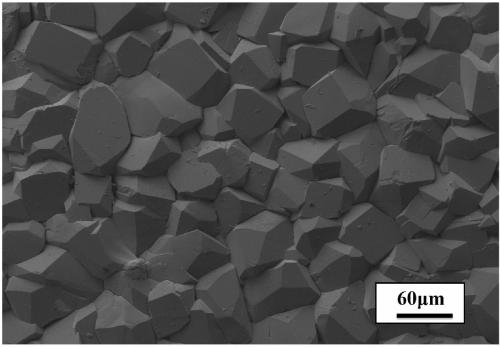
[0027] After derusting and cleaning the NdFeB substrate, the cathode direct current electrodeposition method is used to prepare the surface phosphating film layer, and the cathode current density is 4A / dm 2 , the temperature of the phosphating solution is 80°C, and the phosphating time is 0.5 hours. After phosphating, wash and dry. The film weight after phosphating is about 12g / m 2 , the color is off-white. its microscopic appearance figure 1 , the grain size is uniform, and there are no pores between the grains. The copper sulfate spot test (QB / T3824-1999) time of the prepared phosphating film layer is more than 120 seconds, and the antirust effect is more than 13 months.
Embodiment 2
[0029] In this implementation case, the composition of the phosphating solution is: magnesium oxide 3g / L, zinc dihydrogen phosphate 2g / L, triphosphoric acid 2mL / L, sodium borate 8g / L, glycine 0.2g / L, dodecylbenzenesulfonate Sodium acid 2g / L, sodium citrate 15g / L. And adjust the pH of the phosphating solution to 4.5 with NaOH.
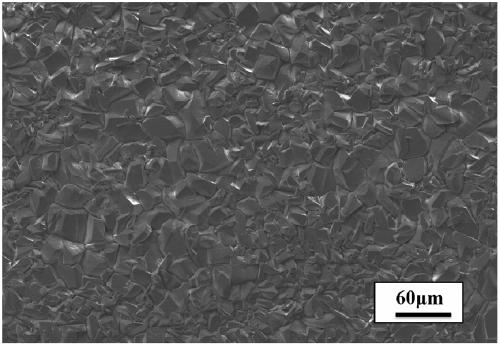
[0030] After derusting and cleaning the NdFeB substrate, the surface phosphating film layer is prepared by cathodic direct current electrodeposition, and the cathodic current density is 3A / dm 2 , the temperature of the phosphating solution is 65°C, and the phosphating time is 1 hour. After phosphating, wash and dry. The film weight after phosphating is about 19.7g / m 2 , the color is off-white. its microscopic appearance figure 2 , the grain size is uniform, and there are no pores between the grains. The copper sulfate spot test (QB / T3824-1999) time of the prepared phosphating film layer is longer than 150 seconds, and the antirust effect is longe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| film density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| film density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com