A system for generating a medium-wave infrared laser output with a wavelength of not less than 3.8 microns by using a laser differential frequency technology
An infrared laser and laser technology, which is applied in the direction of lasers, laser components, and the structure/shape of the active medium, can solve the problem of high pump peak power requirements, and achieve compact structure, high optical frequency conversion efficiency, and reduced complexity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
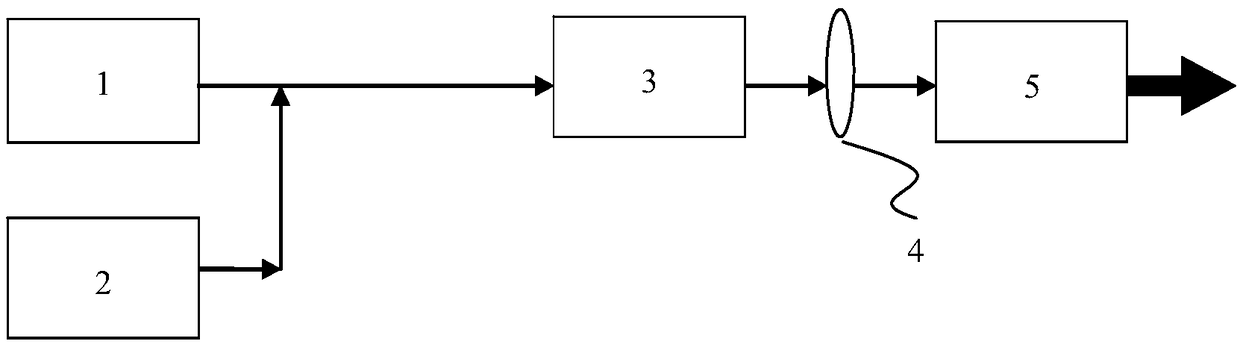
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, a system that uses laser difference frequency technology to generate mid-wave infrared laser output with a wavelength of not less than 3.8 microns, including an ytterbium-doped fiber laser 1 with a wavelength range of 1093-1105nm, and an erbium-doped fiber laser with a wavelength range of 1535-1540nm 2. Fiber beam combiner 3, optical lens 4, nonlinear laser crystal 5, ytterbium-doped fiber laser 1 as a pump source, erbium-doped fiber laser 2 as a signal source, nonlinear laser crystal 5 as an optical frequency conversion device, continuous or The pulsed ytterbium-doped fiber laser 1 and erbium-doped fiber laser 2 respectively output two single-wavelength lasers, which are combined by the fiber beam combiner 3 and then focused by the optical lens 4 to the nonlinear laser crystal 5, using laser difference frequency technology Generate mid-wave infrared laser output with a wavelength not less than 3.8 microns.
[0021] Wherein, the optical fiber...
Embodiment 2
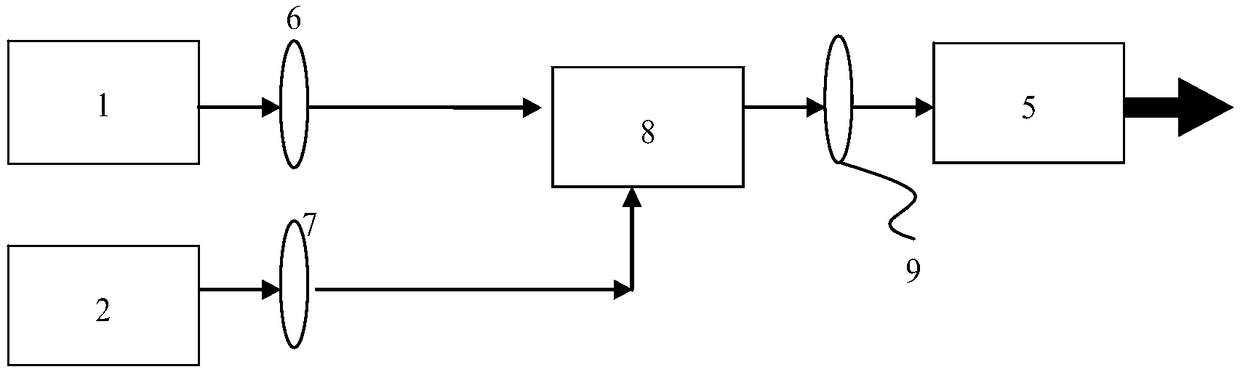
[0023] Such as figure 2 As shown, a system that uses laser difference frequency technology to generate mid-wave infrared laser output with a wavelength of not less than 3.8 microns, including an ytterbium-doped fiber laser 1 with a wavelength range of 1093-1105nm, and an erbium-doped fiber laser with a wavelength range of 1535-1540nm 2. The first optical lens 6, the second optical lens 7, the spatial beam combiner 8, the third optical lens 9, the nonlinear laser crystal 5, the ytterbium-doped fiber laser 1 as the pump source, and the erbium-doped fiber laser 2 as the signal source, The nonlinear laser crystal 5 is used as an optical frequency conversion device, and the continuous or pulsed ytterbium-doped fiber laser 1 and the erbium-doped fiber laser 2 respectively output two single-wavelength lasers, which pass through the first optical lens 6 and the second optical lens 7 respectively. After collimation, the beams are combined by the spatial beam combiner 8, and then focus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com