Method for recycling extracellular polymers and removing heavy metal ions from excess sludge
A technology of extracellular polymers and heavy metal ions, which is applied in the field of extracellular polymer recovery and heavy metal ion removal in excess sludge. It can solve the problems of narrow applicable pH range, difficult separation of extracellular polymers, and large consumption of raw materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
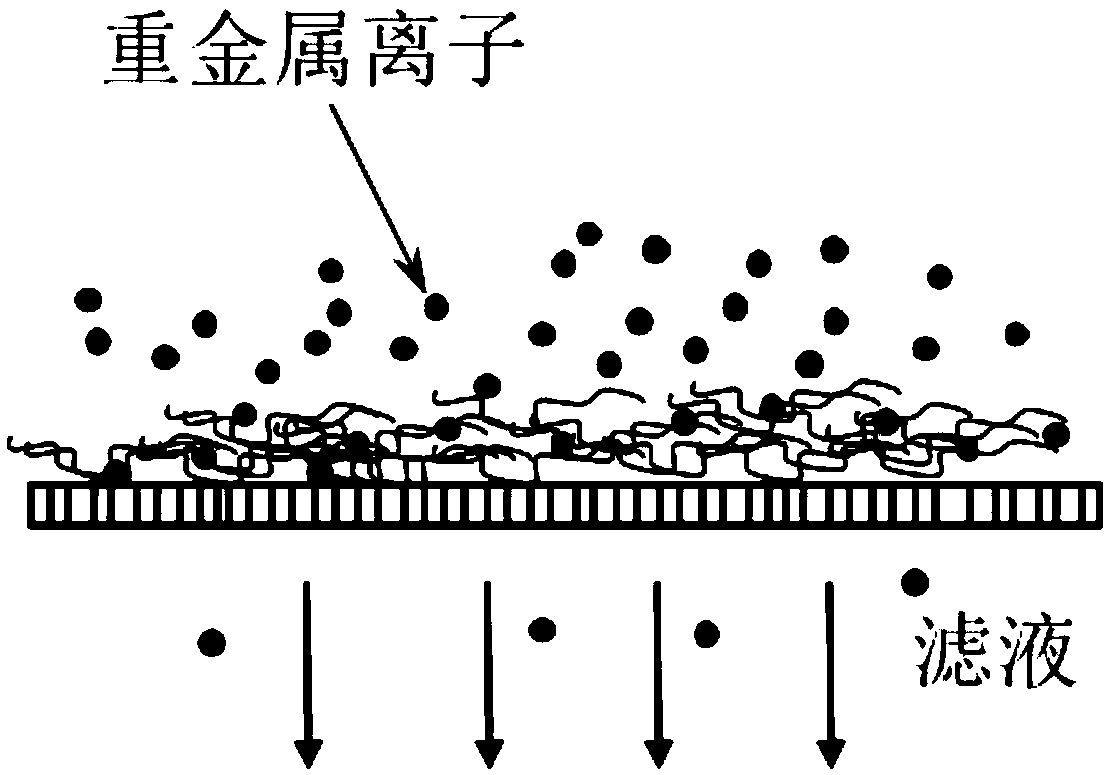
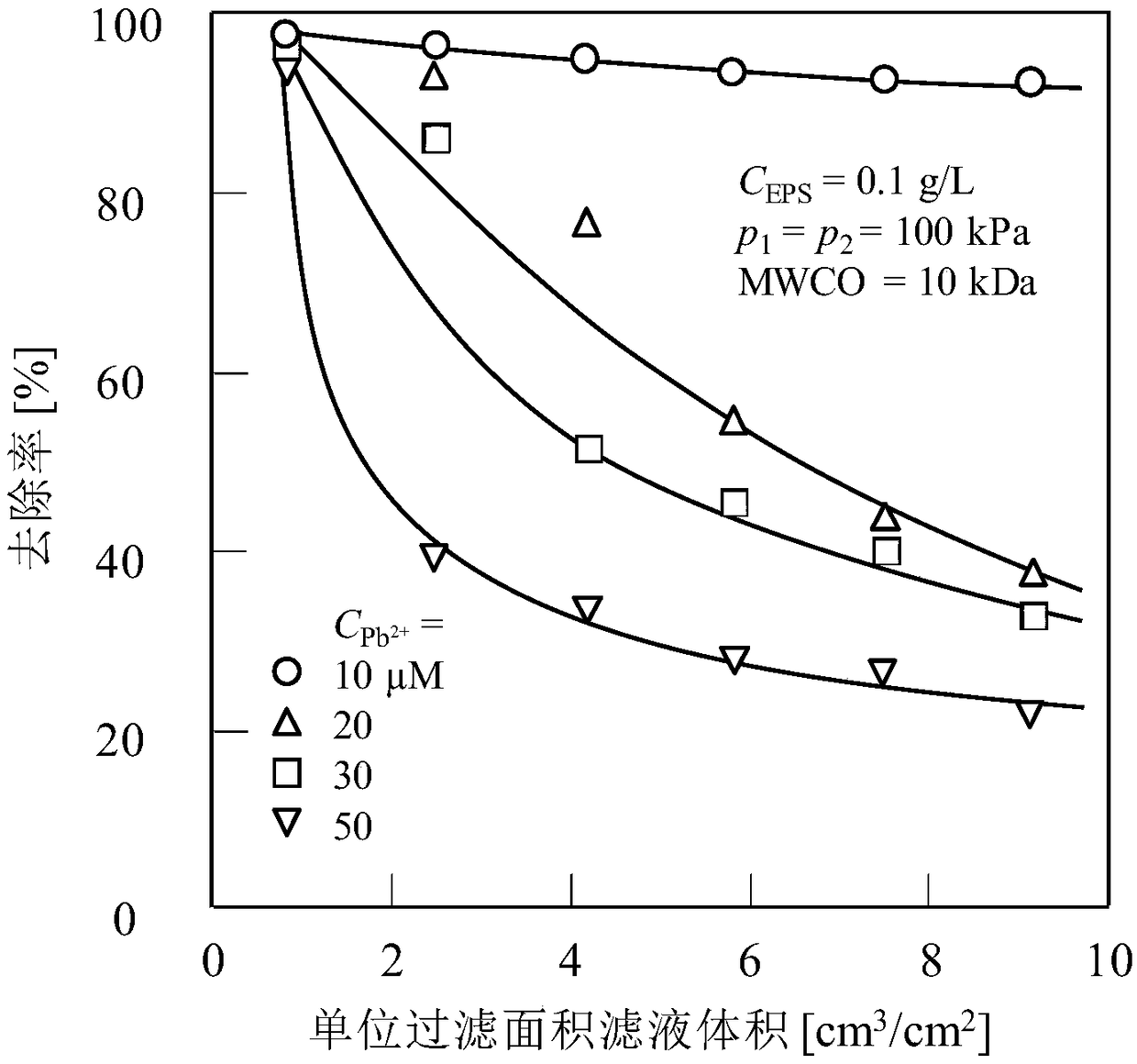
[0039] image 3 It shows that when the dead-end filter cake membrane filtration method is adopted, the Pb concentration at different initial concentrations will increase with the filtration. 2+ change in the removal rate. It can be seen from the figure that at a certain amount of extracellular polymer filter cake (100mL, 0.1g / L extracellular polymer solution at filtration pressure p 1 = filter cake formed when filtering at 100kPa) In the case of filter cake membrane filtration on Pb 2+ The removal rate is a function of the initial concentration, with the Pb 2+ Concentration increased, showing a downward trend; but when dealing with Pb 2+ When the concentration is 10μM, although the removal rate decreases continuously with the filtration, the removal rate still remains above 90%. Due to the certain adsorption sites of extracellular polymer filter cake, the higher the Pb 2+ The initial concentration showed a correspondingly lower absolute removal rate. With continuous membr...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Figure 4 It shows that the filtration membrane with extracellular polymer filter cake layer (also referred to as filter cake membrane) formed by 100mL extracellular polymer solution with a concentration of 0.1-0.5g / L has an initial concentration of 10μM Pb 2+ solution removal rate. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that when the concentration of the extracellular polymer solution is greater than or equal to 0.2g / L, along with the filtration (until the filtrate volume per unit filtration area is 10cm), the Pb 2+ The removal rate is constant and maintained above 99%; it shows that the concentration of the extracellular polymer that forms the extracellular polymer filter cake layer is increased, that is, the amount of extracellular polymer in the extracellular polymer filter cake layer is increased (sorbent quality), can significantly increase the Pb 2+ This also shows that the coupling technology of extracellular polymer recovery and heavy metal ion removal of the pr...
Embodiment 3
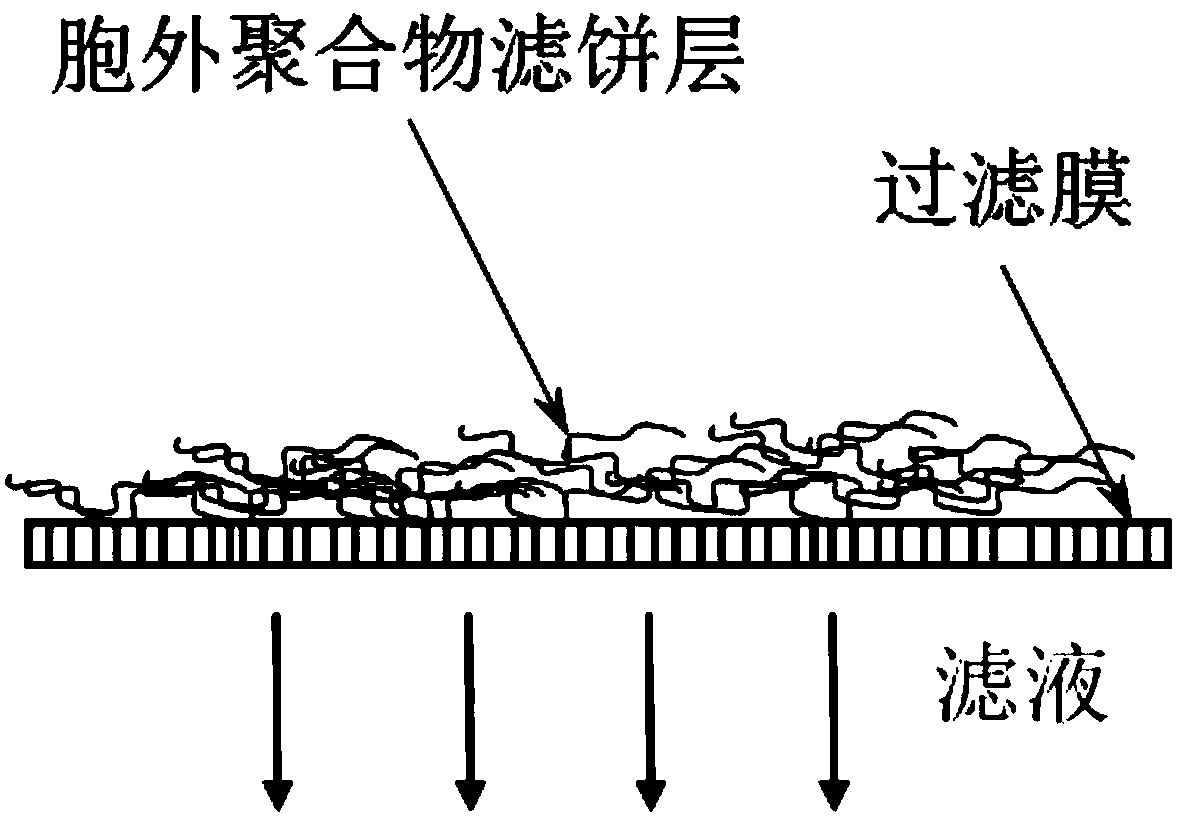
[0043] The present invention is passing through the filter membrane that has extracellular polymer filter cake layer in carrying out concentration recovery process, such as figure 1 As shown, the filtration rate of the filter membrane with the extracellular polymer filter cake layer decreased significantly (ie, the fouling of the filter membrane was serious). In order to reduce the fouling of the filter membrane (filter resistance of the filter membrane), calcium ions (Ca 2+ )Methods. Figure 5 The filtration behavior of the extracellular polymer solution along with the filtration is shown when adding and not adding calcium ions, where the abscissa is the volume of liquid filtered per unit filtration area, and the ordinate is the reciprocal of the filtration speed (the larger the value, the The smaller the filtration speed); the results showed that the decline of filtration speed was significantly slowed down when calcium ions were added, that is, the filtration resistance wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com