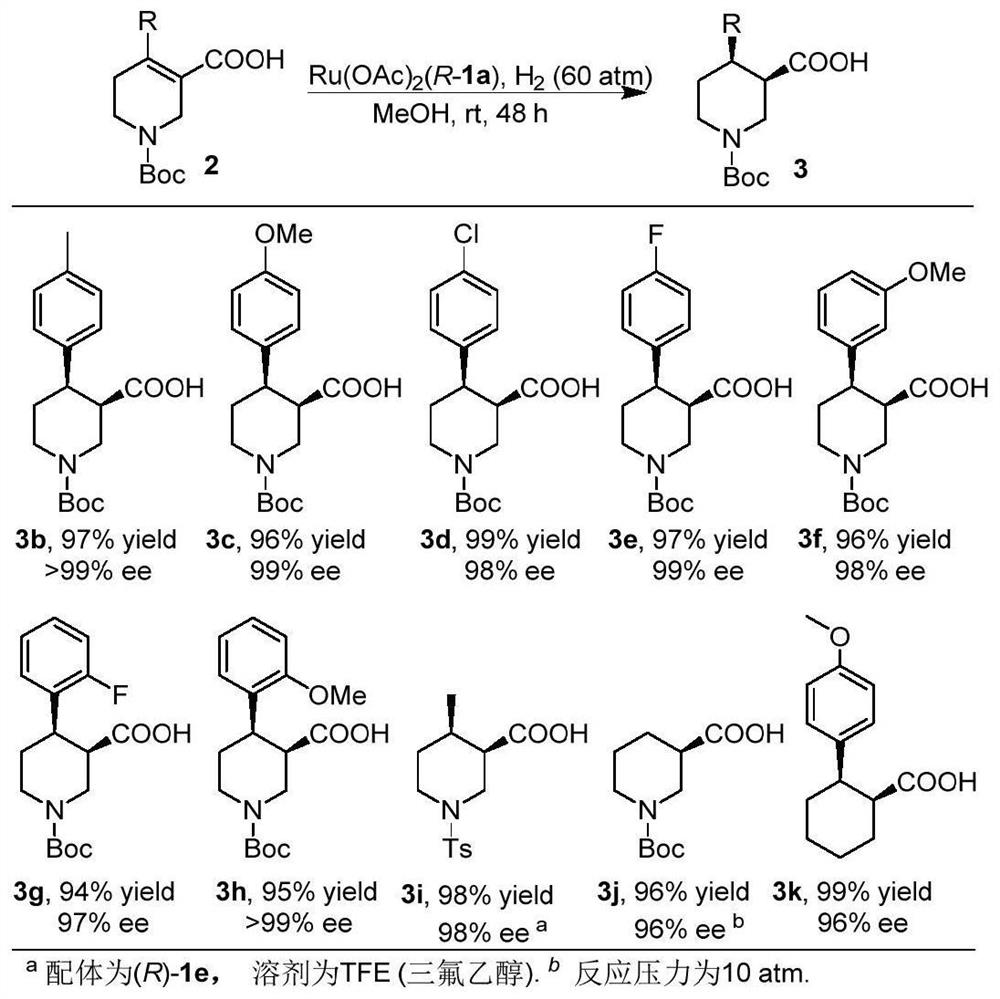
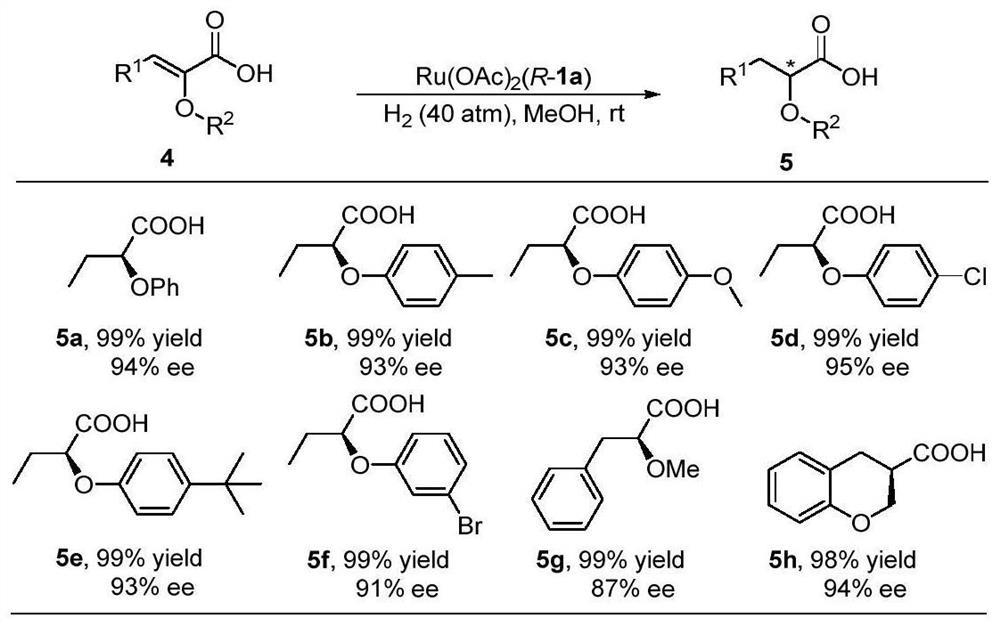
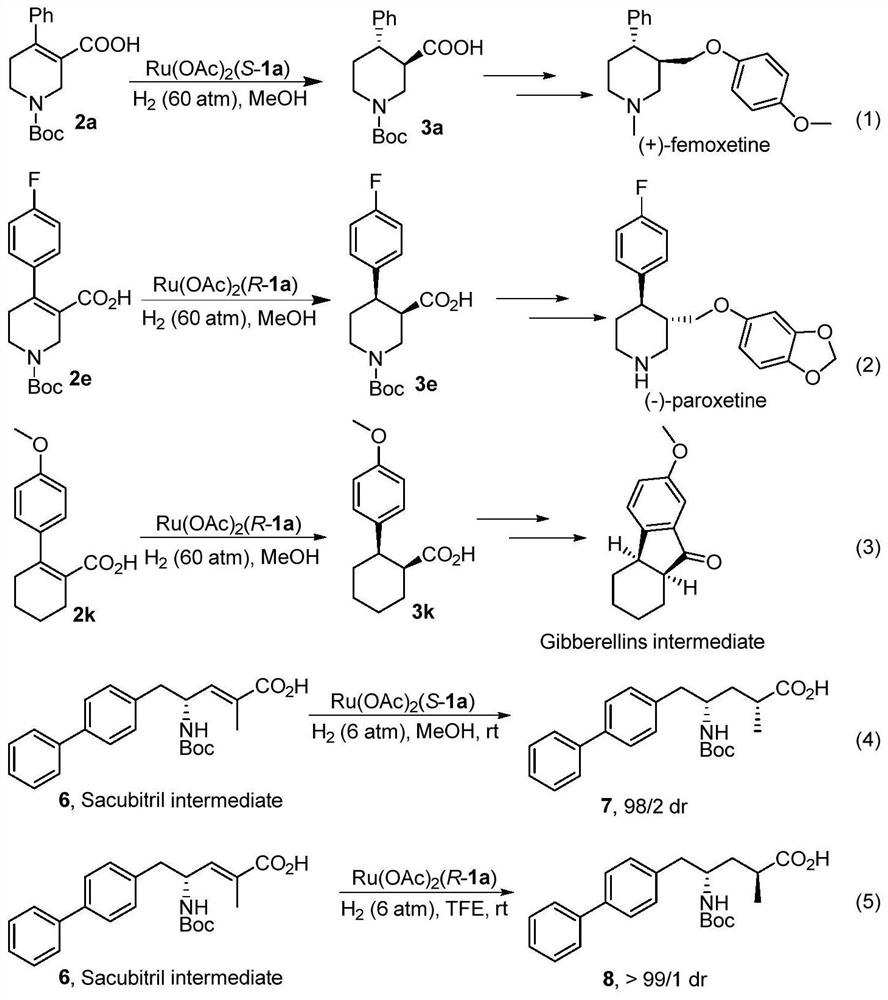
Oxaspirobisphosphine Ligands and Their Applications in Asymmetric Hydrogenation of α,β-Unsaturated Carboxylic Acids
An oxaspiro and asymmetric technology, applied in the field of oxaspirocyclic bisphosphine ligands, can solve the problems of narrow application range, no reactivity of cyclic tetra-substituted carboxylic acids, lack of chiral bisphosphine ligands, etc. High enantioselectivity, high activity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Catalyst Rh(1a)OAc 2 Preparation of:
[0052] in N 2 Under atmosphere, add [RuPhCl 2 ] 2 (25 mg, 0.05 mmol), ligand 1a (61 mg, 0.103 mmol), and then 2 mL of DMF was added. React at 100°C for 3h. After cooling to room temperature, 1.5 mL of anhydrous sodium acetate (0.111 g, 1.3 mmol) in methanol was added. After 20Min, deoxygenated deionized water was added. A gray solid precipitated from the reaction system, filtered, and the solvent and water were removed under reduced pressure to obtain the catalyst Rh(1a)OAc 2 (57 mg, yield = 71%).
Embodiment 2
[0054] Catalyst Rh(1a)(CF 3 CO) 2 Preparation of:
[0055] in N 2 Under atmosphere, add bis-(2-methallyl) cyclooct-1,5-diene ruthenium (32mg, 0.05mmol), ligand 1a (61mg, 0.103mmol) to a 10mL single-necked bottle, and then add 2 mL of acetone. React at 40°C for 0.5h. Then add trifluoroacetic acid (33 mg, 0.3 mmol), stir overnight at 40 ° C, remove the solvent under reduced pressure, then add 1 mL of petroleum ether, and filter to obtain the target product Rh (1a) (CF 3 CO) 2 (81 mg, yield = 88%).
Embodiment 3
[0057] Synthesis of (3R,4R)-1-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-4-phenyl-3-carboxylic acid 3a:
[0058] in N 2 Under atmosphere, add 2a (0.1mmol), catalyst Ru(1a)OAc to the hydrogenation vial 2 (0.8mg, 0.001mmol) and 1mL of methanol. After 24 h under a hydrogen atmosphere of 60 atm, all the raw materials were converted into products. 29.0mg, product yield=95%,>99%ee, [α] 25 D =+38.0 (c=0.5, CHCl 3 ), yellow oil. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ7.29-7.24(m,2H,Ar),7.23-7.17(m,3H,Ar),4.44(d,J=12.7Hz,1H,CH 2 ), 4.26 (d, J=9.0Hz, 1H, CH 2 ), 3.16(d, J=11.1Hz, 1H, CH), 3.01-2.82(m, 3H, CH 2 ),2.55(dt,J=12.0,8.6Hz,1H,CH),1.68(dd,J=13.0,2.8Hz,1H,CH 2 ),1.39(s,9H,CH 3 ). 13 C NMR (101MHz, CDCl 3 )δ176.9, 154.7, 142.1, 128.3, 127.4, 126.6, 79.8, 46.1, 45.2, 43.8, 43.0, 28.2, 25.6. HRMS (ESI) calcd.for C 17 h 22 NO 4 [M-H] - :304.1554, Found: 304.1556.HPLC conditions: Daicel AD-3, injection volume 2μL (c=1mg / mL), Hexane / IPA=97 / 3, 1.0mL / Min, 208nm, t R (major) = 29.6Min,t R (minor) = 31....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com