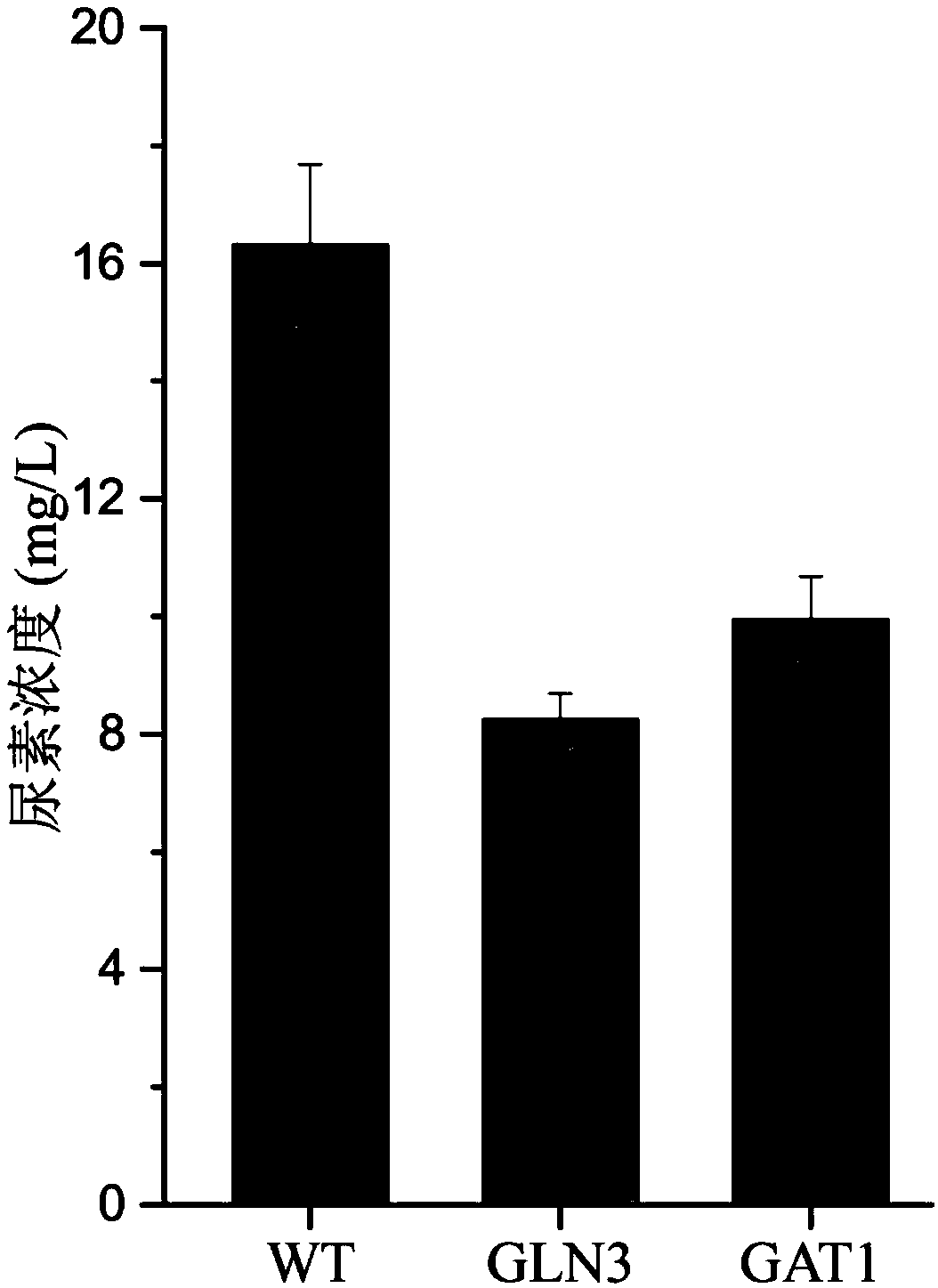
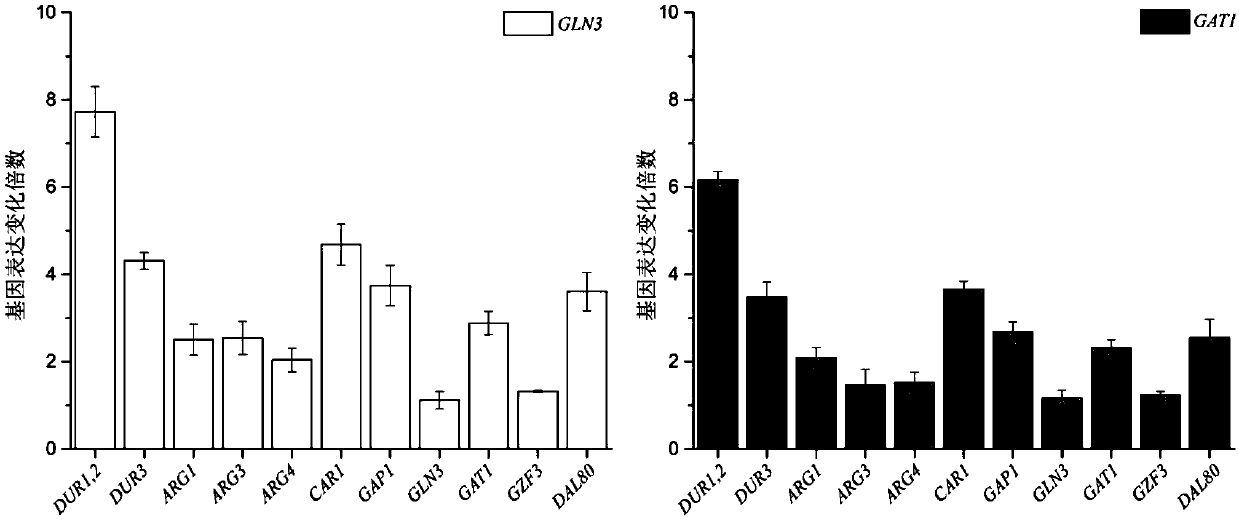
Method for reducing yellow wine yeast urea accumulation by regulating and controlling activating transcription factors
A technology of transcription activator and rice wine yeast, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems affecting the safety of rice wine products and achieve the effect of important industrial application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1 The construction of rice wine yeast suitable for rapamycin-mediated regulatory protein subcellular localization
[0030] (1) Split the diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain XZ-11 used for rice wine production to obtain haploid strains
[0031] According to the paper "Wu D H, Li X M, Shen C, et al.Isolation of a haploid from anindustrial Chinese rice wine yeast for metabolic engineering manipulation[J].Journal of the Institute of Brewing,2013,119(4):288-293 The method and steps described in the method and steps to obtain the haploid XZ-11a strain without resistance gene.
[0032] (2) Construction of auxotrophic haploid rice wine yeast JNZ01
[0033] Using the genome of rice wine yeast XZ-11 strain as a template, the upstream and downstream 300 bp sequences of the URA3 gene were respectively amplified, and the above two amplified fragments were fused by fusion PCR to obtain the URA3 gene knockout frame. The URA3 knockout frame was transformed into the XZ-11a...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Fusion PCR construction fusion expression GLN3, FKBP12 and GAT1, FKBP12 recombination cassette
[0043] (GGGGS) was first transformed by whole-plasmid PCR 3 After the linker was introduced into the BamH I site on the high-copy plasmid vector pRS426-TEF-URA3, pRS426-TEF-GS-URA3 was obtained. The FKBP12 protein whose N-terminus was fused with four SV40 nuclear localization sequences was obtained by gene synthesis, and cloned into the EcoR I and Xho I sites of the vector pRS426-TEF-GS-URA3 by restriction enzyme digestion to obtain pRS426-TEF-GS-SV40-FKBP12 -URA3. The 500 bp sequences without stop codon at the end of GLN3 and GAT1 were respectively amplified from the genome, and cloned into the Spe I and BamH I sites of the vector pRS426-TEF-GS-SV40-FKBP12-URA3 by restriction enzyme digestion, respectively, to obtain pRS426 - TEF-Gln3D-GS-SV40-FKBP12-URA3 and pRS426-TEF-Gat1D-GS-SV40-FKBP12-URA3. Then, PCR amplification was performed using the obtained plasmid ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 eliminates the CRISPR-Cas9 system plasmid
[0047] The positive transformants obtained by screening were subcultured in YPD medium (yeast extract 10g / L, peptone 20g / L, glucose 20g / L), and were transferred to fresh YPD medium with 10% inoculum after every 24 hours of cultivation. . At the same time of each transfer, the 5-FOA and 5-FAA plates (YNB 1.7g / L, ammonium sulfate 5g / L, glucose 20g / L, uracil 25mg / L, tryptophan 25mg / L, 5-FOA 1g / L, 5-FAA 1g / L, agar powder 20g / L) was streaked until transformants were obtained on 5-FOA and 5-FAA plates. It was verified by colony PCR that p426-Gln3sgRNA, p426-Gat1sgRNA and p414-TEF1p-Cas9-CYC1t had been eliminated in the transformants, and recombinant rice wine yeast JNZ02 (MATa, Δura3, Δtrp1, TOR1S1972R, Δfpr1, GLN3::FKBP12) and JNZ03 (MATa , Δura3, Δtrp1, TOR1S1972R, Δfpr1, GAT1::FKBP12).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com