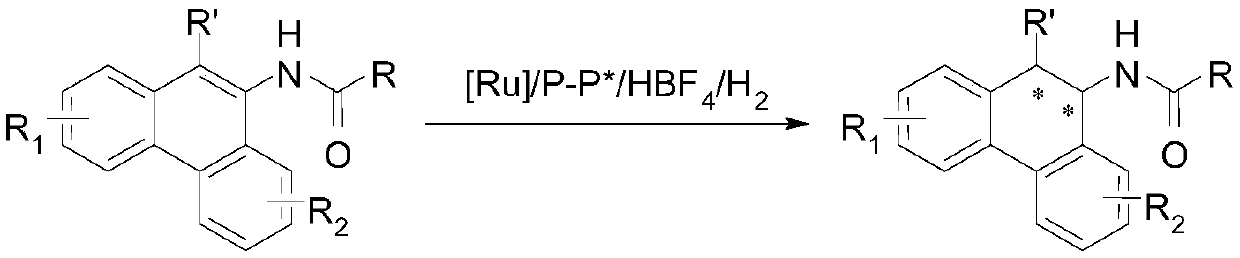Method for synthesizing chiral tertiary amine by asymmetric hydrogenation of arylamine compound under catalysis of ruthenium
An asymmetric and compound technology, applied in organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalysts, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemical methods, etc., to achieve high reactivity and enantioselectivity, convenient separation, and simple reaction operation practical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
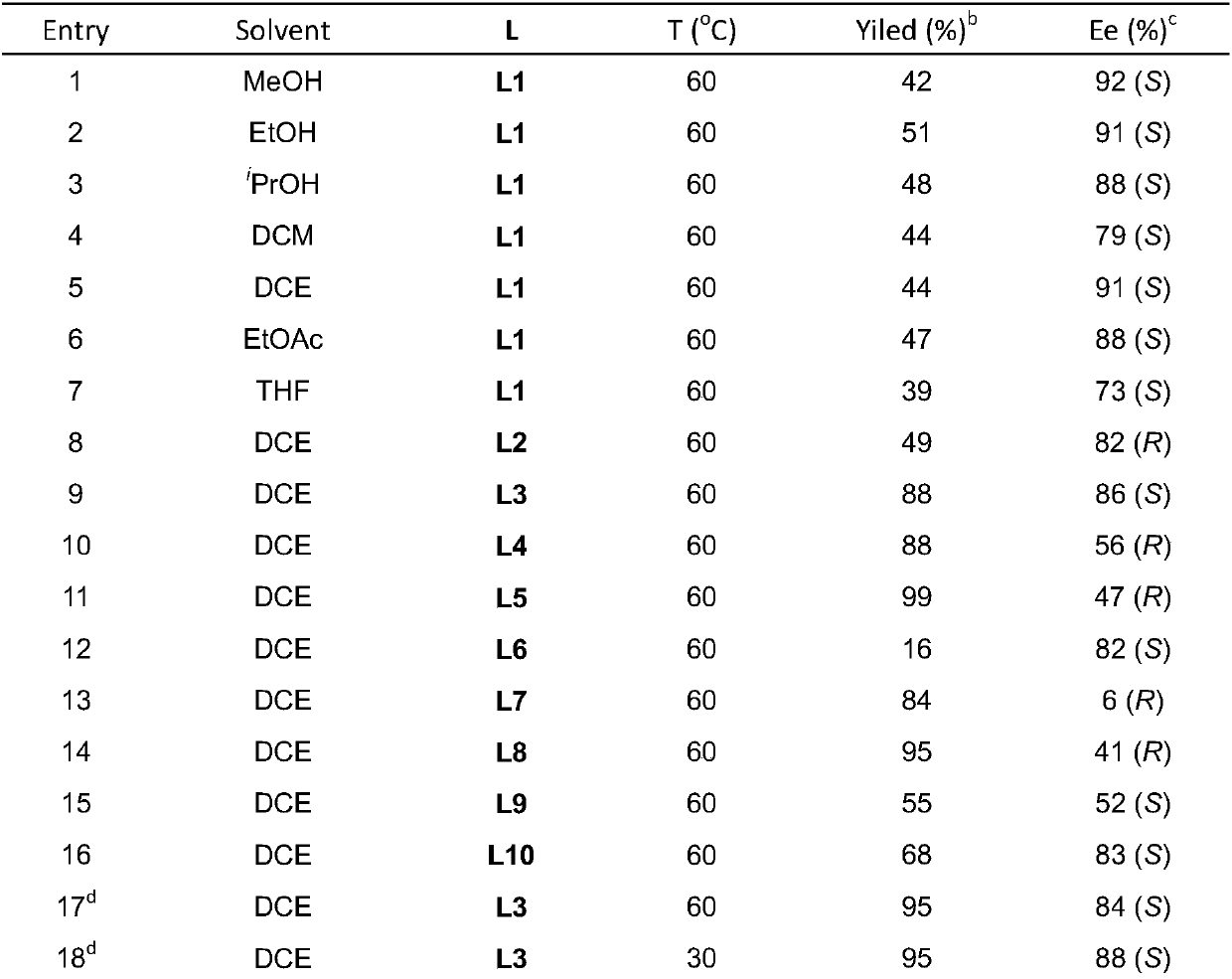
[0026] Embodiment 1: Optimization of reaction conditions for hydrogenation of monosubstituted substrates
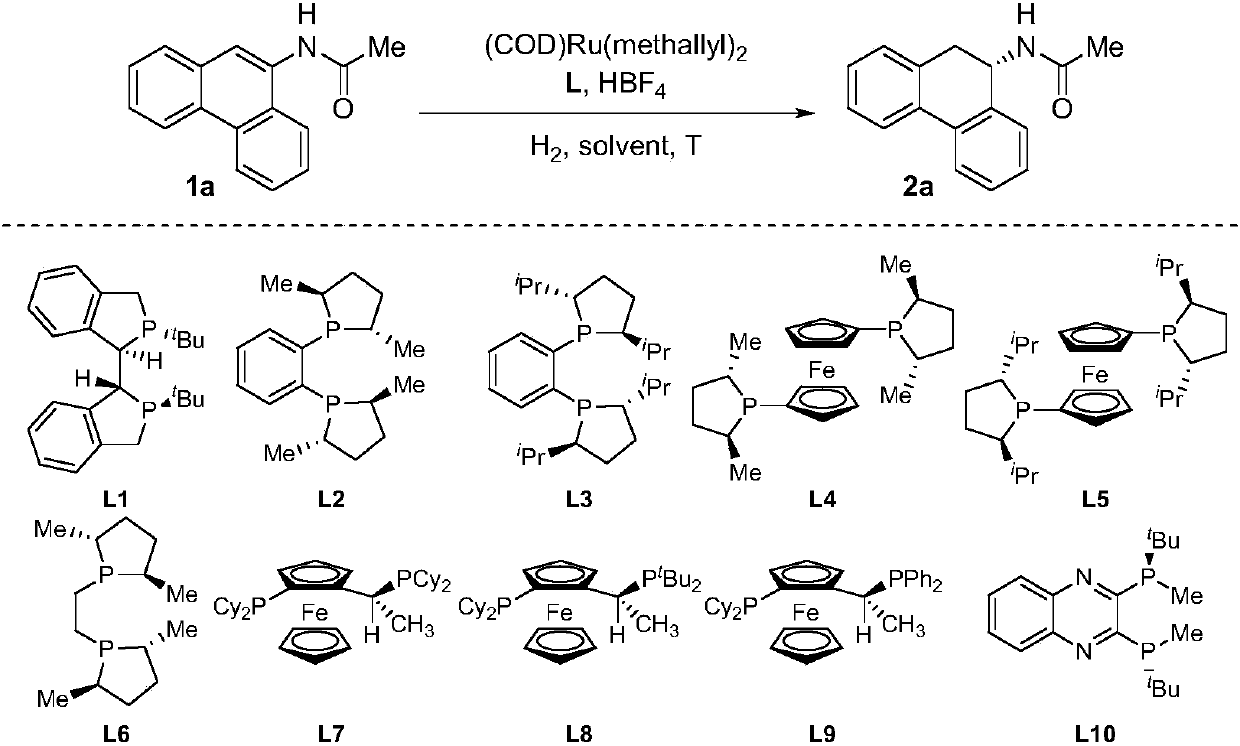
[0027] Drop into two-(2-methallyl) cyclooctyl-1,5-diene ruthenium (2mol%-5mol% of substrate consumption) and chiral bisphosphine ligand (2.2% of substrate consumption) in the reaction flask mol%-5.5mol%), after nitrogen replacement, add organic solvent (1.0-2.0mL) and fluoroboric acid (4mol%-10mol% of the amount of substrate), stir at room temperature for 0.5 hours; then use organic solvent (1.0-2.0mL) Transfer this solution to the reaction flask with arylamine substrate 1a (0.1 mmol) in advance, move it to the reaction kettle, feed hydrogen (600psi-1000psi), and react at 0-50°C for 24 hours; release hydrogen, After removing the solvent, direct column chromatography separates and obtains the pure product, and the reaction formula and the ligand structure are as follows:
[0028]
[0029] The yield is the conversion rate, and the enantiomeric excess of the product is d...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Synthesis of chiral tertiary amine 2 by ruthenium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation
[0034] Put bis-(2-methallyl) cyclooctyl-1,5-diene ruthenium (5 mol% of substrate consumption) and (S, S)- i PrDuPhos (5.5mol% of substrate consumption), after nitrogen replacement, add organic solvent (1.0mL) and fluoboric acid (10mol% of substrate consumption), stir at room temperature for 0.5 hour; then use organic solvent (1.0mL) to turn this solution Put the arylamine substrate 1 (0.2mmol) in the reaction flask in advance, move it to the reaction kettle, feed hydrogen gas (1000psi), and react at 30°C for 24 hours; release the hydrogen gas, remove the solvent and separate directly by column chromatography Obtain pure product, reaction formula is as follows:
[0035]
[0036] The yield is the separation yield, and the enantiomeric excess of the product is determined by chiral liquid chromatography, see Table 2.
[0037] Table 2. Ruthenium-catalyzed asymmetric hydroge...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: Optimization of reaction conditions for hydrogenation of disubstituted substrates
[0041] Drop into two-(2-methallyl) cyclooctyl-1,5-diene ruthenium (5 mol% of substrate consumption) and chiral bisphosphine ligand (5.5mol% of substrate consumption) in the reaction flask , add organic solvent (1.0mL) and fluoroboric acid (10mol% of the substrate amount) after nitrogen replacement, and stir at room temperature for 0.5 hours; then use organic solvent (1.0mL) to transfer this solution to pre-placed arylamine (0.1mmol) in the reaction flask, moved to the reaction kettle, feed hydrogen (1000psi), reacted 24 hours under 30 ℃; Release hydrogen, remove the direct column chromatography separation after solvent to obtain pure product, reaction formula is as follows:
[0042]
[0043] The yield is the conversion rate, and the enantiomeric excess of the product was determined by chiral liquid chromatography, see Table 3.
[0044] Table 3. Optimization of asymmetri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com