SNP molecular marker for detecting lobed-leaf trait of brassica campestris vegetables and applications thereof
A molecular marker, vegetable leaf technology, applied in recombinant DNA technology, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of developmental period limitation and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0182] Acquisition of molecular markers and their primers
[0183] 1. Obtain molecular markers:
[0184] The implementation basis of the present invention is: the inventor's research group resequenced a large number of Brassica vegetable varieties with different leaf margin phenotypes through the Illumina HiSeq2000 platform to obtain SNP variation sites between a large number of varieties.
[0185] The implementation content is: after the candidate genes are obtained through QTL analysis and fine mapping of the leaf margin cleavage phenotype, the well-typed SNP loci located on the candidate genes are used to analyze the SNP loci of the leaf margin cleavage traits, so The molecular marker of the invention can accurately detect the leaf type of the variety.
[0186] Step 1: Obtain the main effect QTL: In order to better and faster screen and obtain Brassica vegetable resources with leaf margin cracks, and promote the practice of molecular marker-assisted selection breeding, thr...
Embodiment 2
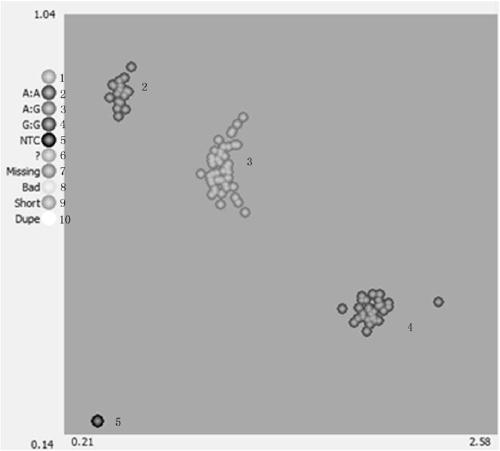
[0215] This example is to use the supporting reagents of UK LGC Company to detect the application of the A1015797093A / G site in the identification of leaf margin cracks and whole margin materials, that is, use the primers obtained in Example 1 to detect 73 materials in Example 1 leaf shape to verify the detection effect. The detection method of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0216] 1. DNA extraction
[0217] Genomic DNA of 73 DH populations were extracted by conventional CTAB method.
[0218] Specifically:
[0219] The leaves of the above 73 varieties at the seedling stage were picked, frozen at -40°C for more than 1 day, and then placed in a vacuum dryer (CoolSafe 55-4) for dehydration; then 20 μg of dry powdered leaves were taken, and DNA was extracted according to the CTAB method. as follows;
[0220] i. Add CTAB extract (2%CTAB, 1.4mM NaCl, 100mM Tris‐HCl pH8.0, 20mM EDTA pH8.0, 1%PVP‐40, 0.2%β‐mercaptoethanol) in the dry powdery leaves, Mix w...
Embodiment 3
[0240] This example is to use the supporting reagents of the British LGC company to detect the application of the A1015797093A / G site in the identification of leaf margin cracks and whole margin materials, that is, use the primers obtained in Example 1 to detect other varieties of Brassica vegetables Leaf shape to verify the detection effect.
[0241] The varieties in this example are: Turnip varieties with leaf edge cracks: Zaosheng Kanamachi, Baili, Xinxingyuan, Hongyuan, Tsuda, Baiyu, Changhuang, purple top white globe, ECD‐01, ECD‐02, ECD‐ 03, ECD-04, a total of 12 copies, whole-edge brassica vegetable varieties: Xiacui, Chunquan, Xingdu Youfeng, Xiabao, Fuqiang, 536, Jiaoerye, Youxiawang, Xiazi, Eryue Bai, Improved Qingza No. 3, Jinqing 60, a total of 12 copies.
[0242] The operation of the detection method of this embodiment includes the following steps:.
[0243] 1. DNA extraction: the same operation steps and parameters as in Example 2.
[0244] 2. Based on competi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com