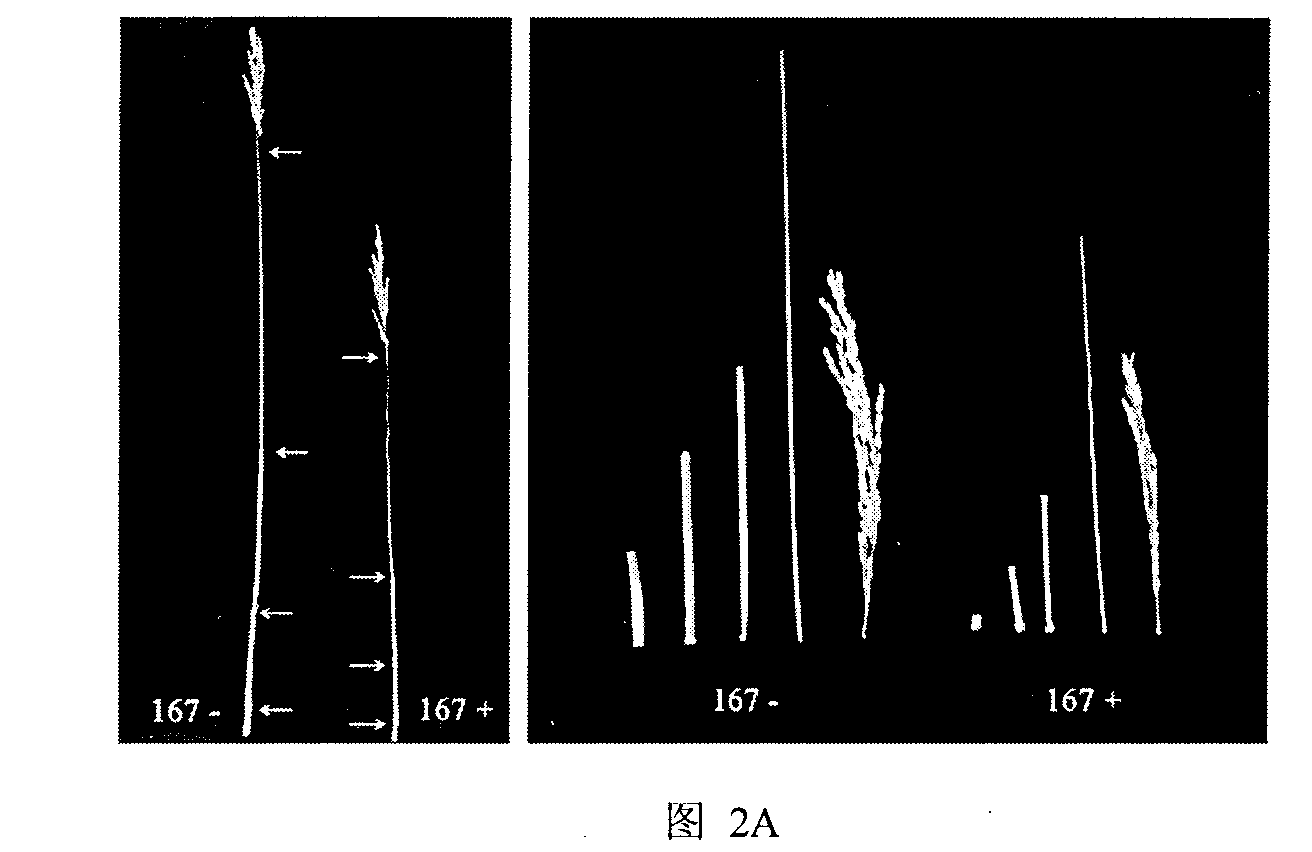
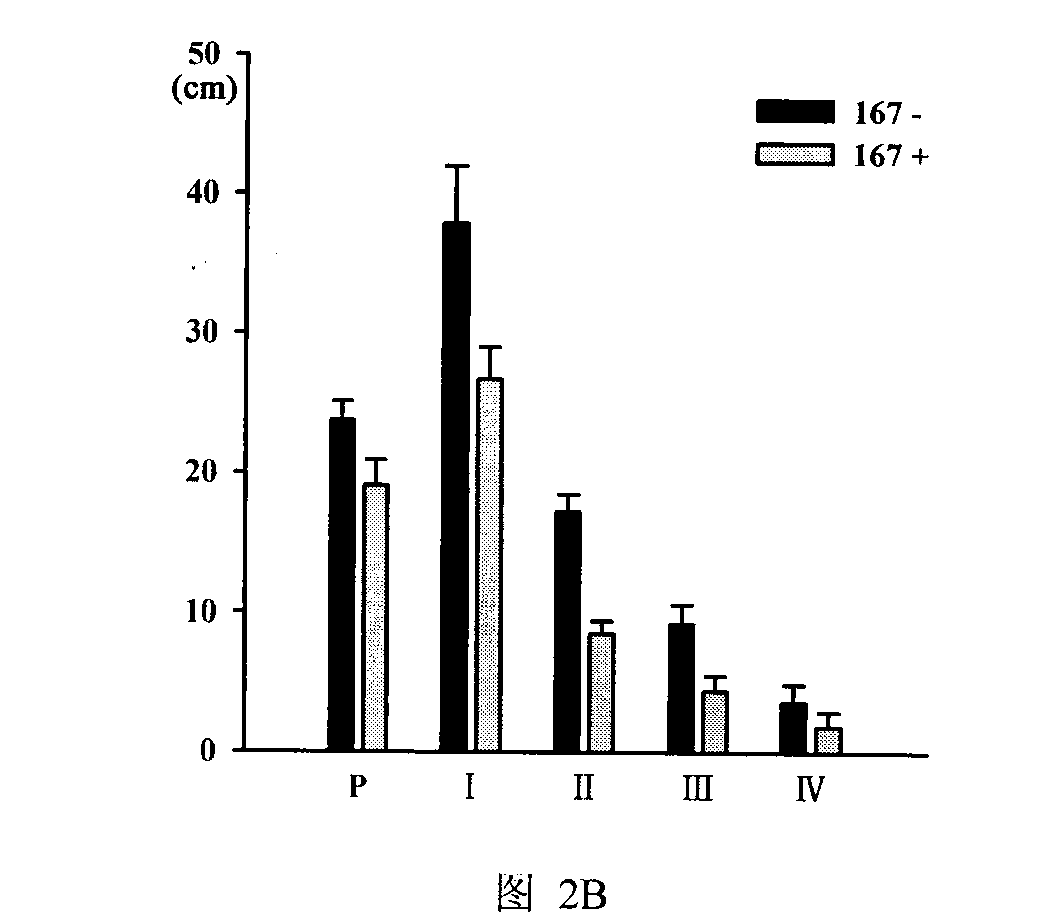
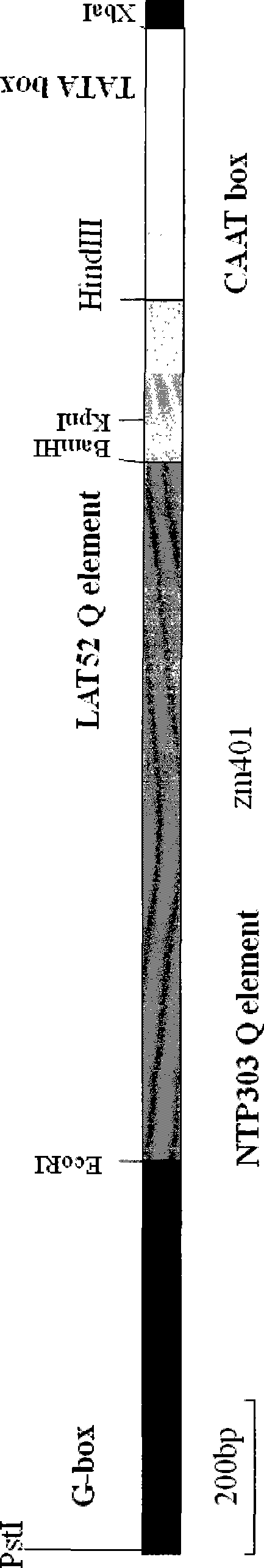
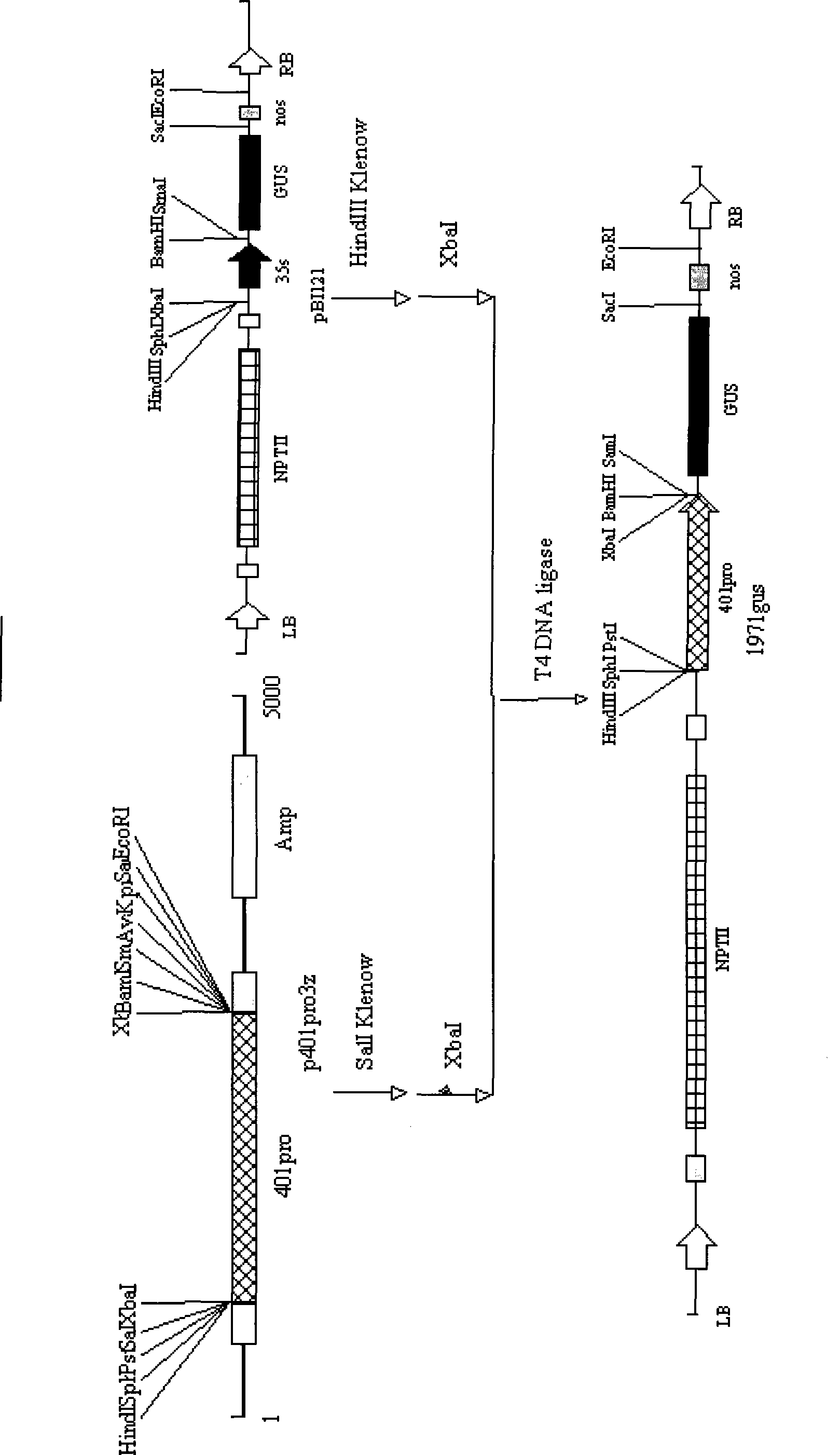
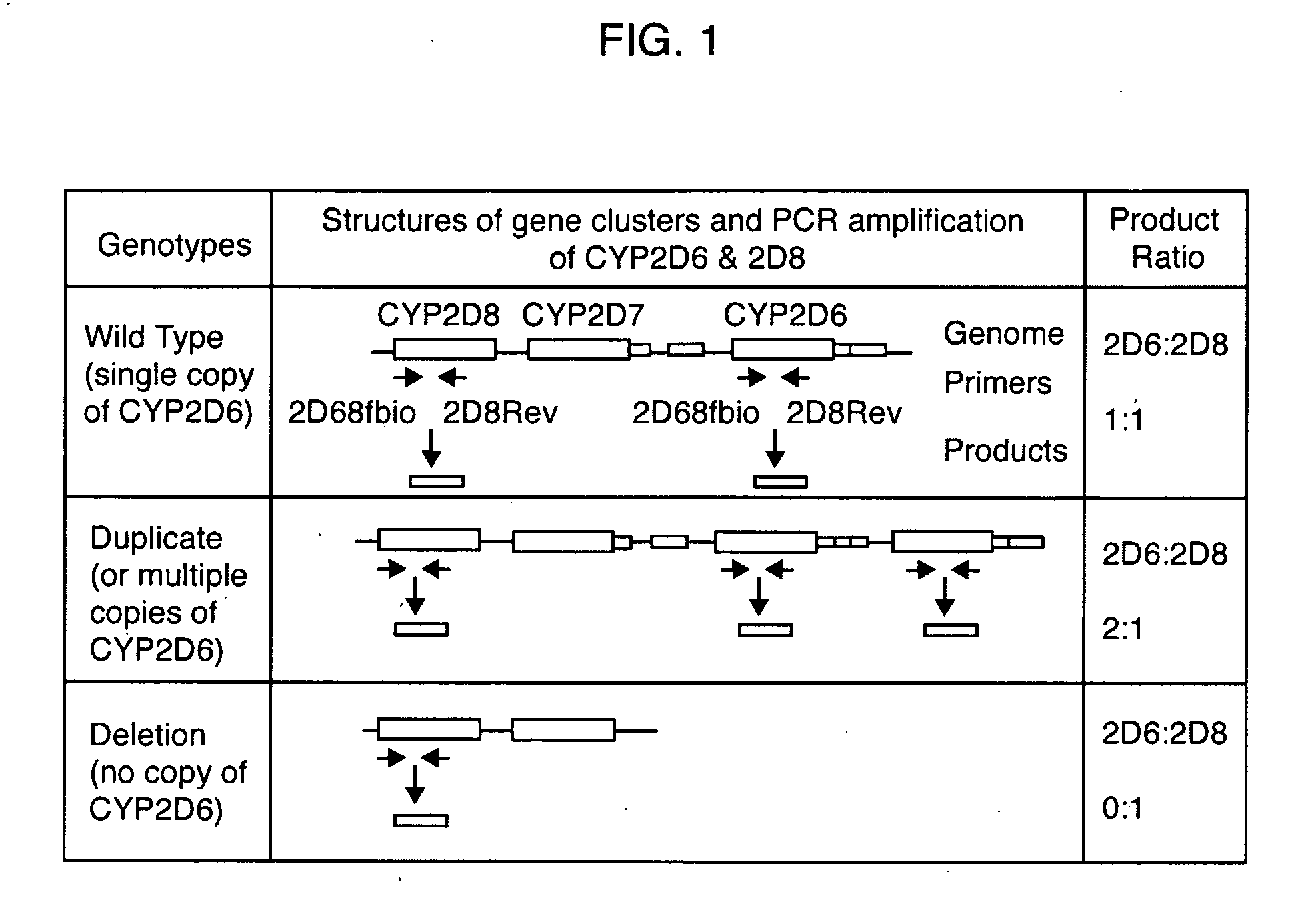
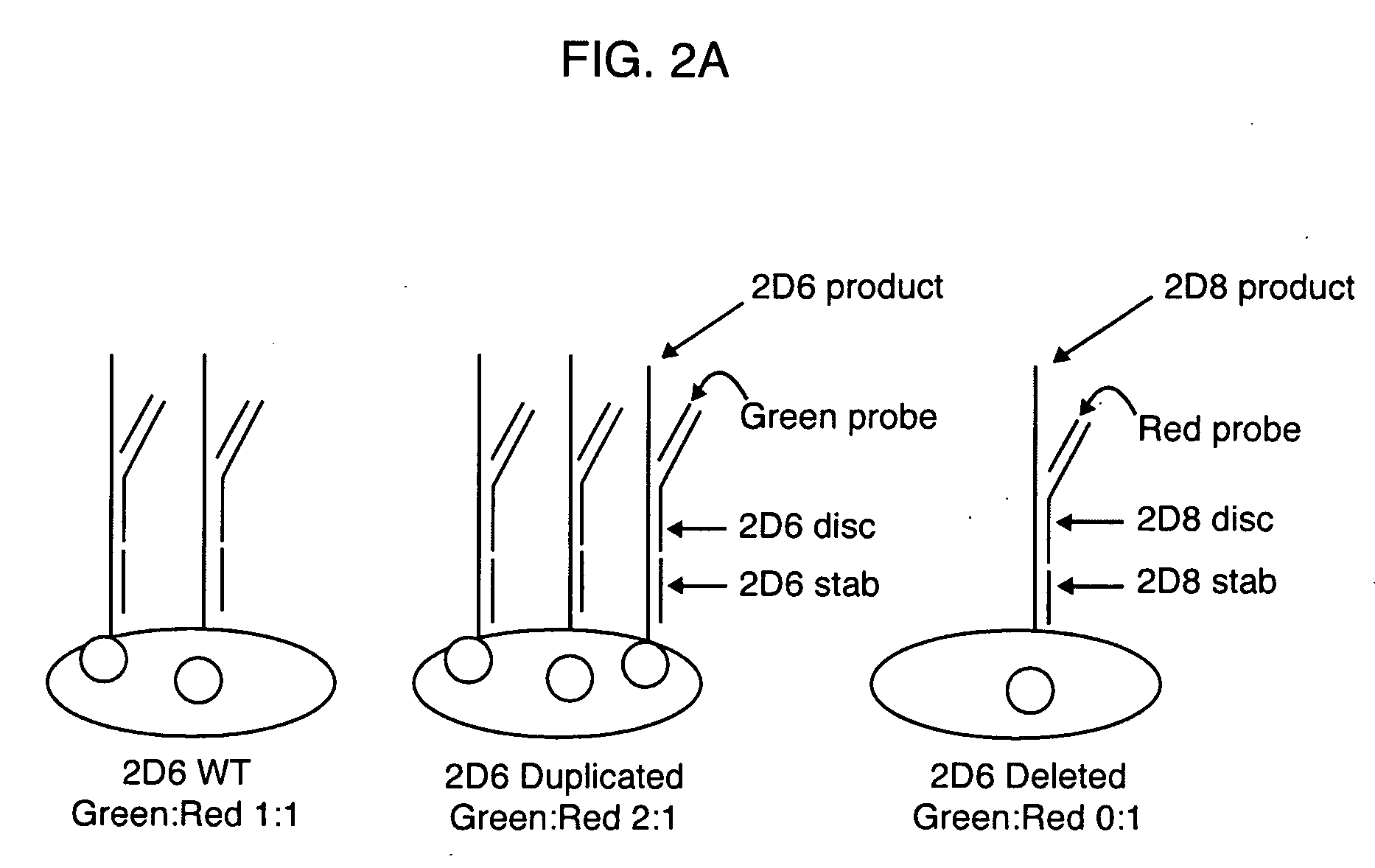
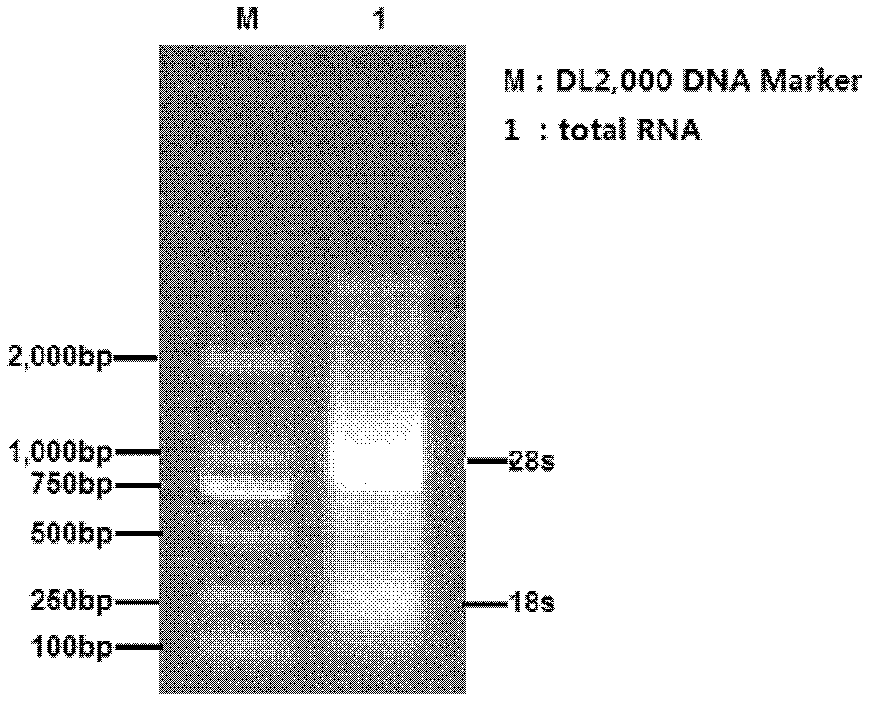
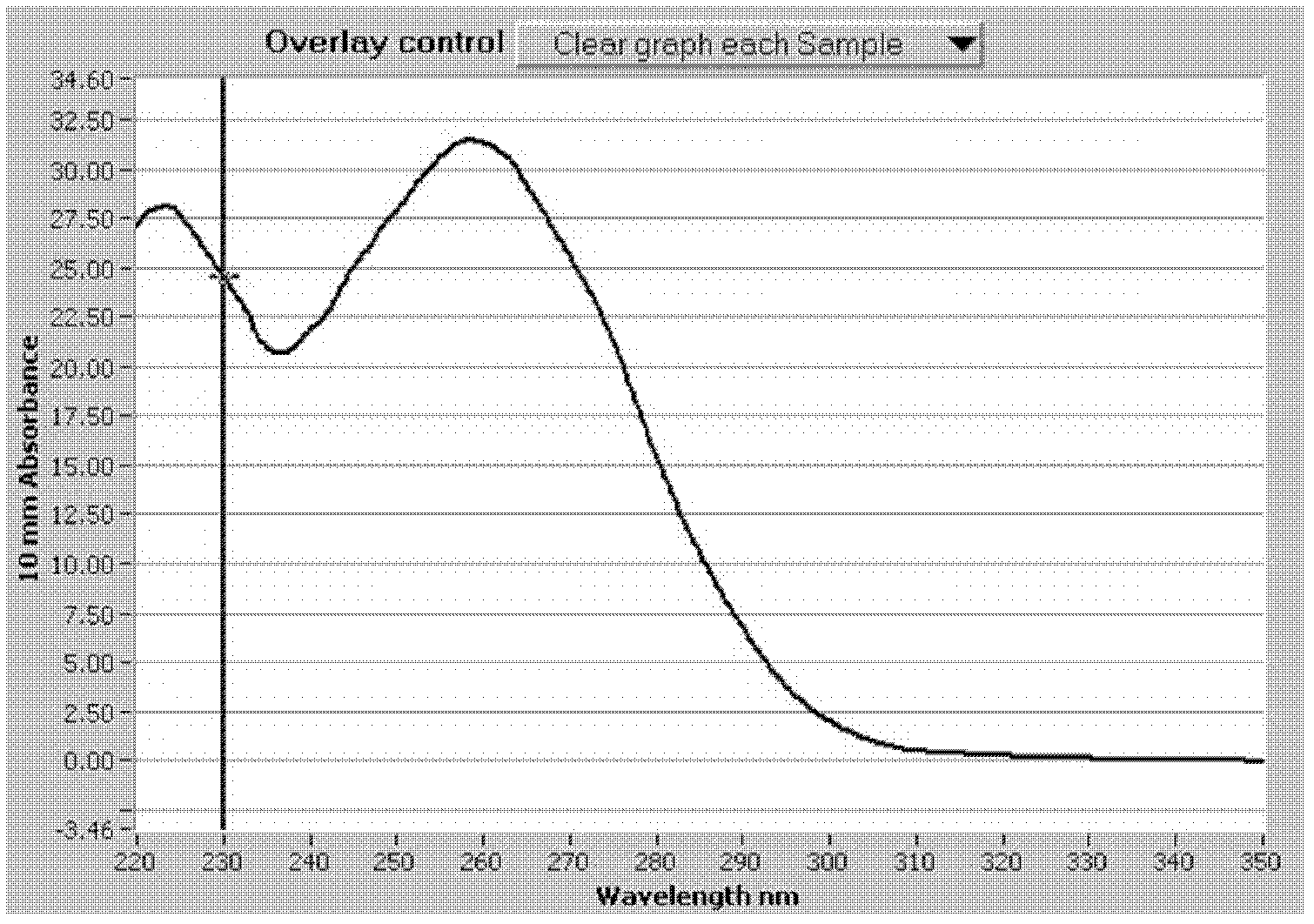
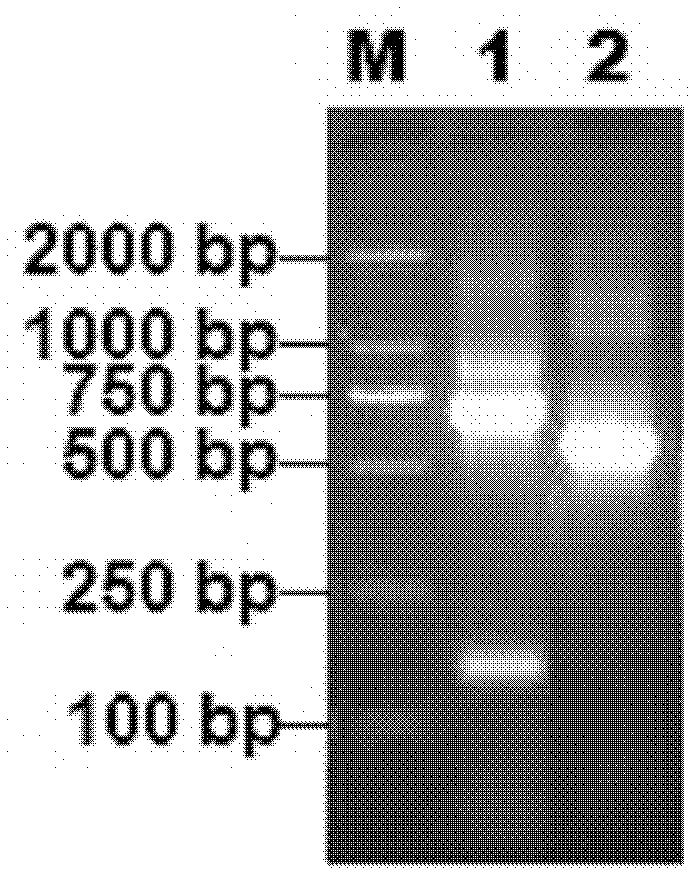
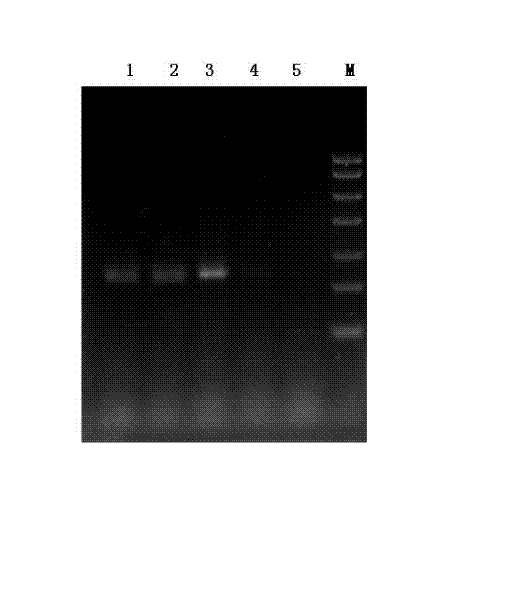
Patents
Literature
99 results about "Homeotic gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In evolutionary developmental biology, homeotic genes are genes which regulate the development of anatomical structures in various organisms such as echinoderms, insects, mammals, and plants. This regulation is done via the programming of various transcription factors by the homeotic genes, and these factors affect genes through regulatory genetic pathways.
Panicle size controlling gene, mutant and application thereof
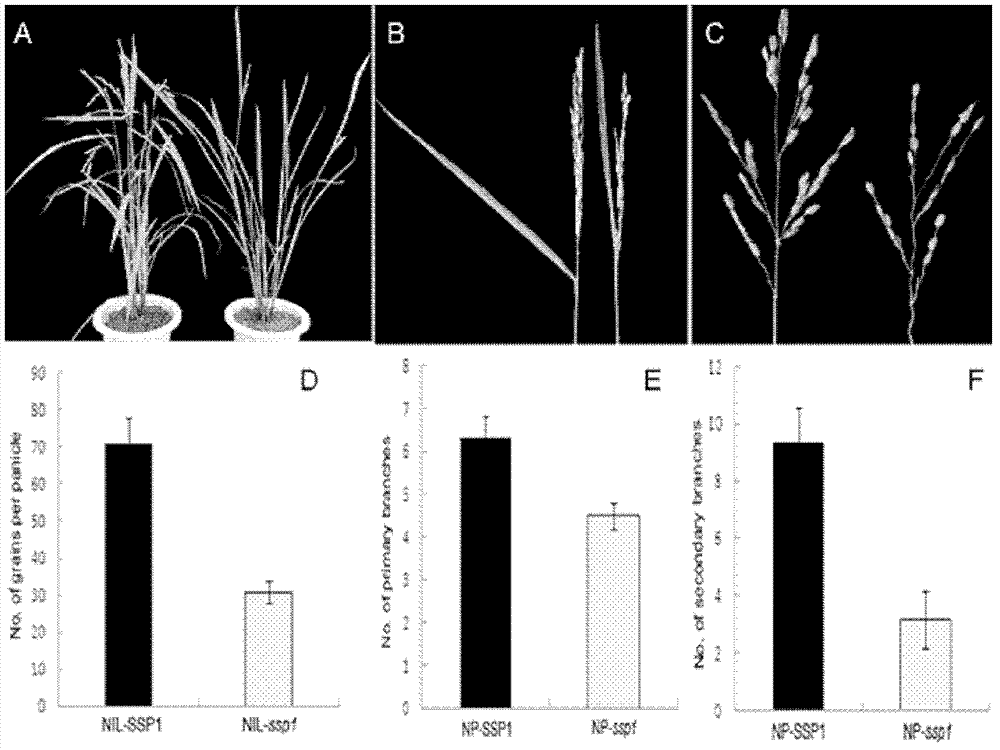
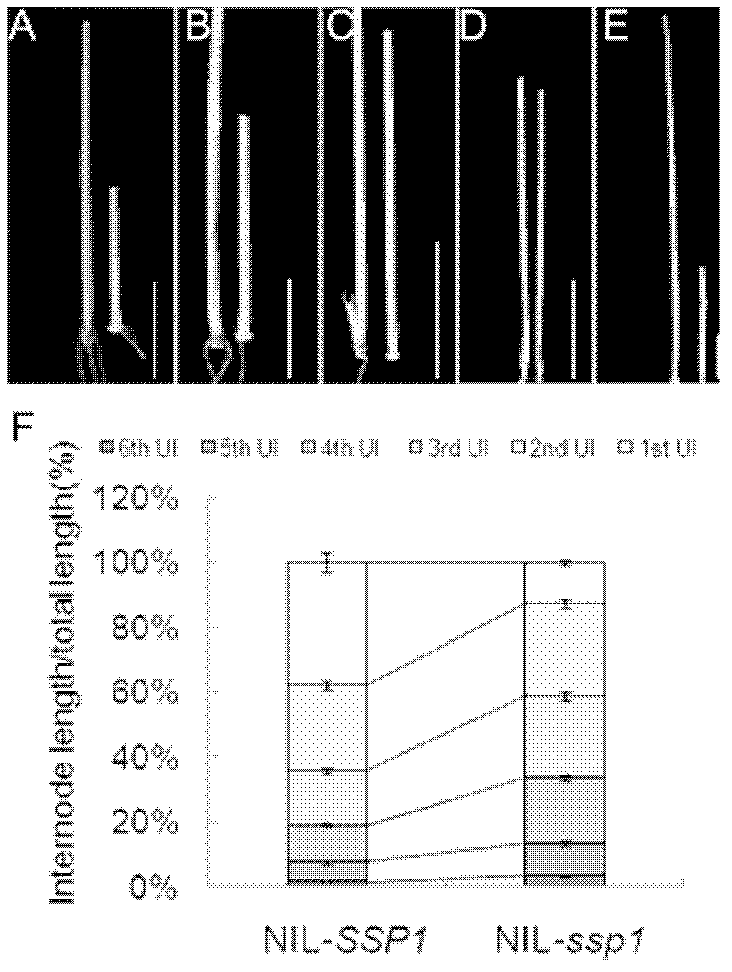
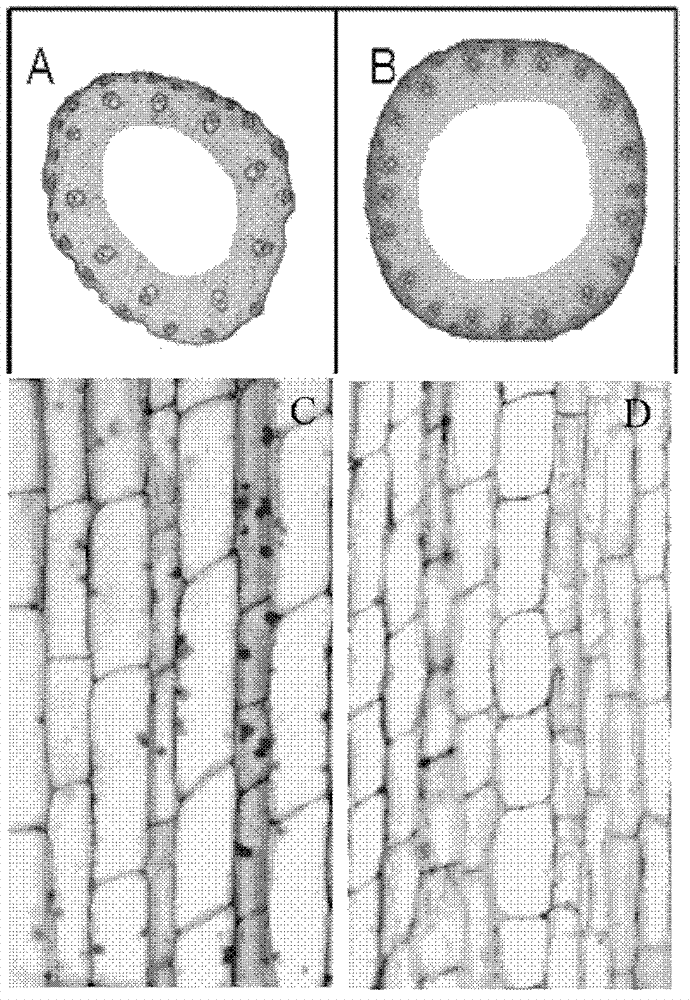
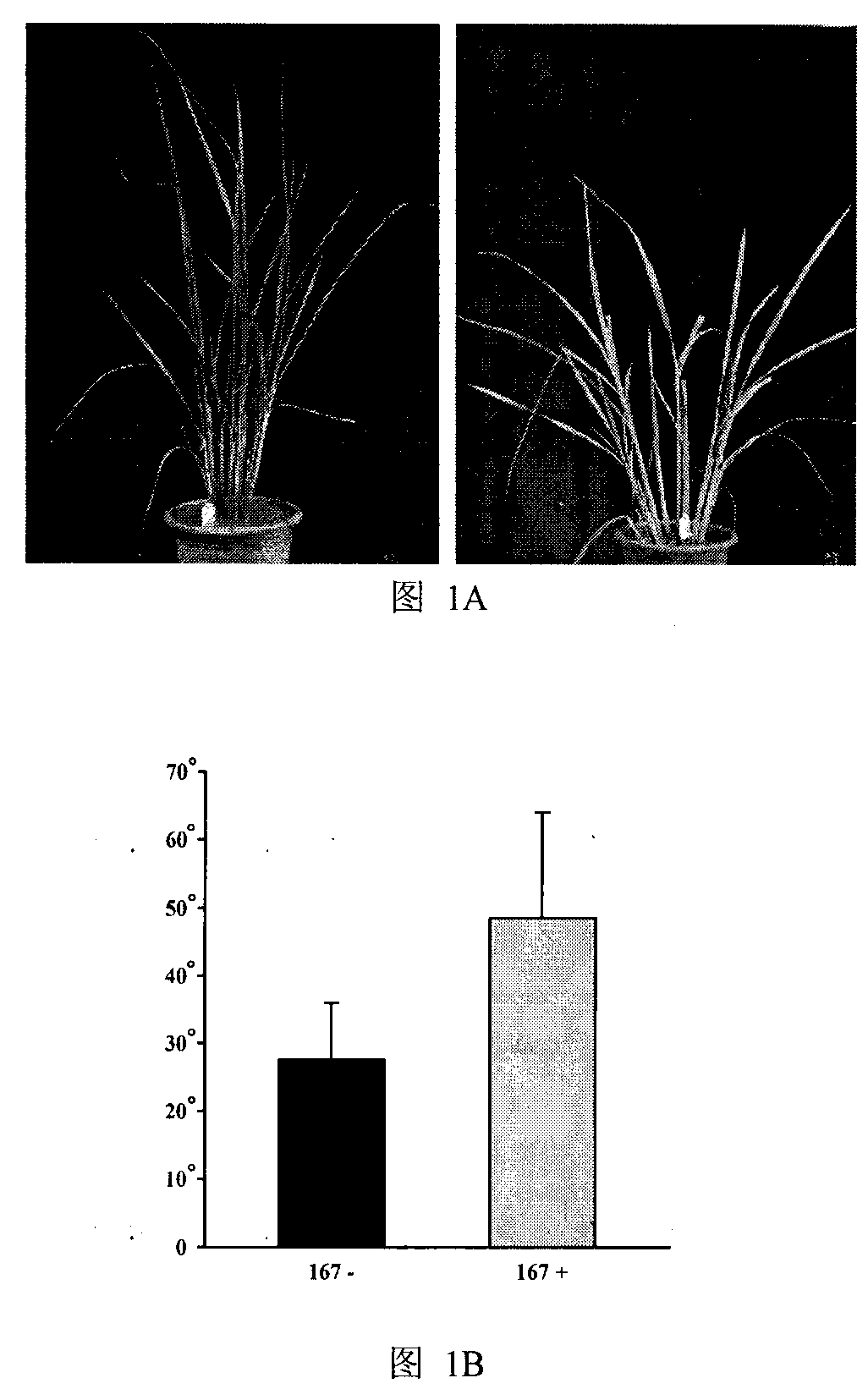
The invention relates to a panicle size controlling gene SSP1 (Small and Sheathed Panicle 1) and a mutant gene ssp1 thereof, and action mechanism thereof in regulating plant height, leaf included angle and panicle size, and provides a gene sequence SEQ IDNO: 3 from the panicle size controlling gene mutant ssp1. The invention also relates to homologous genes of the panicle size controlling gene mutant ssp1 in barley, wheat, maize, corn, sorghum, soybean, cotton, rape, arabidopsis and other plants. The above mentioned genes are all referred to as panicle size controlling genes. The invention also relates to applications of the SSP1 gene and the mutant ssp1 gene in controlling plant height, improving lodging resistance, reducing leaf angle to improve photosynthetic efficiency, changing gibberellin response, suppressing panicle sprouting and breeding.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
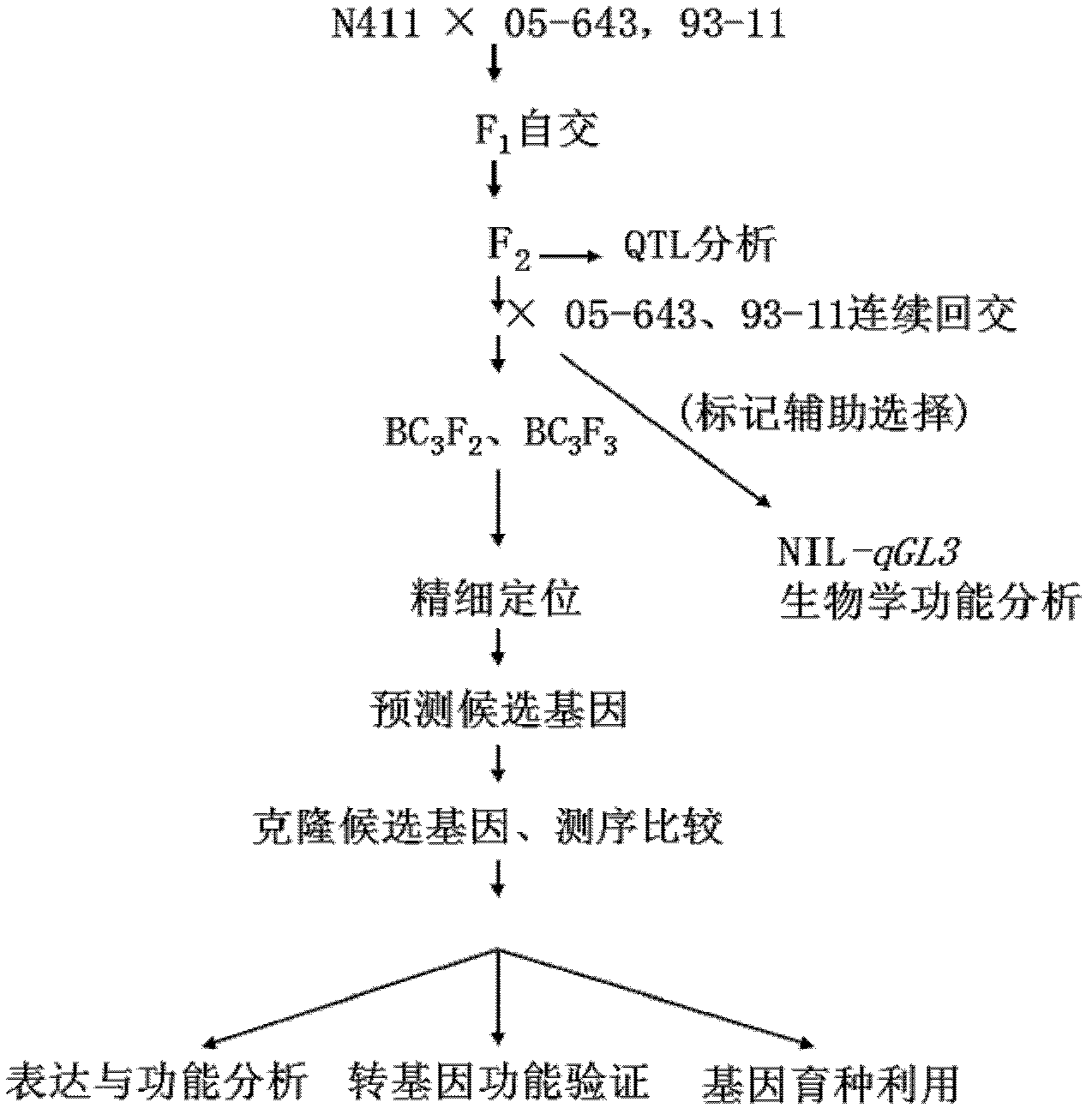
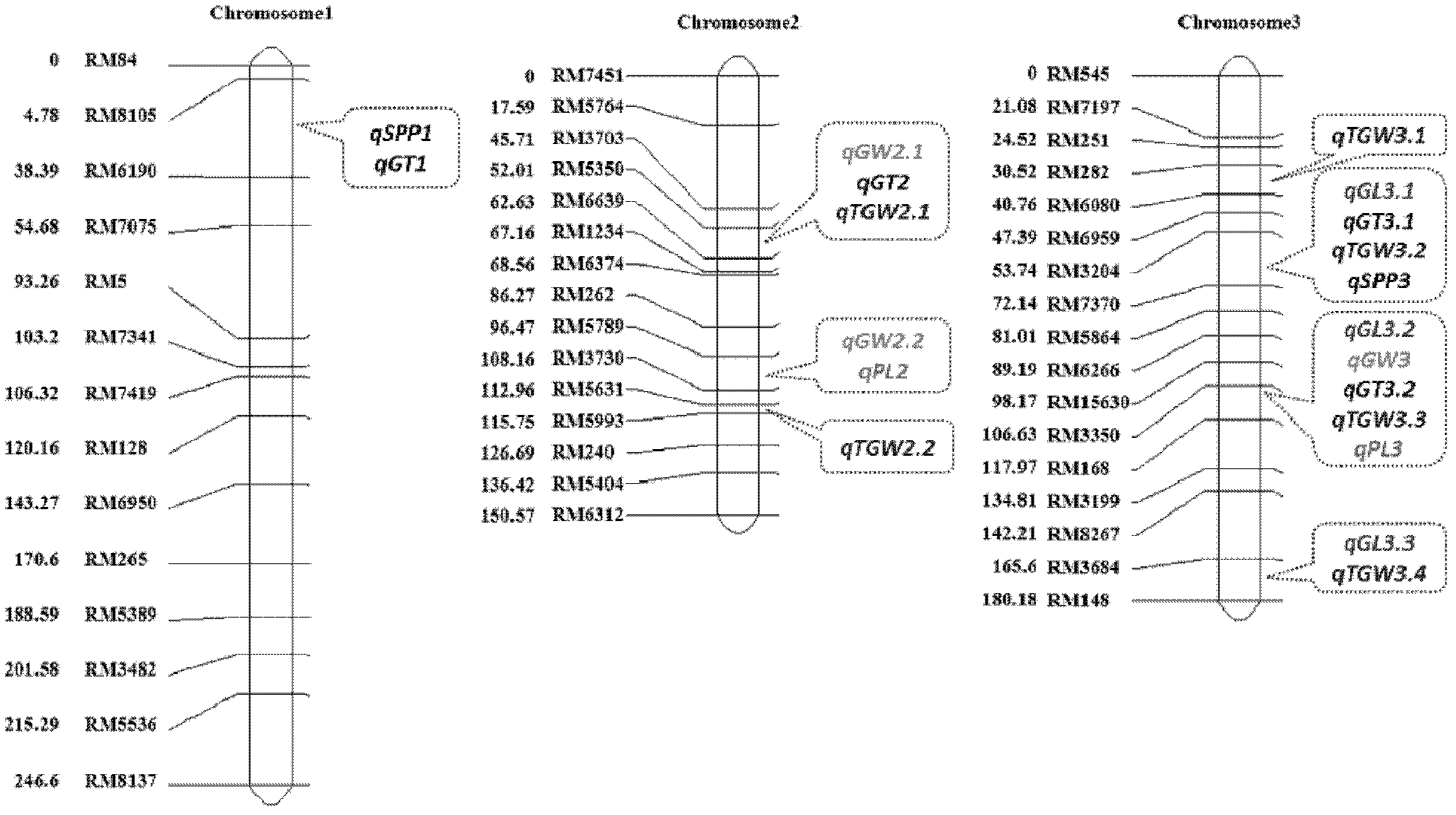
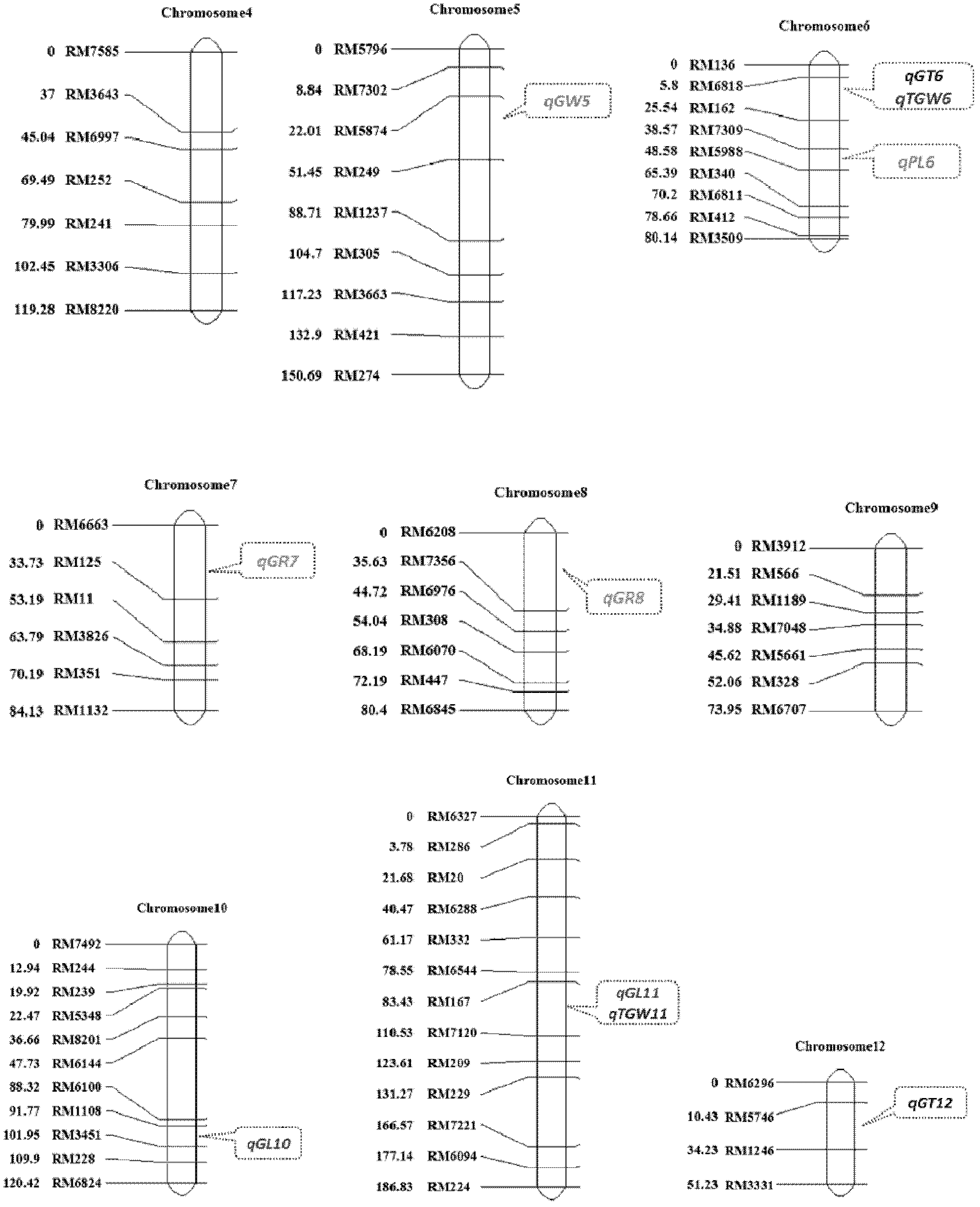
Clone and application of semi-dominant gene qGL3 capable of controlling grain length and grain weight of rice kernel
ActiveCN102352367AIncrease the lengthIncrease grain weightHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGrain weight
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and discloses clone and application of semi-dominant gene qGL3 capable of controlling grain length and grain weight of rice kernel. In the invention, a main-effective QTL (quantitative trait loci) SEQ ID NO:1 which is capable of simultaneously controlling the grain length and grain weight of rice kernel and a semi-dominant allelic gene SEQ ID NO:3 having advantageous function are separated and cloned; the two genes have the capacities of modifying the yield and appearance quality of rice; and at the same time, the two homologous genes of the two genes in rice are cloned and a fact that the two homologous genes have regulation effect on the length of rice kernel as well is proved. Thus, the gene qGL3 and the advantageous allelic gene qGL3-D thereof as well as the two homologous genes of the gene qGL3 all can be applied to crop genetic modification.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
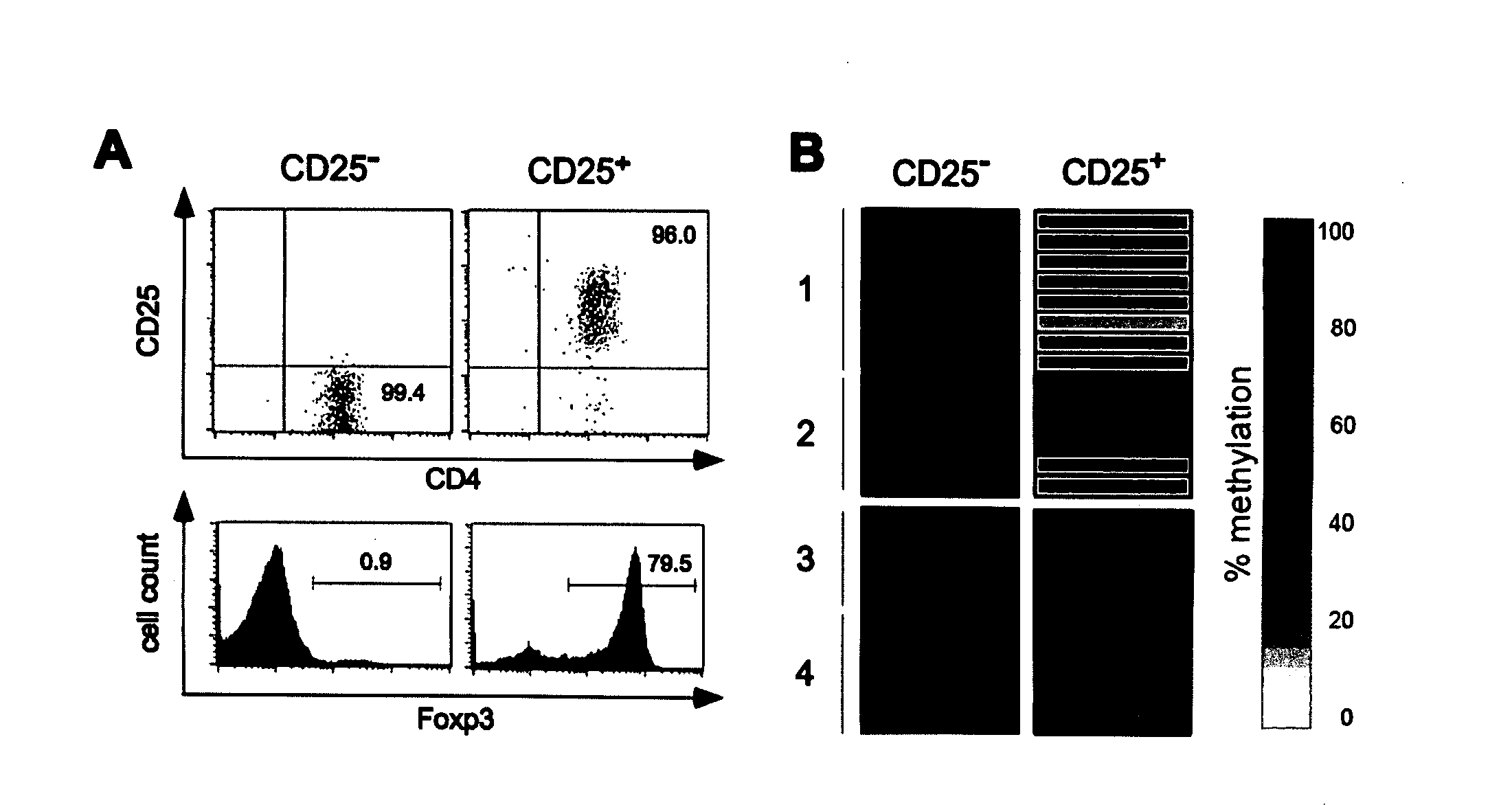
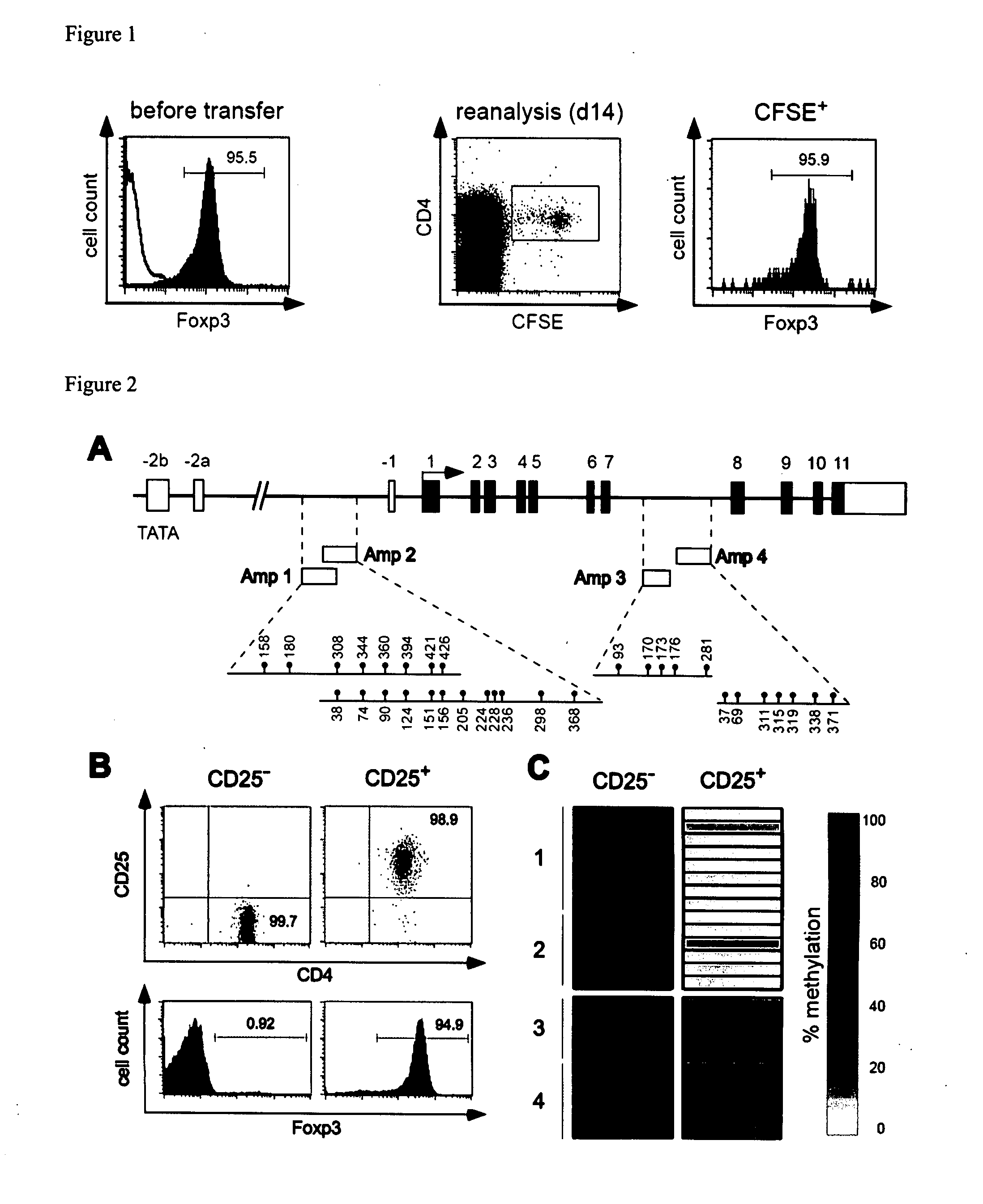
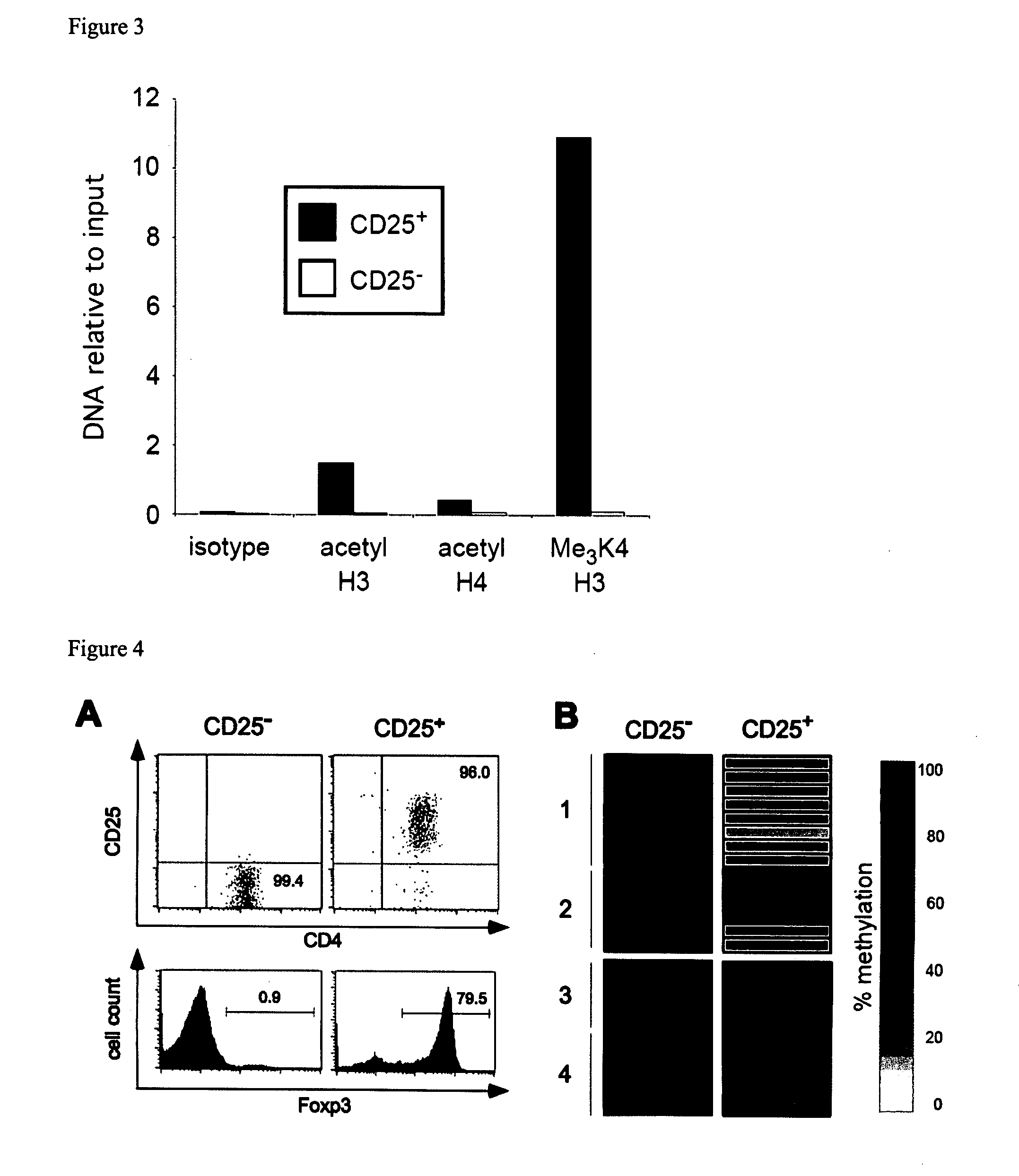
Epigenetic modification of the loci for CAMTA1 and/or FOXP3 as a marker for cancer treatment
PendingUS20070243161A1Short overall survivalConvenient treatmentOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseRegulatory T cell
The present invention relates to a method, in particular an in vitro method, for pan-cancer diagnostics, comprising identifying the amount and / or proportion of stable regulatory T cells in a patient suspected of having cancer through analyzing the methylation status of at least one CpG position in the gene foxp3 and / or the gene camta1 or orthologous or paralogous genes thereof, wherein an increased amount and / or proportion of stable regulatory T cells in said patient is indicative for an unspecific cancerous disease. In a second aspect thereof, the present invention relates to a method for diagnosing the survival of a cancer patient, comprising identifying the amount and / or proportion of stable regulatory T cells in said cancer patient through analyzing the methylation status of at least one CpG position in the gene foxp3 and / or the gene camta1 or orthologous or paralogous genes thereof, wherein a demethylation in the gene foxp3 and / or the gene camta1 or orthologous or paralogous genes thereof, is indicative of a stable regulatory T cell, and wherein an increased amount and / or proportion of stable regulatory T cells in said cancer patient is indicative for a shorter survival for said cancer patient. Furthermore, the present invention relates to an improved treatment of cancers based on the inventive methods, and a kit for performing the above methods as well as respective uses.
Owner:PRECISION FOR MEDICINE GMBH
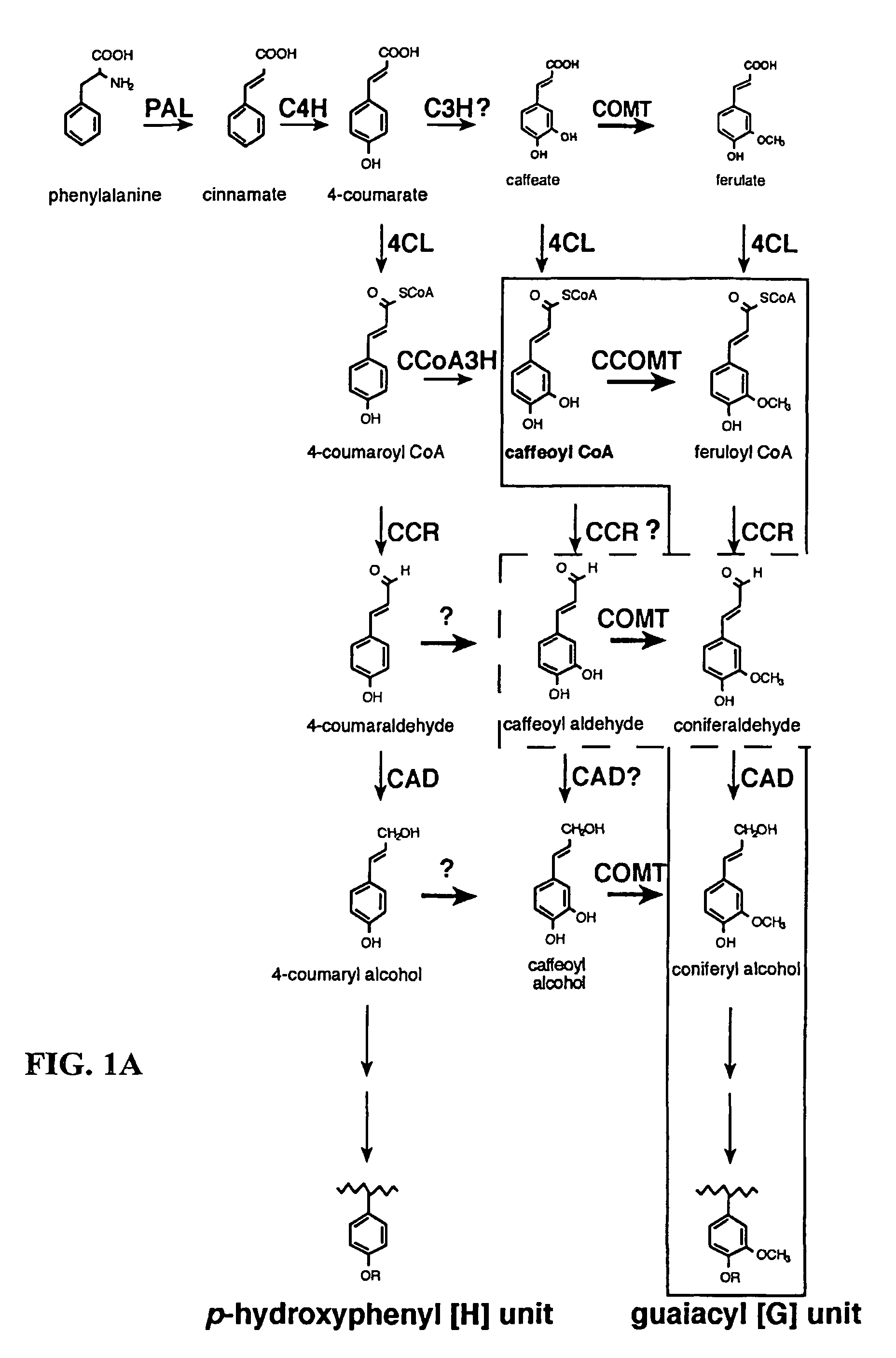
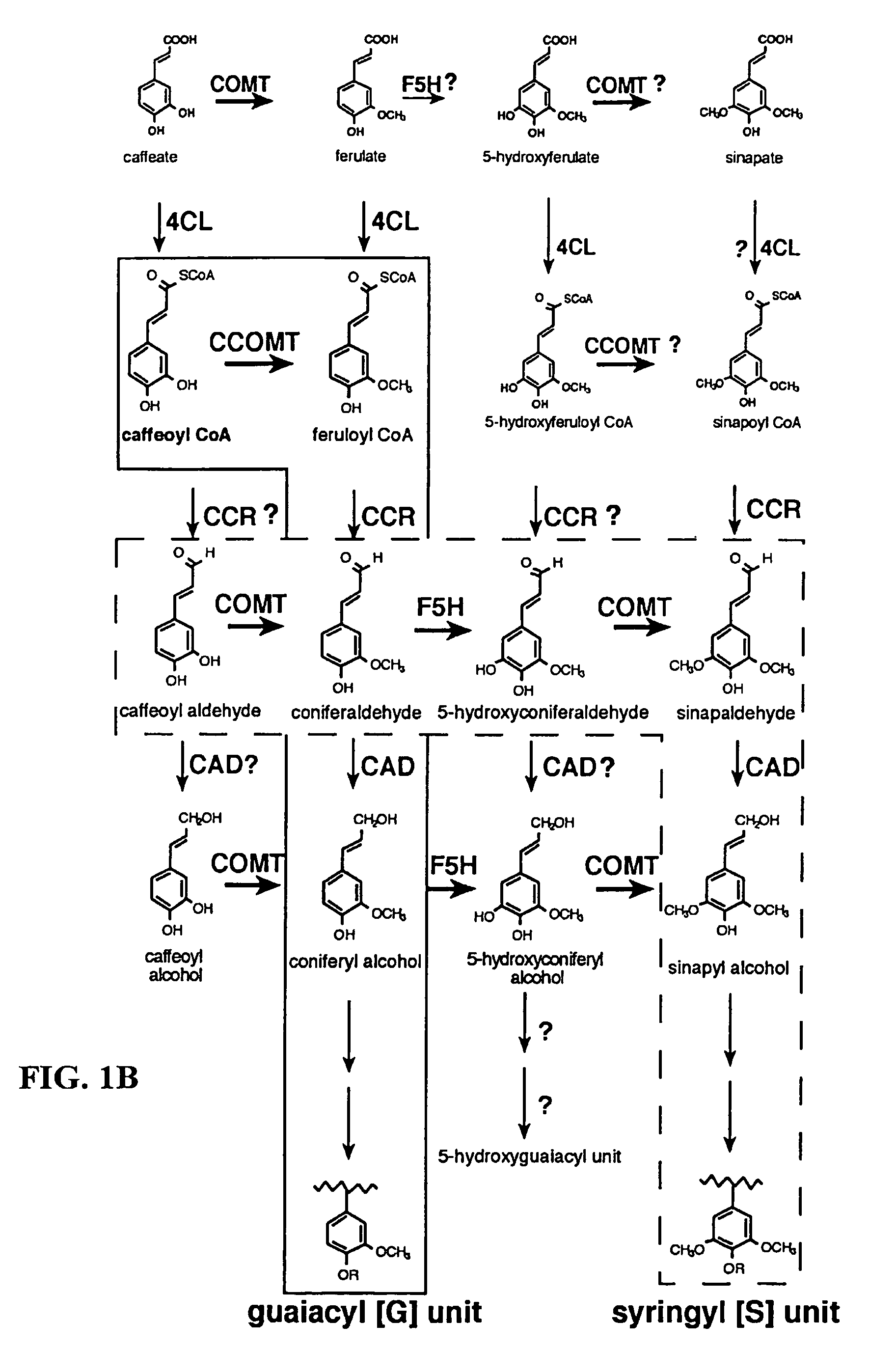
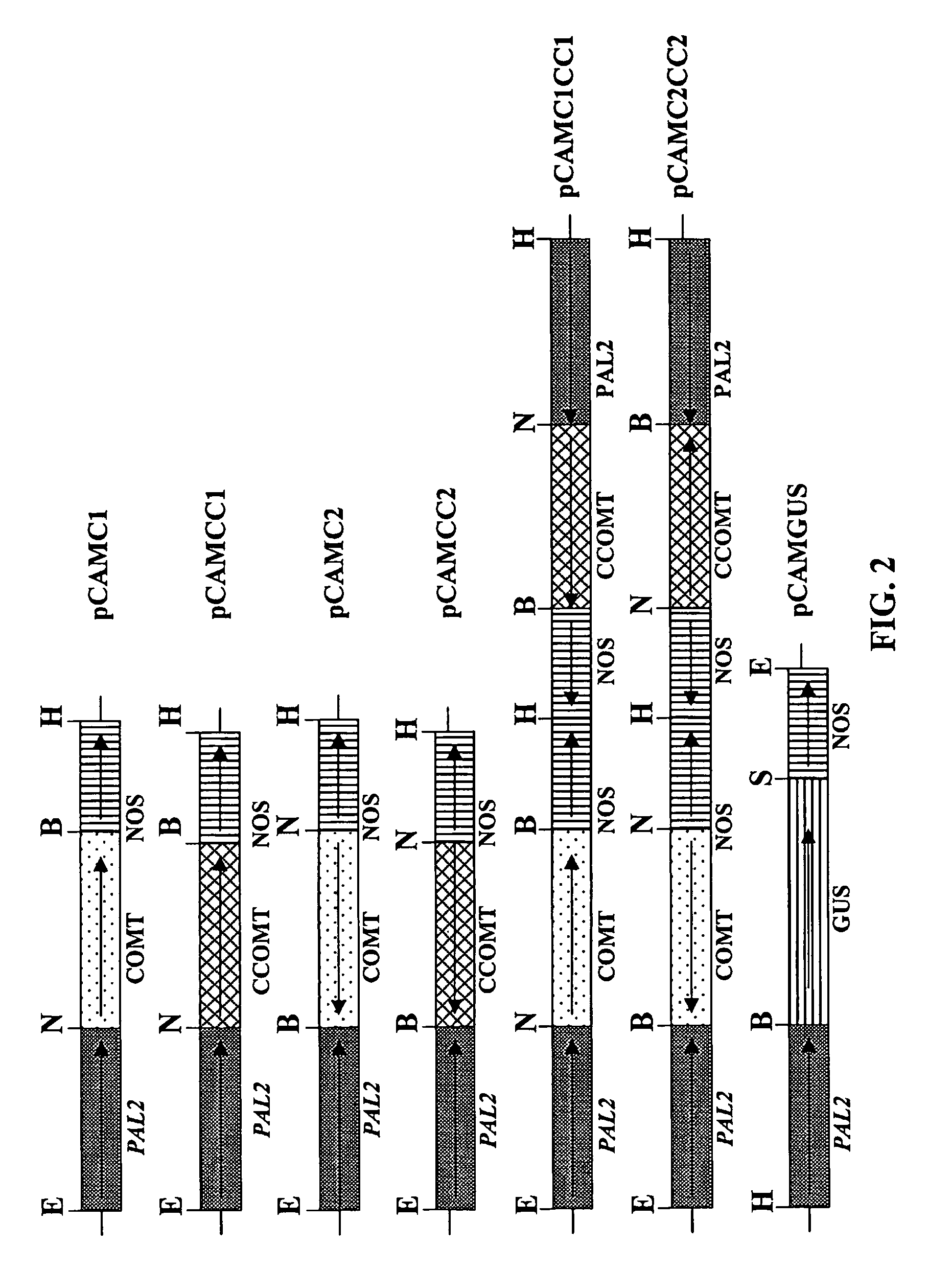
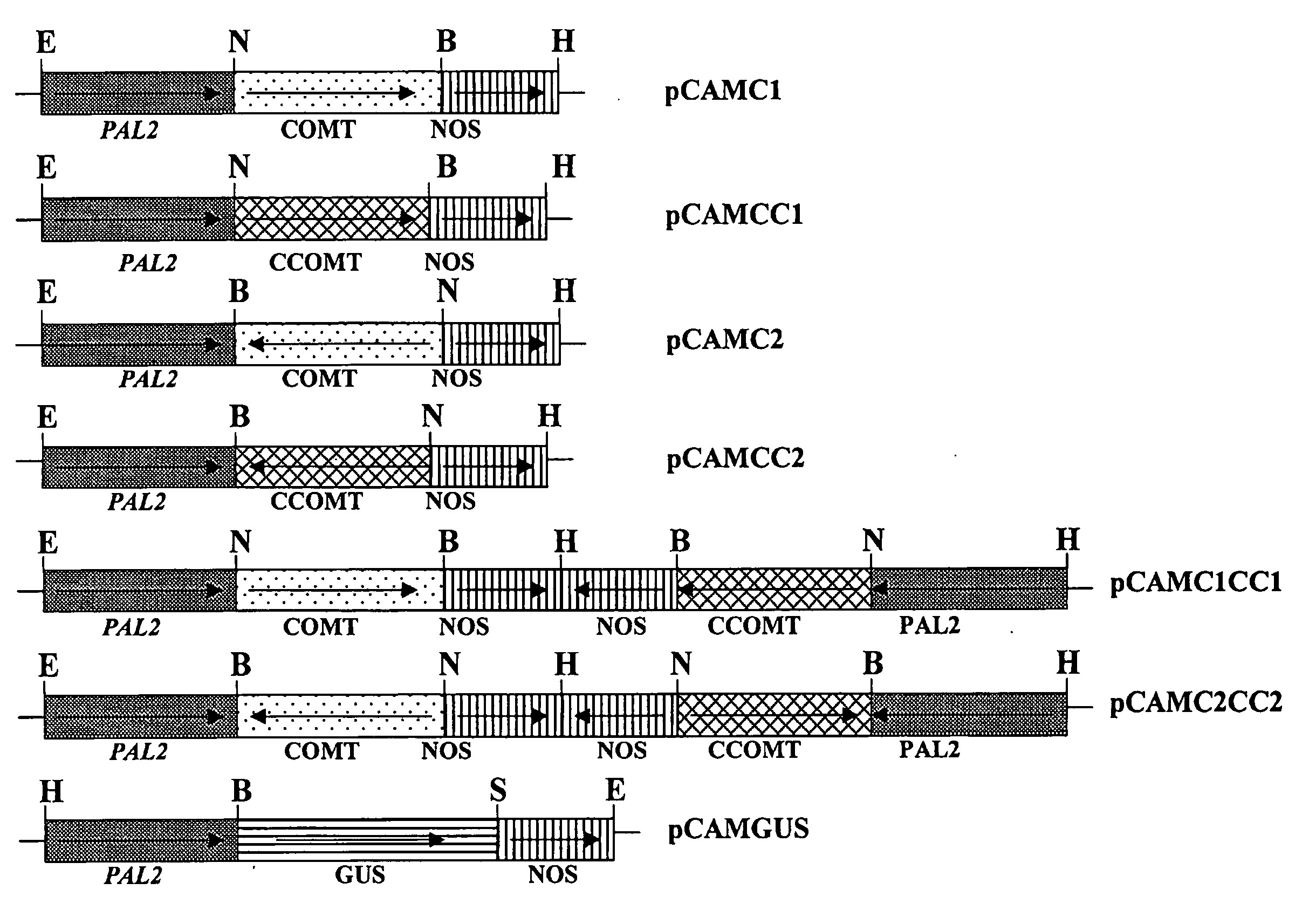
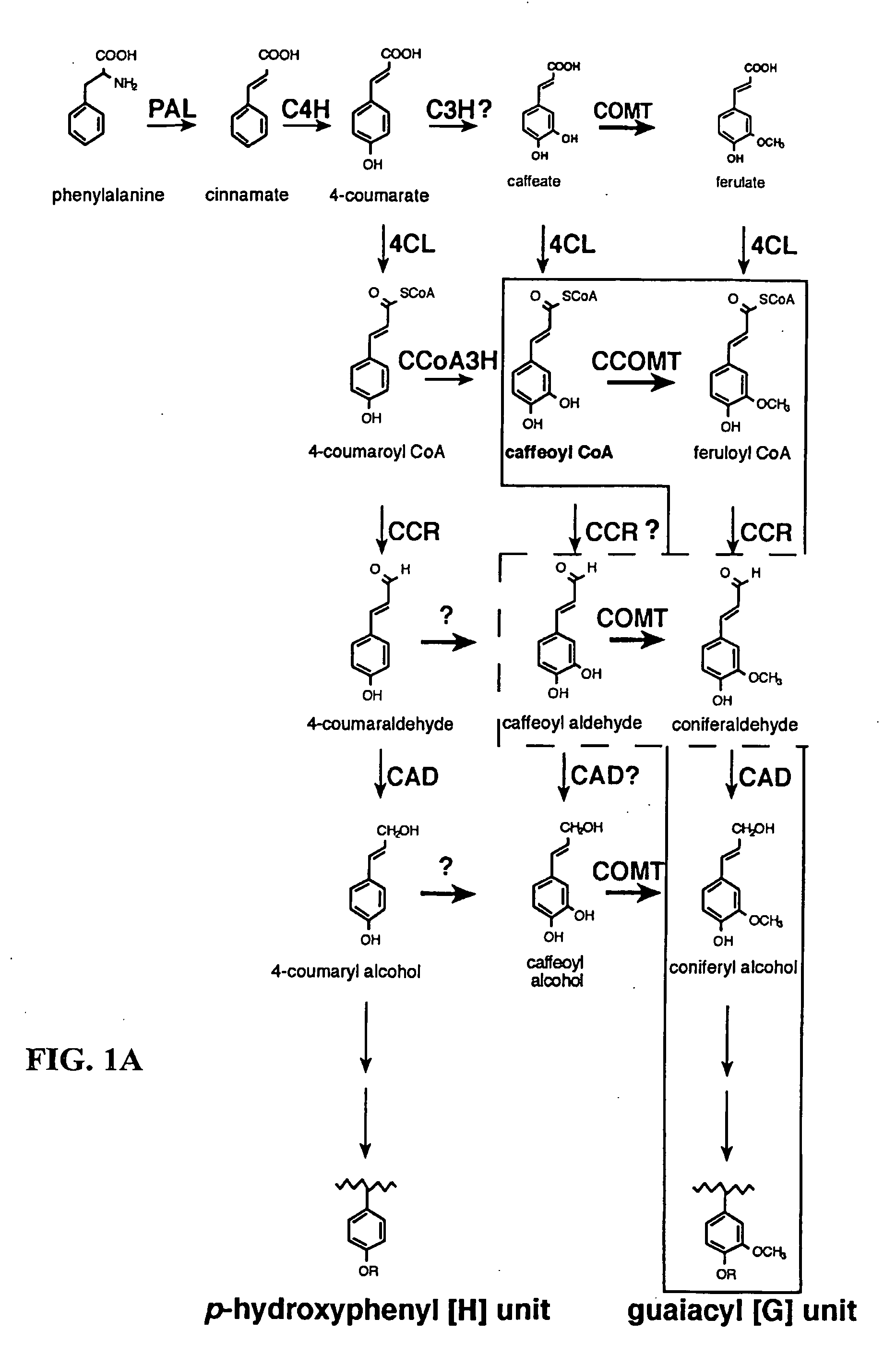
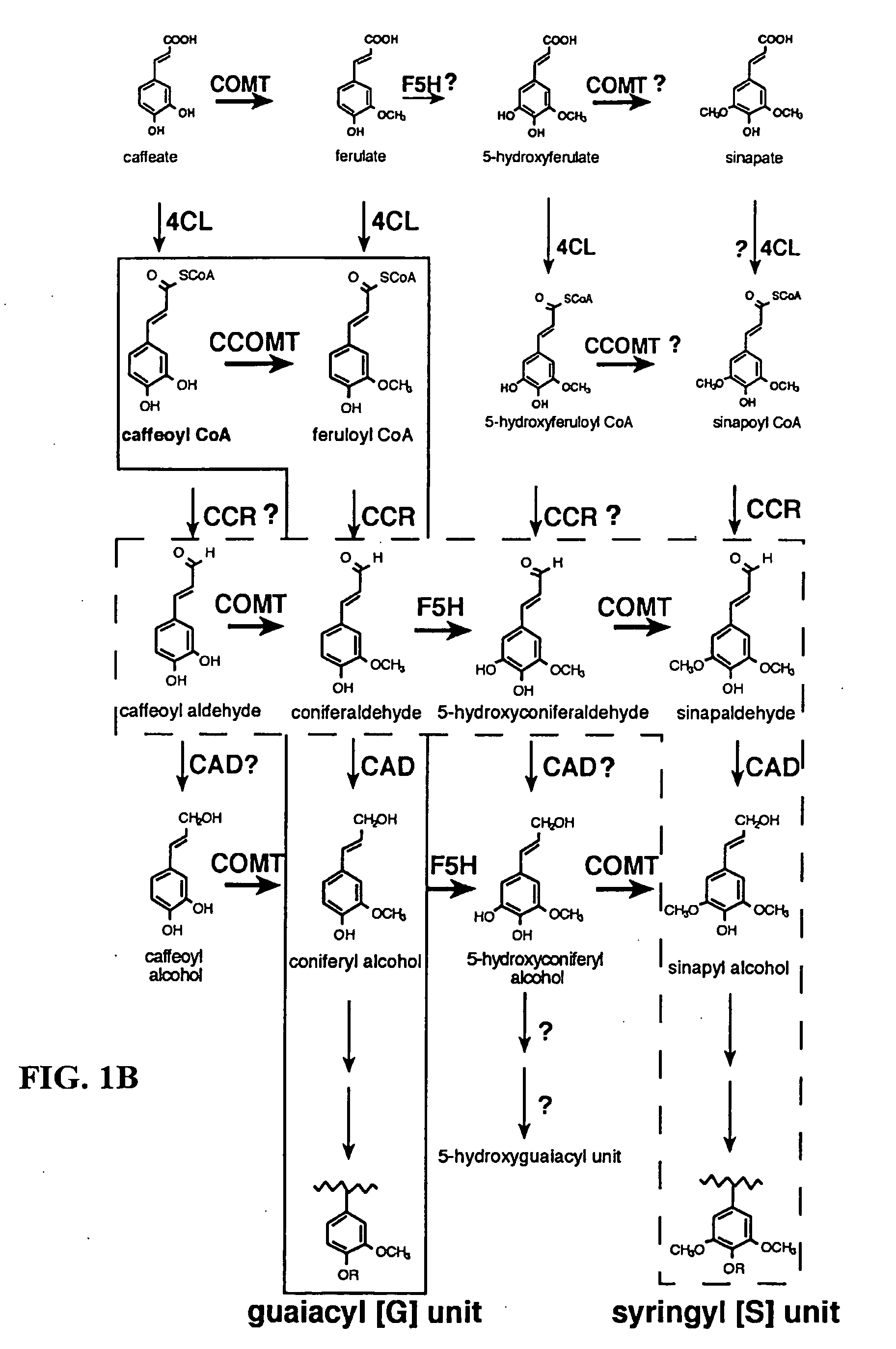
Method for modifying lignin composition and increasing in vivo digestibility of forages
InactiveUS7888553B2Improve digestibilityTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationOpen reading frame
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Method for modifying lignin composition and increasing in vivo digestibility of forages
InactiveUS20090044294A1Improve digestibilityLow lignin contentTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationOpen reading frame
Methods for transforming forage legumes or woody plants with a DNA construct comprising at least one open reading frame encoding for a caffeoyl CoA 3-O-methyltransferase enzyme or a Medicago sativa caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase enzyme or a fragment thereof in either a sense or antisense orientation under a lignification-associated tissue specific promoter have been found, resulting in the down-regulation of the corresponding homologous gene either through antisense inhibition or sense suppression, as well as reduced lignin content and modified lignin composition in the transgenic plants. The expression of the caffeoyl CoA 3-O-methyltransferase transgene produces an increased syringyl lignin to guaiacyl lignin ratio in the transformed plant, and greatly improved forage digestibility.
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Application of osa-MIR167a gene for regulating and controlling plant type of paddy rice
InactiveCN102719433AEasy to breedGenetic improvement has far-reaching implicationsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsNucleotide sequencingPlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering and specifically relates to an application of an osa-MIR167a gene for regulating and controlling plant type of paddy rice. The osa-MIR167a gene has several homologous genes in paddy rice genome and belongs to a same gene family MIR167 as an arabidopsis thaliana ath-MIR167 gene. The osa-MIR167a gene has a function of regulating and controlling the plant type of paddy rice and the nucleotide sequence thereof is shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:1 while the core sequence formed by transcription and splicing is shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:3. An ideal plant type and increased yield are achieved by changing the expression models of the osa-MIR167a gene or other members in the osa-MIR167a gene family through gene engineering and regulating and controlling the tillering angle, the height and the effective tillering number of the plant. The invention discloses the application of the osa-MIR167a gene for regulating and controlling the plant type of paddy rice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Anther tapetum and pollen specific efficient promoter as well as application thereof
InactiveCN101532015AReduce adverse effectsGenetic improvementVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention provides a pollen and anther tapetum specific efficient promoter, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown as the sequence table SEQ ID No.1. The promoter sequence is cloned from a maize genome by screening in a maize genome library and can propel a target gene to have specific expression in the anther tapetum and the pollen. The invention comprises a plant gene engineering method for creating male sterileness by using the promoter sequence, namely, the promoter downstream is joined with a heterologous gene or a homologous gene, and a plant expression vector is constructed, a host plant is transformed, the promoter sequence can propel the downstream genes thereof to express the target protein in the anther tapetum and the pollen in a efficient and specific way to realize creating plant male sterileness or modifying the safety of transgenic plants.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
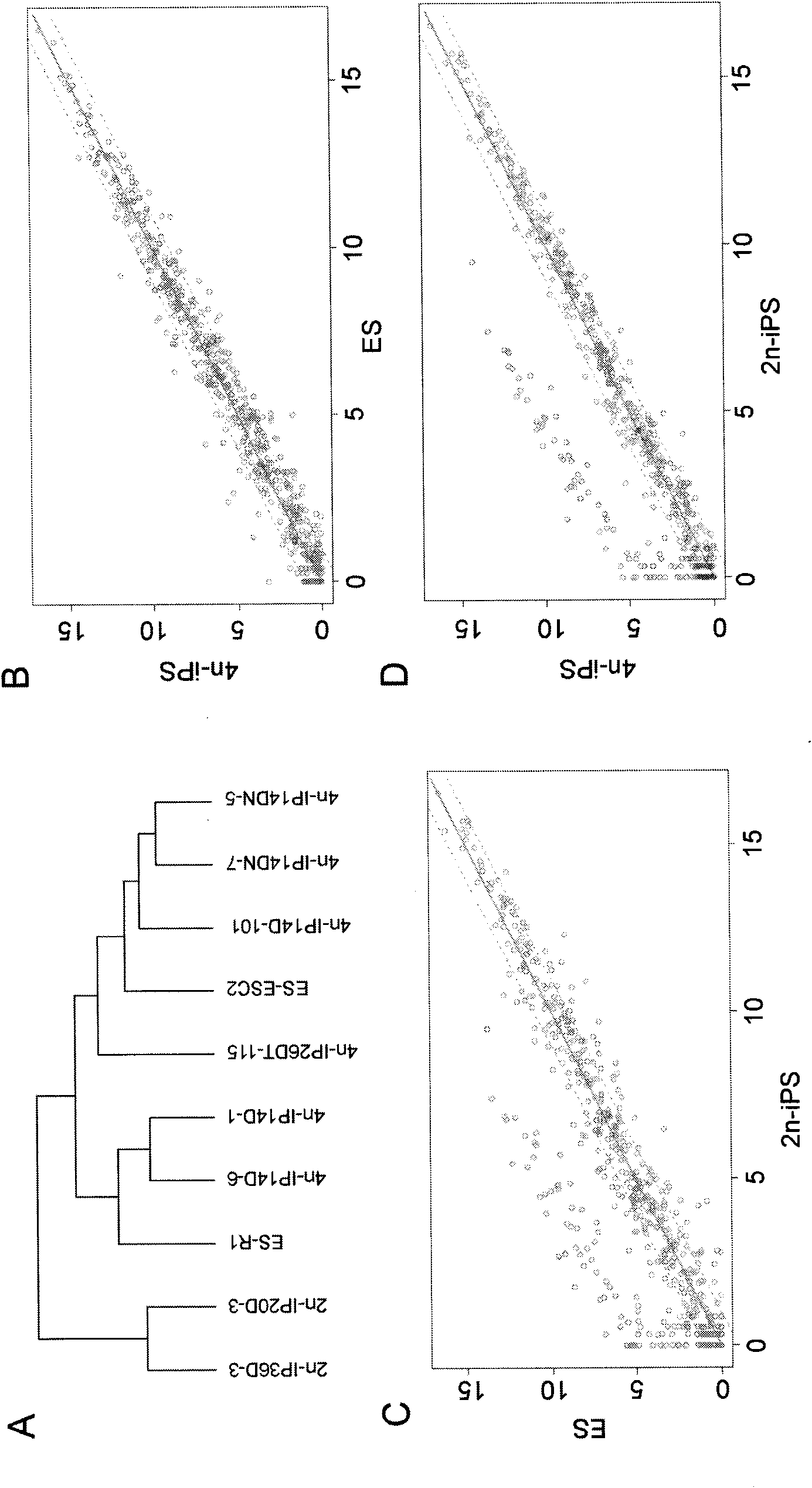
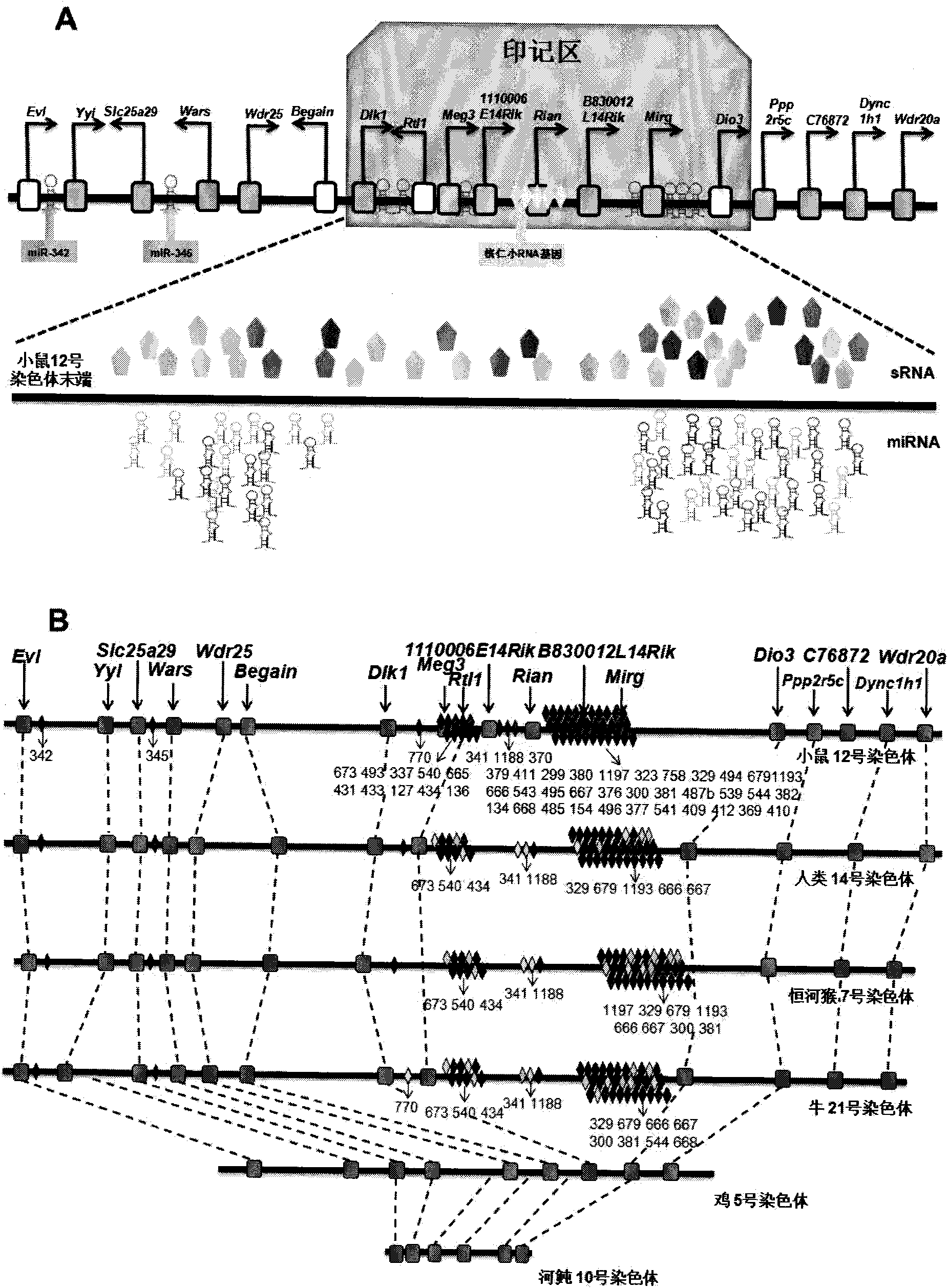
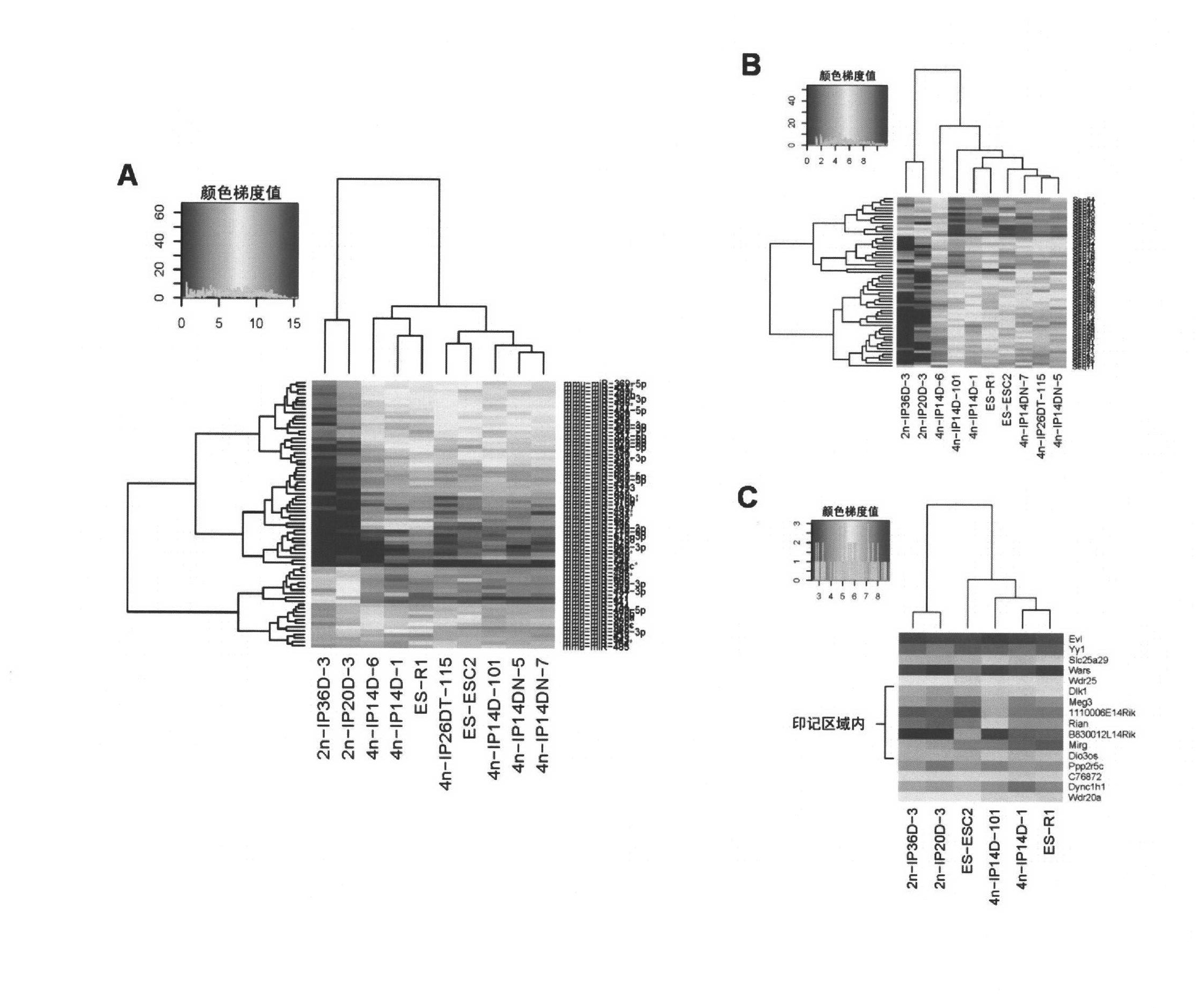
Key genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs or combination thereof used for identifying or regulating cell pluripotency
The invention relates to key genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, or a combination thereof used for identifying or regulating cell pluripotency. The invention is characterized in that the key genes, microRNAs, other non-coding RNAs or a combination is highly expressed in the stem cell with complete pluripotency and the expression is obviously repressed or silent in the stem cell without complete pluripotency. The genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs are the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs positioned in the chromosome imprinting region named as Dlk1-Dio3 on the long arm of mouse chromosome 12 and the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs in the genome collinearity regions of other mammals, which have 70%-100% of homology. The invention also relates to applications of the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, or the combination thereof used for identifying the pluripotency of the stem cell and regulating cell pluripotency, applications in stem cell typing, applications for regulating the cell pluripotency and the pluripotency state and level of the cell, applications in disease treatment, and applications in the drug target development of tumor treatment or the development of antitumor drugs.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
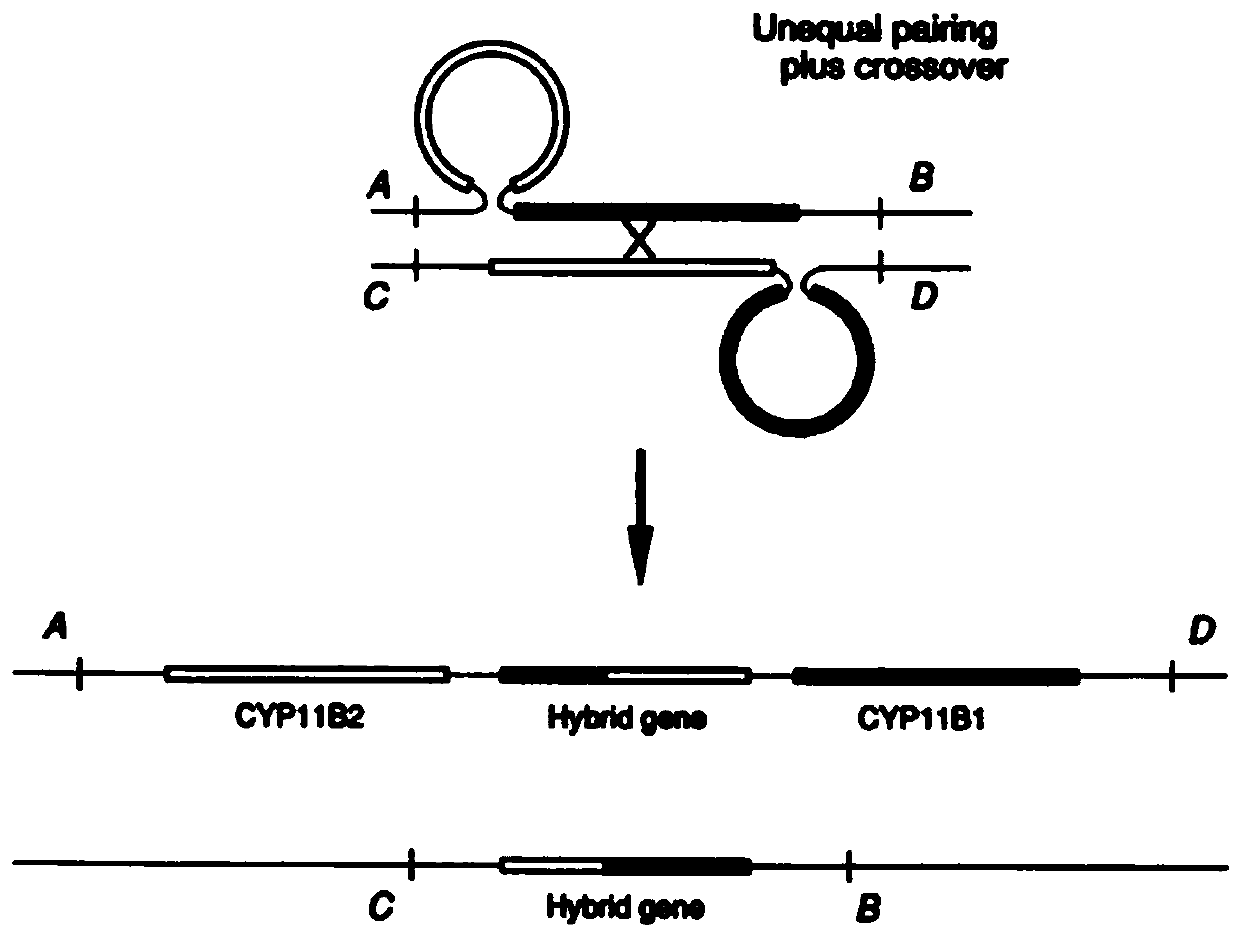
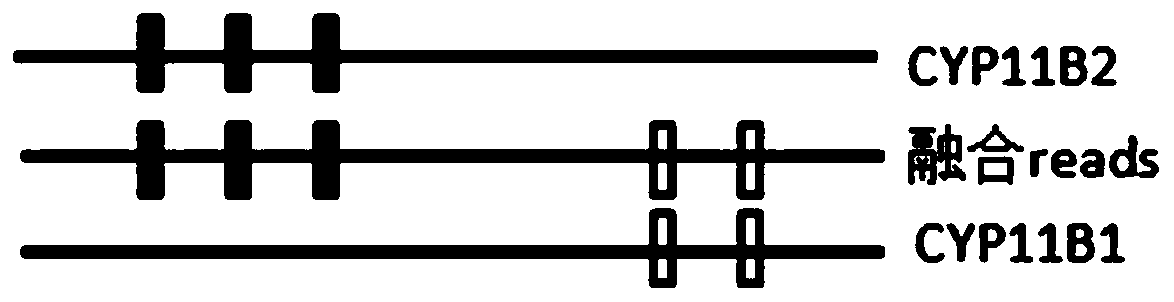
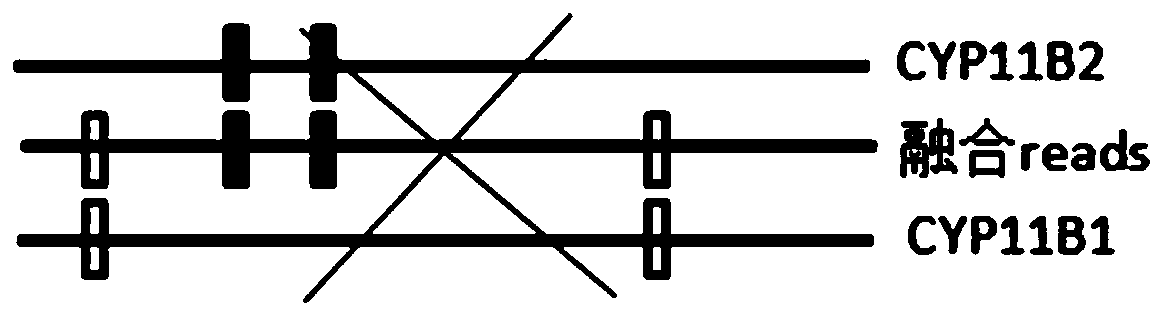
Fusion detection method based on homologous genes of differential SNP markers
ActiveCN110033829AAvoiding problems encountered in repeat sequence detectionProteomicsGenomicsBioinformaticsSnp markers
The invention relates to a fusion detection method based on homologous genes of differential SNP markers. The fusion detection method utilizes differential SNP signals of two genes to distinguish, bypasses the difference in sequencing depth, and performs consistency comparison on each sequencing reads sequence and the homologous gene sequence by using abnormal inserted fragment length of double-ended reads and the soft clip signal of single-end reads, so as to look for a continuous consistency SNP mark and infer the breakpoint interval. The fusion detection method based on homologous genes ofdifferential SNP markers can obtain the interval where the breakpoint is located, that is, the last site of the first half and the first site of the second half, and the separation distance of the interval depends on the physical distance of the detected two sites, thus avoiding the problem that the conventional structural variation detection method encounters in the detection of repeated sequences.
Owner:北京诺禾心康基因科技有限公司
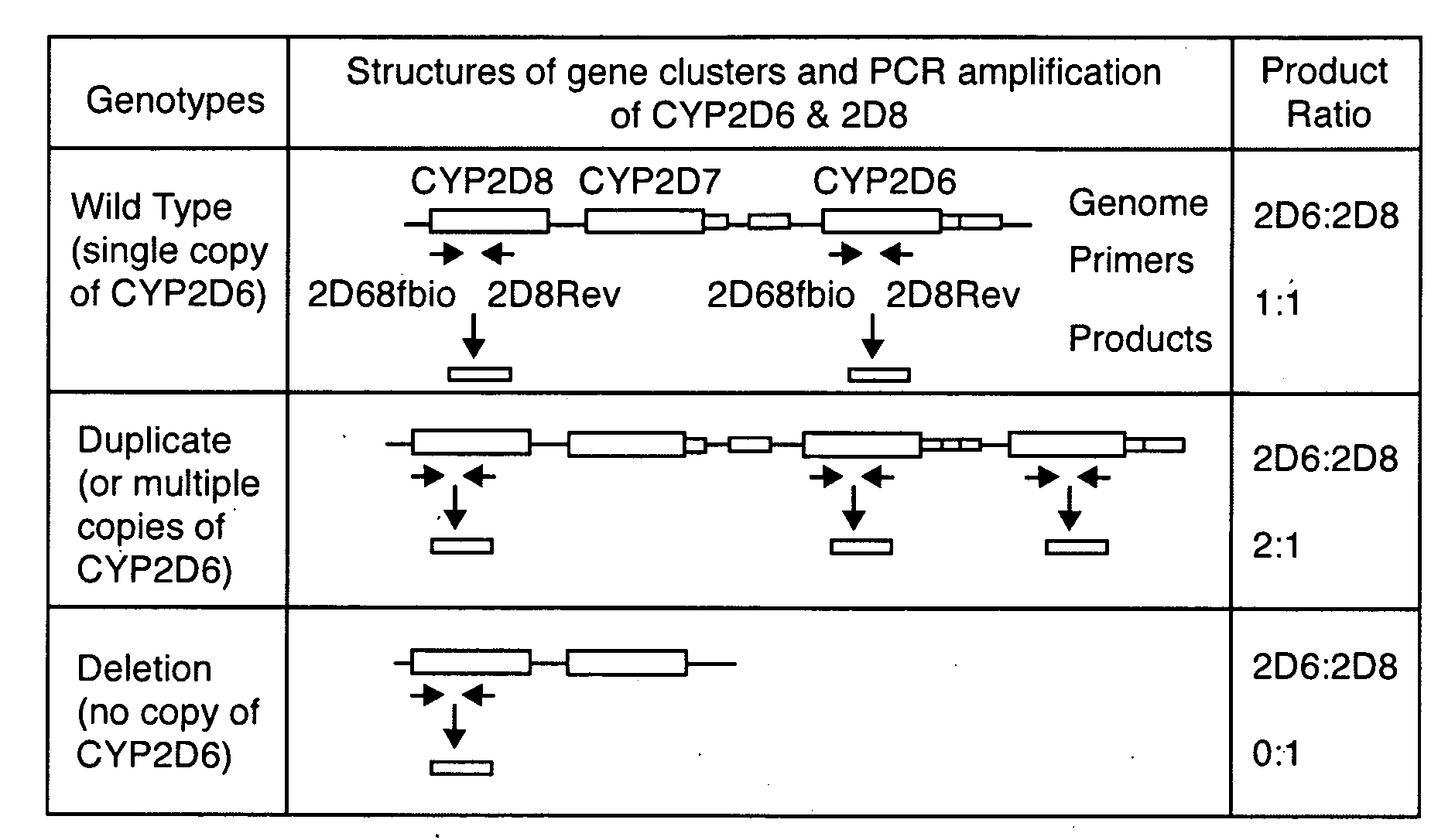
Method for Detecting Large Mutations and Duplications Using Control Amplification Comparisons to Paralogous Genes
InactiveUS20090087846A1Facilitate easy and simultaneous detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDrugs prescriptionsGene mutation
Owner:GAMIDA FOR LIFE
Pichia pastoris omega3-fatty acid dehydrogenase promoter sequence and use thereof
The invention relates toOmega3- fatty acid dehydrogenase promoter sequence separated from Pichia Pastoris and its application. The invention comprises SEQ ID NO:1. The invention includes the microbiological gene engineering method of changing microbiological cells protein components with the promoter sequence, and comprises: connecting heterogenic or homologous gene to the promoter downstream, transferring into microbiological expression vector, transforming microorganism host for the expression of target protein in its cells to realize quality improvement or medical use. Omega3- fatty acid dehydrogenase promoter sequence separated from Pichia Pastoris can be used in all the transgenic microorganisms.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene and applications thereof
InactiveCN103387994AImprove germination rateHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySalt resistance
The invention discloses a malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1. The MhWRKY40a gene is capable of applying to the production of novel species, which are salt resistant and low temperature resistant, and / or plant variety improvement. A novel MhWRKY40a gene is cloned from malus hupehensis for the first time, and the homology between the gene sequence and the arabidopis thaliana, grape and barley is 50.89%. But the protein tertiary structure of the MhWRKY40a is prominently different from the homologous gene of the model plant arabidopis thaliana; the former has 5 beta-folds, while the latter has 4 beta-folds. The MhWRKY40a transgenetic tobacco has the properties of salt resistance and low-temperature resistance, raises the resistance-associated gene expression, and therefore the fact, which the MhWRKY40a gene has the function of improving the salt resistance and low-temperature resistance properties of the plants, is testified.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Yeast mutant and substance production method using the same
According to the present invention, the ability to produce a desired product is significantly improved and the growth rate and the fermentation rate are maintained at excellent levels for yeast upon production of a desired product with the use of yeastA yeast used as a host is introduced with a foreign gene that encodes an enzyme involved in the production of a desired product and the HAP4 gene that can be constitutively expressed or a homologous gene thereof.Preferably a yeast mutant is a mutant strain having lowered alcohol productivity than that of a wild-type strain.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
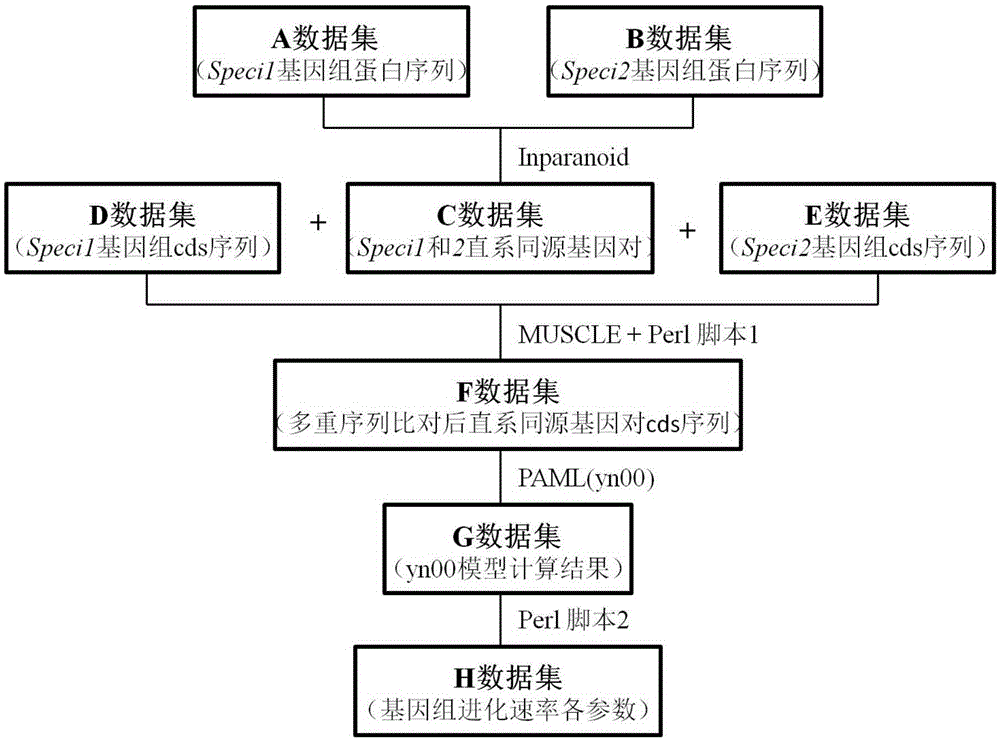
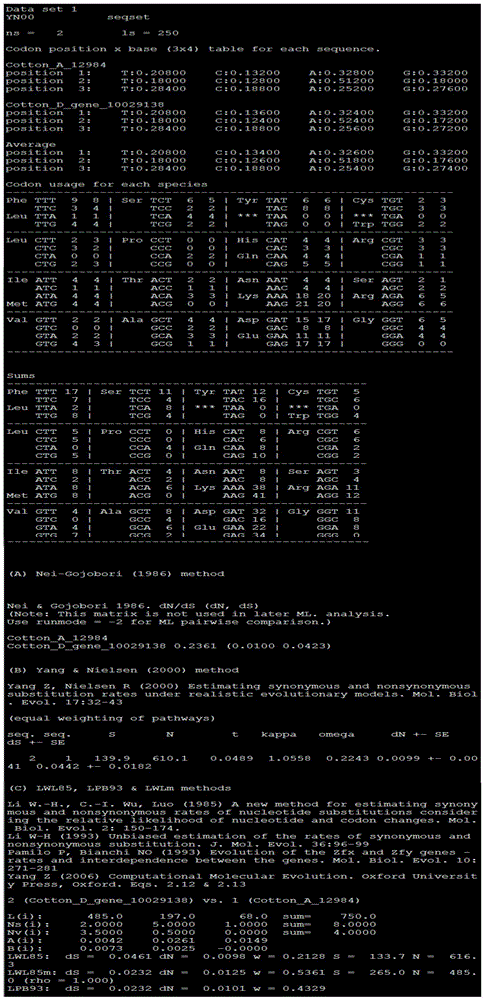
Method for batch computing of evolutionary rate of orthologous genes of genome
ActiveCN105426700ASmooth connectionGood effectBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsOrthologous GeneComputational gene
The invention discloses a method for batch computing of the evolutionary rate of orthologous genes of a genome. According to the method for batch computing of the evolutionary rate of the orthologous genes of the genome, an InParanoid program for clustering searching of orthologous genes after a paired comparing result is obtained based on Blast, an MUSCLE program based on multi-sequence comparative analysis and a PAML software package yn00 program for evaluating the synonymous and non-synonymous substitution ratio based on comparison between coding protein DNA sequences are comprehensively used, and the methods such as Perl scripting language programming are combined. It is proved through experiments that a method comparing system for batch computing of the evolutionary rate of the orthologous genes of the genome is good in repeat effect on various parameter values for detecting the genome and computing the evolutionary rate of the orthologous genes of the genome, high in speed and capable of easily achieving batch computing, automation and processing.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Gene of Lygus lucorum polygalacturonase and application thereof
InactiveCN102492706ASolve the problem of gene sequence acquisitionSolving Recombinant Expression ProblemsFungiBacteriaPichia pastorisEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a gene sequence of Lygus lucorum polygalacturonase (PG) and a method for preparing the Lygus lucorum polygalacturonase. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting total RNA (ribonucleic acid) of Lygus lucorum; designing a primer according to the conserved sequences of the Lygus lucorum polygalacturonase; amplifying by utilizing an RT-PCR (reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction) method to obtain homologous gene sequences of three PGs; obtaining 5' and 3' unknown sequences by utilizing an RACE experiment; and finally, respectively carrying out the recombinant expression, purification and property analysis of the Lygus lucorum polygalacturonase by utilizing an Escherichia coli expression system and a Pichia pastoris expression system. By using the method, the obtaining problem of the gene sequence of the polygalacturonase of the Lygus lucorum is solved firstly, and the recombinant expression problem of the polygalacturonase derived from insects is also solved for the first time. The gene disclosed by the invention has the application prospect in the aspects of food (fruit juice squeezing), oil material extraction, traditional Chinese medicinal material treatment, paper-making industry, oligo-pectin health care products and the like. In addition, an inhibitor aiming at the Lygus lucorum polygalacturonase can be used as a policy for preventing and controlling a piercing-sucking type pest, thereby achieving the prevention and control on the target pest.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
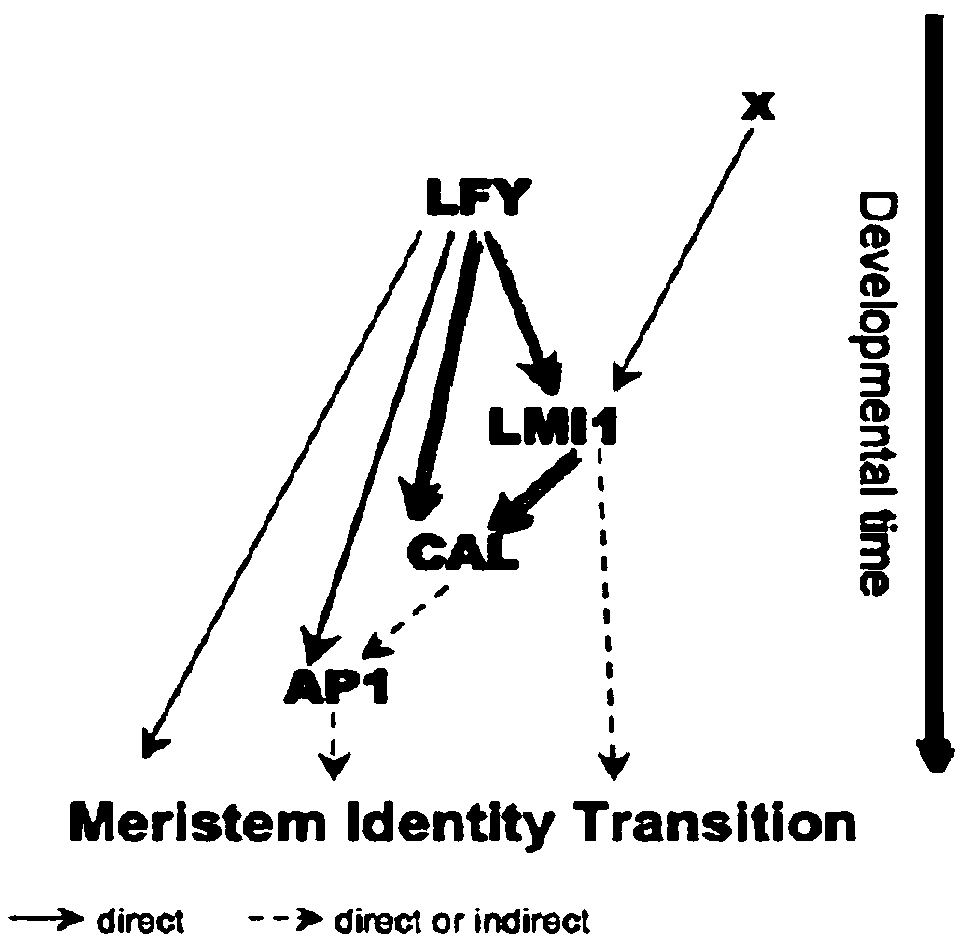
Rapid cloning method and special primers for lfy/flo homologous fragments of plant flowering-related genes
InactiveCN102268429ARich varietyOptimization of PCR reaction conditionsFermentationPlant genotype modificationBryophyteNucleotide
The invention relates to a rapid cloning method of plant flowering related gene LFY / FLO homologous fragments and special primers thereof, and relates to the technical field of rapid isolation and cloning of plant homologous genes. The method is characterized in that the used special primer LYF has a nucleotide sequence of 5'-TAYATIAAYAARCCIAARATG-3', and LYR has a nucleotide sequence of 5'-ARIYKIGTIGGIACRTACCA-3'; the primer concentration is 25 muM, and the annealing temperature is 44 DEG C. The method of the invention can clone to obtain homologous fragments of LFY / FLO genes of plants from bryophytes to spermatophytes, and has a wide range of the kinds of applicable plants; the potential problem that a gene fragment is difficult to be amplified due to no expression or low expression of homologous fragments of the LFY / FLO gene when cDNA is used as a template is well avoided; and the method is rapid, simple, economical, and effective.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Yeast mutant and substance production method using the same
The object aims to largely improve the productivity of a desired product and maintain an excellent growth rate and an excellent fermentation rate in the production of the desired product by using yeast. A foreign gene which encodes an enzyme involved in the production of the desired product and HAP4 gene which can be expressed constitutively or a homologous gene thereof are introduced into a yeast host. The yeast mutant is preferably a mutant strain having reduced alcohol productivity compared to its wild-type one.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
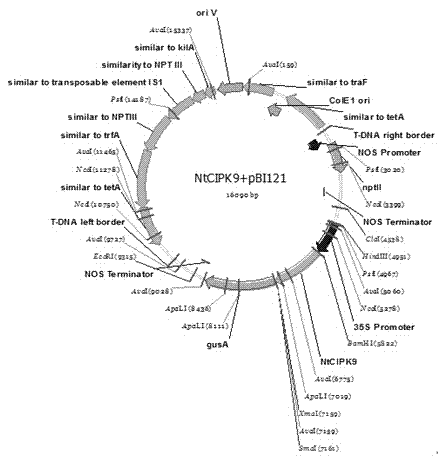
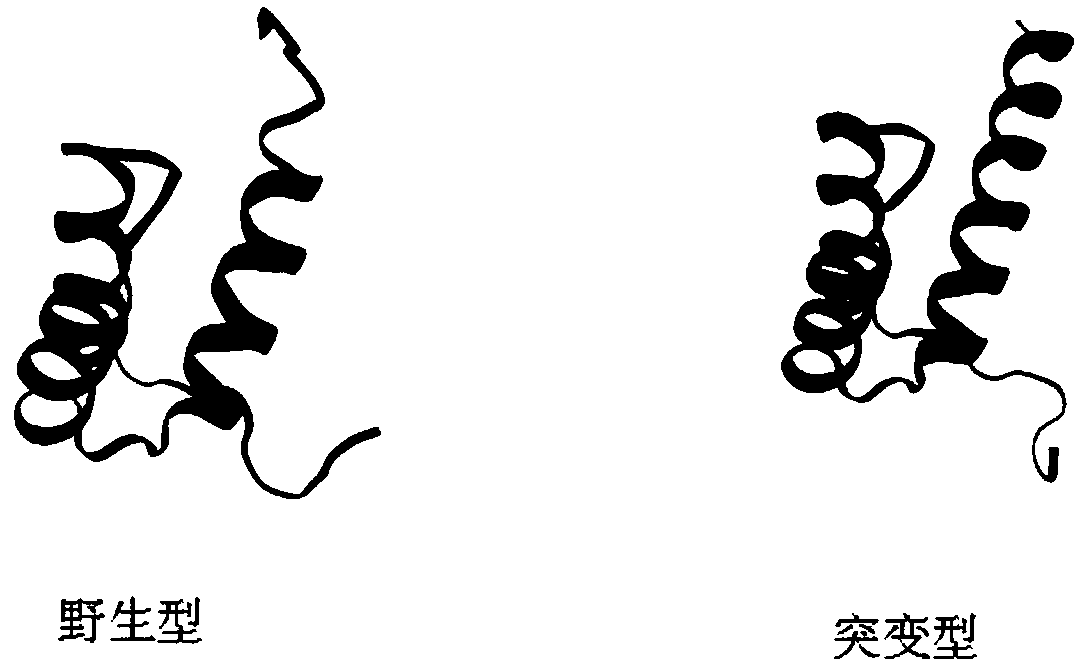
Nitraria tangutorum CBL-interacting protein kinase 9 (NtCIPK9) gene, expressed protein thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN104498514AImprove salt tolerance researchIncrease resourcesBacteriaTransferasesNucleotideAmino acid
The invention discloses a nitraria tangutorum CBL-interacting protein kinase 9 (NtCIPK9) gene, expressed protein of the NtCIPK9 gene and application of the NtCIPK9 gene. The nucleotide sequence of the NtCIPK9 gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the NtCIPK9 gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.2. According to the NtCIPK9 gene, a full-length gene related to stress resistance of nitraria tangutorum is cloned in a homological mode by using leaf blade tissue of the nitraria tangutorum on the basis of a part of existing transcriptome data according to the stress resistance characteristic of the nitraria tangutorum, and is named NtCIPK9 according to a homologous gene in arabidopsis. The function of plant salt tolerance of the NtCIPK9 gene is proved through analysis of salt tolerance of an NtCIPK9 gene homozygous arabidopsis plant, and resources are increased for a plant stress resistance gene pool.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
SNP molecular marker for detecting lobed-leaf trait of brassica campestris vegetables and applications thereof
ActiveCN109609671AHelps to filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaMolecular marker
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a SNP molecular marker for detecting lobed-leaf trait of brassica campestris vegetables and applications thereof. The SNP molecular marker is selected from: (a) the 358th locus of a template strand of Bra009510 gene, wherein the rna polymorphism is G or A; and (b) a homologous gene homologous to the Bra009510 in a brassica campestris vegetable variety with an integrifolious trait maintained, wherein the rna polymorphism corresponding to the 358th locus of SEQ ID NO.1 is G, and / or a homologous gene homologous to the Bra009510 in a brassica campestris variety with a lobed-leaf trait, wherein the rna polymorphism corresponding to the 358th locus of the SEQ ID NO.1 is A. The brassica campestris vegetable variety with an integrifolious trait maintained and / or the brassica campestris variety with a lobed-leaf trait are selected from: natural varieties, hybrid varieties and artificial mutagen varieties. The sequence of the template strand of the Bra009510 gene is as shown in the SEQ ID NO.1. The molecular marker provided by the invention and corresponding primers have a selection accuracy of 100% whether in lobed-leaf or integrifolious materials, and can be used for molecular marker-assisted selection breeding.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
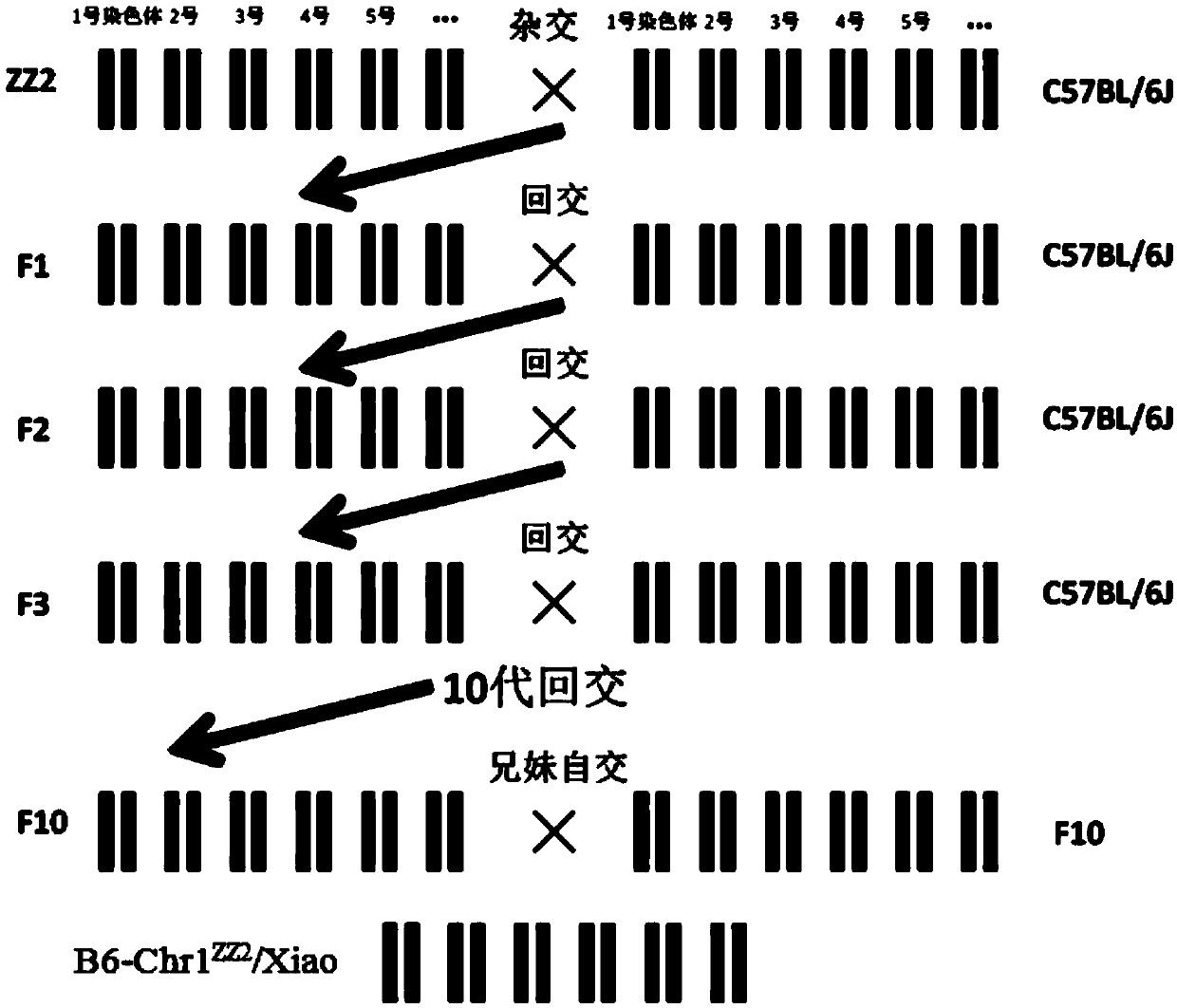
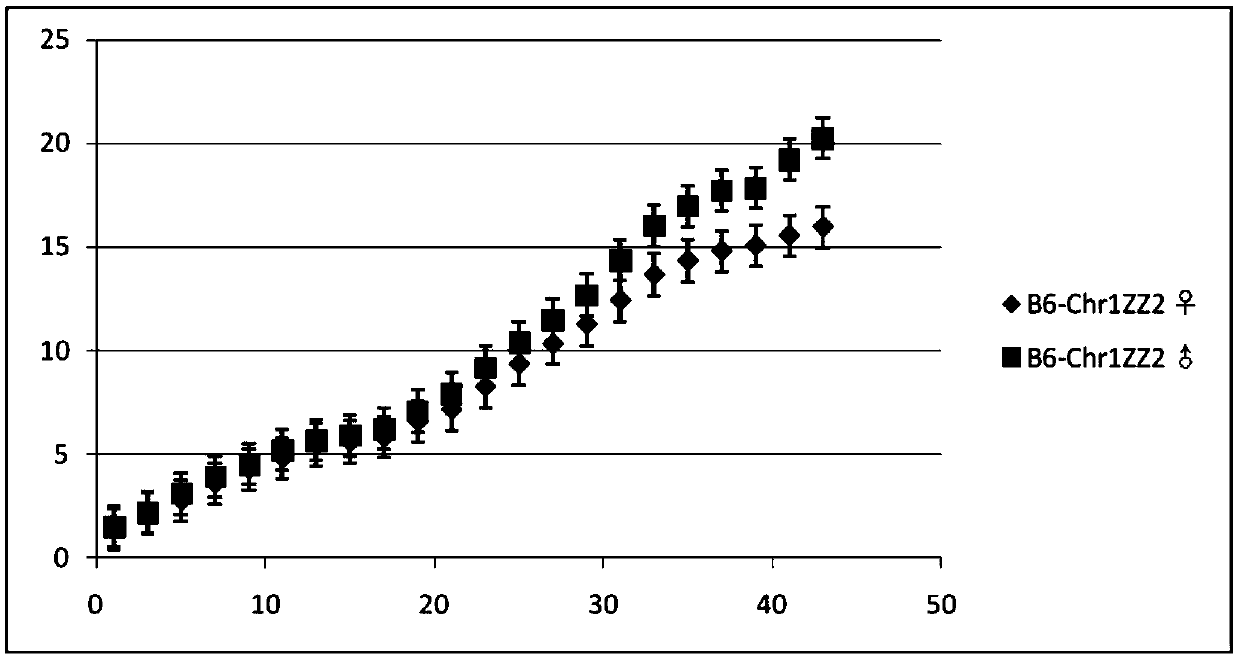
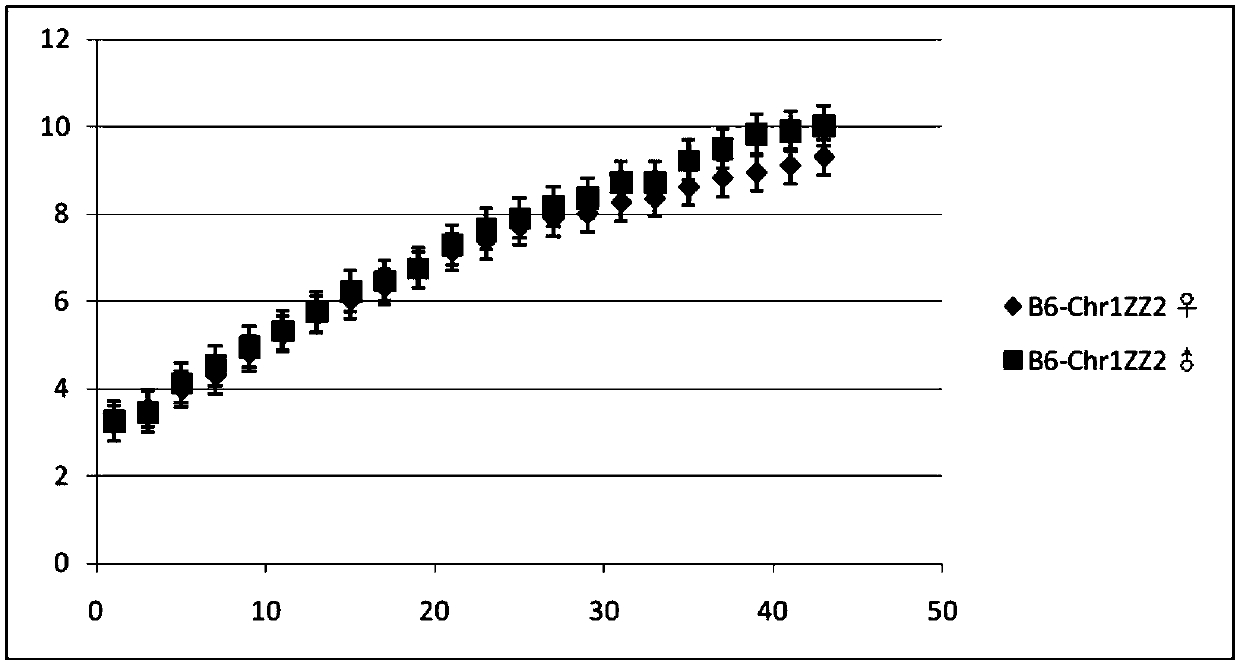
Method for constructing B6-Chr1<ZZ2>/Xiao mouse model through replacing No. 1 chromosome based on ZZ2 mus musculus source
The invention relates to a method for constructing a B6-Chr1<ZZ2> / Xiao mouse model through replacing the No.1 chromosome based on a ZZ2 mus musculus source. The method comprises the steps as follows: a ZZ2 mus musculus is hybridized with a mouse C57BL / 6J, so as to obtain a F1-generation mouse; secondly, the F1-generation mouse is backcrossed with the C57BL / 6J, and a F2-generation mouse is obtained; thirdly, a mouse of which the No. 1 chromosome is in a heterozygosis state is screened out through genotyping; fourthly, the F2-generation mouse is backcrossed with the C57BL / 6J; fifthly, the same method is adopted for backcross until a 10-generation is screened out, and a mouse group of which the No.1 chromosomes are in the heterozygosis state while the other chromosomes are all pure C57BL / 6J genotypes is formed; sixthly, the DNA of the genes of the backcross mouse is identified; finally, when the backcross mouse with the No.1 chromosome in the heterozygosis state of ZZ2 and B6 is subjected to the 10-generation backcross, homologous genes carrying the No.1 chromosome of the ZZ2 mus musculus is bred and introduced into an inbred strain, and the mouse model is obtained through brother-sister selfing and gene identification.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
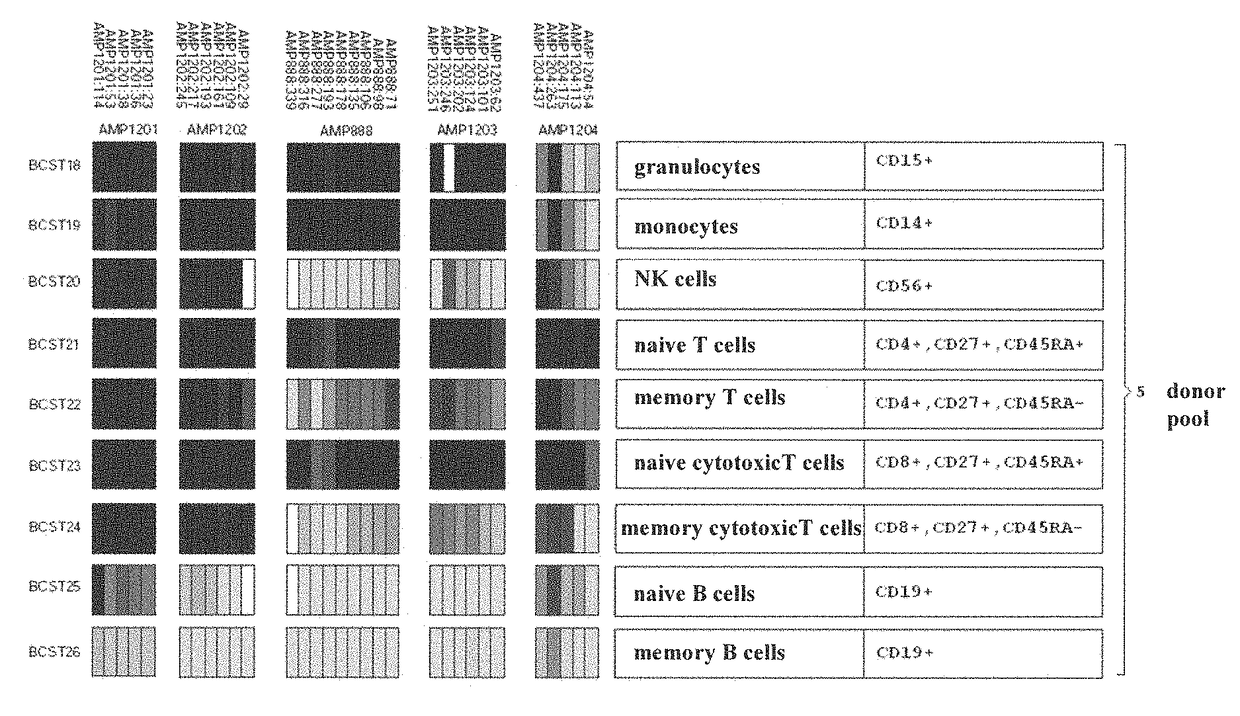
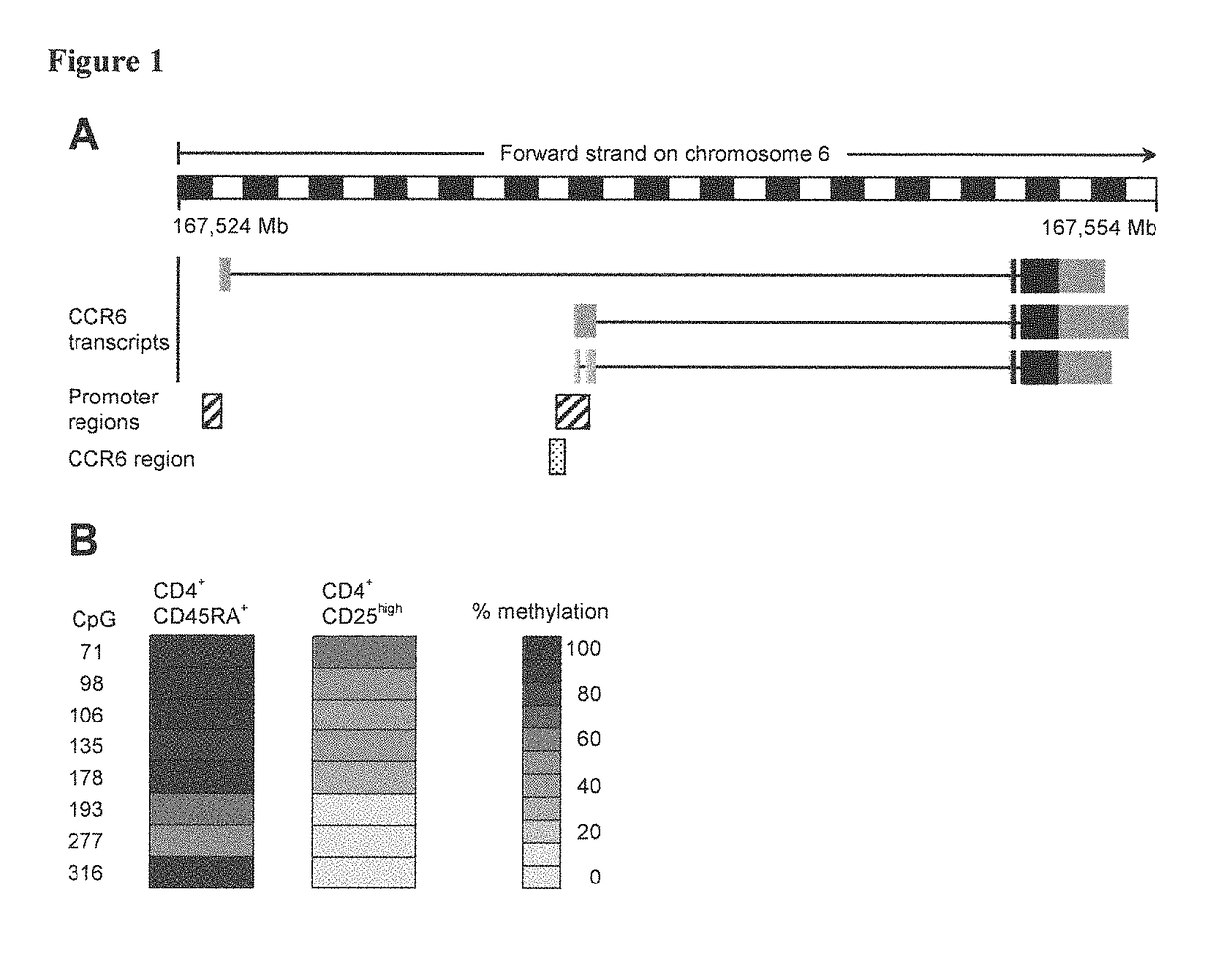
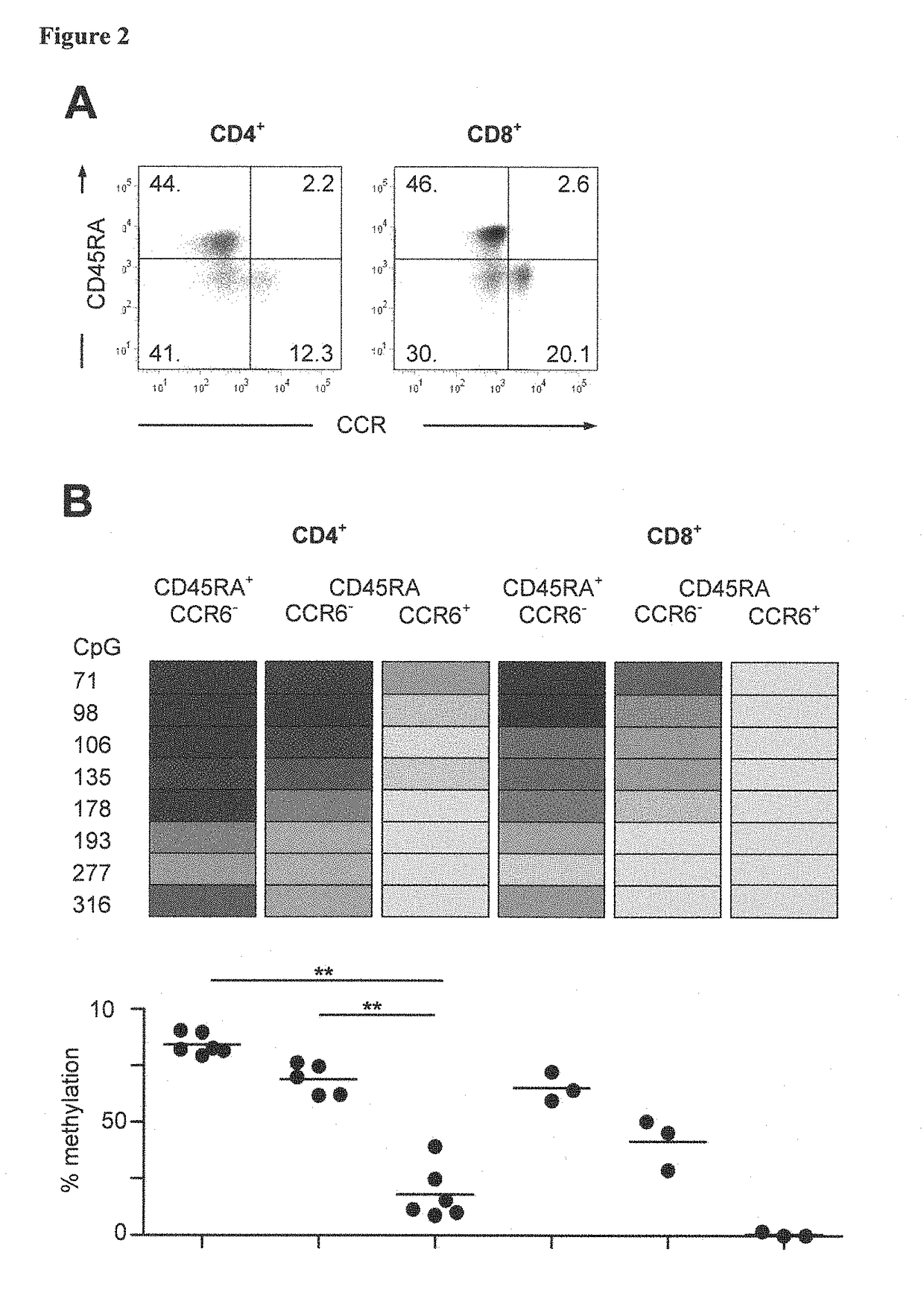
Detection of immune cells, in particular T cells through DNA-methylation analysis of the genes CCR6 and BLR1
ActiveUS9783846B2Quantity minimizationImproved and effective and preventionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationQuality assurance
The present invention relates to a method, in particular an in vitro method, for identifying certain immune cells of a mammal, comprising analyzing the methylation status of at least one CpG position in the gene CCR6 and / or BLR1 or an orthologous or paralogous gene thereof, and the use of DNA-methylation analysis of the genes of the proteins CCR6 and / or BLR1 for a detection and quality assurance and control of certain immune cells. In particular, the present invention relates to analyzing the methylation status of at least one CpG position in the gene CCR6 in T cells. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a kit for performing the above methods, as well as to respective uses.
Owner:EPIONTIS GMBH
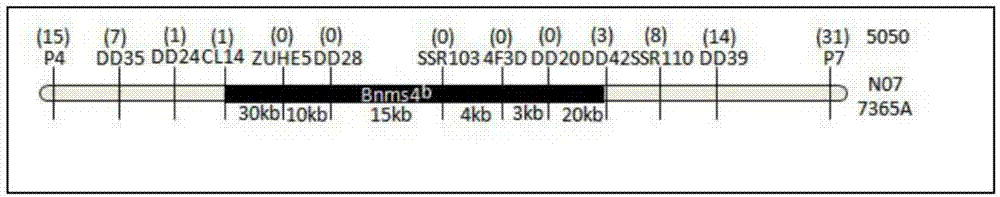
Brassica napus nucleic male sterility gene Bnms4 and preparation method and application
The invention discloses a brassica napus nucleic male sterility gene Bnms4 and a preparation method and application. The method comprises the steps that 1, a CDS nucleotide sequence or promoter nucleotide sequence or coded aminoacid sequence of the gene is utilized for designing and developing a primer capable of amplifying the gene, and the primer is synthesized; 2, by means of the synthesized primer, the gene or any section of interested nucleotide or one section of polynucleotide homologous with the gene is amplified from a genome, mRNA and cDNA. The gene or a homologous gene is screened and obtained from the cDNA and a genome library by adopting the cloned polynucleotide as a probe. The method is easy to carry out and easy and convenient to operate, the primer is used for amplifying the gene, the gene is cloned to various carriers and converted into brassica napus, stable and thorough male sterility can be caused, and breeding application is conducted; a sequence of the gene itself is used for designing a specific primer for molecular marker-assisted selection, and the advantages of being rapid, economical, effective and accurate are achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cultivated silkworm glutathione-S-transferase BmGSTe5 gene
The invention provides a glutathione-S-transferase BmGSTe5 gene for silkworms, which is obtained by getting Epsilon homogenetic gene through retrieving in silkworm gene group by taking use of the known Epsilon family members of other species' GST and by cloning. The activity of the expression product over the mode background CDNB (1-Cl-2,4-dinitrobenzene) is 12 micro mol / min / mg protein. With this gene target, it is hopeful to design a medicine that can prevent and treat Lepidoptera destructive insects but is no harm to those useful insects. The invention is of high value for developing medicine and preventing and treating destructive insects.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
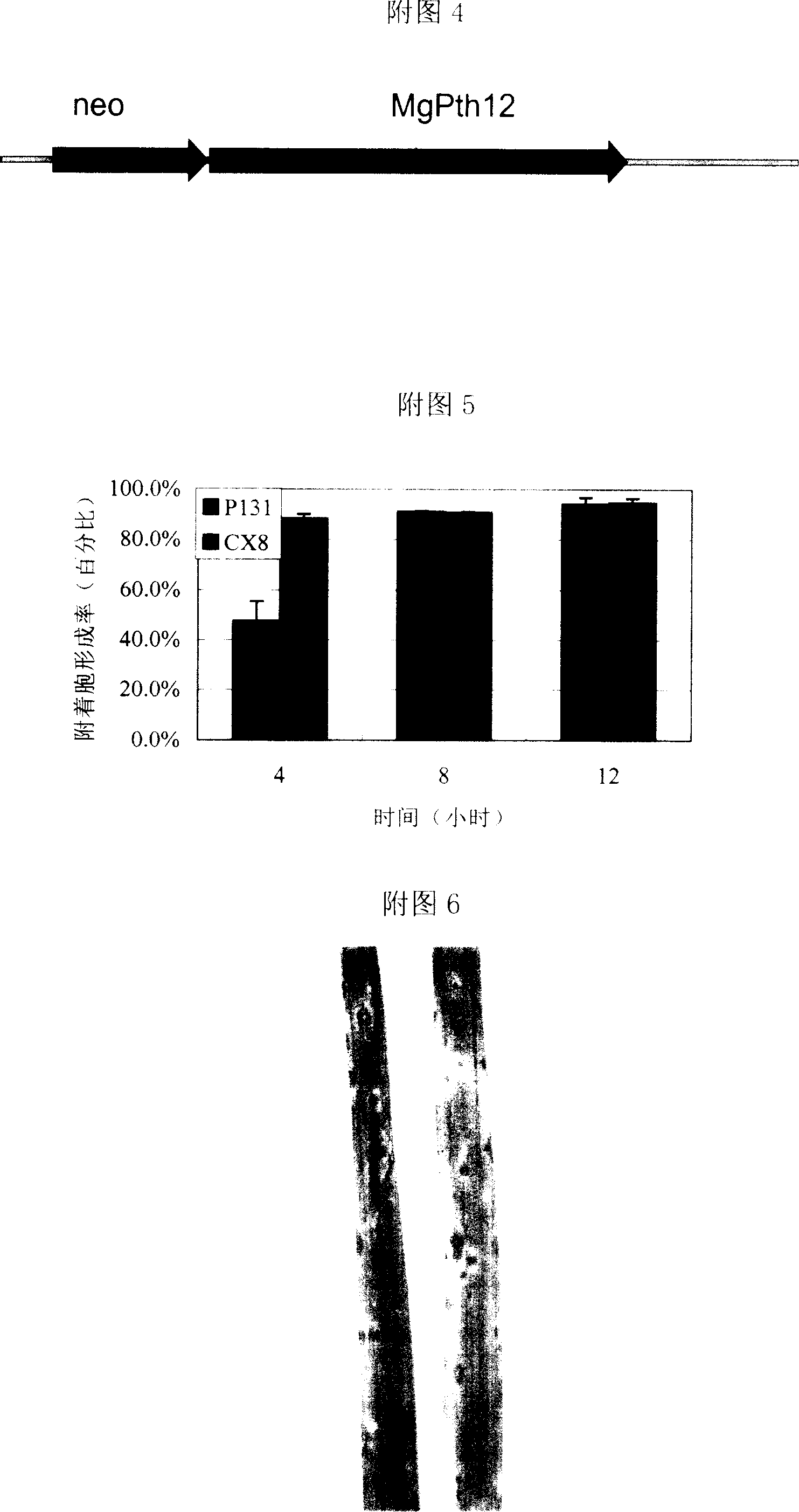
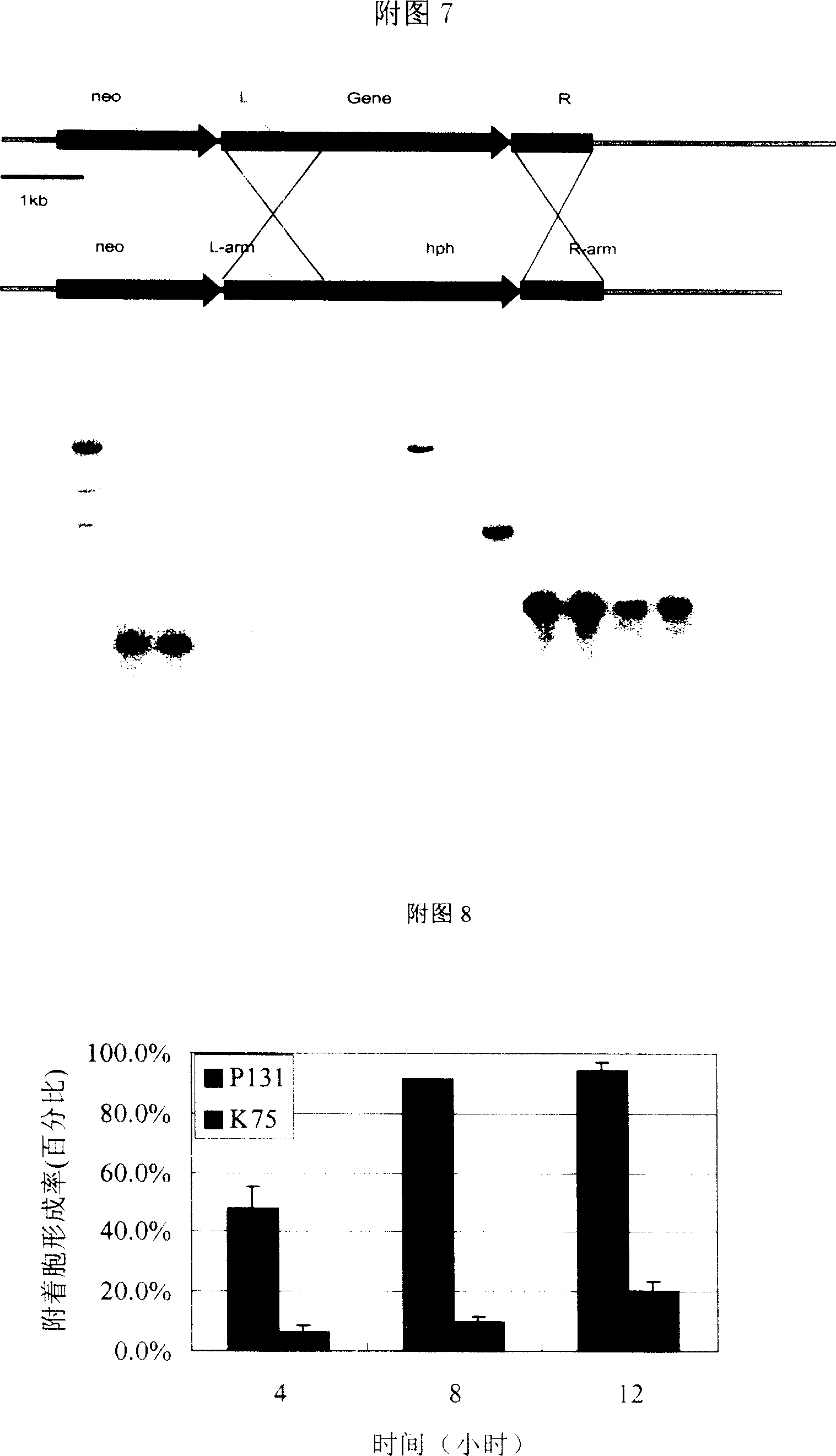
Gene MgPTH12 for controlling mature and pathogenicity of fungi appressorium derived from Magnaporthe grisea and its uses
The invention discloses a new necessary MgPTH12 gene and utility to make pear spore bacterium attach to mature and lead to disease, which is characterized by the following: the gene and its cDNA and coding product possess the sequence in the SEQ ID No.:1, No.:2 and No.:3; the protein of coded gene possesses homeo structural region, which is not similar to known functional protein; the gene removes abnormal and matured attaching cell, which reduces forming frequency of infecting tin and extending infecting hypha without pathogenic ability for rice; the homologous gene of gene lies in the plant pathogenic bacteria widely, which can be applied to design and sieve new drug to prevent fungus.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
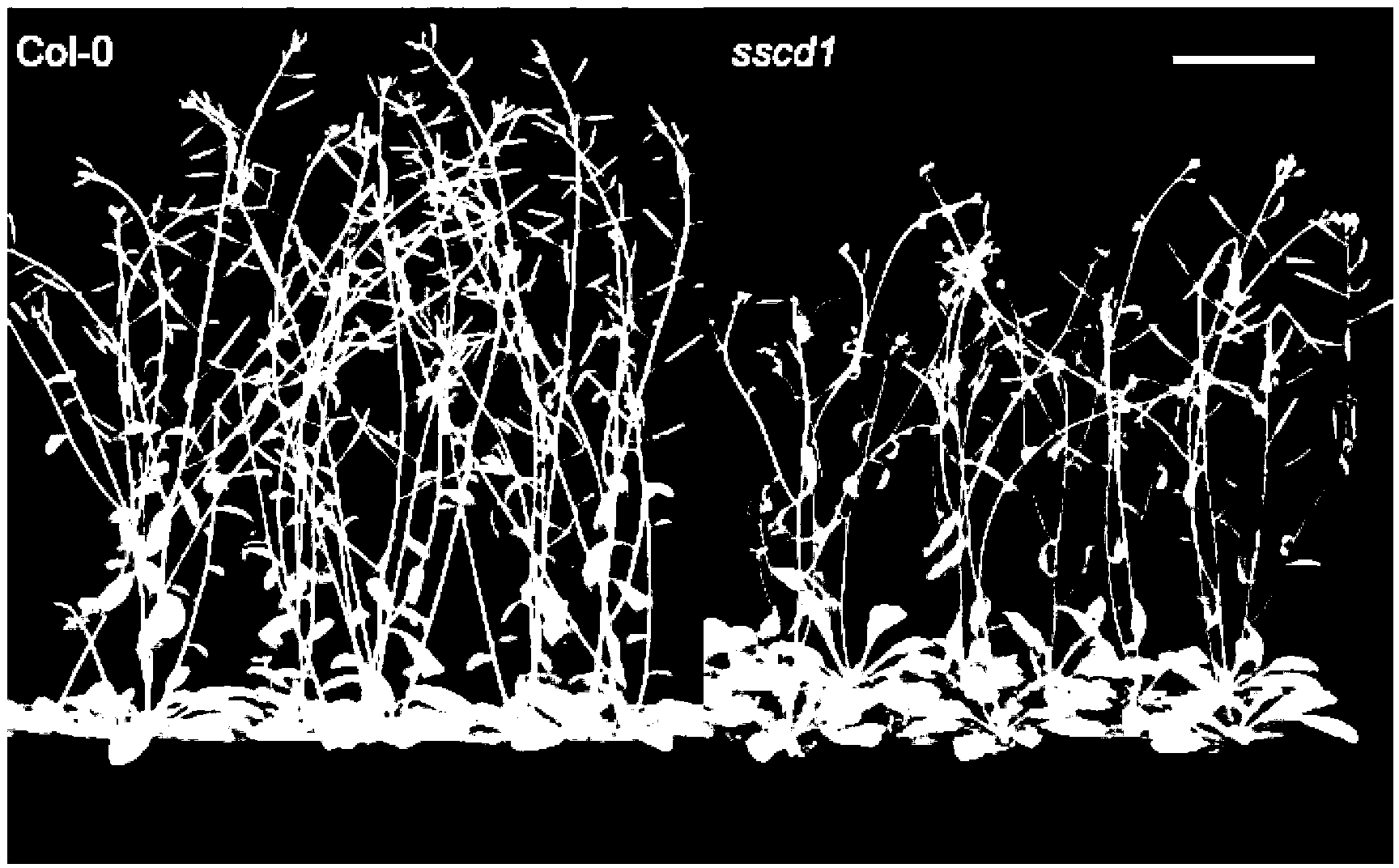
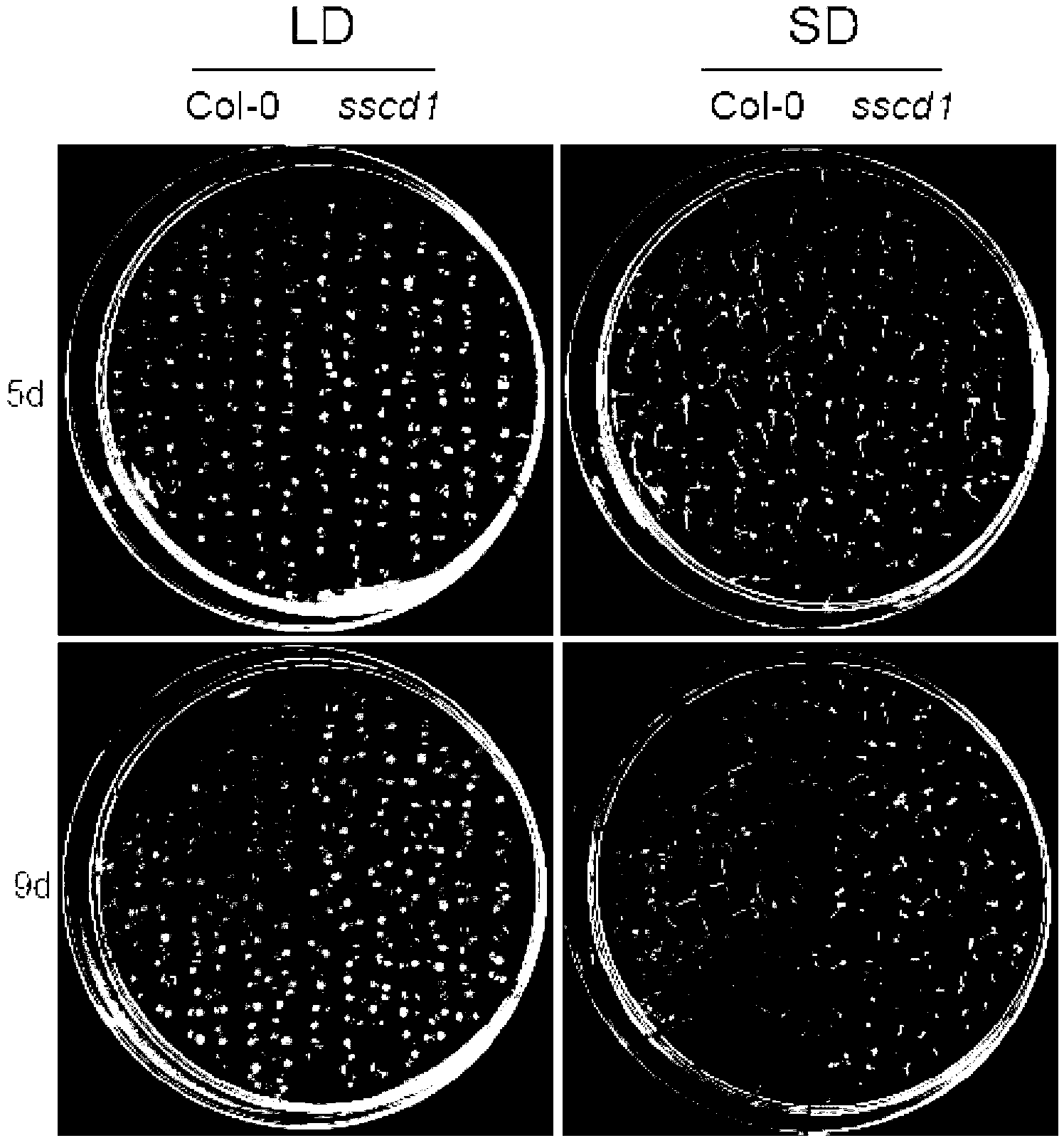
Short-day sensitive cell death SSD1 gene and coded protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a short-day sensitive cell death SSD1 gene and a coded protein and application thereof. The SSD1 gene has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. According to the invention, by using a model plant arabidopsis thaliana as a test material, through EMS (ethyl methanesulfonate) mutagenesis, an ssd1 mutant is obtained through screening. The SSD1 gene is separated by adopting a map-based cloning method, a gene mutational site is found, and the cell death is caused by deletion of the gene under the condition of short day. The SSD1 gene is necessary for the growth of arabidopsis thaliana under the condition of short day, and has a wide homology in plants. The finding of the biological function of the gene and the relevant research on a homologous gene are beneficial to deepening of the research on the controlling of the plant cell death by photoperiod, have important scientific significance in researching a molecular mechanism of the plant cell death, and also have important application value in improvement of crop varieties in a short-day region.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
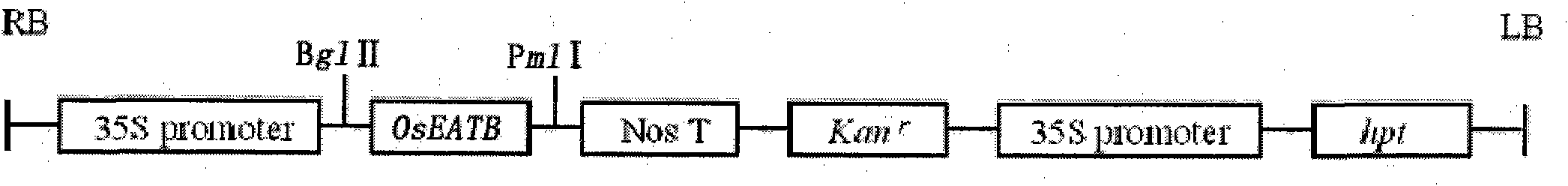
Application of rice OsEATB gene in modifying rice yield traits
InactiveCN101886083AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceTriticeae
The invention belongs to the field of transgenic technology, and particularly relates to application of rice OsEATB gene in modifying rice yield traits. In the invention, rice AP2 transcription factor OsEATB gene and homologous gene thereof are used to transform subspecies japonica rice and nonglutinous rice so as to modify the yield traits of the rice; in addition, the rice AP2 transcription factor OsEATB gene and the homologous gene thereof are also used to transform corns, wheat, broomcorn and other cereal crops so as to modify the yield traits of the cereal crops; furthermore, OsEATB gene and homologous gene thereof are used to transform dicotyledon so as to modify the yield traits of the dicotyledon, including the increase of branch number, grains, fruit number and volume and weight of the grains and the fruits.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Methods to identify evolutionarily significant changes in polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences in prokaryotes
InactiveUS20050181387A1High sensitivityIncrease virulenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
Methods for identifying polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences which may be associated with commercially relevant or useful traits in prokaryotes are provided. The methods employ comparison of homologous genes from two closely related prokaryote species to identify evolutionarily significant changes. Sequences thus identified may be useful in developing therapeutics, diagnostics, or vaccines.
Owner:EVOLUTIONARY GENOMICS LLC
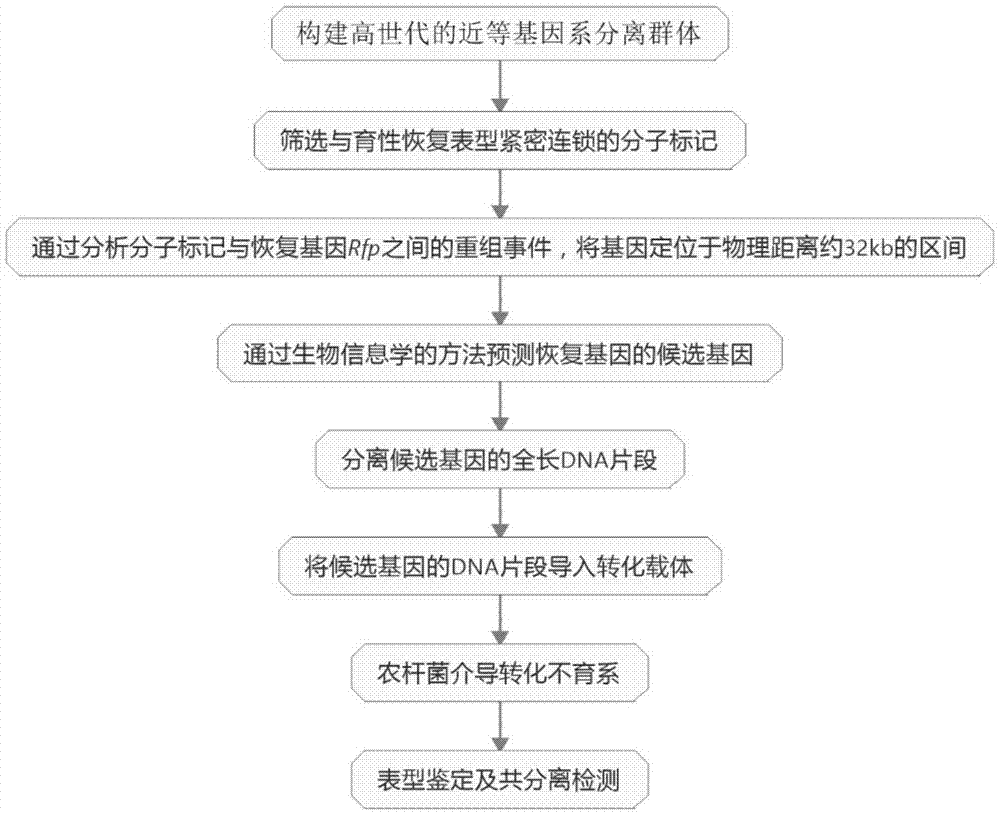
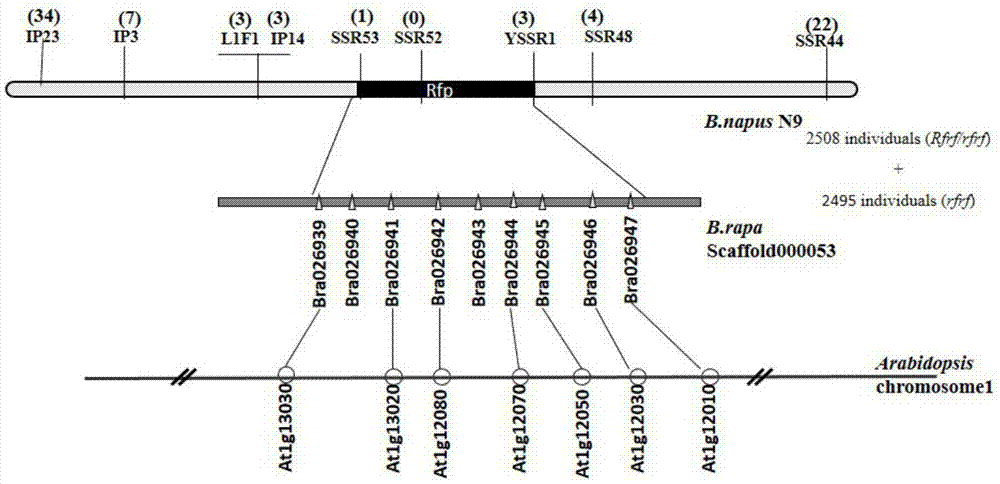
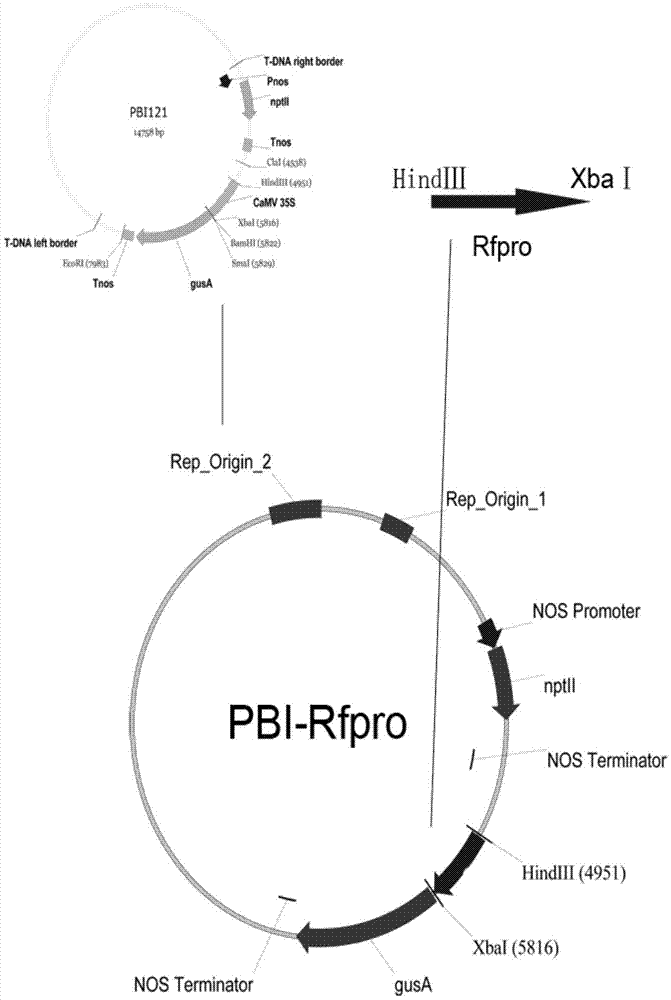
Brassica napus Polima cytoplasmic male sterility restoring gene Rfp and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of rapeseed breeding. It specifically relates to the Brassica napus polima cytoplasmic male sterility restorer gene Rfp and its application. The dominant gene Rfp involved in the present invention is the homologous gene of the function gain variation of the recessive gene rfp. The invention also discloses the cloning, verification and application of the restorer gene Rfp and the breeding of cytoplasmic male sterile lines, maintainer lines and restorer lines of crops such as rapeseed. The nucleotide sequence of the Brassica napus polima cytoplasmic male sterility restorer gene Rfp of the present invention is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and its protein sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The cloned gene of the present invention can also be directly used in the cultivation of the restorer line of Brassica napus through transgenic technology.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of TEL gene in regulation and control of agronomic characters of Zea mays
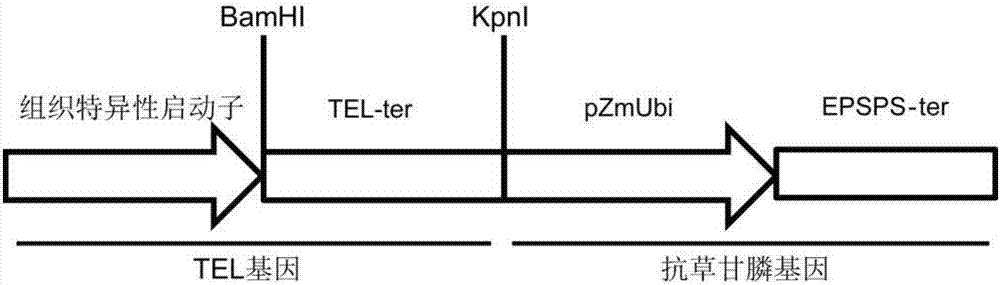
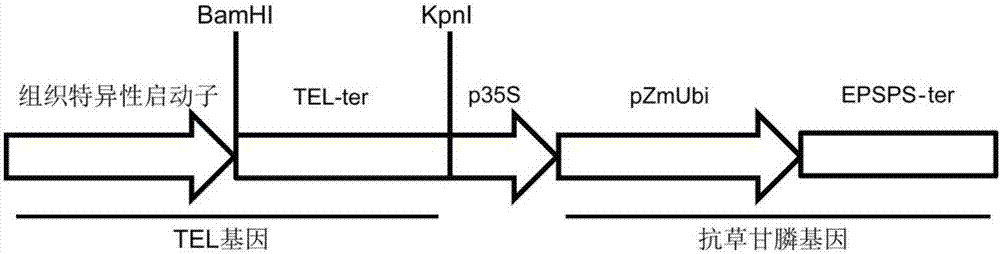
The invention discloses application of a TEL gene in regulation and control of agronomic characters of Zea mays. The TEL gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, and an encoding protein of the TEL gene has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3. According to the application, the function that characters such as plant height, growth potential and seed yield of the Zea mays can be regulated and controlled through regulating and controlling the expression of a TE1 gene and homologous genes thereof in the Zea mays is discovered for the first time; the condition that the characters such as the plant height, the growth potential and the seed yield of the Zea mays can be regulated and controlled through increasing the TE1 gene and the homologous genes thereof by using a regulating and controlling element is discovered for the first time, and then, the yield of the Zea mays is increased; and the condition that the characters such as the plant height, the growth potential and the seed yield of the Zea mays can be improved through regulating and controlling the overexpression of the TE1 gene and the homologous genes thereof in the Zea mays by using a tissue-specific promoter is discovered for the first time, and then, the yield of the Zea mays is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ompa in vaccine compositions and as diagnostic targets
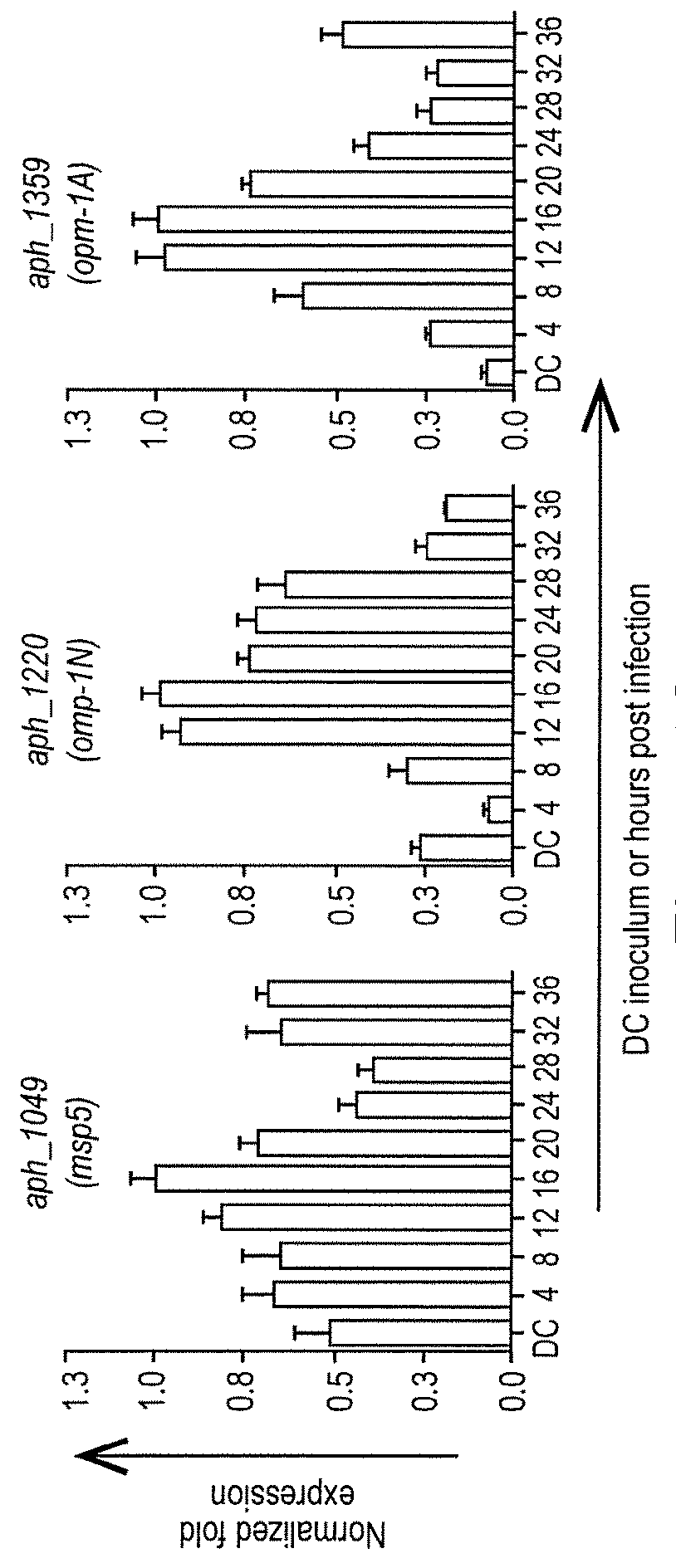
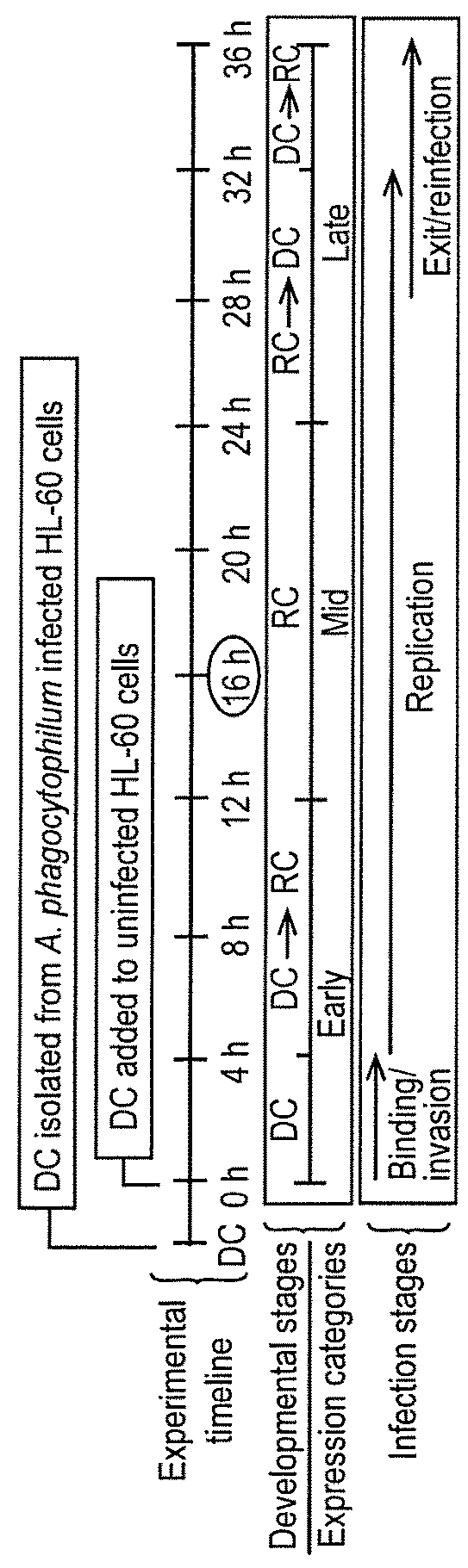
ActiveUS20170269080A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAnaplasma marginalePeptide fragment
Anaplasma Marginale surface protein OmpA and homologous genes from Anaplasmatacaea family members are used in compositions suitable for vaccines to treat or prevent infections caused by tick-born bacteria of the Anaplasmatacaea family. OmpA proteins or peptide fragments may be used in combination with other Anaplasmatacaea surface proteins to elicit an immune response. Furthermore, antibodies to OmpA proteins can be used in diagnostic methods to determine whether an individual has contracted an Anaplasmatacaea infection.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com