Gain switch laser adopting thulium-doped fiber laser for pumping
A fiber laser, gain switch technology, applied in lasers, laser parts, phonon exciters, etc., can solve problems such as inferiority and inconvenience in application, and achieve the effect of reducing threshold energy, stable time-domain state, and strong scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
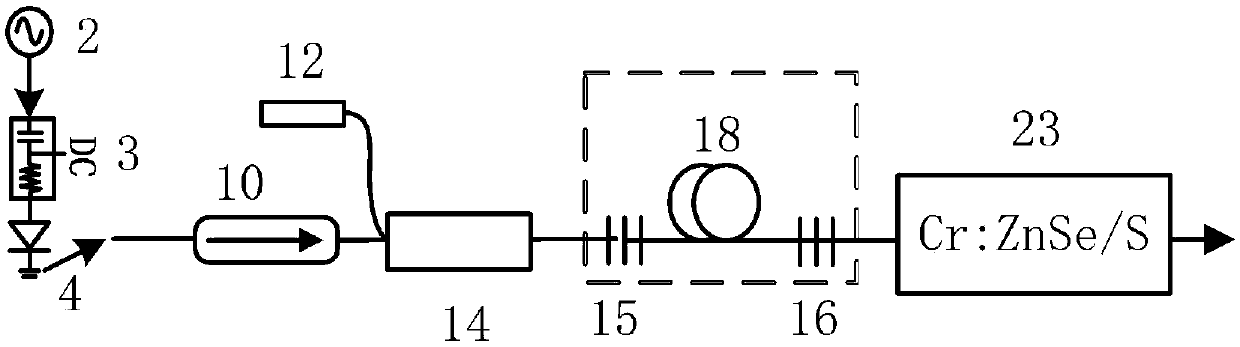
[0026] like figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention discloses a gain-switched laser pumped by a thulium-doped fiber laser, comprising sequentially connected 2, a bias T-shaped circuit driver 3, a nanopulse pump source 4, and a first fiber isolator 10 , the output end of the first fiber isolator 10 is connected to the first input end of the fiber combiner 14, the output end of the fiber combiner 14, the first fiber Bragg grating 15, the gain fiber 18 and the second fiber Bragg grating 16 in sequence connection, the second input end of the fiber combiner 14 is connected with the first semiconductor laser 12, the output end of the second fiber Bragg grating 16 outputs the optical fiber to the Cr:ZnSe / S crystal 23, and finally outputs laser light. The first fiber Bragg grating 15, the gain fiber 18 and the second fiber Bragg grating 16 constitute a first laser resonant cavity.
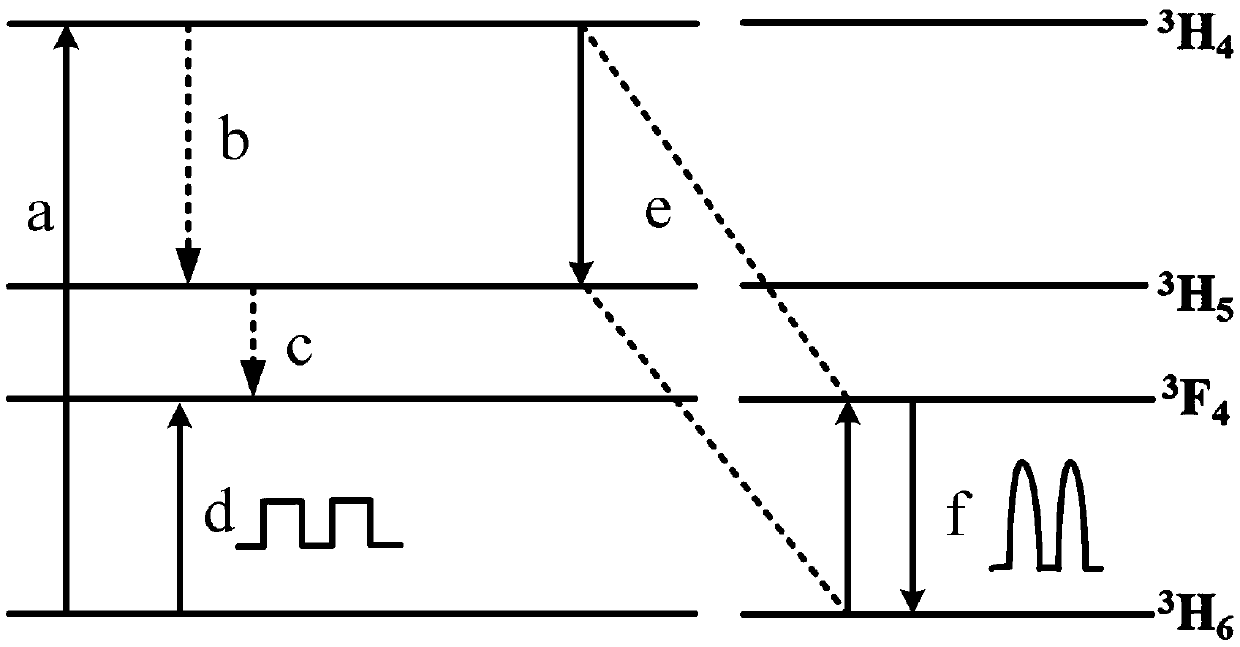
[0027] The working principle of the gain-switched laser pumped by the thulium-doped...
Embodiment 2
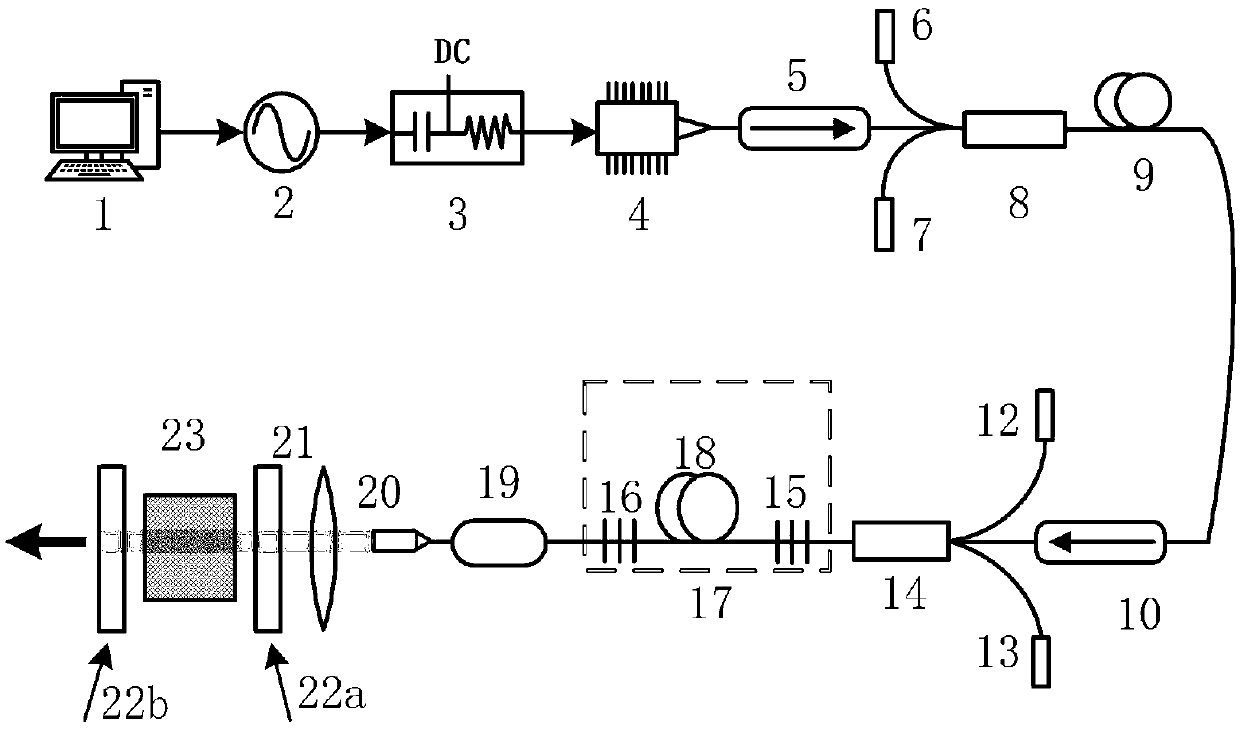
[0030] In the present embodiment, it differs from Embodiment 1 in that the computer 1LabVIEW program controls the pulse generator 2 to generate the set pulse waveform, and the third input end of the fiber combiner 14 is connected with the second semiconductor laser 13, and the nanopulse A second optical fiber isolator 5, a wavelength division multiplexer 8 and an erbium-doped optical fiber / erbium-ytterbium co-doped optical fiber 9 connected in sequence between the pumping source 4 and the first optical fiber isolator 10, the wavelength division multiplexer 8 The first input end is connected to the output end of the second optical fiber isolator 5, and the second input end and the third input end of the wavelength division multiplexer 8 are respectively connected to the third semiconductor laser 6 and the fourth semiconductor laser 7. Between the second fiber Bragg grating 16 and the Cr:ZnSe / S crystal 23, a pumping stripper 19, a collimating isolator 20, a focusing lens 21 and a...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The difference between the gain switch laser pumped by the thulium-doped fiber laser in this embodiment and the second embodiment is that the upper ends of the first cavity mirror 22a and the second cavity mirror 22b are all towards the direction close to the Cr:ZnSe / S crystal 23 Oblique setting, a grating 24 and an output coupler 25 are provided below the Cr:ZnSe / S crystal 23, so that the laser light passes through the focusing lens 21, the first cavity mirror 22a, the Cr:ZnSe / S After the crystal 23 and the second cavity mirror 22b, a part of the laser light is reflected from the second cavity mirror 22b to the grating 24, and after passing through the grating 24 and reflected back to the second cavity mirror 22b, the laser light is finally output through the output coupler 25. In this embodiment, the first cavity mirror 22a, the Cr:ZnSe / S crystal 23, the second cavity mirror 22b, the grating 24 and the output coupler (OC) 25 constitute a Cr:ZnSe / S laser resonator with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com