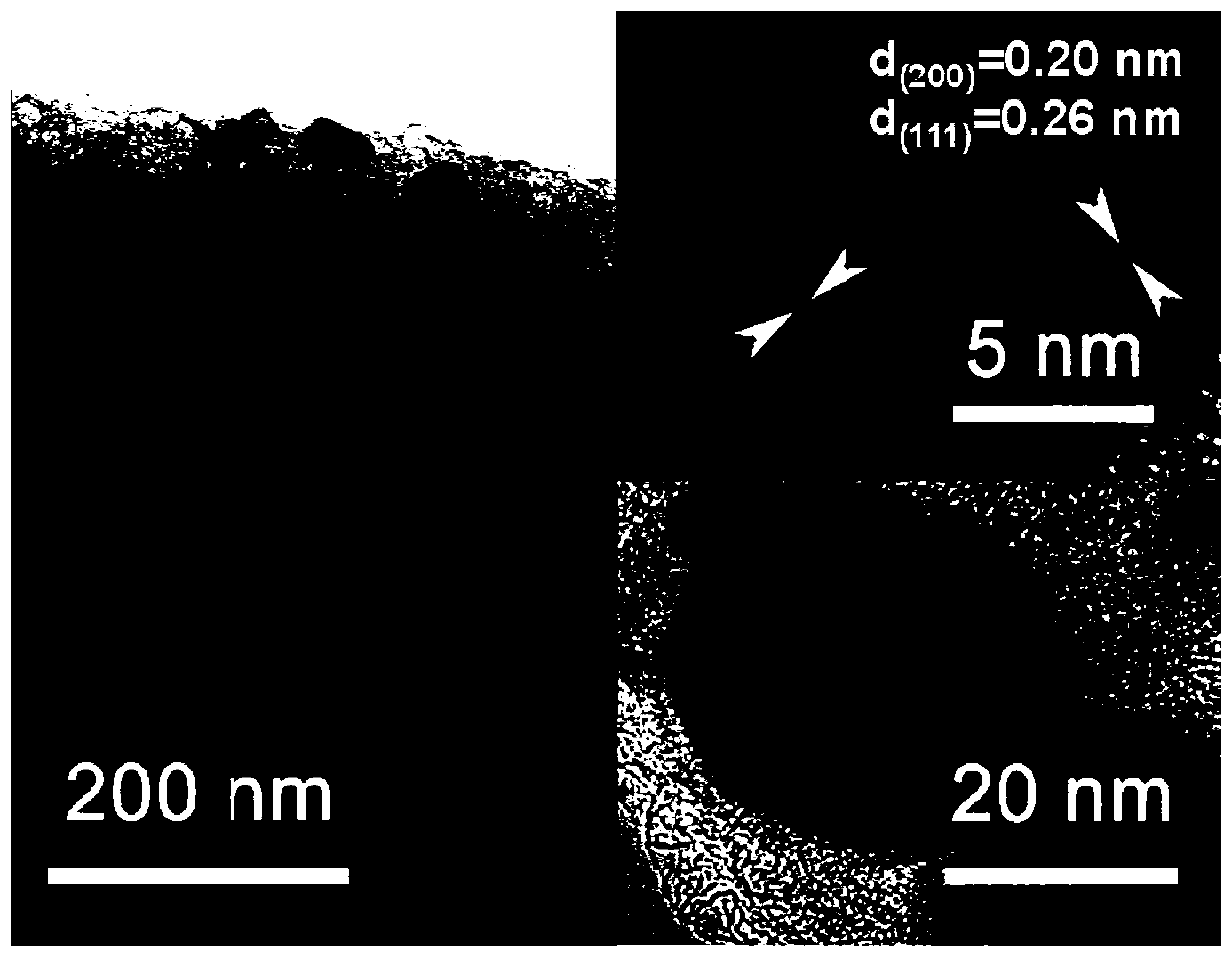
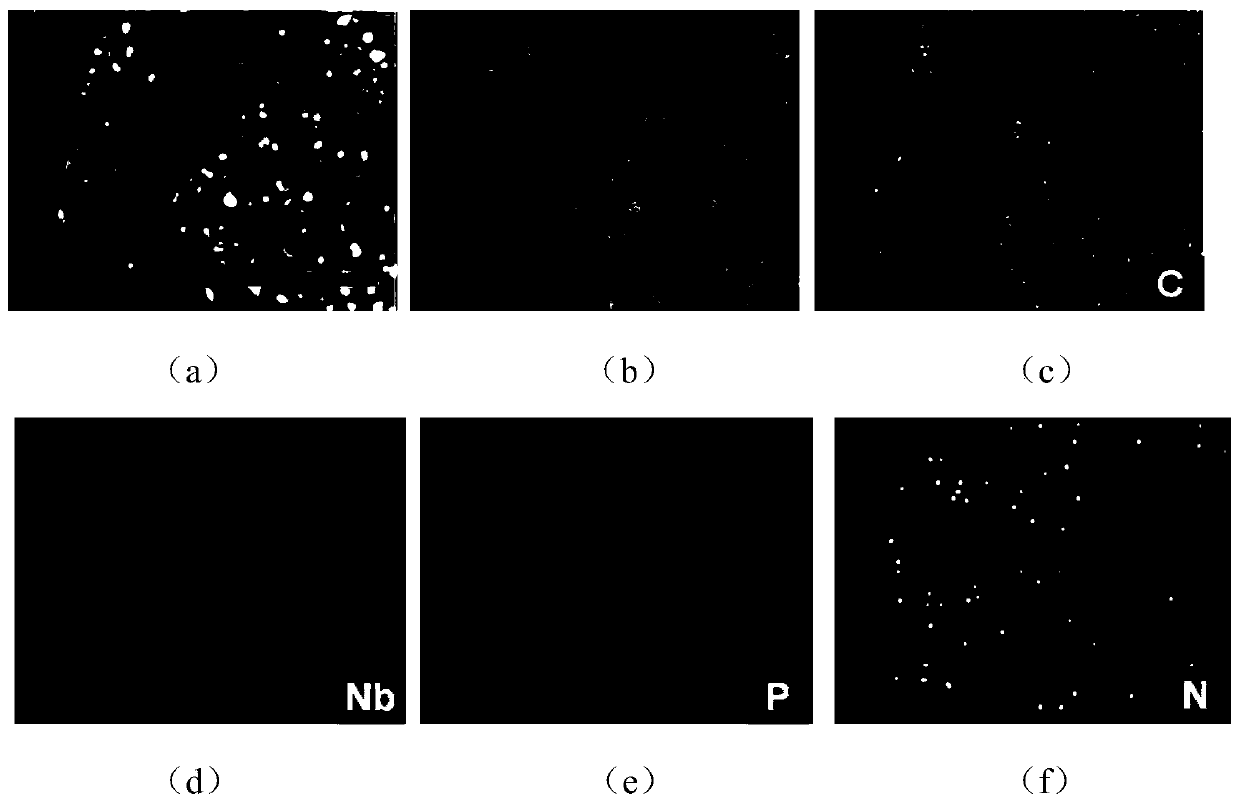
Sulfur-spore carbon/niobium carbide composite electrode material and preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and composite electrode technology, which is used in nanotechnology, battery electrodes, circuits, etc. for materials and surface science to achieve the effects of improving adsorption, accelerating interface reactions, and improving electrochemical performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Trichoderma spores were obtained using cottonseed hulls as nutrients, and 2.0 g of Trichoderma spore carbon was weighed in a hydrothermal reaction kettle. Using niobium pentachloride (NbCl 5 ) was used as a precursor for solvothermal reaction at 200°C for 6h, and then cooled with the furnace. The obtained samples were washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol and dried. Under the protective atmosphere of argon, they were treated at 800°C and 1000°C for 2 hours respectively, and the heating rate was 5°C / min to obtain spore carbon / niobium carbide composite materials. . Mix the spore carbon / niobium carbide composite material and sulfur element evenly, then put it into a high-pressure reactor, heat it to 120-140°C, and the reaction time is 16 hours. After the reactor cools down, take out the reaction product to obtain sulfur-spore carbon / Niobium carbide composites.
Embodiment 2
[0050] Using sawdust as a nutrient to obtain Trichoderma spores, weigh 2.0 g of Trichoderma spore carbon in a hydrothermal reaction kettle. Using niobium pentachloride (NbCl 5 ) was used as a precursor for solvothermal reaction at 200°C for 9 h, and then cooled with the furnace. The obtained samples were washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol and dried. Under the protective atmosphere of argon, they were treated at 800°C and 1000°C for 2 hours respectively, and the heating rate was 5°C / min to obtain spore carbon / niobium carbide composite materials. . Mix the spore carbon / niobium carbide composite material and sulfur element evenly, then put it into a high-pressure reactor, heat it to 140-150°C, and the reaction time is 14 hours. After the reactor cools down, take out the reaction product to obtain sulfur-spore carbon / Niobium carbide composites.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Trichoderma spores were obtained using wood segments as nutrients, and 2.0 g of Trichoderma spore carbon was weighed in a hydrothermal reaction kettle. Using niobium pentachloride (NbCl 5 ) as a precursor for solvothermal reaction at 200°C for 12 hours, and then cooled with the furnace. The obtained samples were washed several times with deionized water and absolute ethanol and dried. Under the protective atmosphere of argon, they were treated at 800°C and 1000°C for 2 hours respectively, and the heating rate was 5°C / min to obtain spore carbon / niobium carbide composite materials. . Mix the spore carbon / niobium carbide composite material and sulfur element evenly, then put it into a high-pressure reactor, heat it to 160-170°C, and the reaction time is 12 hours. After the reactor cools down, take out the reaction product to obtain sulfur-spore carbon / Niobium carbide composites.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com