LED epitaxial structure growth method
A growth method and epitaxial structure technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of low recombination efficiency of quantum well luminous radiation, reduce luminous attenuation effect, increase the window of stress control, and improve luminous efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
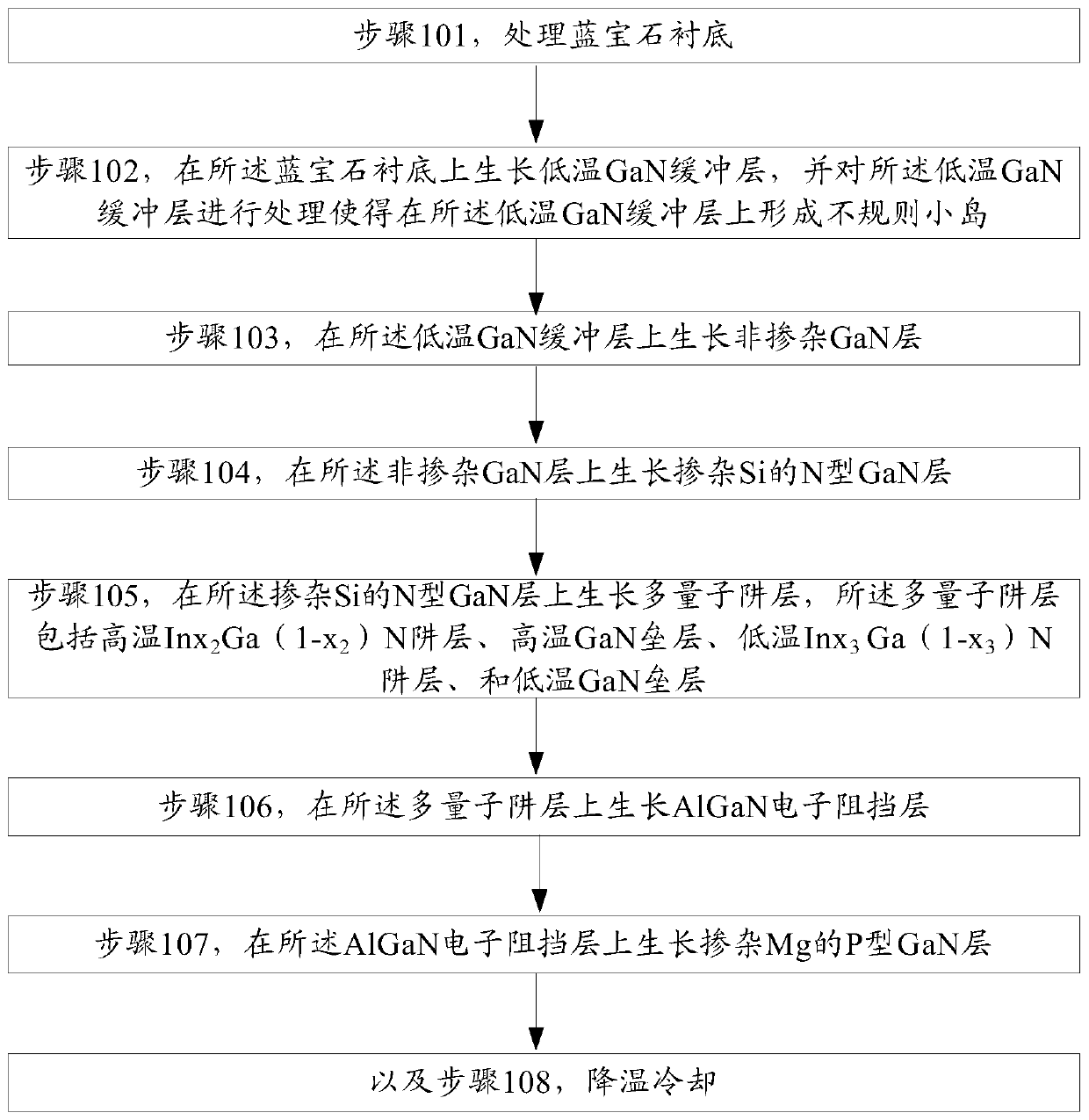
[0048] combine figure 1 , this embodiment provides a method for growing an LED epitaxial structure, the specific steps are as follows:
[0049] Step 101, processing the sapphire substrate:
[0050] At a temperature of 620°C and a reaction chamber pressure of 100mbar, 100L / min of H 2 Conditions, process the sapphire substrate for 5 min.
[0051] Step 102, growing a low-temperature GaN buffer layer on the sapphire substrate, and processing the low-temperature GaN buffer layer to form irregular islands on the low-temperature GaN buffer layer, the specific steps are as follows:
[0052] 1): At a temperature of 500°C and a reaction chamber pressure of 300mbar, 10000sccm of NH is introduced 3 , 50sccm TMGa, 100L / min H 2 Under the condition of , growing the low-temperature GaN buffer layer on the sapphire substrate, the thickness of the low-temperature GaN buffer layer is 20nm;
[0053] 2) At a temperature of 1000°C and a reaction chamber pressure of 300mbar, 30000sccm of NH is ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] This embodiment also provides a method for growing an LED epitaxial structure, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0080] Step 201, processing the sapphire substrate:
[0081] At a temperature of 650°C and a reaction chamber pressure of 300mbar, 130L / min of H 2 Conditions, process the sapphire substrate for 10 min.
[0082] Step 202, growing a low-temperature GaN buffer layer on the sapphire substrate, and processing the low-temperature GaN buffer layer to form irregular islands on the low-temperature GaN buffer layer, the specific steps are as follows:
[0083] 1): At a temperature of 600°C and a reaction chamber pressure of 600mbar, 20000sccm of NH is introduced 3 , 100sccm TMGa, 130L / min H 2 Under the condition of growing the low-temperature GaN buffer layer on the sapphire substrate, the thickness of the low-temperature GaN buffer layer is 40nm;
[0084] 2) At a temperature of 1100°C and a reaction chamber pressure of 600mbar, 40,000 sccm of NH is introduce...
Embodiment 3
[0104] This embodiment also provides a method for growing an LED epitaxial structure, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0105] Step 301, processing the sapphire substrate:
[0106] At a temperature of 635°C and a reaction chamber pressure of 200mbar, 120L / min of H 2 conditions, process the sapphire substrate for 7 min.
[0107] Step 302, growing a low-temperature GaN buffer layer on the sapphire substrate, and processing the low-temperature GaN buffer layer to form irregular islands on the low-temperature GaN buffer layer, the specific steps are as follows:
[0108] 1): At a temperature of 550°C and a reaction chamber pressure of 450mbar, 15000 sccm of NH is introduced 3 , 75sccm of TMGa, 115L / min of H 2 Under the condition of growing the low-temperature GaN buffer layer on the sapphire substrate, the thickness of the low-temperature GaN buffer layer is 30nm;
[0109] 2) At a temperature of 1050°C and a pressure of 450mbar in the reaction chamber, 35000 sccm of NH i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com