Distance error correction system for laser radar
A technology of laser radar and compensation system, which is applied in the field of compensation system, can solve problems affecting measurement results, signal strength fluctuation, signal broadening, etc., achieve good stability and repeatability, reduce signal noise, and enhance stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
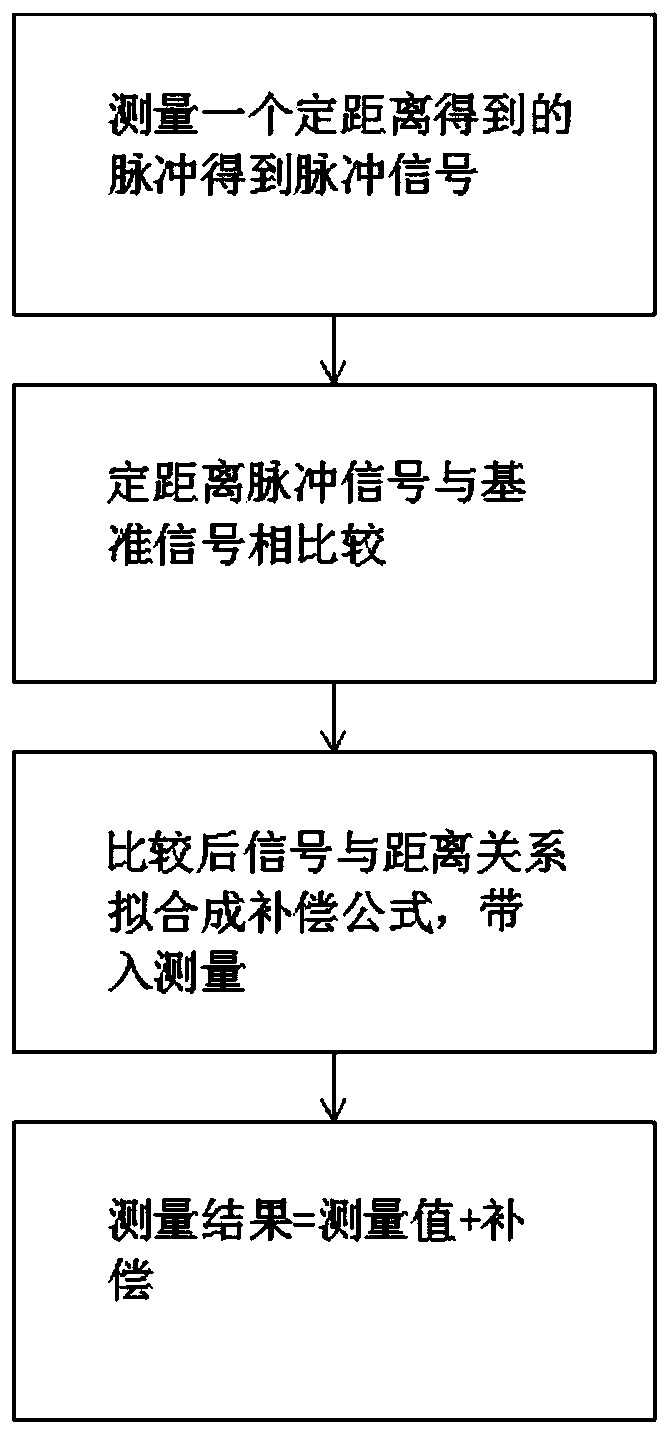
[0036] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 Be the flow chart of the steps of the whole compensation system of the present invention in
[0037] The laser radar is placed in a fixed position, adjust the left and right position and pitch position of the emitting laser point, and keep the laser beam and the measurement target at the discovered position, so that an accurate distance value can be measured. If the laser beam is offset, the measured distance and the actual distance will have a plane or space angle θ. Δ=L-Lsinθ, Δ is the measurement distance error
[0038] L is the actual measurement distance
[0039] θ is the angle between the laser beam and the normal of the measurement target
[0040] The tooling for placing the lidar and measuring objects can adjust the left and right rotation angles and pitch angles.
[0041] The laser radar and the measurement target are placed on an automated test guide rail, which can automatically walk to the required measurement distance, and the ...
Embodiment 2
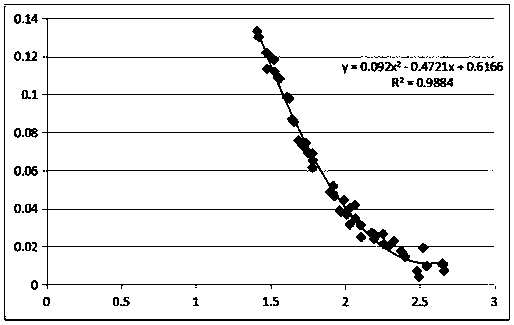
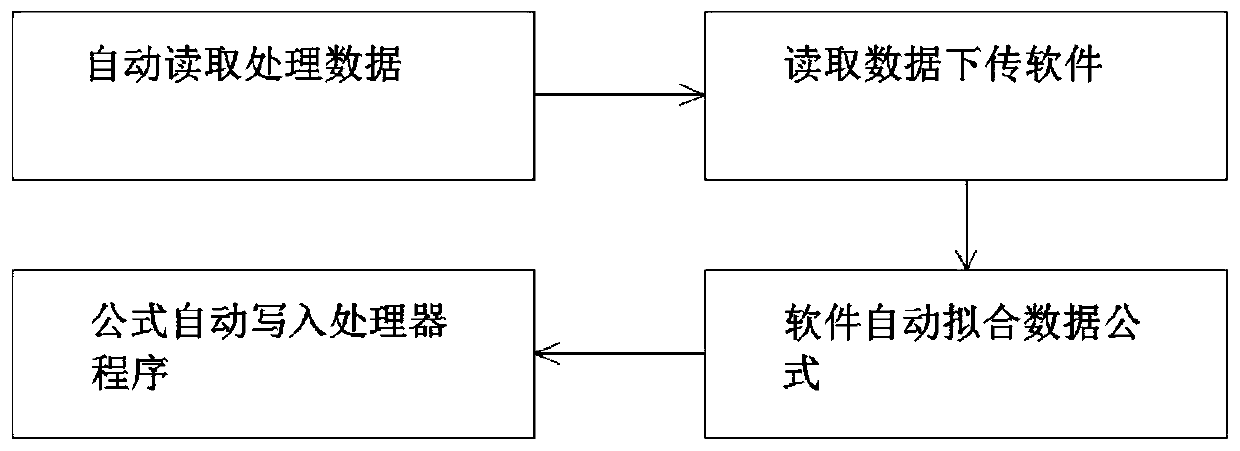
[0044] Embodiment 2: as figure 2 In the middle is a flow chart of key data receiving and receiving and data fitting of the present invention:
[0045] The data is read multiple times, the average value of all data is calculated, and a threshold range is set. If the value is greater than the threshold range, it will be treated as abnormal data, and then the average value will be calculated and sent to the data processing software as valid data after removing the abnormal data.
[0046] The test software obtains the measured echo signal characteristic values B1, B2, B3...Bn
[0047] The automatic test guide rails are set with fixed distances L1, L2, L3...Ln, the obtained time t1, t2, t3...tn, the obtained time is calculated by the formula (d=1 / 2ct) to obtain the distance d1, d2, d3...dn , when calculating the error value Δ(Δ=D-L) between the measured distance and the real distance.
[0048] The figure shows the polynomial curve fitted between the measurement error Δ and the...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: as image 3 The middle is a schematic diagram of a TOF-based miniaturized coaxial lidar system:
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com