Method for Enhanced Treatment of Organic Wastewater with Fenton-like System Constructed Based on Glyoxylic Acid
A technology for enhanced treatment of organic wastewater, applied in water/sewage treatment, water treatment parameter control, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as low iron cycle efficiency, achieve mature preparation process, reduce secondary pollution, and improve efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
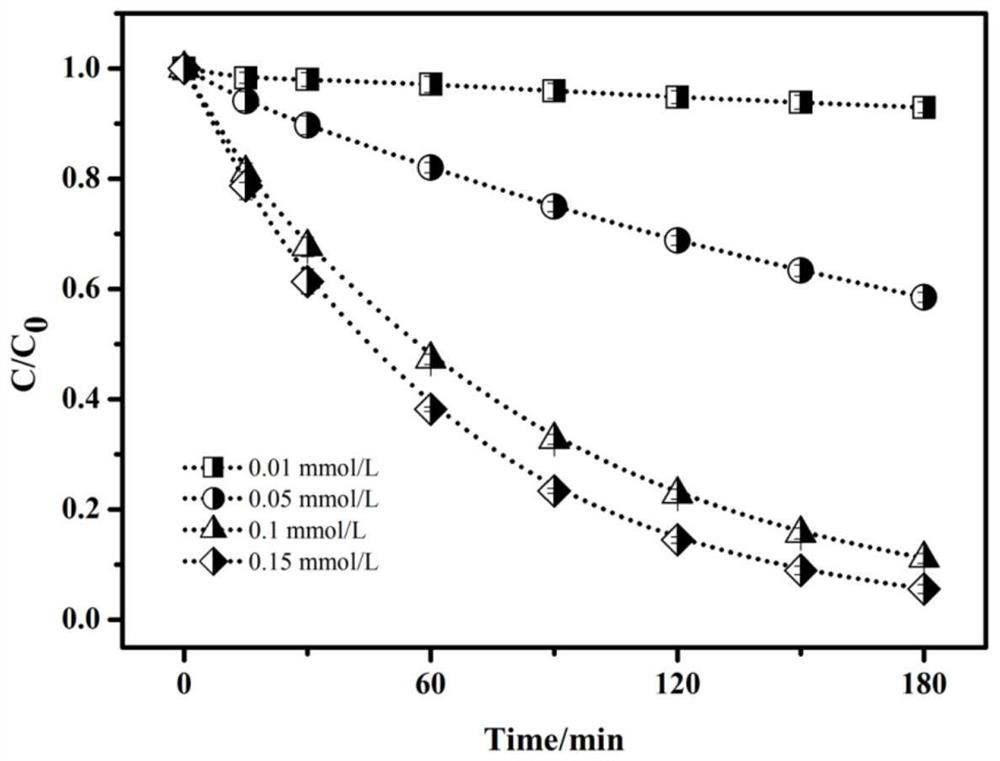
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
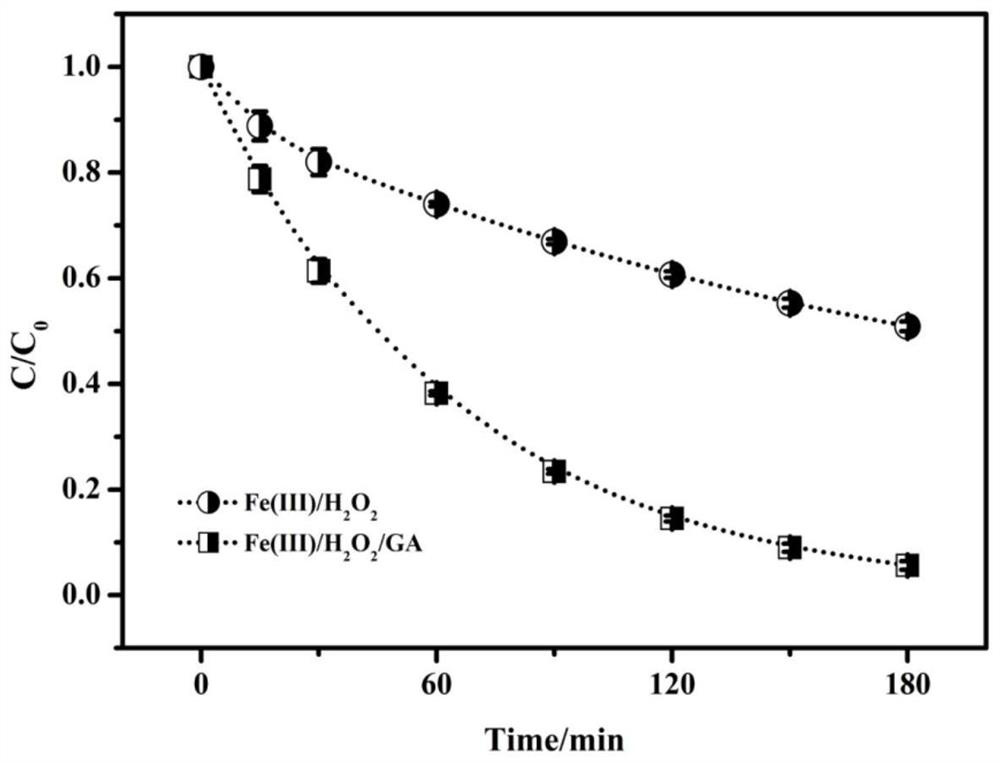
[0026] Take 50 milliliters of organic wastewater containing atrazine (5 mg / liter), add a certain amount of glyoxylic acid, ferric nitrate nonahydrate and hydrogen peroxide to it, so that the final concentrations are 0.3, 0.1 and 2 mmol / liter respectively At this time, the initial pH value of the solution is 3.6, and the mixed solution is placed in a shaker, and shaken at a speed of 200 rpm for 0-180 minutes to complete the treatment of organic wastewater. At the same time, no glyoxylic acid was used as a control experiment, and the results were as follows: figure 1 . from figure 1 It can be seen that after 180 minutes of reaction, Fe(III) / H 2 o 2 The degradation efficiency of atrazine in the system is only 49.2%. When glyoxylic acid is added to the system, the degradation efficiency of atrazine reaches as high as 94.4%.
Embodiment 2
[0028] Atrazine, rhodamine B and ofloxacin were selected as typical pollutants in organic wastewater, and their initial concentrations were 5, 5 and 10 mg / L, respectively. Get 50 milliliters of above-mentioned organic waste water, add a certain amount of glyoxylic acid, ferric nitrate nonahydrate and hydrogen peroxide to it, make its final concentration be 0.3, 0.1 and 2 mmol / liter respectively, and the initial pH value of solution is 3.6 now, The mixed solution is placed in a shaker and shaken at a speed of 200 rpm for 0-180 minutes to complete the treatment of organic wastewater. The results are shown in Table 1. The system can degrade 94.4% and 99.2% of 5 mg / L atrazine and Rhodamine B in 180 minutes, and can degrade 99.9% of 10 mg / L ofloxacin in 120 minutes.
[0029] Pollutants Initial concentration (mg / L) Removal time (min) Removal rate Atrazine 5 180 94.4% Rhodamine B 5 180 99.2% Ofloxacin 10 120 99.9%
Embodiment example 3
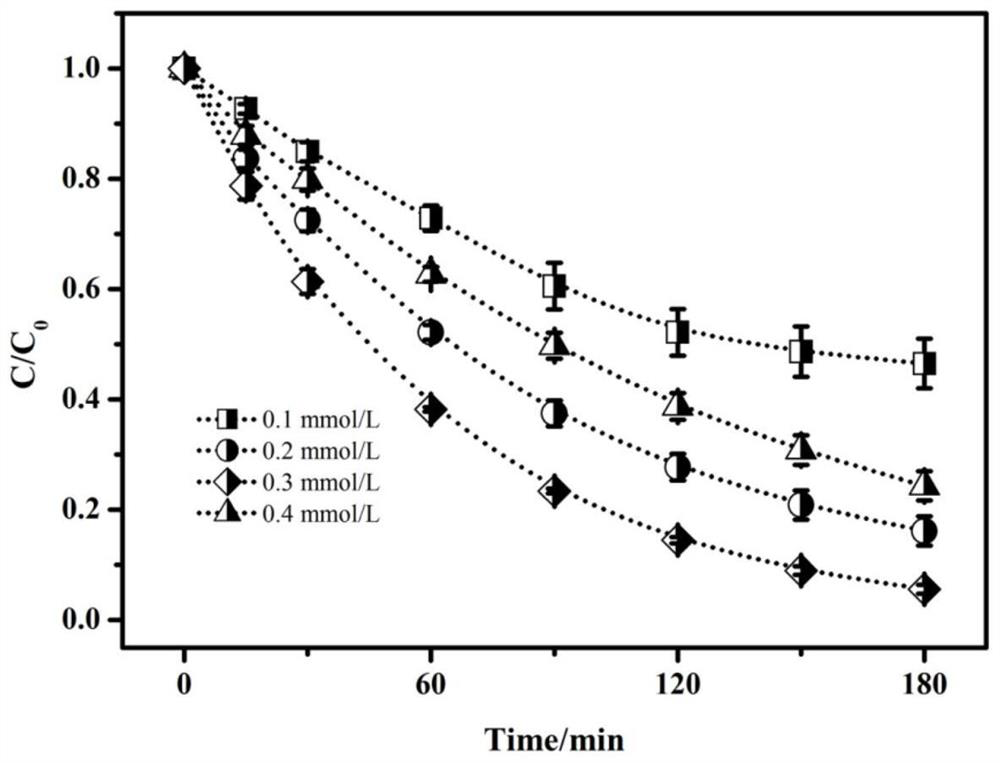
[0031] Take 50 milliliters of organic wastewater containing atrazine (5 mg / L), add a certain amount of glyoxylic acid, ferric nitrate nonahydrate and hydrogen peroxide to it, wherein the concentration of glyoxylic acid is 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 and 0.4 milliliters respectively mol / L, the concentrations of ferric nitrate and hydrogen peroxide are 0.1 and 2 mmol / L respectively, and the initial pH value of the solution is 3.6 at this time, the mixed solution is placed in a shaker and shaken for 0-180 minutes at a speed of 200 rpm. Complete the treatment of organic wastewater. from figure 2 It can be seen that when the initial concentration of glyoxylic acid is 0.1-0.3 mmol / L, the degradation efficiency of atrazine increases with the increase of the initial concentration of glyoxylic acid. When the initial concentration of glyoxylic acid continued to increase to 0.4 mg / L, the efficiency of the system to degrade atrazine decreased instead.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com