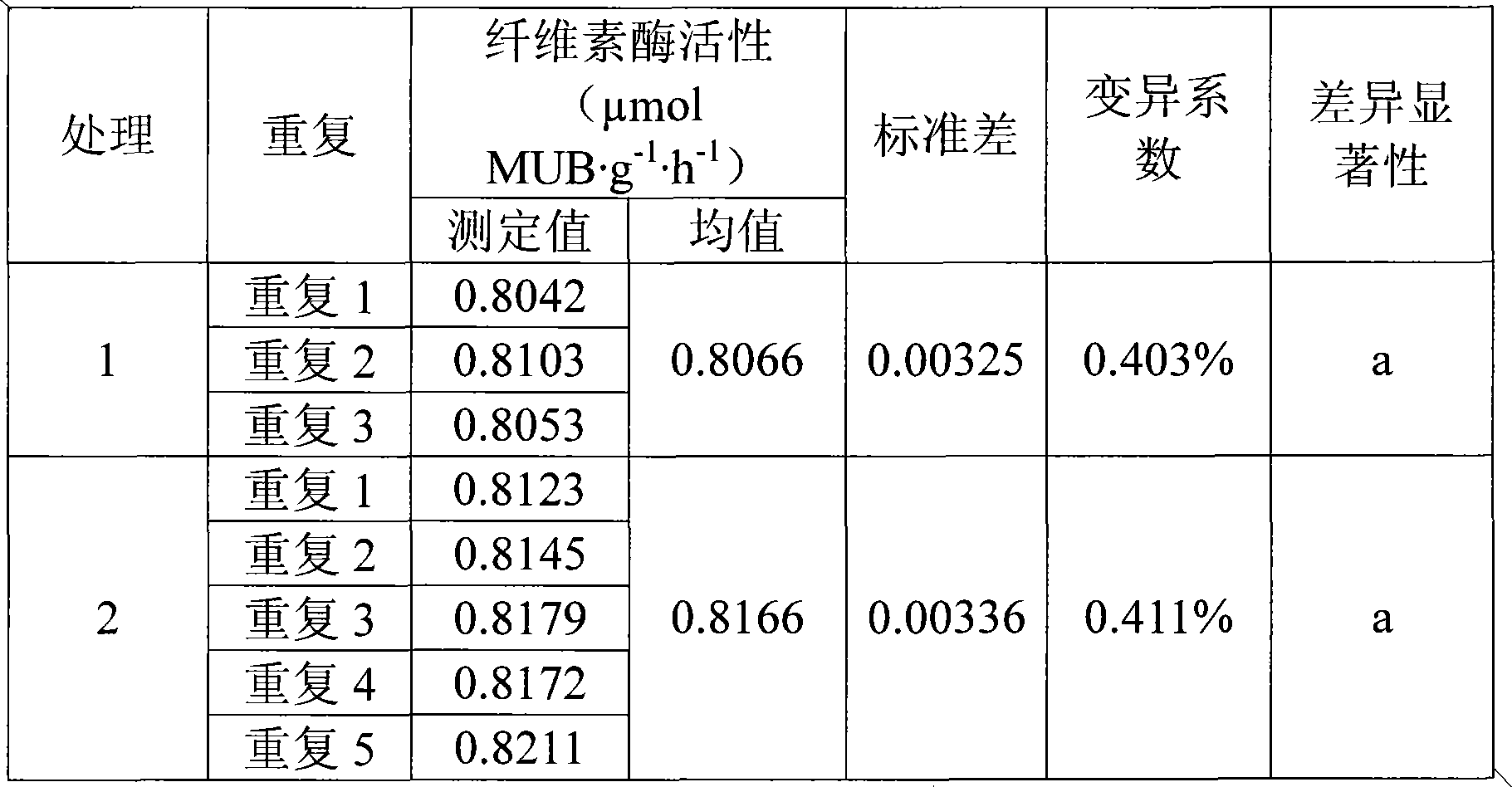
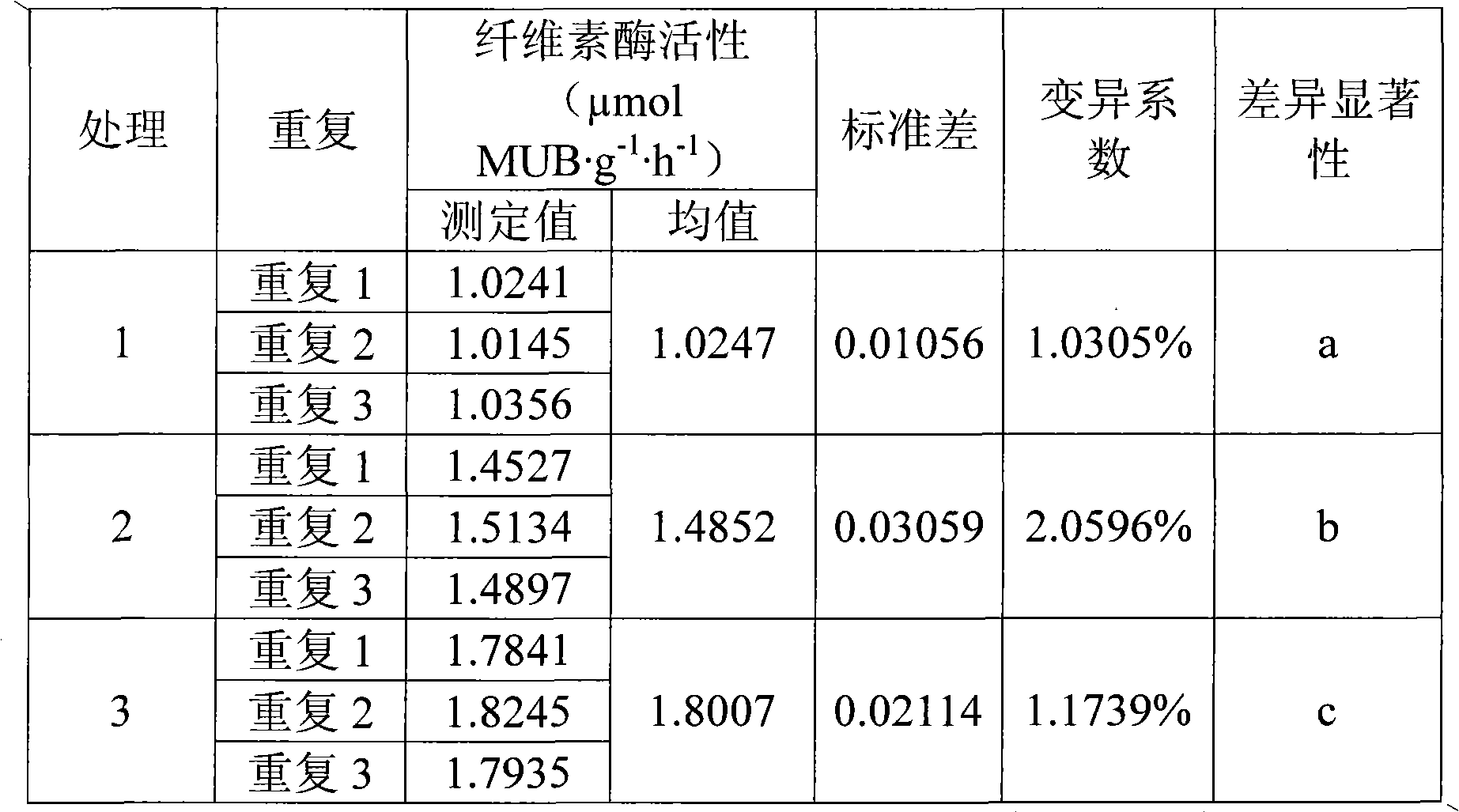
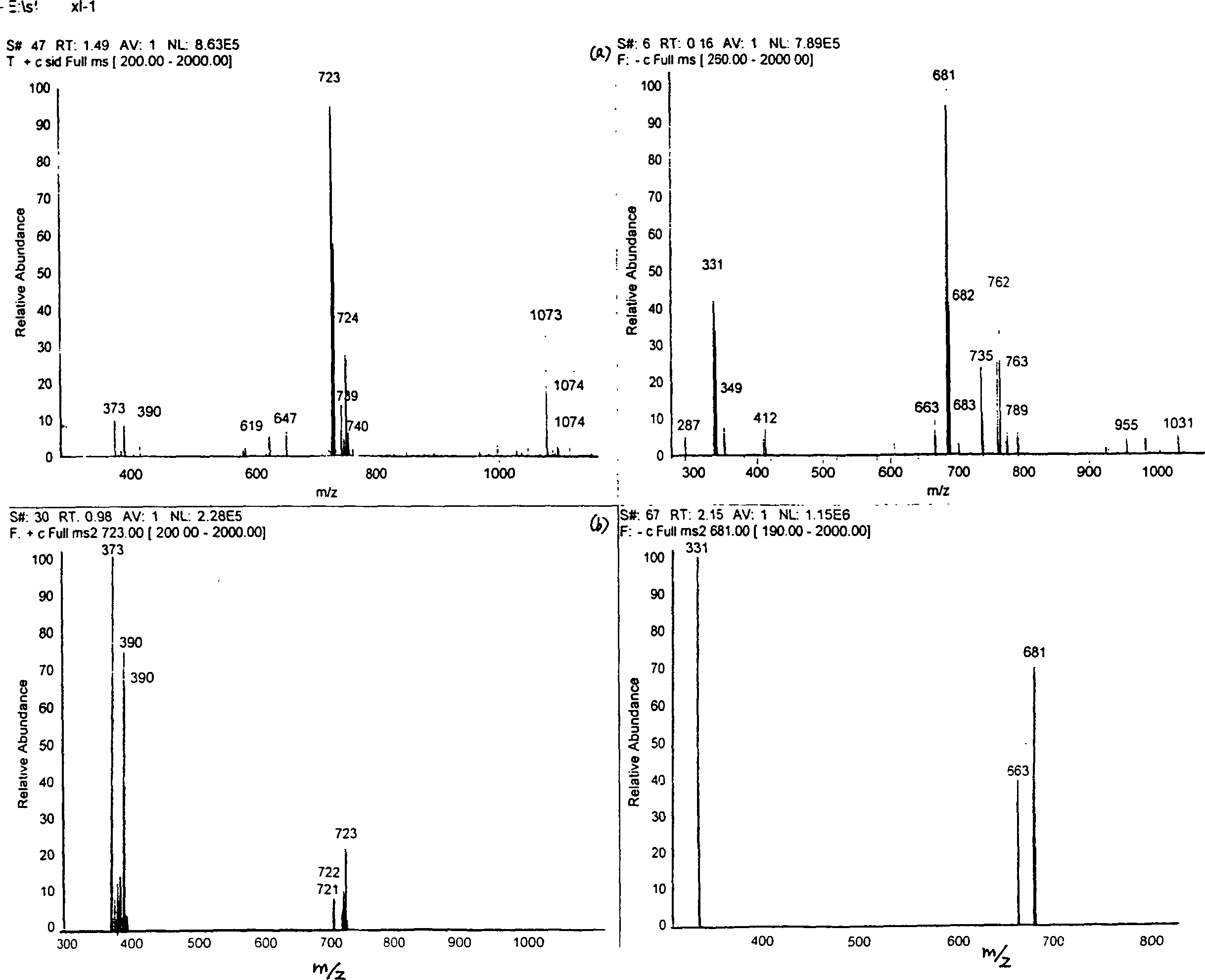
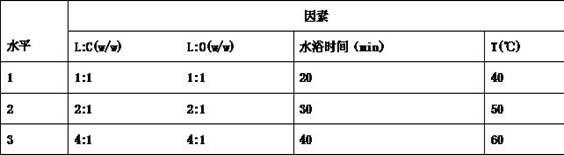
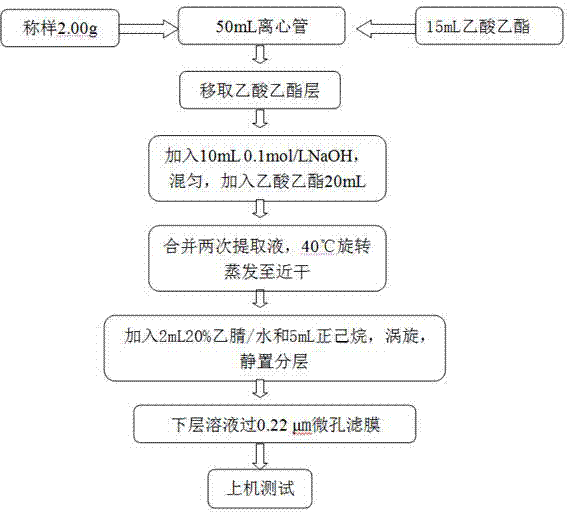
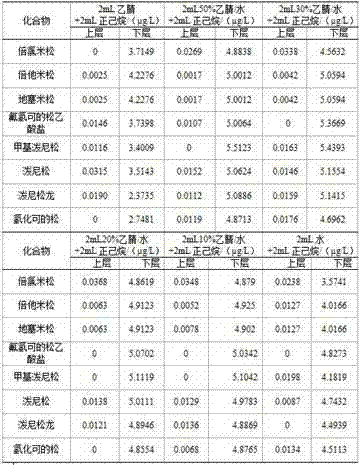
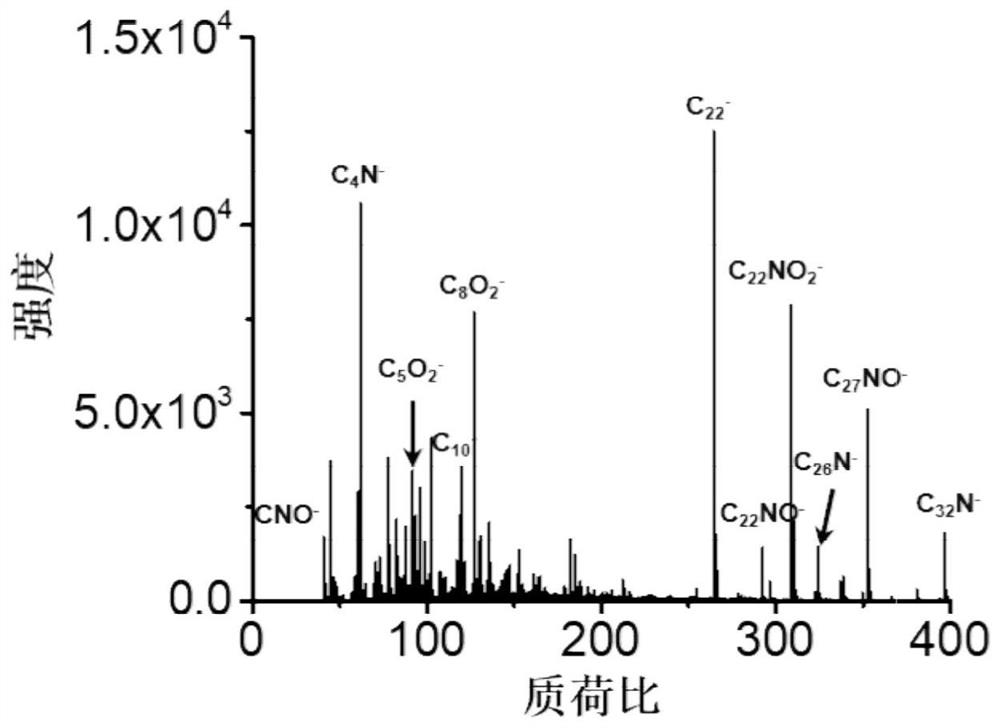
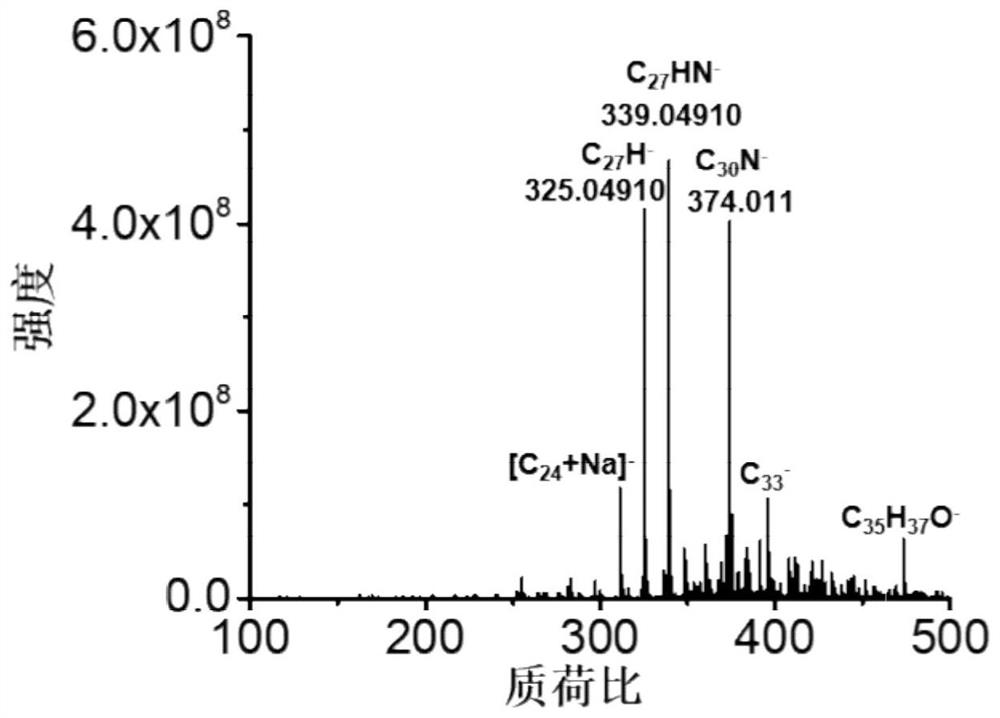
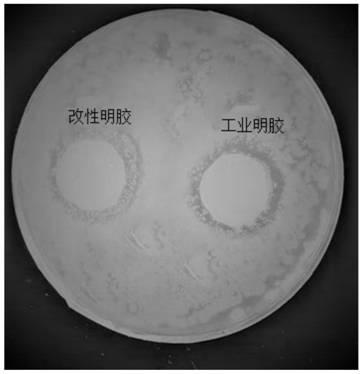
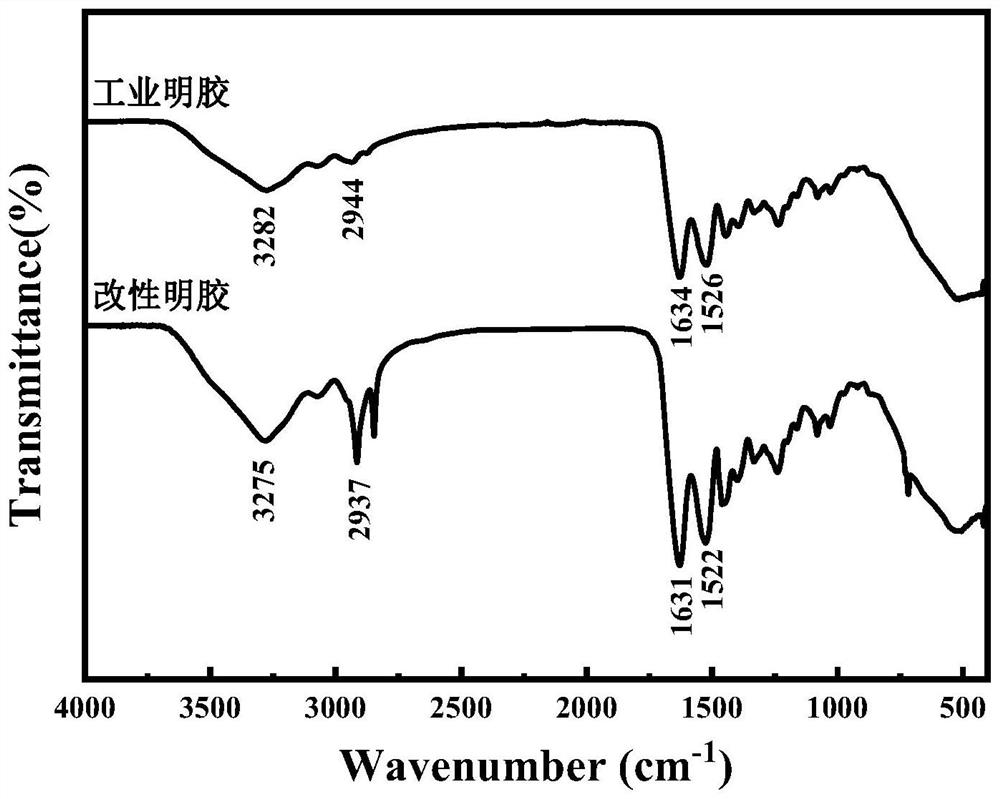
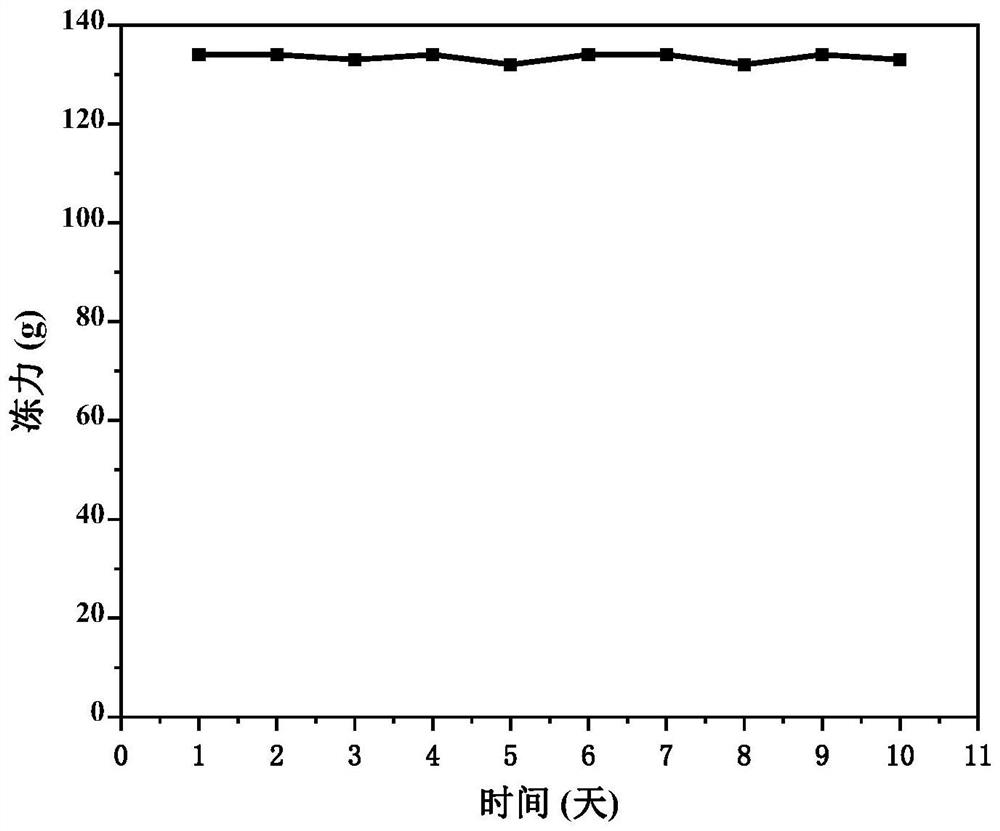
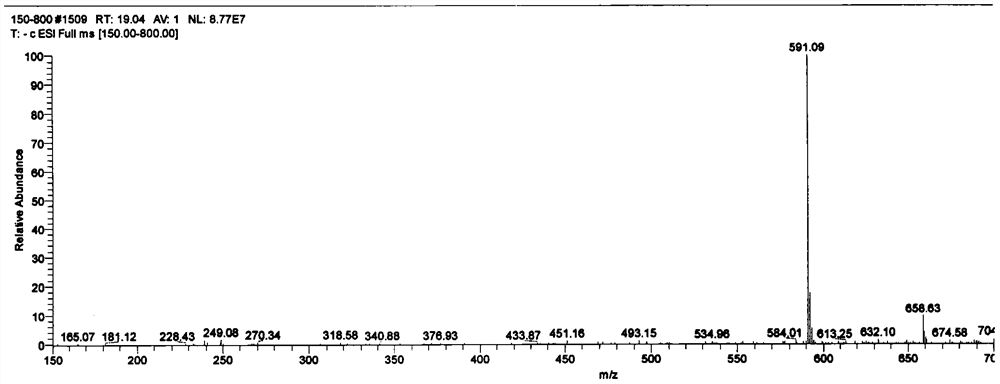
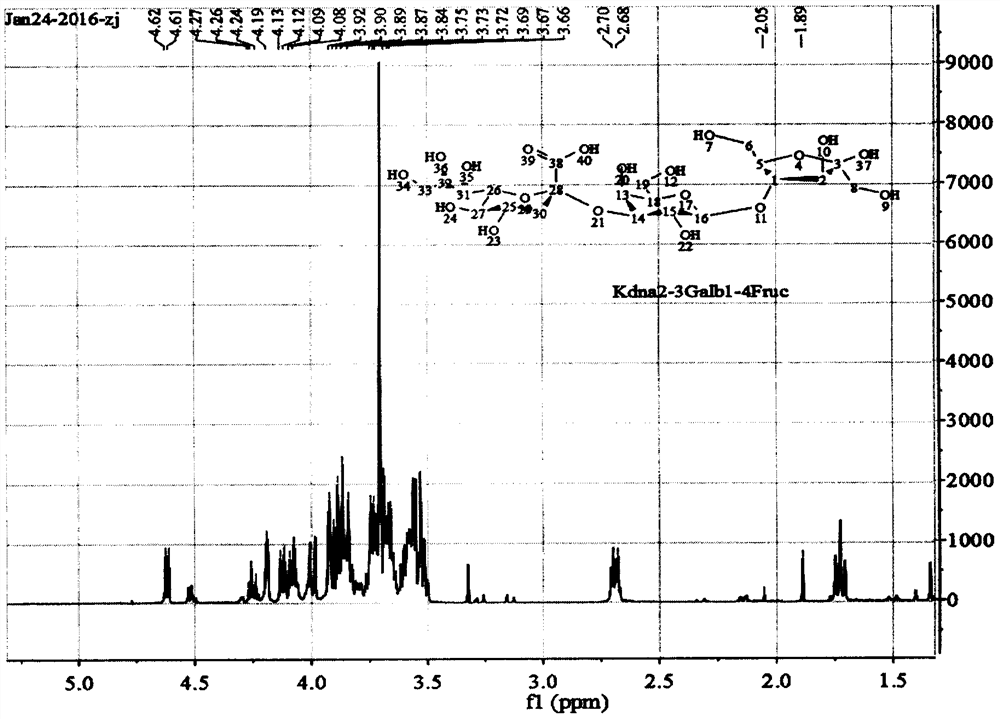
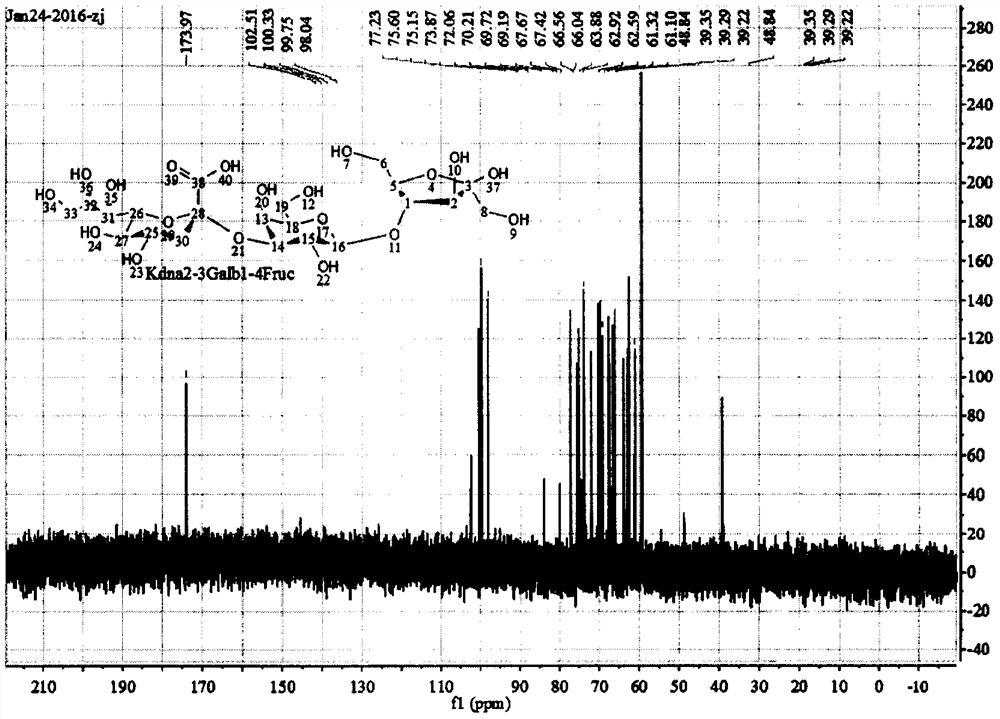
Patents
Literature
52 results about "Oscillarin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Analyzing method for detecting activity of soil xylanase
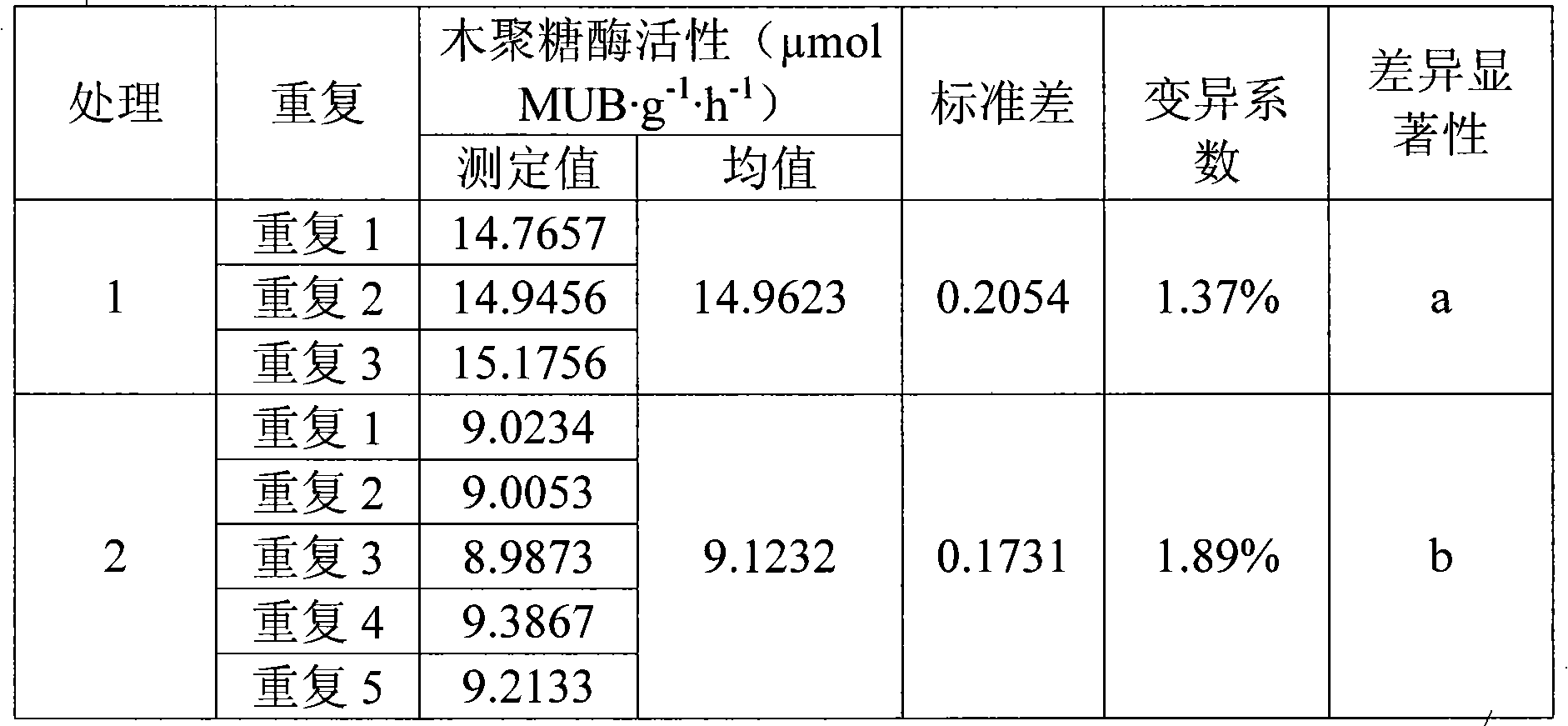
InactiveCN101586145AReduce incubation timeShort training timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiltrationExoxylanase activity
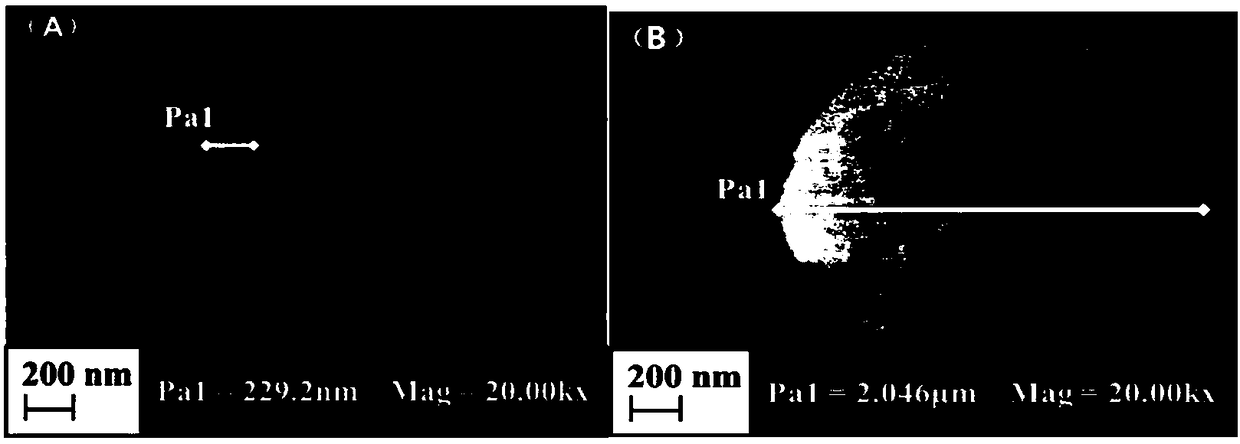
The invention relates to an analyzing method for detecting activity of soil xylanase, which comprises the following steps: firstly, weighting n sieved air dry soil samples into n thick test tubes, adding acetic acid buffer solution into each test tube, oscillating by a vortex oscillator, getting soil suspension into 96 micropore plates under the oscillation condition, adding 4-MUB-7-Beta-D-xyloside substrate solution into n-1 holes, and adding water with equal quantity into the other one hole so as to be used as non-substrate contrast, adding substrate solution with equal quantity and water with equal quantity into the (n+1)th hole so as to be used as soli-free contrast, oscillating and culturing under constant temperature; secondly, adding NaOH into the micropore plates to terminate the reaction after the culture is finished; thirdly, performing the fluorimetric determination to resultant of reaction by a multifunctional microplate reader; and fourthly, calculating the activity of the xylanase. Compared with the traditional method, the invention shortens the culture time, omits the operation procedures of filtration, and the like, and simplifies the operation steps; meanwhile, the determination data of fluorescent materials in the micropore plate can be obtained within 15s through the multifunctional microplate reader, huge samples are allowed to be simultaneously determined; and moreover, the invention has high accuracy and easy operation, stable and reliable result and good reproduction quality.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting synanthrin from burdock
InactiveCN102965410AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce economic costsFermentationCellulasePharmacology
The invention belongs to the field of extraction methods of synanthrin, and in particular relates to a method for extracting the synanthrin from burdock. The method for extracting the synanthrin from the burdock comprises the following steps in sequence: cleaning fresh burdock; adding immobilized cellulose and immobilized papain to mix with burdock solution; and oscillating at constant temperature by an oscillator. The method for extracting the synanthrin from the burdock has the beneficial effects that the immobilized cellulose and immobilized papain are adopted and used for extracting the synanthrin from the burdock, and the immobilized cellulose and immobilized papain can be recycled, so that the utilization efficiency of the cellulose and the papain can be improved, and the economic cost can be saved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Brasenia schreberi polysaccharide extraction method
The invention discloses a brasenia schreberi polysaccharide extraction method. According to the method, freeze-dried brasenia schreberi is pulverized, petroleum ether is adopted for extraction degreasing at 50 DEG C, after solvents are dried through volatilization at the room temperature, the crushed brasenia schreberi is placed in a drying box to be dried at 40 DEG C, the dried brasenia schreberi is obtained, a NaOH solution is added, oscillation extraction is carried out on a water bath oscillator, then, the centrifugal treatment is carried out, supernatant containing brasenia schreberi polysaccharide is obtained, the supernatant is extracted out, brasenia schreberi powder precipitates are left, the NaOH solution is added for continuous extraction, the number of extraction times is totally four, the supernatant obtained in each time is merged, the final supernatant containing polysaccharidec is obtained, and the polysaccharidec yield is measured. The brasenia schreberi polysaccharide extraction method has the beneficial effects that the utilization rate of brasenia schreberi raw materials is high, the effect is good, and the yield of brasenia schreberi polysaccharide extracted by the method provided by the invention is high.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
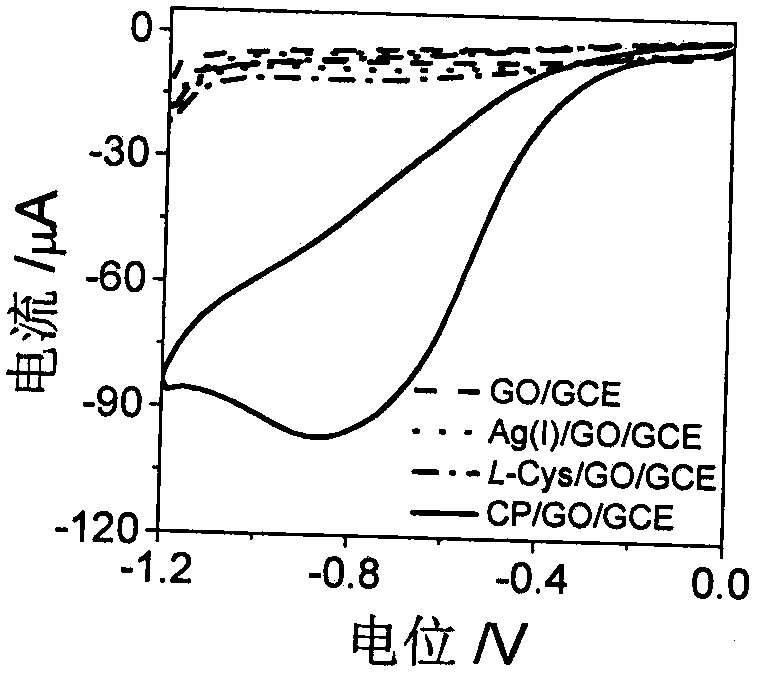
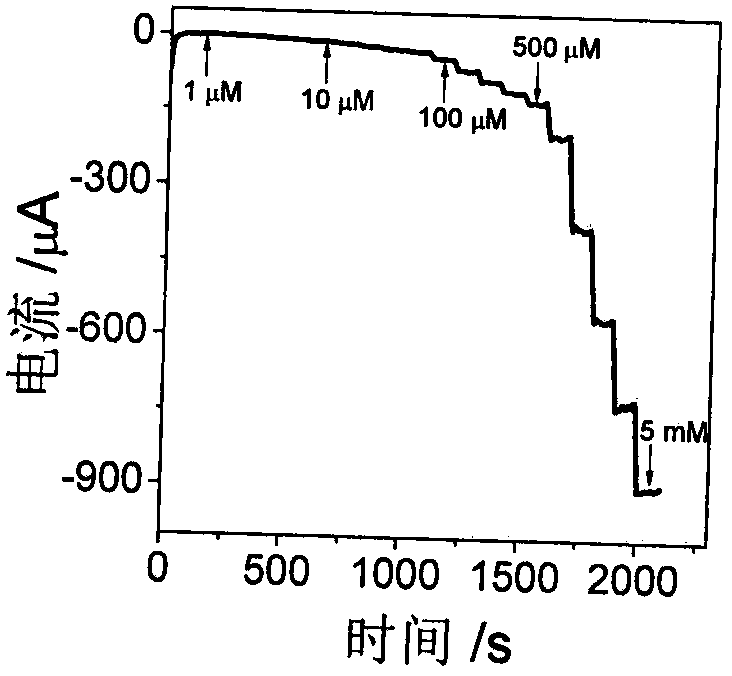
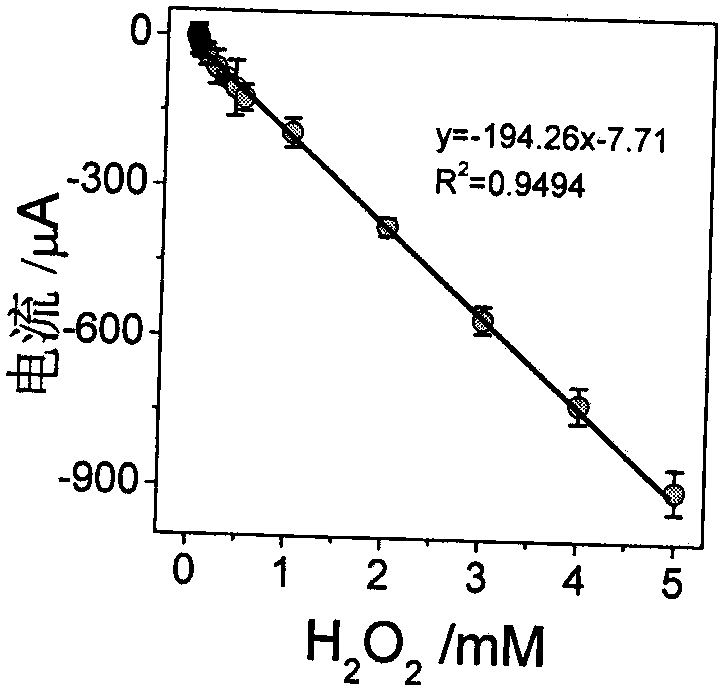
Electrochemical biosensor based on polypeptide analog with electrocatalytic activity for acetylcholin esterase detection
ActiveCN108120761AThe result is accurateLess reagent consumptionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesNafionGraphene
The invention discloses an electrochemical biosensor based on polypeptide analog with the electrocatalytic activity for acetylcholin esterase detection. The biosensor for acetylcholin esterase detection is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) intensively stirring and uniformly mixing silver nitrate, L-cysteine and secondary distilled water on a stirrer, and incubating in an oscillator; (2) electrodepositing graphene onto a bare glassy carbon electrode by utilizing an electrochemical method, mixing 0.05 weight percent of a Nafion solution with the solution obtained in the step (1), and dropwise coating GO / GCE to obtain an electrochemical biosensor based on the polypeptide analog with electrocatalytic activity (CP / GO / GCE); (3) performing acetylcholin esterase activity detection, namely catalyzing acetylcholine in one step to generate H2O2, uniformly mixing acetylcholine, AchE and choline oxidase, and incubating to generate H2O2, and detecting the solution with the sensorprepared in the step (2) with good specificity, high sensitivity, high detection speed, accurate and reliable result; and (4) performing AChE inhibitor malathion detection, namely uniformly mixing acetylcholine, AChE, malathion and choline oxidase, incubating, and detecting the solution with the sensor prepared in the step (2). The biosensor has the advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity, high detection speed and accurate and reliable result.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Analyzing method for detecting activity of soil xylanase
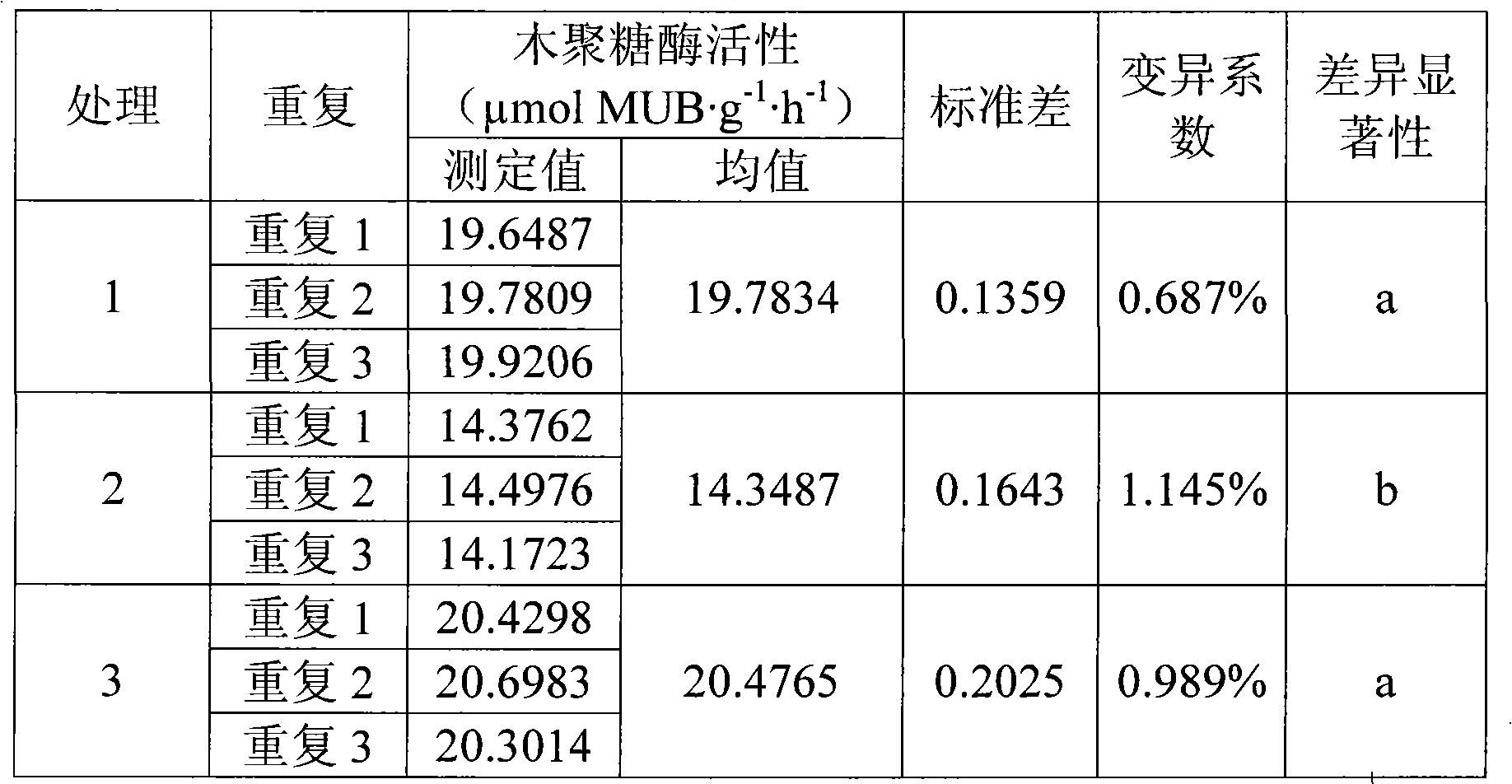
InactiveCN101586146AImprove work efficiencyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnvironmental chemistryAnalysis method
The invention relates to an analyzing method for detecting activity of soil xylanase, which comprises the following steps: firstly, weighting n sieved air dry soil samples into n thick test tubes, adding acetic acid buffer solution into each test tube, oscillating by a vortex oscillator, getting soil suspension into 96 micropore plates (occupies n micropores) under the oscillation condition, adding 4-MUB-7-Beta-D-cellobioside substrate solution into n-1 holes, and adding water with equal quantity into the other one hole so as to be used as non-substrate contrast, adding substrate solution with equal quantity and water with equal quantity into the (n+1)th hole so as to be used as soli-free contrast, oscillating and culturing under constant temperature; secondly, adding NaOH into the micropore plates to terminate the reaction after the culture is finished; thirdly, performing the fluorimetric determination to resultant of reaction by a multifunctional microplate reader; and fourthly, calculating the activity of the xylanase. Compared with the traditional method, the invention shortens the culture time, omits the operation procedures of filtration, and the like and simplifies the operation step; meanwhile, the determination data of fluorescent materials in the micropore plate can be obtained within 15s through the multifunctional microplate reader, huge samples are allowed to be simultaneously determined; and moreover, the invention has high accuracy and easy operation, stable and reliable result and good reproduction quality.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
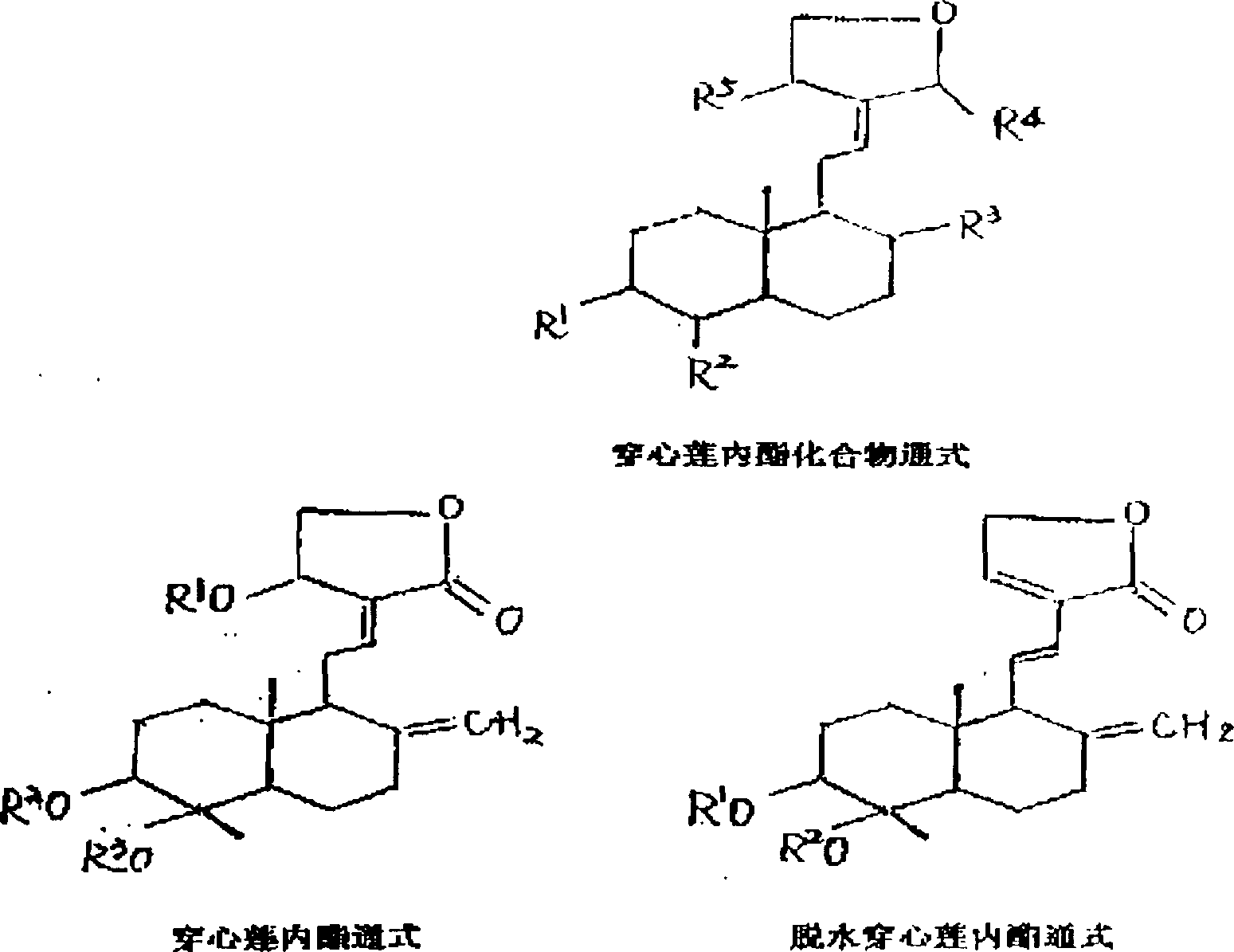
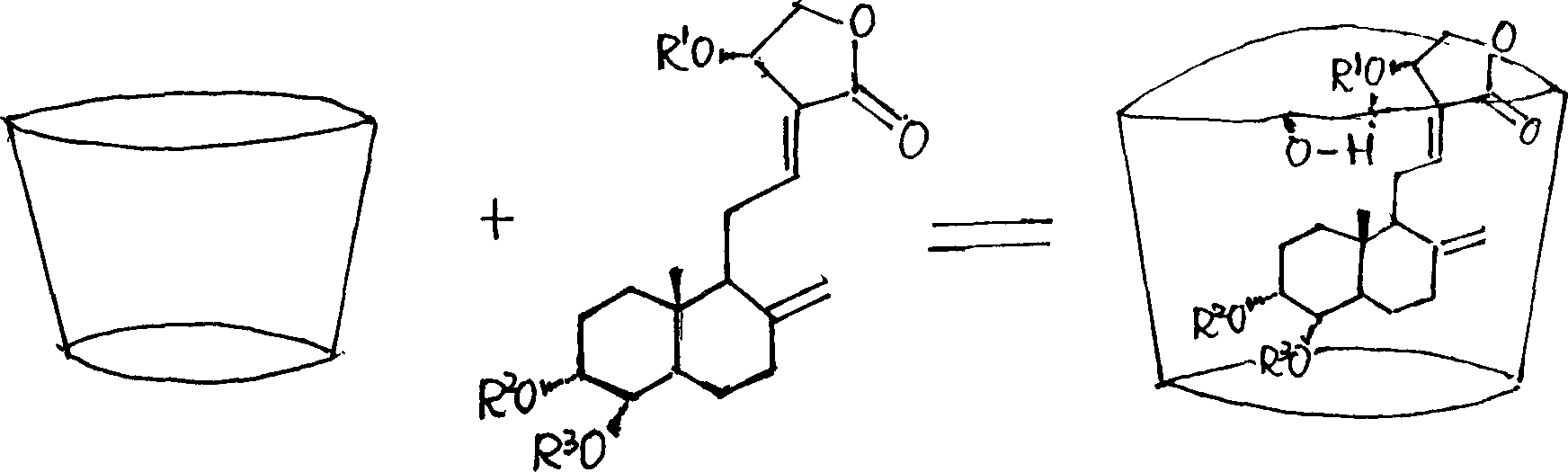
Andrographolide compound solubilizing preparing method and medicinal preparation
InactiveCN1552320AImprove insolubleLittle side effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsVegetable oilCyclodextrin
A process for preparing the andrographolide compound (or medicine with improved solubility includes such steps as proportionally mixing the andrographolide with solubilizer (cyclodextrin, amino acid, phosphatide, water-soluble high polymer and vegetable oil), adding water or organic cosolvent, mechanical grinding, ultrasonic processing, and mixing with medicinal auxiliary.
Owner:侯文阁
Kiwi fruit seed oil liposome oral liquid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102641311AImprove stabilityPromote absorptionMetabolism disorderAntinoxious agentsCholesterolKiwi fruit
The invention discloses a kiwi fruit seed oil liposome oral liquid and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a phosphate buffer solution with pH of 6.8 in a constant temperature oscillator, heating in a water bath to 60 DEG C and keeping constant temperature; (2) based on anhydrous ethanol as a solvent, preparing a mixed solution containing15-25mg / ml of lecithin, 5-20mg / ml of cholesterol and 5-20mg / ml of kiwi fruit seed oil; and (3) injecting the mixed solution in the step (2) into the phosphate buffer solution in the step (1), placing in the constant-temperature water bath at the temperature of 60 DEG C, then performing ultrasonic treatment, adding distilled water to a certain volume, sealing and sterilizing to obtain the kiwi fruit seed oil liposome oral liquid. According to the kiwi fruit seed oil liposome oral liquid prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, kiwi fruit seed oil has high stability and safety, unsaturated fatty acid in the kiwi fruit seed oil can be prevented from being oxidized, and the purposes of convenience in transportation and long-term preservation can be further achieved.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
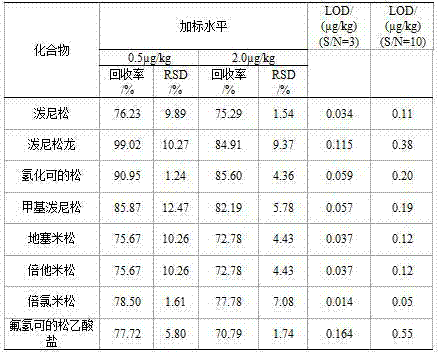
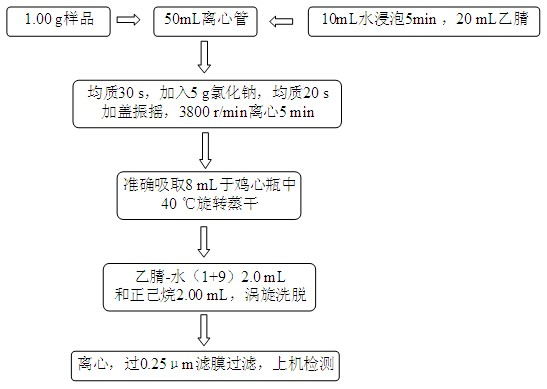
Pretreatment method of residue detection of eight glucocorticoid drugs in chicken
InactiveCN104849119AReduce pretreatment costsShort analysis timePreparing sample for investigationFluid phaseBiochemical engineering
The invention provides a pretreatment method of residue detection of eight glucocorticoid drugs in chicken. The method comprises the steps of weighing a to-be-detected sample, carrying out liquid-liquid extraction, carrying out rotary evaporation and the like. The method adopts instruments such as a constant temperature oscillator, a centrifugal machine and the like; the sample solution prepared by the pretreatment method can be directly detected by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Compared with the existing method, the pretreatment method has the advantages of being simple and effective in operation, less in time consumption, low in cost, good in reproducibility and the like; the method has very high operability, can be expected to be popularized and applied in industries such as environmental friendliness, commodity inspection, entry and exit inspection and quarantine and the like on a large scale, and has remarkable economical benefit.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
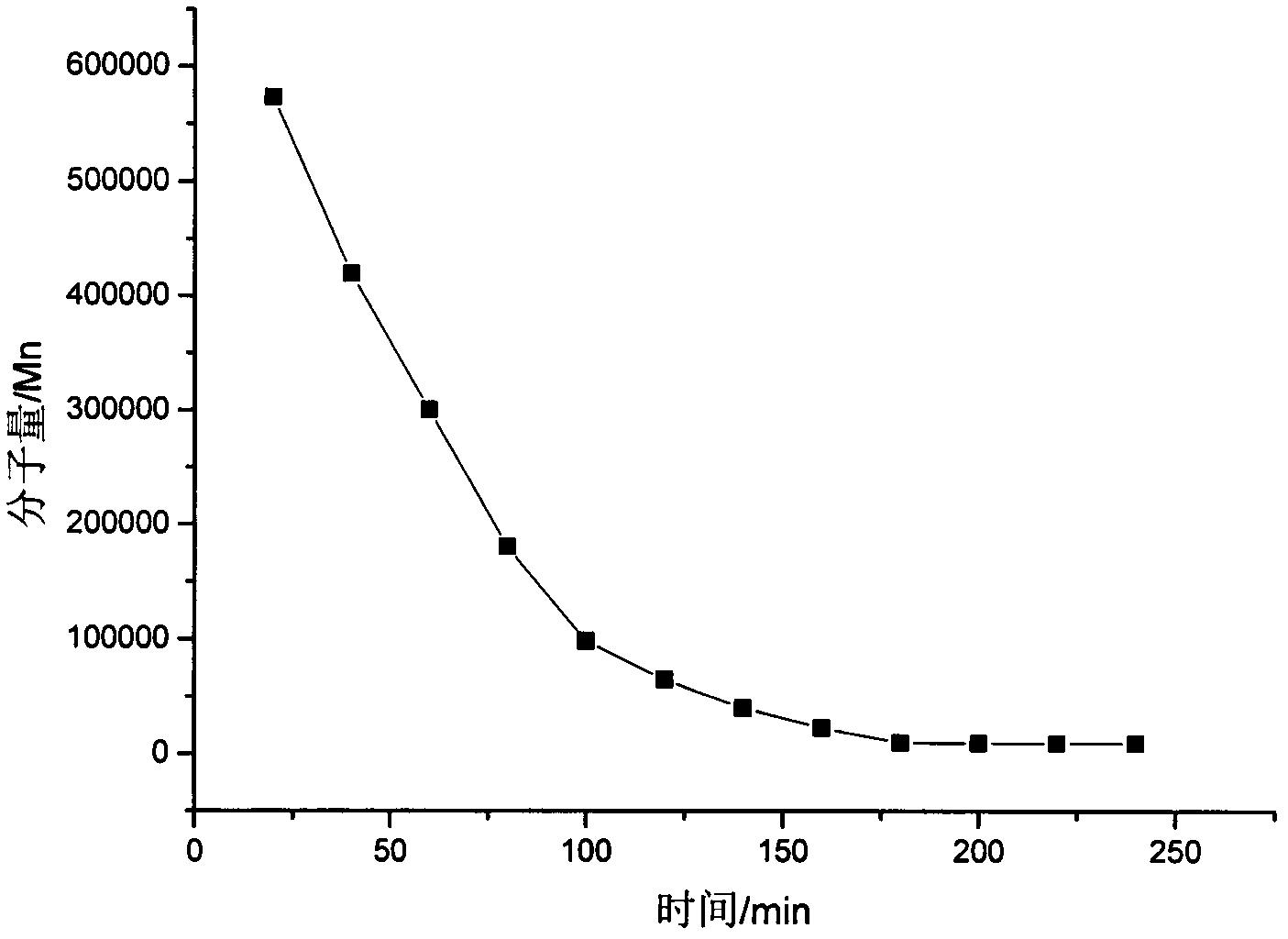
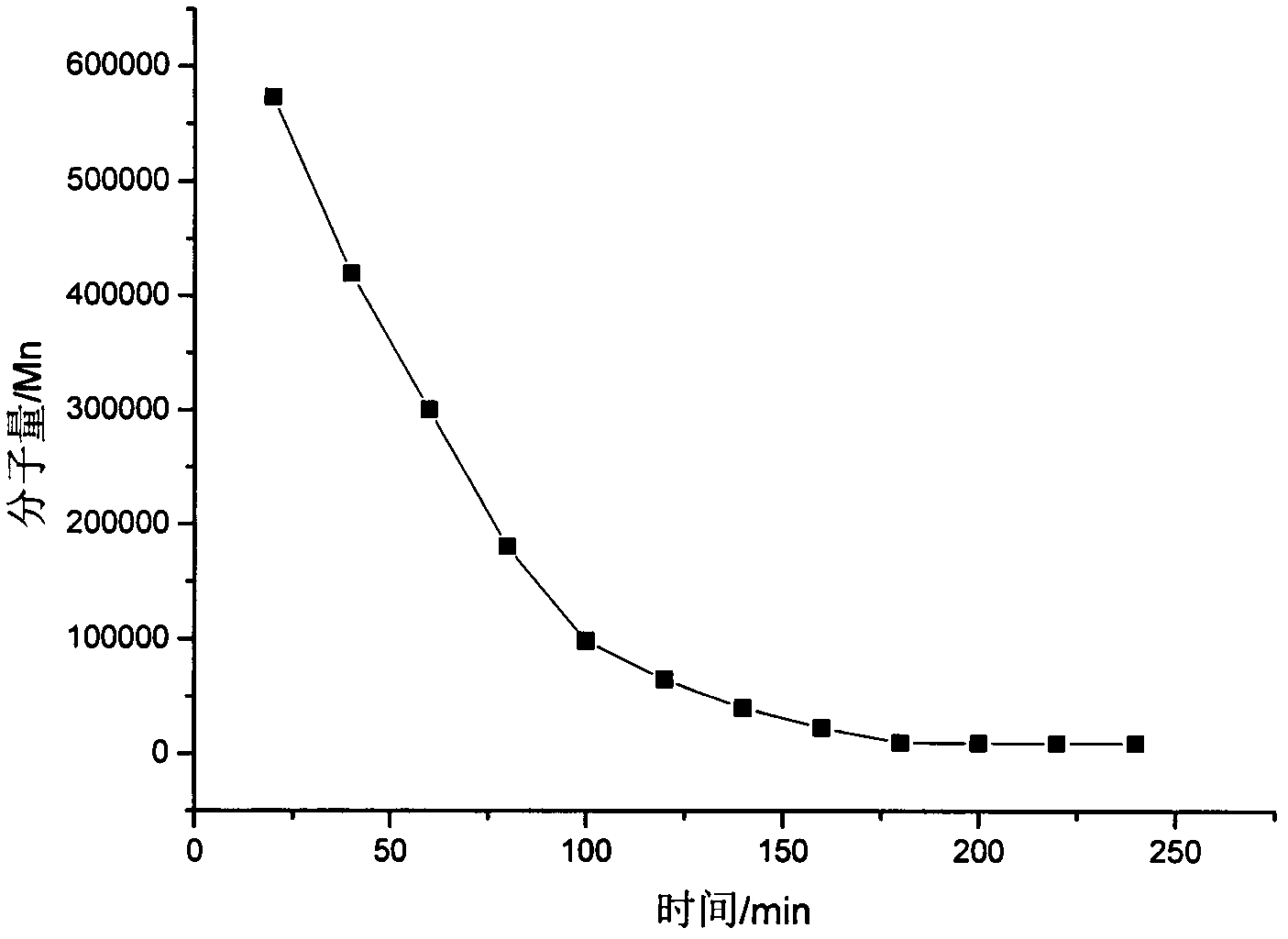
Method for detecting in-vitro enzymolysis of cross-linked hyaluronic acid by utilizing water-phase gel permeation chromatography
The invention relates to a method for detecting in-vitro enzymolysis of cross-linked hyaluronic acid by utilizing water-phase gel permeation chromatography. Whether the cross-linked hyaluronic acid completely achieves enzymolysis is determined by detecting changes of molecular weight of the hyaluronic acid after the enzymolysis. The method comprises putting small granulated cross-linked hyaluronic acid products of 1mL into a color comparison tube, adding 300unis of hyaluronidase, diluting to the volume of one time with water into a water bath chader with the constant temperature of 37 DEG C, starting to time after dilution, fetching 50mum L supernate through a micro syringe every twenty minutes from the twentieth minutes, putting the fetched supernate into a refrigerator and quickly cooling the supernate to the temperature of 5 DEG C, fetching enzymolysis supernate for 3-5 hours, detecting the molecular weight of the supernate at different time intervals respectively through the water-phase gel permeation chromatography (GPC), and determining that the enzymolysis of the product is finished when the molecular weight trends to be a constant. The method for detecting the in-vitro enzymolysis of the cross-linked hyaluronic acid by utilizing the water-phase gel permeation chromatography is simple, easy to operate, low in cost, safe and reliable.
Owner:IMEIK TECH DEV CO LTD
Pretreatment method for detection of acetamiprid in dry fruits and vegetable
InactiveCN102621254ASimplified separation stepsShort analysis timeComponent separationRotary evaporatorPretreatment method
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
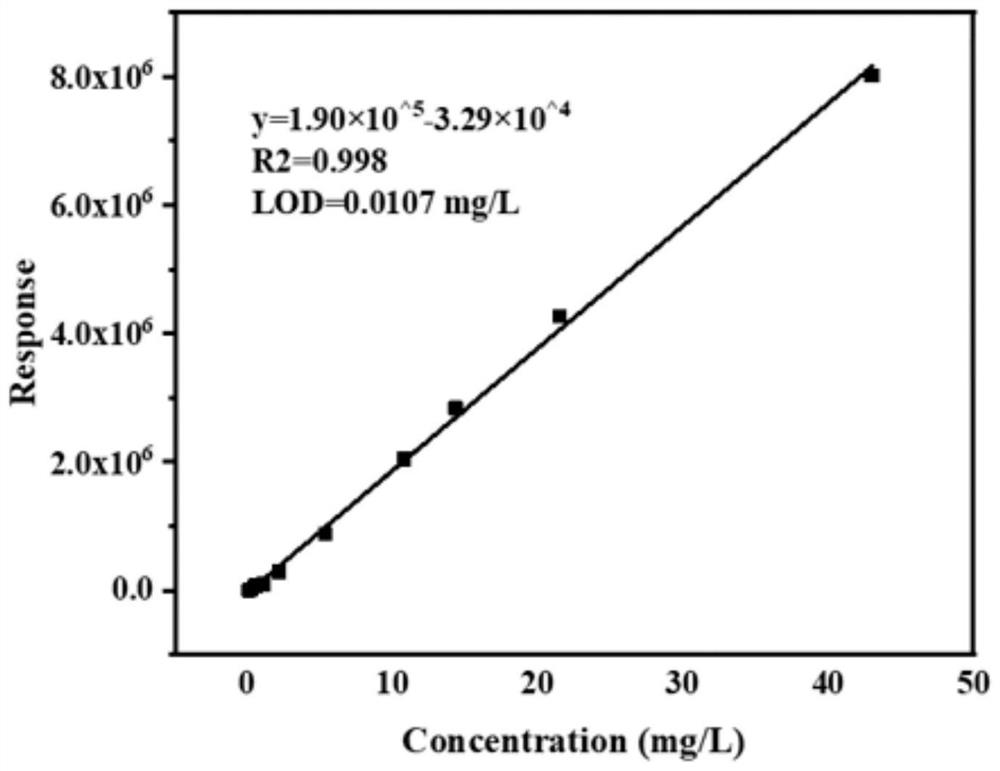
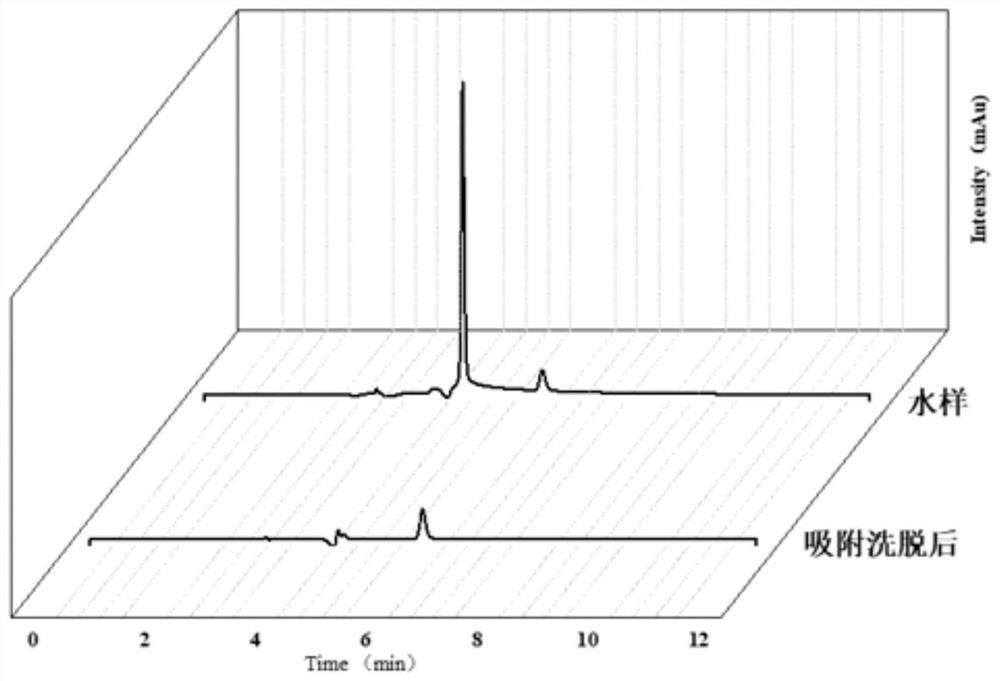
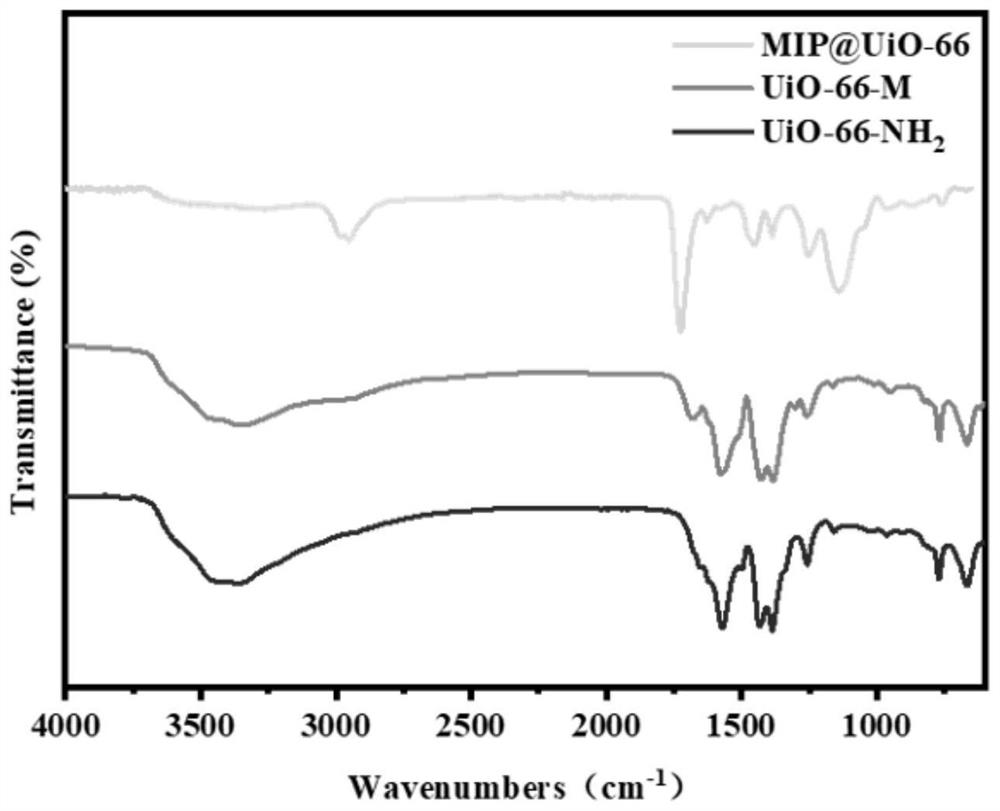
Detection method of norfloxacin based on MOFs (Metal-Organic Frameworks) type molecularly imprinted polymer
ActiveCN113567594ALow costSimple qualitative and quantitative detectionComponent separationAgainst vector-borne diseasesFluid phaseCentrifugation
The invention discloses a detection method of norfloxacin based on an MOFs (Metal-Organic Frameworks) type molecularly imprinted polymer. The detection method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing the MOFs type molecularly imprinted polymer UiO-66 (at) MIP; S2, establishing a norfloxacin liquid phase standard working curve; S3, detecting an actual water sample: mixing the actual water sample with the UiO-66-coated MIP prepared in the step S1, incubating on an oscillator at 500rpm for 40 minutes, and centrifuging to remove supernate; then adding an eluent, and collecting the eluent after ultrasonic centrifugation; and extracting a norfloxacin aqueous solution, concentrating the eluent by a nitrogen blowing concentrator, fixing the volume to the initial actual water sample volume by using water, detecting the obtained aqueous solution by using high performance liquid chromatography, determining whether the norfloxacin is contained or not by using dead time, and substituting the peak area into a norfloxacin liquid phase standard working curve to calculate the content of the norfloxacin in the actual water sample. According to the detection method, the detection cost and the operation difficulty of norfloxacin are effectively reduced, and meanwhile, the detection efficiency is improved.
Owner:FOSHAN SANSHUI FOSHUI WATER SUPPLY CO LTD
Cadmium-lead-arsenic polluted soil composite eluting agent and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113736471AAvoid secondary pollutionEfficient rinseContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersArsenic pollutionEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to a cadmium-lead-arsenic polluted soil composite eluting agent and a preparation method thereof. The cadmium-lead-arsenic polluted soil composite eluting agent comprises a hydroxyethylidene-1, 1-diphosphonic acid solution, an L-lactic acid solution, a pyruvic acid solution and a FeCl3 solution. The volume ratio of the hydroxyethylidene-1, 1-diphosphonic acid to the L-lactic acid to the pyruvic acid to the FeCl3 solution is 6: 2: 1: 1. The preparation method of the cadmium-lead-arsenic polluted soil composite eluting agent comprises the following steps: (1) mixing 10% of a 1-hydroxyethylidene-1, 1-diphosphonic acid solution, 10% of an L-lactic acid solution, 10% of a pyruvic acid solution and a 0.1 mol / L FeCl3 solution according to a volume ratio of 6: 2: 1: 1 to obtain a mixed solution A; and (2) placing the mixed solution A in a reciprocating oscillator for oscillation treatment, sealing, and storing in a dark place. According to the invention, thehydroxyethylidene-1, 1-diphosphonic acid solution, the L-lactic acid solution, the pyruvic acid solution and the FeCl3 solution are compounded, so that not only can the efficient leaching of the soil polluted by the high cadmium, lead and arsenic be realized, but also the problem of secondary pollution to the soil can be avoided.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
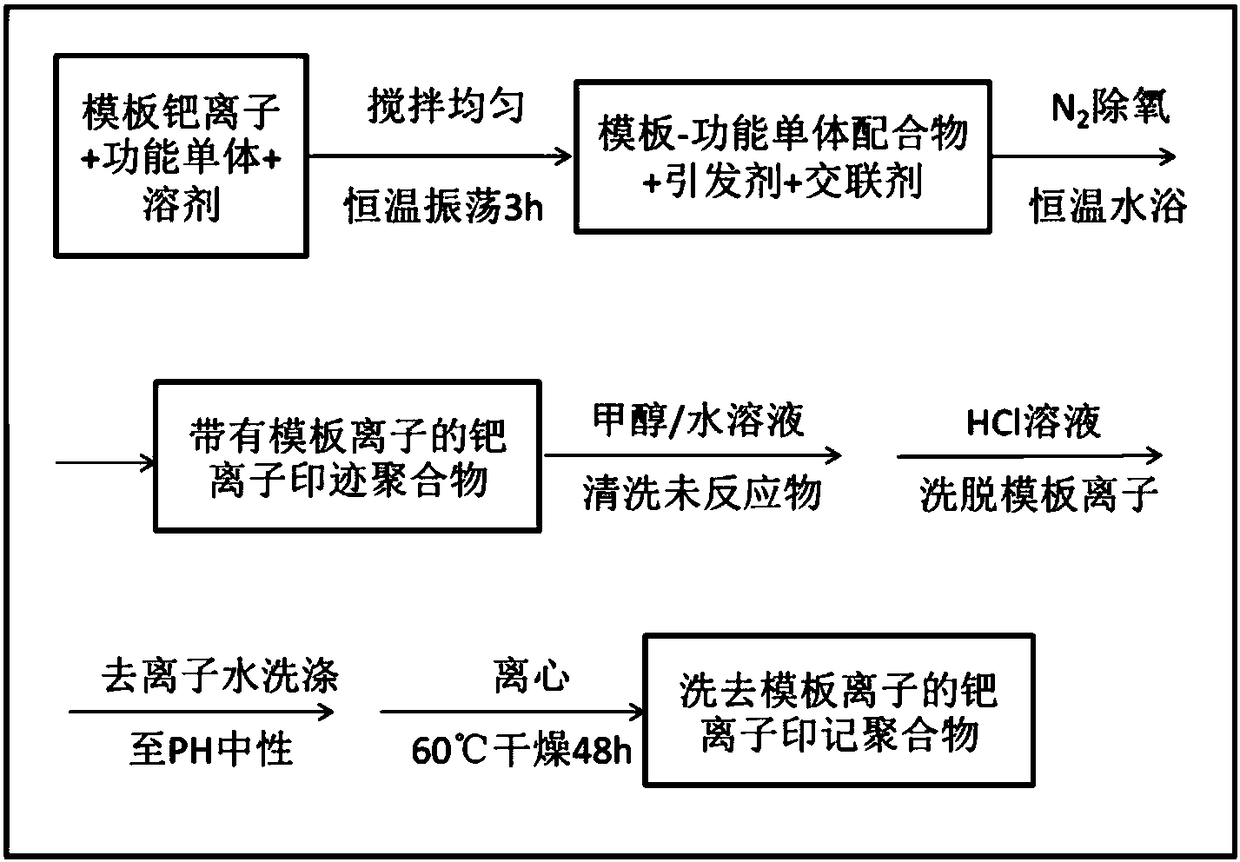
Palladium ion imprinted polymer and preparation method and application thereof
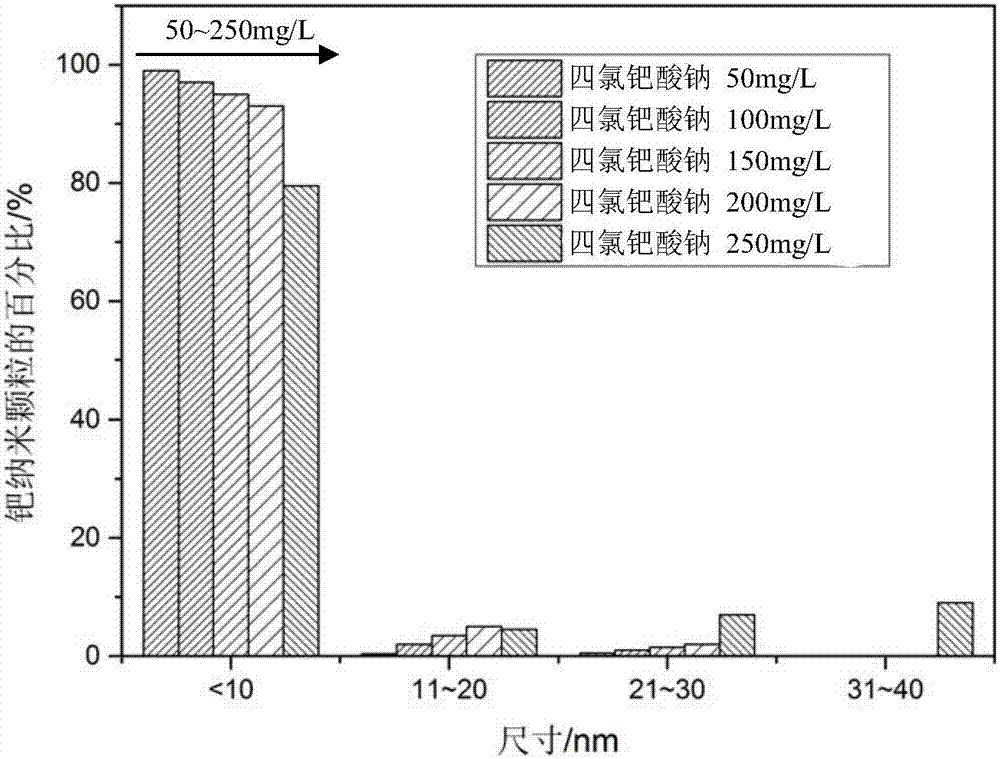
InactiveCN108559024AHigh selectivityReduce manufacturing costOther chemical processesWater contaminantsCross-linkFunctional monomer
The invention provides a palladium ion imprinted polymer and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the steps that template palladium ion PdC142- and functional monomers are mixed and dissolved in methyl alcohol, and placed in a thermostatic oscillator for oscillatory reaction to form a template functional monomer complex, and initiator and a cross-linking agent are added and mixed evenly; nitrogen is introduced in the obtained evenly-mixed solution, and a precipitation polymerization method is adopted to obtain the ion imprinted polymer with template ions; the initiator, the cross-linking agent and the unreacted functional monomers are removed; centrifugal treatment is carried out on an obtained sample, supernate is discarded, the obtained polymer is placed ina vacuum drying oven and dried, and the palladium ion imprinted polymer is obtained. The provided palladium ion imprinted polymer has high affinity and significant selectivity for heavy metal palladium, and can effectively separate and recycle the heavy metal contaminated water body containing palladium.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
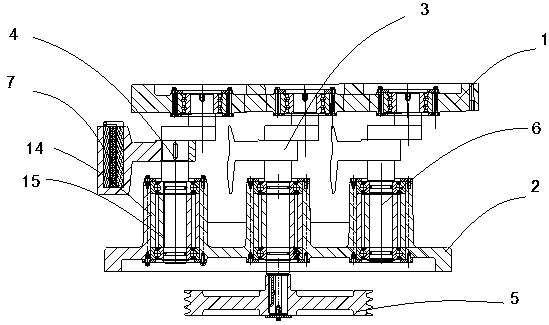
oscillator
ActiveCN108393018BModerate impactImprove the vibration effectShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingMicroorganismPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides an oscillator, comprising: an upper plate of the oscillator; a lower plate of the oscillator, which is located directly below the upper plate of the oscillator; The lower plate, the end of which protrudes downward from the active eccentric shaft and is fixedly connected to the driven pulley; the driven eccentric shaft, one end is rotatably installed on the upper plate of the oscillator, and the other end is rotatably installed on the lower plate of the oscillator; multiple counterweights, Respectively detachably installed on the active eccentric shaft and the driven eccentric shaft; the counterweight is an arc-shaped column; at least one of the counterweights on the driven eccentric shaft faces downwards and forms several There are two parallel installation slots, and a center-of-gravity adjustment plate matching the installation slots is placed in the installation slots. The invention avoids the excessive or insufficient oscillation of the sample solution; at the same time, the collision force between the drug particles or microorganisms in the liquid and the bottle wall is moderate.
Owner:浙江兆华机械制造有限公司
Biological palladium catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107008256AEasy to prepareGood chemical stabilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHalogenPollutant
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental microorganism materials, and discloses a biological palladium catalyst, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) cultivating enterococcus faecalis till being in stable stage, then filtering, collecting, cleaning and preparing a bacterium suspension; and (2) adding the bacterium suspension to a palladium precursor solution, adjusting pH, and adding an electron donor solution; and putting into a thermostatic oscillator for cultivation, carrying out ultrasonication, cleaning and drying to obtain the nanosized palladium. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the preparation method is simple, other chemical reagents do not need to be introduced, and the catalyst prepared by the method has uniform particle size and a good catalytic performance and can be used for catalytic degradation of halogen-containing organic pollutants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for measuring content of glyceryl triacetate
InactiveCN103926353AEasy to removeThe measurement result is accurateComponent separationAcetic acidGas liquid chromatographic
The invention provides a method for measuring the content of glyceryl triacetate. The method is characterized by including the following steps: (1) putting 0.1 mL of glyceryl triacetate sample in a 50 mL of conical flask; (2) adding 10 mL of acetone; (3) oscillating on an oscillator for 10 minutes, and sampling for waiting for testing on a machine; (4) measuring the sample to be measured by a gas chromatographic method, wherein the gas chromatographic condition and the quantitative method are the same as those of YC144-2008. On the condition that the dilution ratio of an original method is almost unchanged, the measuring method provided by the invention is used for optimizing the sample extracting volume, a vessel, a dilution solvent, solvent dosage and the like of the original method. Compared with the prior art, the measuring method has the advantages of simplifying the operation, improving the efficiency, saving the cost and ensuring better stability.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT
Method for detecting in-vitro enzymolysis of cross-linked hyaluronic acid by utilizing water-phase gel permeation chromatography
Owner:IMEIK TECH DEV CO LTD
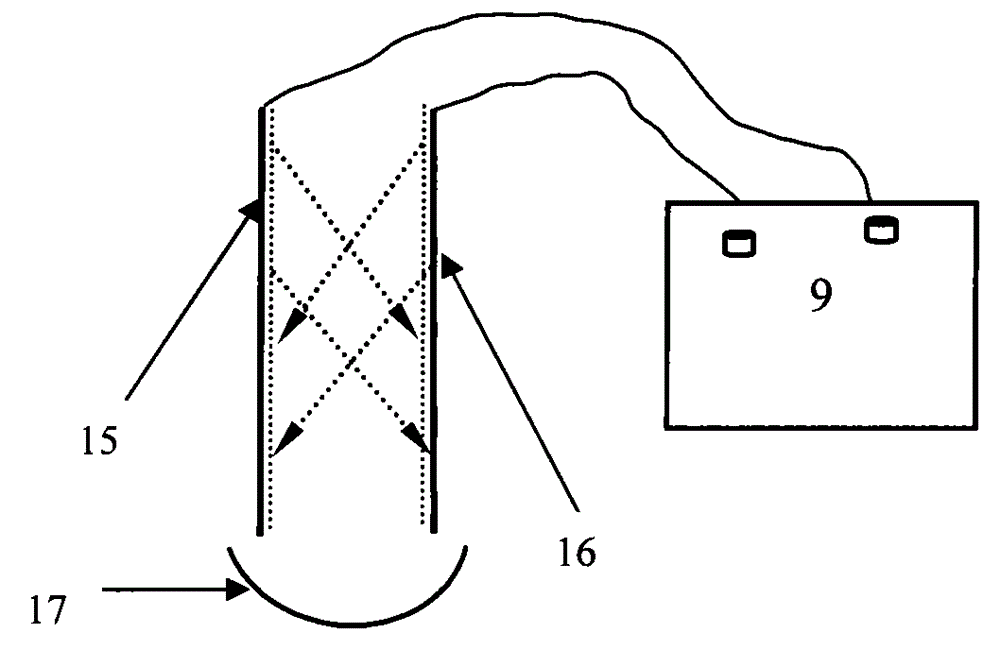
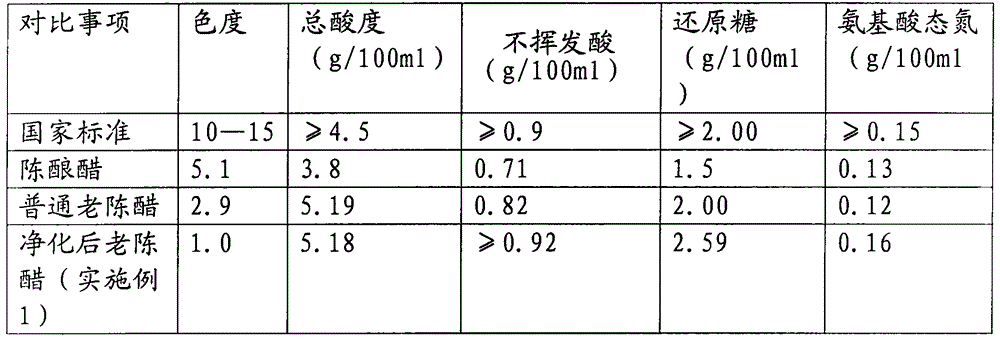
Purification process and purification device for super-mature vinegar
The invention relates to a purification process for super-mature vinegar. The purification process comprises the following steps: firstly, performing coarse filtration on the mature vinegar; secondly, performing oscillation gathering treatment, sterilization and aging treatment on the vinegar subjected to the coarse filtration for the first time; thirdly, performing oscillation gathering treatment and sterilization treatment for the second time, wherein a most key step is the oscillation gathering treatment, and a treatment mode is that voltage of not lower than 3,000 V is adopted for carrying out discharge on positive and negative electrode plates, and negative and positive ions generated by the positive and negative electrode plates in electrode space are utilized to adsorb sediments and microorganisms in the vinegar; in addition, oscillators connected to the positive and negative electrode plates are utilized to remove the sediments adhered to the positive and negative electrode plates and enable the sediments to drop into a sediment collecting tray, and the sediments are discharged through a residue discharge pipeline and a residue discharge hole. The process effectively solves serious turbidity and precipitation problems ubiquitous in super-mature vinegar and a problem of over-standard of mixed strains caused by easy microorganism propagation of the super-mature vinegar in the prior art.
Owner:山西太谷通宝醋业有限公司
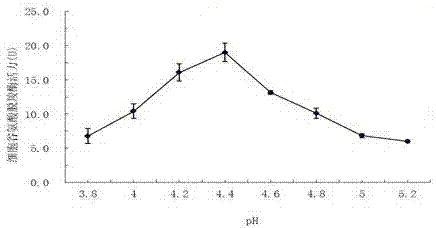
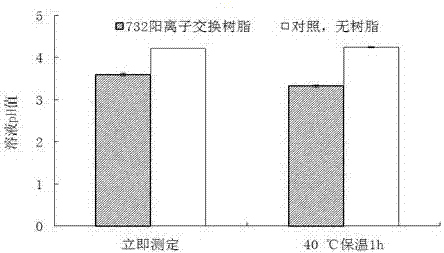
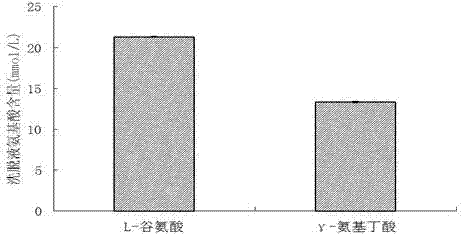
Method for improving activity of glutamate decarboxylase by virtue of 732 cation exchange resin
ActiveCN107574192AHigh selectivityEasy post-processingMicroorganism based processesFermentationWater bathsGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention relates to a method for improving activity of enterococcus faecium glutamate decarboxylase by virtue of 732 cation exchange resin, and belongs to the field of bio-technology. According to the method provided by the invention, the 732 cation exchange resin is taken as an enzyme activity accelerant of the enterococcus faecium glutamate decarboxylase; a 732 cation exchange resin-glutamate decarboxylase composite catalysis system is constructed by mixing the 732 cation exchange resin, an L-glutamic acid solution and an enterococcus faecium suspension or glutamate decarboxylase free enzyme liquid at the ratio of 1 to 1 to 1 of the mass of the 732 cation exchange resin to the volume of the L-glutamic acid solution to the volume of the enterococcus faecium suspension or glutamate decarboxylase free enzyme liquid; and the yield of [gamma]-aminobutyric acid can be improved by 25.31-143.23% when it conducts a reaction in a water-bath oscillator at 80r / min and 37-43 DEG C or it conducts a stirring reaction at a low speed for 24-36h. According to the method provided by the invention, the 732 cation exchange resin can obviously improve the activity of the glutamate decarboxylase,and meanwhile, an exchange adsorption effect of the 732 cation exchange resin on [gamma]-aminobutyric acid is a process of purifying the [gamma]-aminobutyric acid, so that a downstream extraction andpurification process is simplified and production cost is reduced; and the method is simple and convenient and is green and environment-friendly.
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for removing hexavalent chromium in waste water by utilizing gel beads prepared from tartaric acid modified oyster mushrooms
ActiveCN104826609AMany adsorption sitesImprove adsorption efficiencyOther chemical processesWater contaminantsChemistryHexavalent chromium
The invention discloses a method for removing hexavalent chromium in waste water by utilizing gel beads prepared from tartaric acid modified oyster mushrooms. The method comprises the following steps: adjusting the pH value of a certain amount of Cr(VI)-containing waste water into 1.0-10.0, adding a certain amount of gel beads prepared from the tartaric acid modified oyster mushrooms into waste water, wherein the gel beads prepared from the tartaric acid modified oyster mushrooms with the wet weight of 5g-15g is added in each liter of waste water, reacting in a constant-temperature oscillator at the rotation speed of 100-200 turns / min at the temperature of 10 DEG C-50 DEG C for 1-48 hours, separating the gel beads prepared from the tartaric acid modified oyster mushrooms from the solution after reaction so as to remove Cr(VI) in wastewater. The method has the advantages of low cost, convenience in operation, high treatment efficiency, easiness in separation and recycling and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
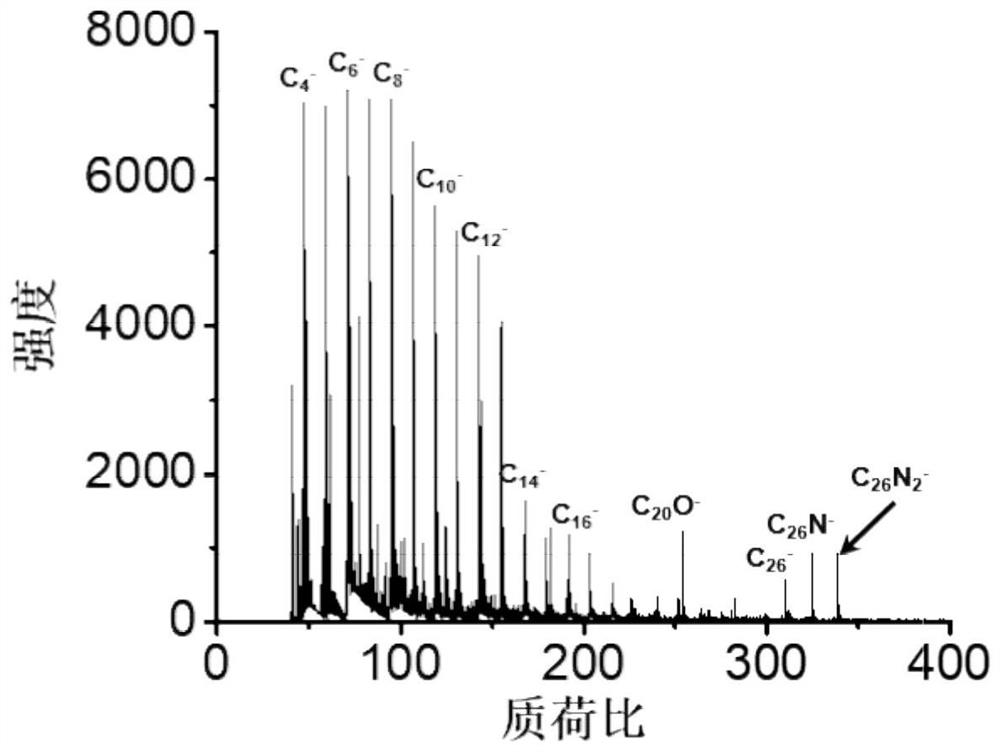
Method for biodegradation of carbon black particles induced by metabolic enzyme and method for analyzing product thereof
ActiveCN112903804ARenew knowledgeReduce preparation timePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMetabolic enzymesLiving body
The invention discloses a method for biodegradation of carbon black particles induced by metabolic enzyme and a method for analyzing a product thereof. The method comprises the following steps: step (1), weighing a proper amount of carbon black sample; (2) dispersing the weighed carbon black sample with water and preparing a dispersion liquid with a certain concentration; (3) mixing the carbon black dispersion liquid with a metabolic enzyme solution, and uniformly mixing the mixed liquid in a vortex oscillator; and (4) placing the mixed solution in a waterproof incubator for incubation. The method disclosed by the invention reveals the action of the enzyme through complementary multiple technologies, and proves that the enzyme can induce the conversion of the carbon black particles. According to a typical carbon cluster mass spectrum peak and changes of carbon-oxygen and carbon-nitrogen bonds in a spectrum, a conversion mechanism of carbon black particles in a living body is provided.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving jelly strength of gelatin
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
In-vitro dissolution method of cross-linked sodium hyaluronate gel
The invention discloses an in-vitro dissolution method of cross-linked sodium hyaluronate gel, and belongs to the technical field of in-vitro dissolution of cross-linked sodium hyaluronate gel. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting cross-linked sodium hyaluronate gel into an AmicronUltra-15 tube; and enabling the AmicronUltra-15 tube to sequentially pass through a constant-temperature oscillator and a centrifugal machine, so as to realize in-vitro dissolution of the cross-linked sodium hyaluronate gel, thereby obtaining supernate. According to the technical scheme, the effect that liquid on the lower layer of the AmicronUltra-15 tube is uniform after centrifugation is achieved.
Owner:浙江美华鼎昌医药科技有限公司
Automatic benthonic animal releasing oscillator
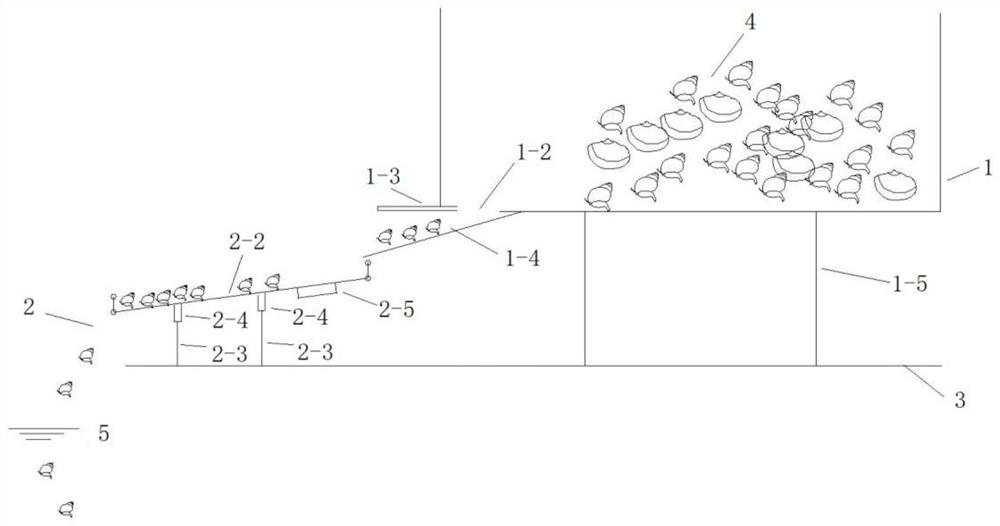
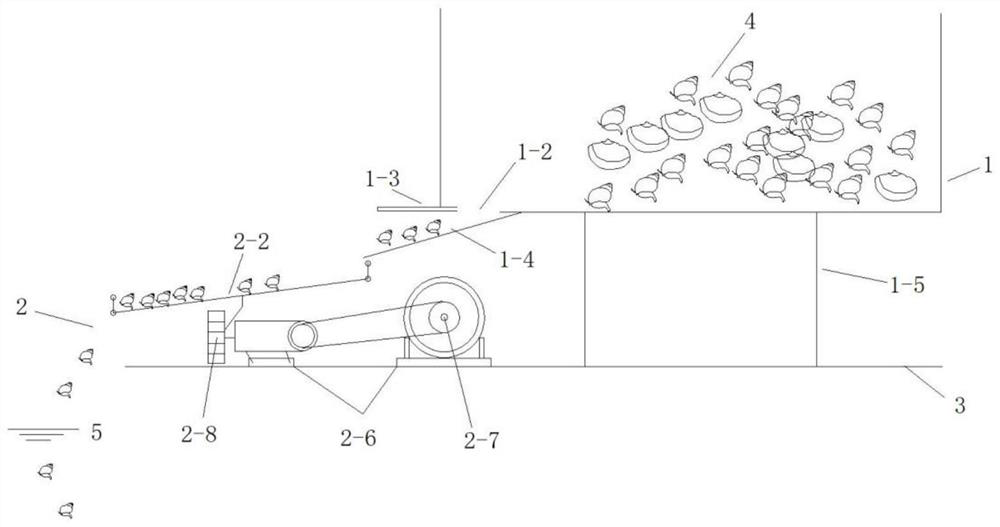
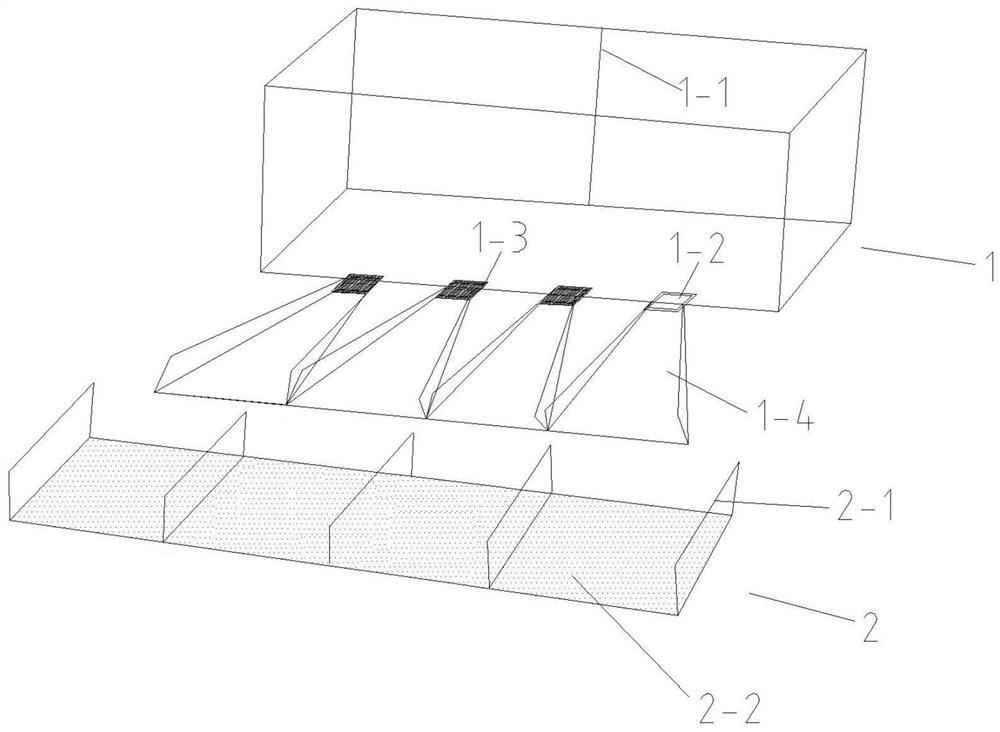
PendingCN113845231ASolution areaSolve densityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEcological environmentFishery
The invention discloses an automatic benthonic animal releasing oscillator which comprises a releasing container, the releasing container is arranged on a ship body through a container support, a feeding door and a lower discharging opening are formed in the releasing container, the top of a sliding way is located below the corresponding lower discharging opening, the bottom of the sliding way extends to the position above the top of an oscillating plate, the sliding way and the oscillating plate are both in a slope shape, the oscillating plate is arranged on an oscillating plate support through an oscillating spring, the oscillating plate support is arranged on the ship body, and a vibrator is arranged at the bottom of the oscillating plate. The problems that in water ecological environment treatment, since the benthonic animals are thrown mainly through manpower, releasing is uneven, efficiency is low, manpower and material resources are consumed and the like are solved, and the releasing mode of the benthonic animals is changed; and the automatic benthonic animal releasing oscillator is simple in structure, convenient to use and remarkable in effect.
Owner:WUHAN ZHONGKE HYDROBOLOGY ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
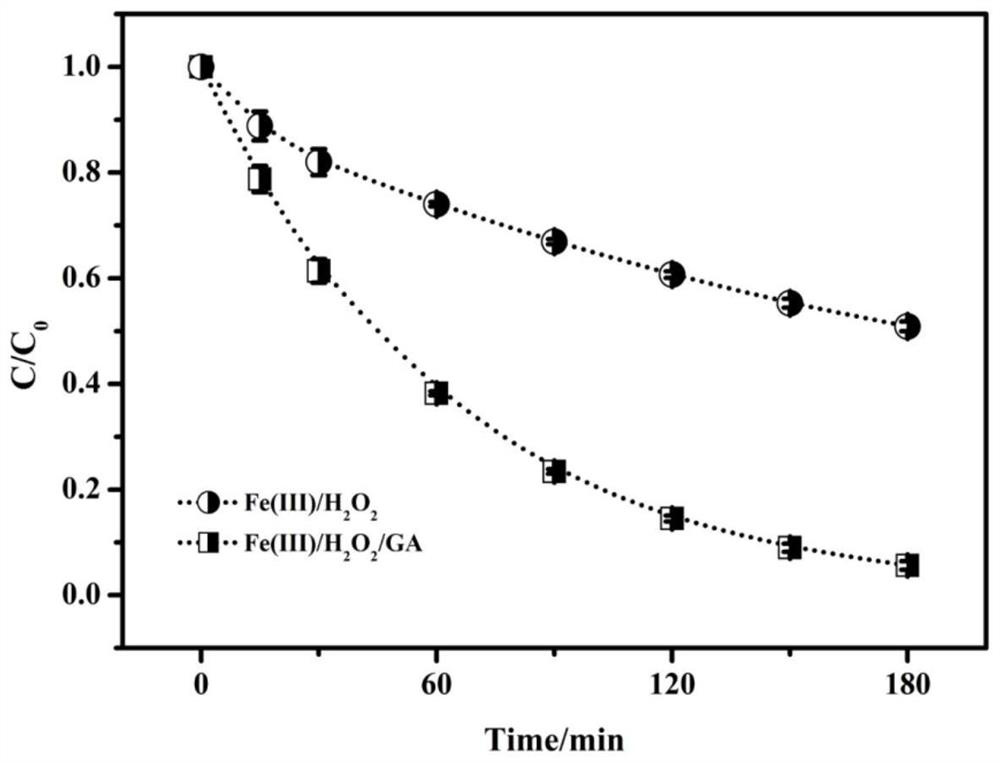
Method for Enhanced Treatment of Organic Wastewater with Fenton-like System Constructed Based on Glyoxylic Acid
ActiveCN109987692BPrevent precipitationImprove the efficiency of treating organic wastewaterWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsGlyoxylic acidIron salts
The present invention specifically relates to a method for enhancing treatment of organic waste water with a Fenton-like system constructed based on glyoxylic acid. The method is as follows: adding ferric salt and glyoxylic acid to the organic waste water to be treated, and controlling the system under acidic conditions , add hydrogen peroxide, place the mixed solution in a shaker, and vibrate at a speed of 200 rpm for 0-180 minutes to complete the treatment of organic wastewater. This method can accelerate the iron cycle in the Fenton-like system and enhance the degradation efficiency of organic pollutants. The invention has the advantages of low cost, non-selectivity, no secondary pollution and the like.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Target protein separation and purification system
InactiveCN113234119AConvenient crushing operationPrecise control of titerPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesProtein targetMagnetic valve
The invention relates to a target protein separation and purification system which comprises an ultrasonic oscillator, a base plate is arranged at the bottom of the ultrasonic oscillator, two sets of vertical rods are connected to the rear side of the top of the base plate, the tops of the two sets of vertical rods are jointly connected with a top plate, and a control panel is arranged on the side portion of the top plate. A display screen is arranged on the control panel, a lifting mechanism is arranged on the top plate, a fixing ring is arranged on the lifting mechanism, a burette is movably inserted into the inner cavity of the fixing ring, scales are arranged on the burette, a limiting ring is fixedly connected to the periphery of the burette in a sleeving mode, and a monitoring mechanism is arranged in an inner cavity of the burette. An electromagnetic valve is arranged on the burette, and a titration nozzle is communicated with the bottom of the burette. According to the system, when the crushed cells are quantitatively titrated with the buffer solution, the accuracy of the titration amount of the buffer solution is ensured, and the extraction rate of the target protein in the water-blooming cyanobacteria is favorably improved.
Owner:上海点拾科技有限公司
Fluorescent quantitative PCR kit for detecting vancomycin-resistant vanA gene of enterotoxin
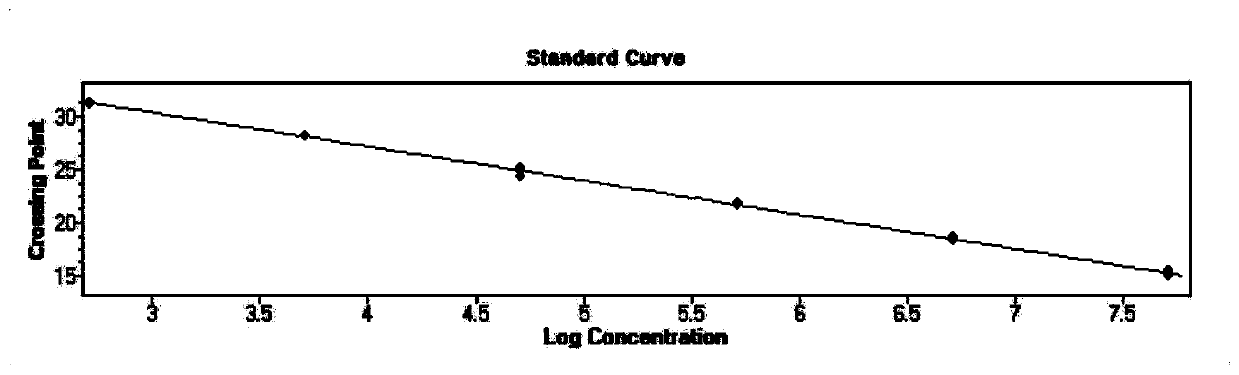
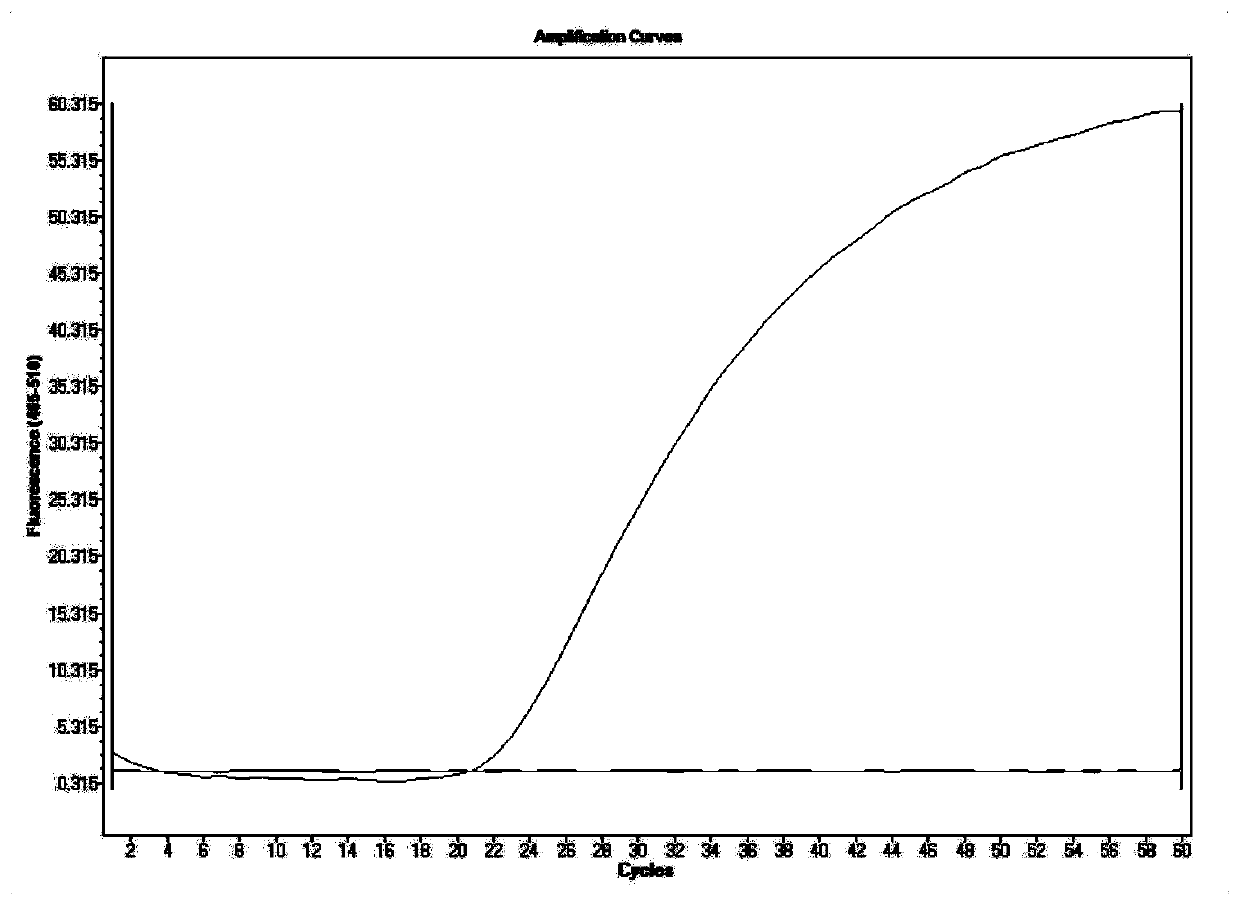
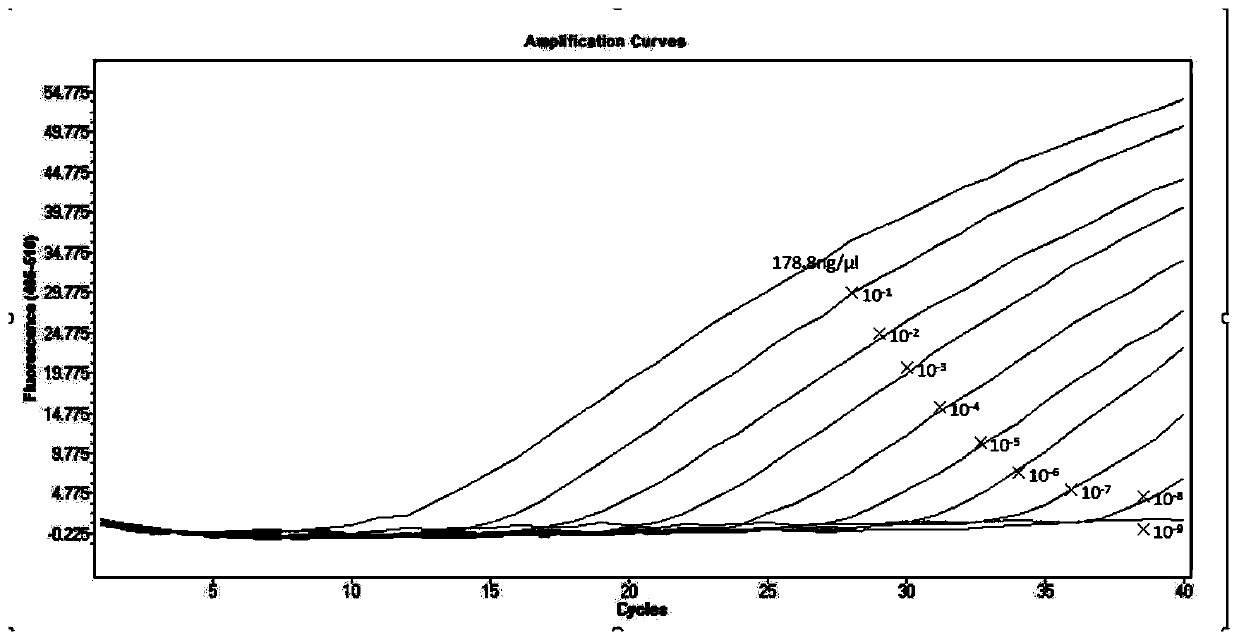
PendingCN111057774AQuick checkValidation of Assay SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPackaging TubeOscillarin
The invention relates to the technical field of bioengineering, and especially relates to a fluorescent quantitative PCR kit for detecting a vancomycin-resistant vanA gene of enterotoxin. SEQ ID NO:1upstream primer F:5'-GCTACGTTTACCTATCCTG-3', SEQ ID NO:2 downstream primer R:5'-CAGCCTGCTCAATTAAGA-3' and SEQ ID NO:3 TaqMan probe sequence P:5'-FAM-TTGCTGTCATATTGTCTTGCCGATTC-BHQ-3' are designed through software. Fluorescent RT-PCR detection is carried out, an RT-PCR reaction liquid, a hot start Taq enzyme and a probe are taken and mixed into a centrifugal tube according to the number n (n = (thenumber of samples to be detected) + 2) of detection samples, the centrifugal tube is oscillated on a vortex oscillator, sub-packaging is carried out according to each tube, each tube is covered witha tube cover for later use, a negative control liquid is added into a sub-packaging tube, and DNA of each sample is taken, and is added into a corresponding reaction tube; and finally, a positive control is taken out and is added into another reaction tube, and all the reaction tubes are labeled and centrifuged, and are taken out of a fluorescent PCR instrument. The kit can rapidly detect the enterococcus vancomycin VanA drug-resistant gene, and provides guidance for drug therapy after super bacterial infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI ANIMAL EPIDEMIC PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
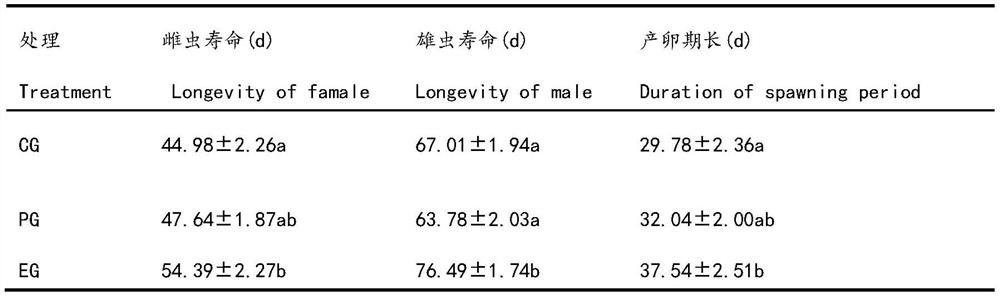
A kind of method for prolonging the lifespan of adult beetles
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
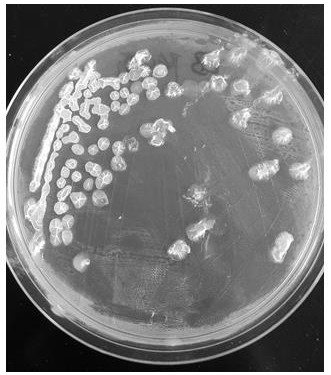
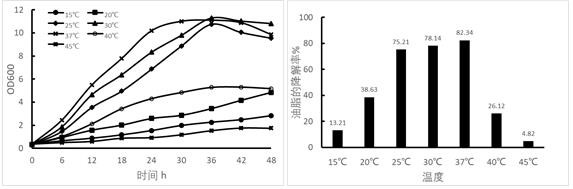
Bacillus siamensis capable of degrading grease and application of bacillus siamensis in grease-containing wastewater
The invention discloses bacillus siamensis capable of degrading grease and the application of the bacillus siamensis in grease-containing wastewater. The bacillus siamensis BS1 disclosed by the invention has the preservation number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2021840 in the China Center for Type Culture Collection). The bacillus siamensis BS1 disclosed by the invention can be used for degrading grease. In a grease culture medium containing soybean oil with the initial concentration of 9.5-10.5 g / L, after being cultured for 48 hours, the grease degradation rate reaches 82.34%, wherein the culture temperature is controlled at 37 DEG C, and the rotating speed of a constant-temperature culture oscillator is 200 rpm. The invention also discloses the application of the bacillus siamensis BS1 in grease-containing wastewater, and the bacillus siamensis BS1 has a relatively good grease degradation capability.
Owner:FOSHAN YUHUANG ECOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT TECH
A kind of preparation method of α-2,3 deaminosialyllactulose
The invention discloses a method for preparing alpha-2,3 deaminosialyl lactulose. The method is characterized in that 40-80 parts by weight of mannose, 100-200 parts by weight of sodium pyruvate, 50-100 parts by weight of lactulose and 125-260 parts by weight of sodium cytidine triphosphate (CTP) are dissolved in 4000-8000 parts by weight of ultrapure water, the pH is adjusted to 8.5 with 4 mol / liter of NaOH, and 400-1000 parts by weight of 1 mol / liter of Tris-HCl with pH of 8.5 are added; 40-100 parts by weight of 2 mol / L of MgCl2 are added; 5-8 parts by weight of sialic acid aldolase areadded, and 6-10 parts by weight of CMP-sialyltransferase are added; 6-10 parts by weight of alpha-2,3 sialyltransferase are added. Reaction is conducted for 24 hours at 37 DEG C in a vapour-bathing constant temperature vibrator. After lactulose is completely reacted, 95% of ethanol of the same volume is added to a reaction solution, the reaction solution is placed in a refrigerator at 4 DEG C for30 min, and then is centrifuged at 7000 rpm for 30 min, and supernatant is concentrated through rotary evaporation. Purification is conducted with biogel columns, concentration is conducted through the rotary evaporation, and pure products are obtained through freezing and drying.
Owner:河南省熙康食品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com