Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, fermented seed liquid thereof, application and soybean meal fermentation method
A technology for dissolving starch spores and fermentation method, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory treatment effect of antigen protein, single strain, no degradation treatment of soybean meal antigen protein, etc., achieves good application prospects, improves quality, and improves the content of small peptides Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1: the screening separation of strain
[0044] Use sterile tweezers to collect samples of fermented soybeans, intestinal contents of livestock and poultry, soil, etc., put them into bags and mark them. Take 1g of each collected sample and pour it into a test tube containing 9mL of sterile water, shake it up and put it in a constant temperature water bath at 80°C for 20 minutes, then shake it up and dilute, take 10 -4 、10 -5 and 10 -6 Three dilutions were applied to the nutrient plate medium, and each dilution was repeated three times, and placed upside down in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C for 24 hours. Observe the transparent circle around the colony on the nutrient plate medium, and calculate the (H / C) ratio, and record the number.
[0045] The colony with transparent circle in the nutrient plate medium was streaked and purified on the skim milk plate. Finally, the isolated single colony was inoculated into the slant medium for strain prese...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: Re-screening and identification of strains
[0052] 1) Double screening
[0053] The strains screened in Example 1 were inoculated into spore seed medium, and cultured at 180 r / min and 37°C for 18 hours.
[0054] The activated strains were inoculated into the re-screening medium (250mL Erlenmeyer flask, 50mL re-screening medium, 1mL of strains, 5.5×10 6 cfu / mL), cultured at 180r / min, 37°C for 48h to obtain a fermentation broth.
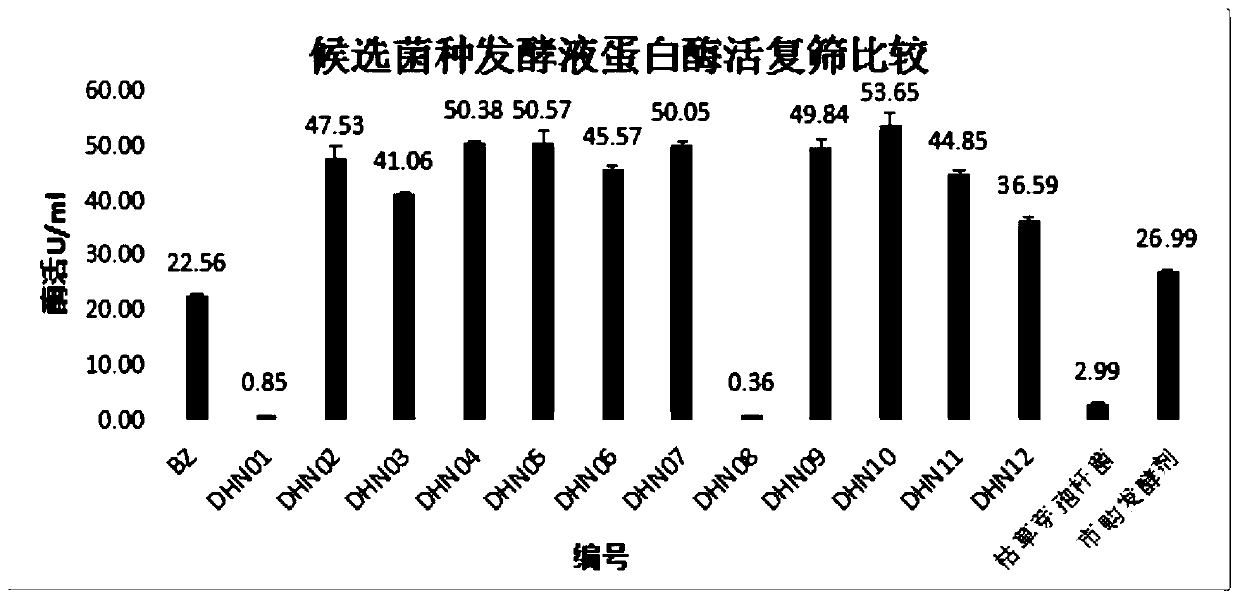
[0055] The fermentation broth was taken, and centrifuged at 10,000 r / min for 10 min at 4°C. Compared with the BZ standard strain, commercially available Bacillus subtilis and commercially available starter, the protease activity of the supernatant was determined by the Folin-phenol method. method. The result is as figure 2 .
[0056] Among them, the enzyme activity of BZ standard strain was 22.56 U / mL, the lowest enzyme activity of DHN08 was 0.36 U / mL, the highest enzyme activity of DHN10 was 53.65 U / mL, and the enzyme ac...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3: soybean meal fermentation method
[0069] 1) Preparation of fermented seed liquid: smear Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DHN04 on the nutrient plate medium, and after culturing at 28-40°C for 12 hours, pick a single colony of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DHN04 on the plate and put it in the spore seed medium, Activate at 28-40°C for 12 hours to obtain the primary seed liquid, then add the primary seed liquid at 2% to 100mL spore seed medium and activate at 28-40°C for 12 hours to obtain the fermented seed liquid;
[0070] 2) Fermentation: Mix soybean meal and water at a weight ratio of 1:1 to obtain soybean meal mixture, put 100g of soybean meal mixture into the triangle flask, add 2g of the fermented seed solution obtained in step 1), and adjust the pH to 7.5-8.5 , fermented and enzymatically hydrolyzed at 40°C;
[0071] 3) Detection: After 48 hours of fermentation, the sample was dried at 50°C, crushed and passed through an 80-mesh sieve, and the content of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com