L-Glutamic acid (L-Glu) detection method and sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) membrane modified electrode
A technology for modifying electrodes and molecular imprinting, which is applied in the field of chemical/biological sensing to achieve the effects of increasing sensitivity, increasing electronic conductivity, and superior detection limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] All the reagents used in the examples are of analytical grade (AR), and the experimental water is all ultrapure water (resistivity ≥ 18.3 MΩ·cm). In the following description, the descriptions of amino acids all use English abbreviations.
[0031] 1. Experimental process
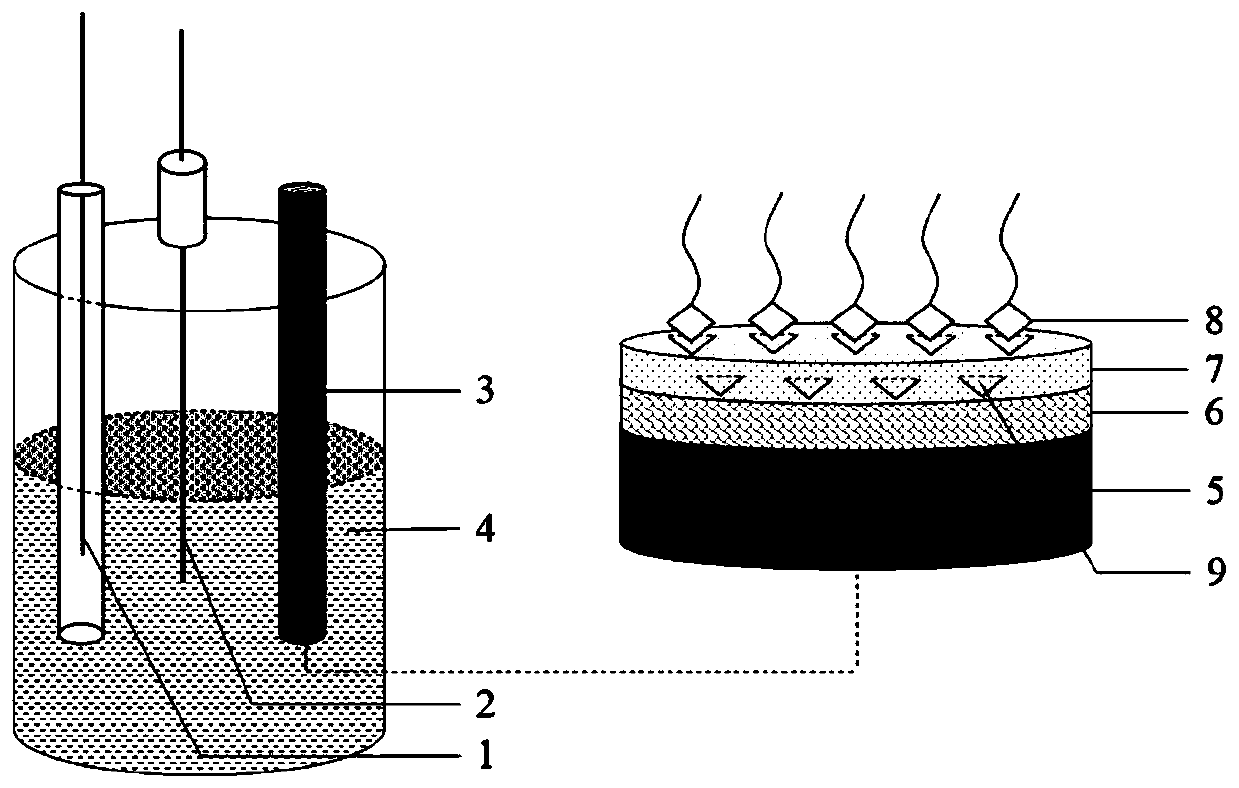
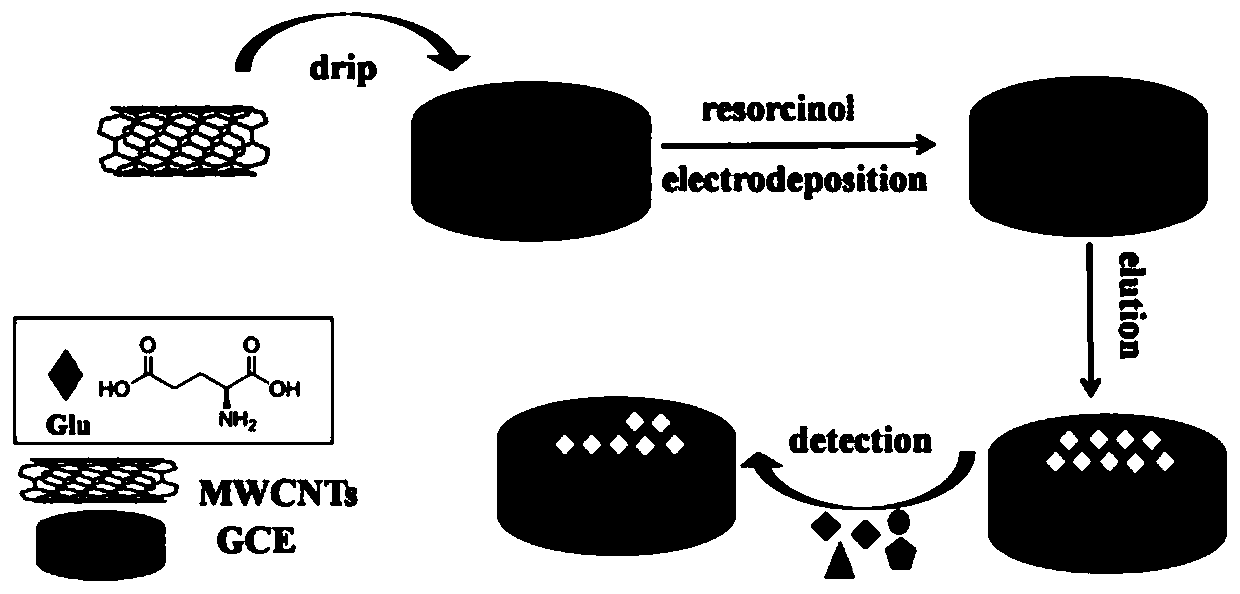
[0032] 1. Preparation of MWCNTs dispersion
[0033] 1.0mg of MWCNTs was placed in 1.0mL of N-N dimethylformamide solution and sonicated for 1h to obtain MWCNTs dispersion (1.0mg / mL).
[0034] 2. Preparation of electropolymerization base solution
[0035] Accurately weigh 0.5606g 4,6-diaminoresorcinol (monomer) and 0.1471g L-glutamic acid (template), dissolve with PBS buffer solution of pH = 5.0 and set the volume to 100mL to prepare 4,6 -Diaminoresorcinol (4.0mM) and L-glutamic acid (1.0mM) mixed liquid, that is, the electropolymerization base solution with a monomer and template molar concentration ratio of 4:1.
[0036] 3. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Membrane Modified Electrode ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com