Porous carbon electrode material with easily-regulated microstructure as well as preparation method and application of porous carbon electrode material
A porous carbon electrode and microstructure technology, which is applied in the preparation/purification of carbon, negative electrodes, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of complex hard template removal process, high cost, and complicated preparation of soft template reagents, etc., to achieve pore structure Easy to control, high conductivity, and ensure the uniformity of dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
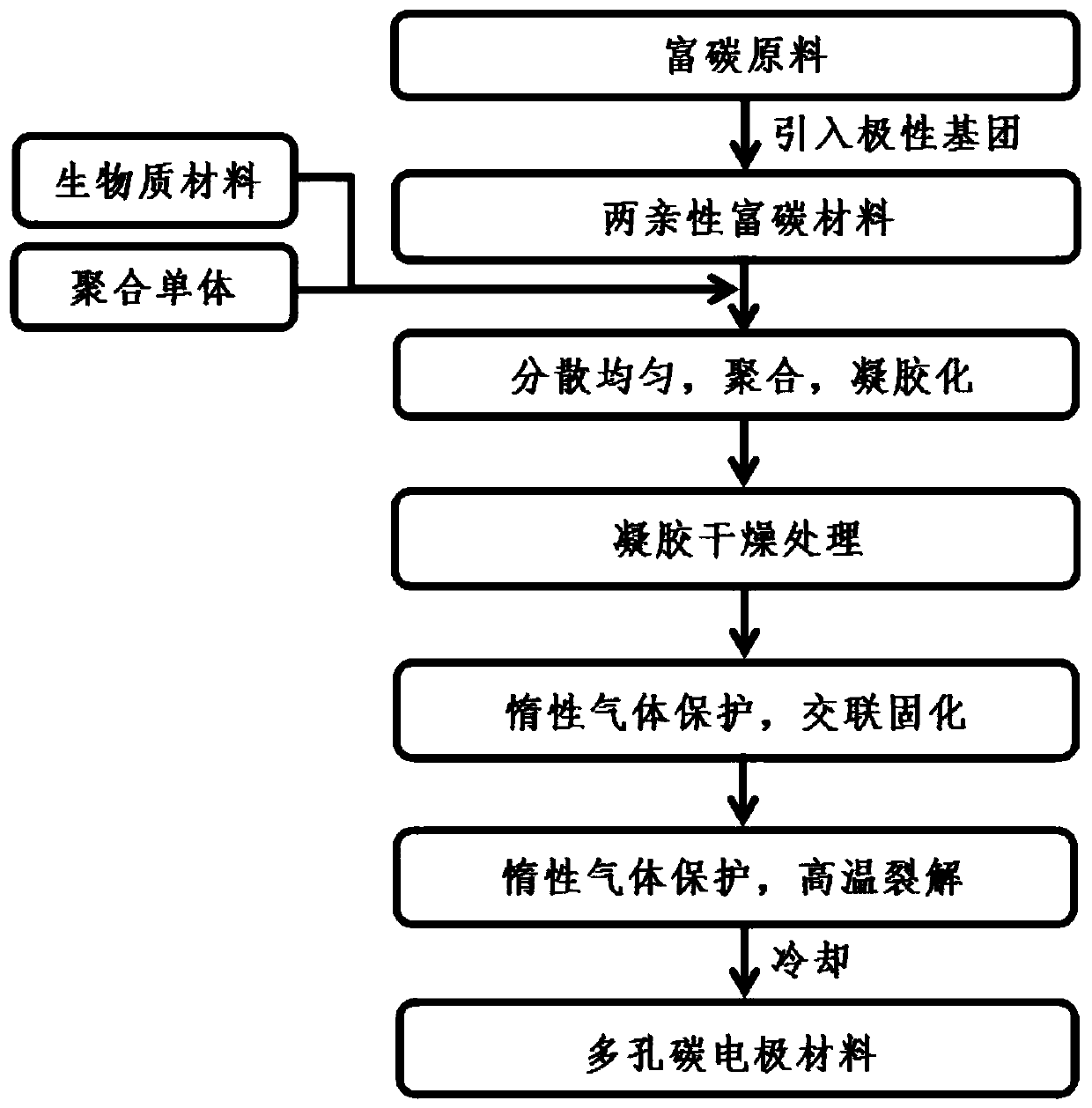
[0048] Such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of the porous carbon electrode material that a kind of microstructure of the present invention is easy to regulate comprises the steps:
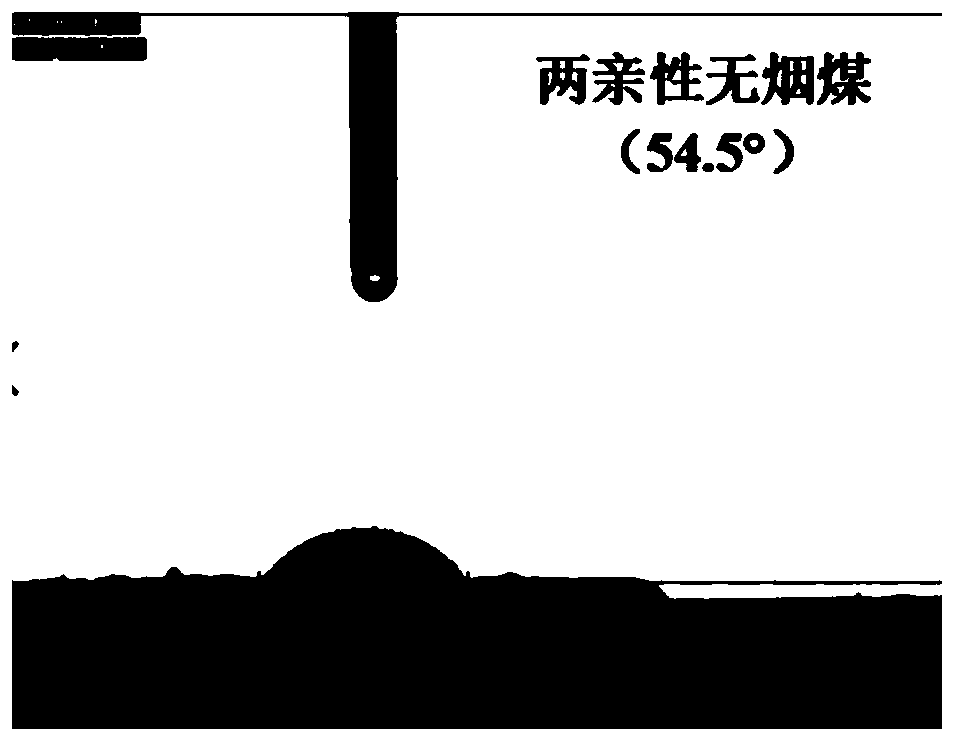
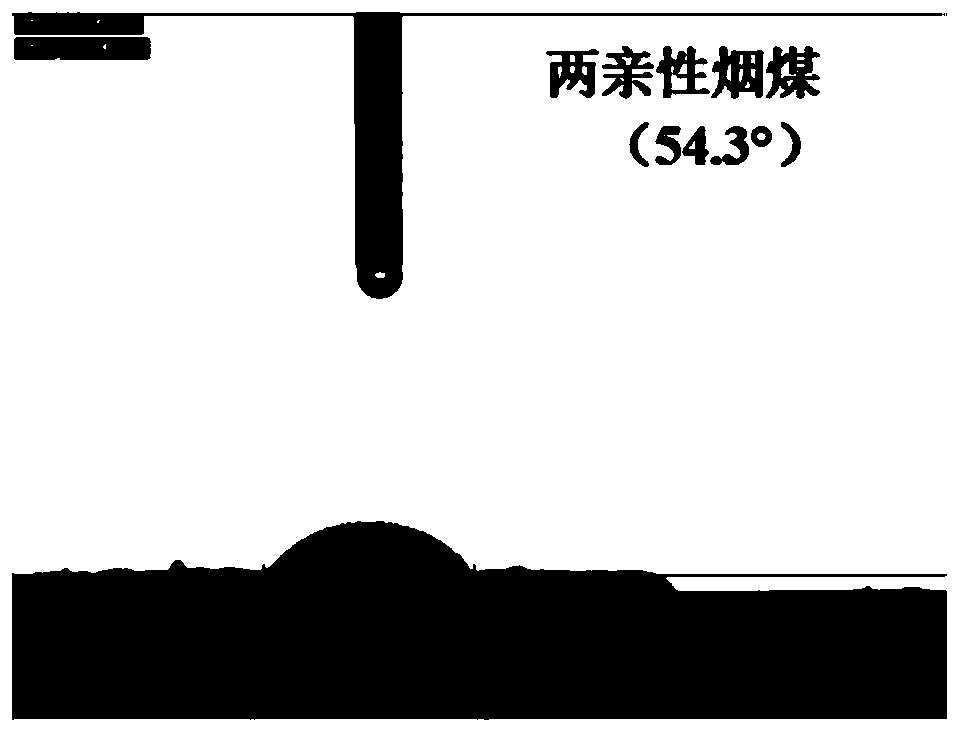
[0049] 1) Introduce -COOH, -OH, -SO into carbon-rich raw materials by oxidation method 3 H,-NH 2 、-C=O,-NO 2 Hydrophilic groups to make amphiphilic carbon-rich materials;
[0050] 2) Disperse amphiphilic carbon-rich materials, biomass materials, and polymerized monomers in 1 to 100 parts by weight of water in a weight ratio of 1: (0.01 to 5): (0 to 5), mix them uniformly, and obtain The gel is dried and solidified; during this process, if the amount of polymerized monomers > 0, then add a cross-linking agent and an initiator in sequence to carry out the polymerization reaction; wherein the amount of the cross-linking agent is 0.01 to 10% of the weight of the acrylamide; The amount of agent used is 0.01-5% of the weight of acrylamide; if the amount of polymerized monomer added is zero,...
Embodiment 1
[0065] Weigh 2g of oxidatively modified amphiphilic anthracite, 2g of lignin, 2g of acrylic acid and 30g of water into the reactor, stir and mix at room temperature for 0.5h, add 0.2g of crosslinking agent and 0.01g of initiator, and heat up to 60~ Make it polymerized and gelatinized at 70°C; dry the obtained gel directly in an oven, then put it into a magnetic boat and put it into a tube furnace; first pass nitrogen as a protective gas, and then heat up at a rate of 0.5°C / min To 600°C, hold for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to 1000°C at a rate of 3°C / min, and hold for 4 hours; then cool naturally to room temperature under the protection of nitrogen, take out the material, and get the porous carbon electrode material after crushing. The Raman spectrum of the porous carbon anode material is shown in image 3 As shown, the SEM image is shown in Figure 4 shown.
[0066] Sodium ion electronic assembly and testing: Mix the prepared porous carbon electrode material powder w...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Weigh 2g of oxidatively modified amphiphilic anthracite, 10g of lignin, 10g of acrylic acid and 100g of water into the reactor, stir and mix at room temperature for 0.5h, add 0.2g of crosslinking agent and 0.01g of initiator, and heat up to 60~ Make it polymerized and gelatinized at 70°C, dry the obtained gel directly in an oven, then put it into a magnetic boat and put it into a tube furnace; first pass nitrogen as a protective gas, and then heat up at a rate of 2°C / min Heat to 500°C, hold for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to 1600°C at a rate of 3°C / min, and hold for 4 hours; then cool naturally to room temperature under the protection of nitrogen, take out the materials, and obtain porous carbon electrode materials after crushing.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com