L-asparaginase XiDL and coding gene and application thereof
An asparaginase, gene technology, applied in the application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, to achieve the effect of high tolerance, wide reaction pH, high enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
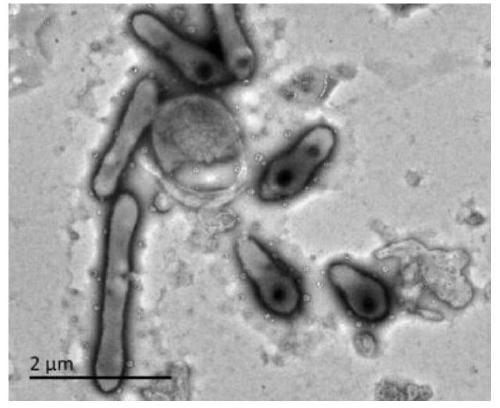
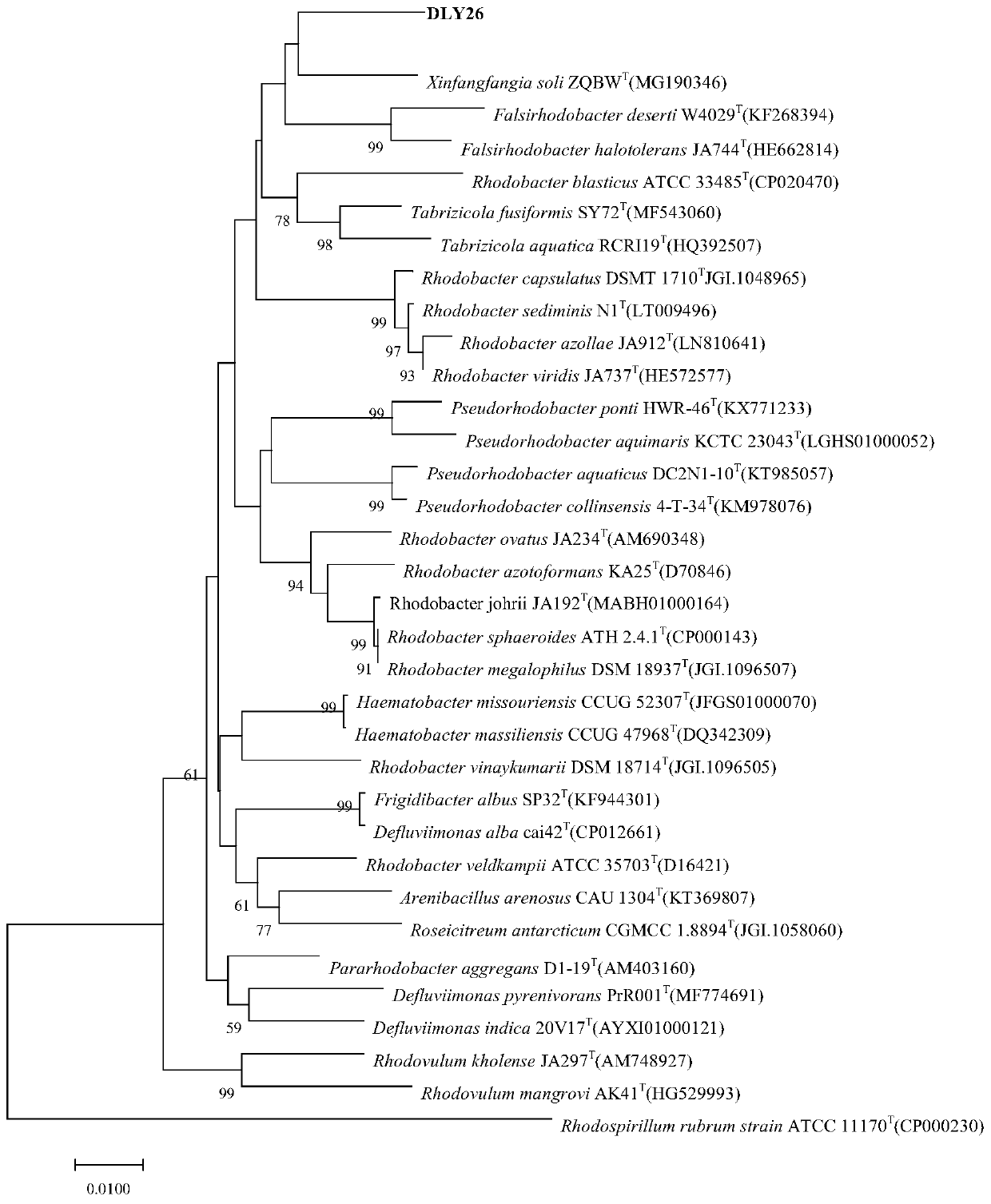
[0036] Example 1, Isolation, Identification and Preservation of Xingfangfangbacterium DLY26
[0037] 1. Separation
[0038] Take about 1ml of activated sludge sample (taken from the petrochemical refinery sewage treatment system), and dilute to 10 times volume, 20 times volume, 50 times volume, 100 times volume and 1000 times volume in turn with sterile distilled water. Spread 100 μl of the diluted sample on the surface of the solid medium by the coating plate method, incubate at 30°C, and observe the growth of the colonies on the surface every day. Pick colonies with different colors and shapes, and purify and culture them by the three-section line method until a single colony with the same shape and size can be observed on the surface of the culture medium.
[0039] 2. Identification
[0040] The purified bacterial strains were inoculated on TSA plates, cultivated at 30°C for 24h, and then observed the morphology, size and other characteristics of the cells using a transmi...
Embodiment 2
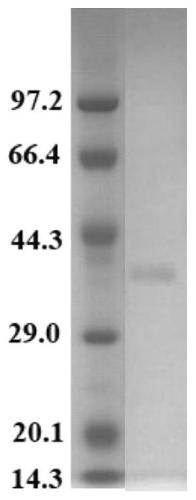
[0057] The preparation of embodiment 2, L-asparaginase (XiDL protein)
[0058] After a large number of sequence analysis, alignment and functional verification, a new protein was found from DLY26 of Xingfangxiang bacteria, and it was named as XiDL protein, as shown in sequence 1 of the sequence table. The gene encoding the XiDL protein in Xylorrhizae DLY26 is named XiDL gene, and its coding frame is shown in sequence 2 of the sequence list.
[0059] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0060] 1. Using the genomic DNA of A. syringae DLY26 as a template, a primer pair composed of DL-F and DL-R is used for PCR amplification, and the PCR amplification product is recovered.
[0061] DL-F: 5'- CACC GCAGAAAAATCGCACATCT-3';
[0062] DL-R: 5'-CGCGTGAATGGGAACAGGCG-3'.
[0063] 2. Take the PCR amplification product obtained in step 1 and connect it to the pDE1 vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pDE1-XiDL.
[0064] The pDE1 vector (pDE1Vector) is a component of the pDE1 D...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Embodiment 3, the enzymatic property of L-asparaginase (XiDL protein)
[0078] Tris-HCl buffer solution (50mM, pH 7.4): Weigh 6.06g Tris, dissolve it in ultrapure water, and adjust the pH to 7.4 with HCl.
[0079] Substrate solution (25 mM asparagine): Weigh 3.303 g of L-asparagine, dissolve it in Tris-HCl buffer, and dilute to 1 L.
[0080] 1. The effect of pH on the activity of L-asparaginase
[0081] 1. Optimal pH
[0082] Take the XiDL protein solution prepared in Example 2, dilute it to 2 times the volume with buffer, and use the diluted solution as the test solution.
[0083] Detection method: Add 200 μL of test solution and 700 μL of substrate solution (prepared with pH buffer solution), react at 37°C for 15 minutes, add 100 μL of 15% TCA (trichloroacetic acid) to stop the reaction, centrifuge at 10000g for 10 minutes, and then take the supernatant 200μL, add 4.8mL ammonia-free water and 200μL Nessler's reagent in turn, let stand at room temperature for 10min,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com