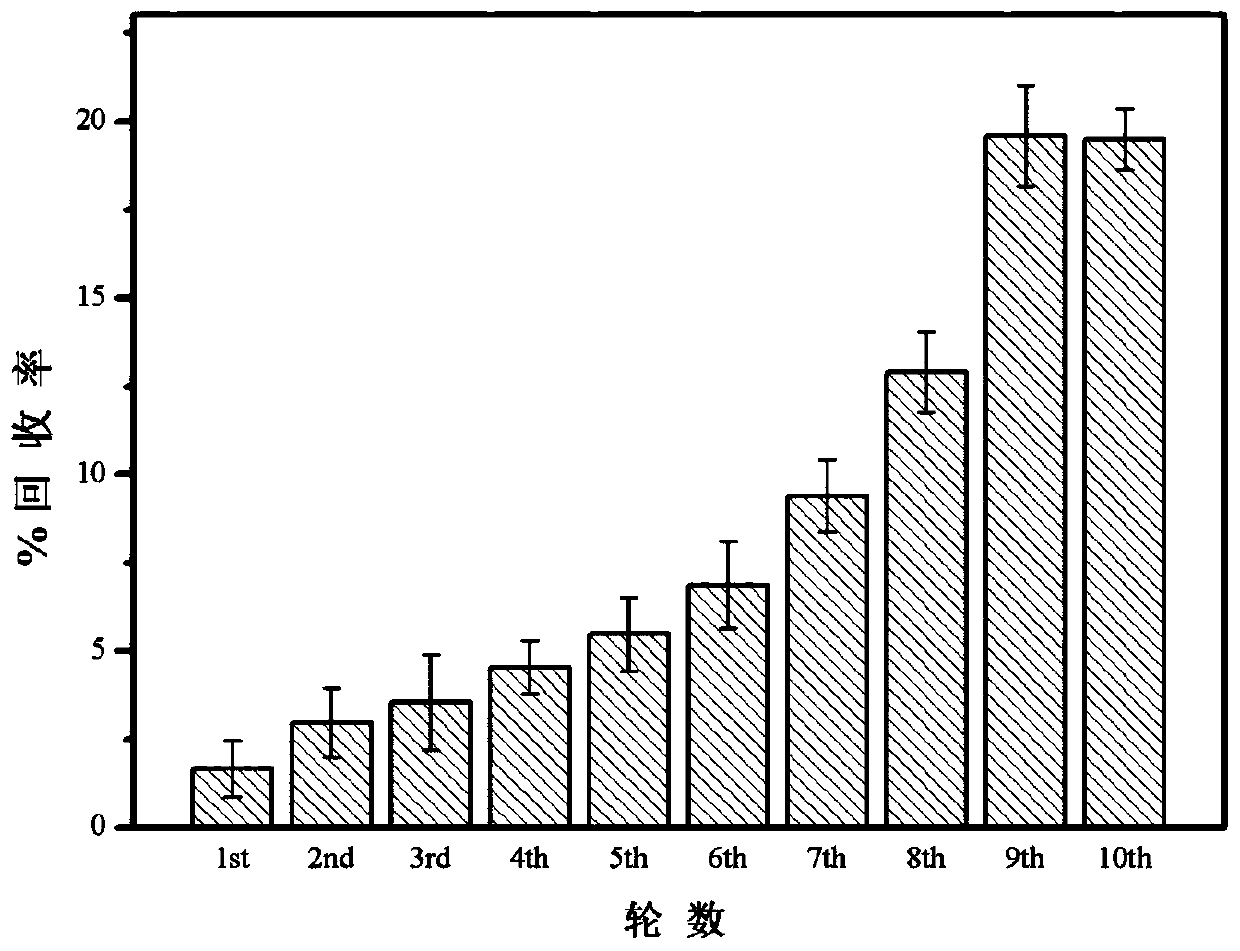
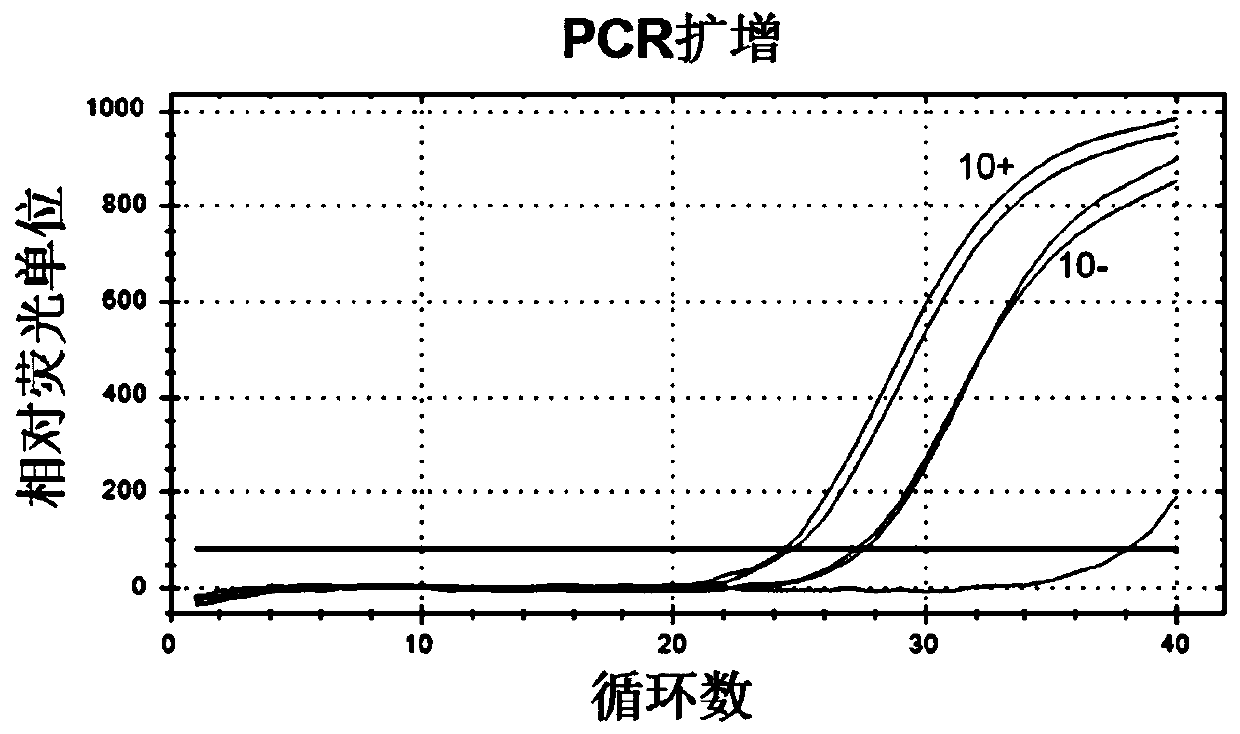
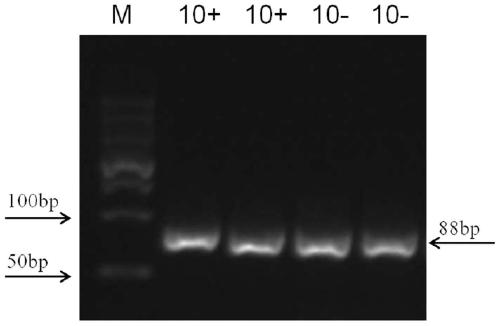
Nucleic acid aptamer for identifying intestinal cancer serum marker and screening method and application of nucleic acid aptamer
A nucleic acid aptamer and marker technology, used in biochemical equipment and methods, pharmaceutical formulations, and microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of complex aptamer screening process and low application value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] The screening of embodiment 1 nucleic acid aptamer sequence:
[0081] 1. Blood sample processing
[0082] Collect blood samples from 20 first-time patients (not receiving treatment), centrifuge at 3000rpm for 10min at room temperature to remove blood cells, and collect serum; then centrifuge at 15000×g for 30min at 4°C to remove sediment and surface oil, and collect the middle supernatant. Store at -80°C for later use. The blood samples of 20 cases of healthy people were processed in the same way as above.
[0083] 2. Acetonitrile precipitation method to remove high-abundance proteins in serum
[0084] The serum of the above 20 patients with intestinal cancer was mixed thoroughly, prepared according to serum: water: acetonitrile = 1:2:0.5, ultrasonicated in a water bath for 5 min, 15000×g, centrifuged for 30 min, the supernatant was collected, and the precipitate was discarded. Serum from healthy subjects was treated the same as above.
[0085] 3. Synthetic primary ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2 Nucleic acid aptamer secondary structure prediction:
[0113] The RNA structure 5.7 software was used to predict the secondary structure of the four nucleic acid aptamers obtained from the above screening. The secondary structure prediction results of the four nucleic acid aptamers are as follows: Figure 4 shown.
Embodiment 3 4
[0114] Example 3 Affinity determination between four nucleic acid aptamers and targets:
[0115] Incubate overnight with 8 mL of treated colon cancer serum and 2 mL of carboxy-sepharose magnetic beads, wash with PBS three times, and centrifuge to divide into 40 parts of magnetic bead-serum protein complexes. Dilute the synthesized FAM-labeled 4 nucleic acid aptamers to 0nM, 1nM, 2nM, 5nM, 10nM, 20nM, 50nM, 100nM, 200nM and 500nM, respectively, and then incubate with the magnetic bead-serum complex respectively to prepare mark. Wash 5 times with 1×TPBS, 1 time with ultrapure water, and remove the supernatant. Add 200 μL ultrapure water to resuspend the magnetic beads, and measure the fluorescence value by flow cytometry. Taking the fluorescence intensity as the ordinate and the aptamer concentration as the abscissa, the curve was fitted according to the formula Y=(Bmax×X) / (Kd+X) to obtain the dissociation curves of the four nucleic acid aptamers and calculate the Kd value. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com