Synchronous laser heat treatment method for laser additive manufacturing nickel-based high-temperature alloy
A technology of nickel-based superalloy and laser heat treatment, which is applied in the direction of additive manufacturing, additive processing, and energy efficiency improvement. The effect of stress concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] The preparation process of the nickel-based superalloy specifically includes the following processes:
[0039](1) Put the GH4169 superalloy spherical powder with a particle size of -80 to +325 mesh into the powder feeder, or put the GH4169 wire into the wire feeder.
[0040] (2), put the substrate or the repaired part into the atmospheric environment or an argon-filled inert atmosphere processing room, and fix it on the workbench; when the substrate is selected, the substrate is made of carbon steel, stainless steel or a superalloy; when the substrate is a superalloy, it is preferably Forging GH4169 superalloy; when an argon-filled inert atmosphere is used, the inlet and outlet of the argon-filled inert atmosphere processing chamber are opened, and the additive manufacturing of GH4169 superalloy starts after the argon gas is replaced until the oxygen content is below 100ppm.
[0041] When argon is replaced, high-purity argon with a purity greater than or equal to 99.99%...
Embodiment 1
[0052] (1) Put the GH4169 superalloy spherical powder with a particle size of -80 to +325 mesh into the powder feeder;
[0053] (2) Fix the forged GH4169 superalloy substrate on the workbench in the atmospheric environment;
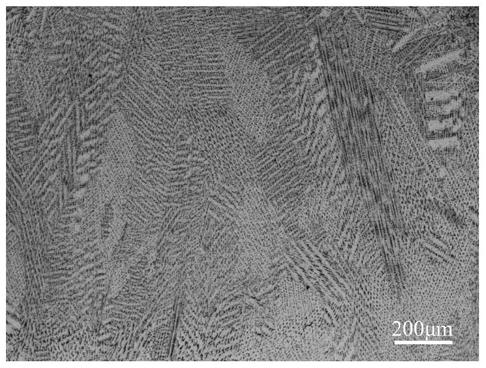
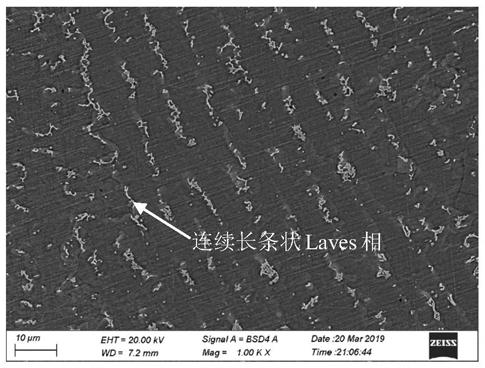
[0054] (3) The laser heat source fiber laser is introduced, and the laser additive manufacturing process parameters are: laser cladding power 700W, spot diameter 1mm, powder feeding rate 9g / min, lap rate 50%, scanning speed 8mm / s. The CNC system is used to synchronously open the powder feeder to transport GH4169 superalloy powder; prepare a GH4169 superalloy part with a height of 2.8mm and retain the Laves phase, and its microstructure is as follows figure 1 with figure 2 shown; figure 1 It shows that the as-deposited structure is dominated by columnar crystals that grow epitaxially along the deposition direction. from figure 2 It can be seen from the figure that there are a large number of Laves phases with continuous strips and irregular shapes in...
Embodiment 2
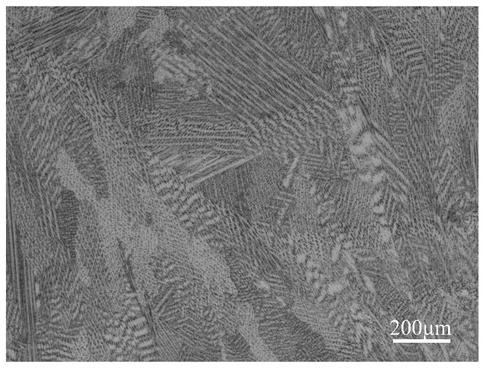
[0060] The process parameters of laser heat treatment are: laser power 200W, spot diameter 1mm, scan rate 20mm / s, laser beam is used to continuously scan the GH4169 superalloy parts with Laves phase for 3min, and the Laves phase volume fraction of the overall sample is 1.36%. Compared with the state, it is 60.58% lower. The microstructural characteristics of the obtained GH4169 superalloy after heat treatment are as follows: Figure 7 , Figure 8 , Figure 9 shown. Figure 7 The grain morphology of its macroscopic morphology has not changed significantly, and the columnar crystals that grow epitaxially along the deposition direction are still the main ones. Figure 8 The Laves phase size and volume fraction are shown to be further reduced. Figure 9 It shows that after laser heat treatment, the strengthening phase γ”+γ’ phase inside the forging base material is diffusely distributed in the matrix without dissolution.
[0061] All the other unrelated steps are the same as ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com