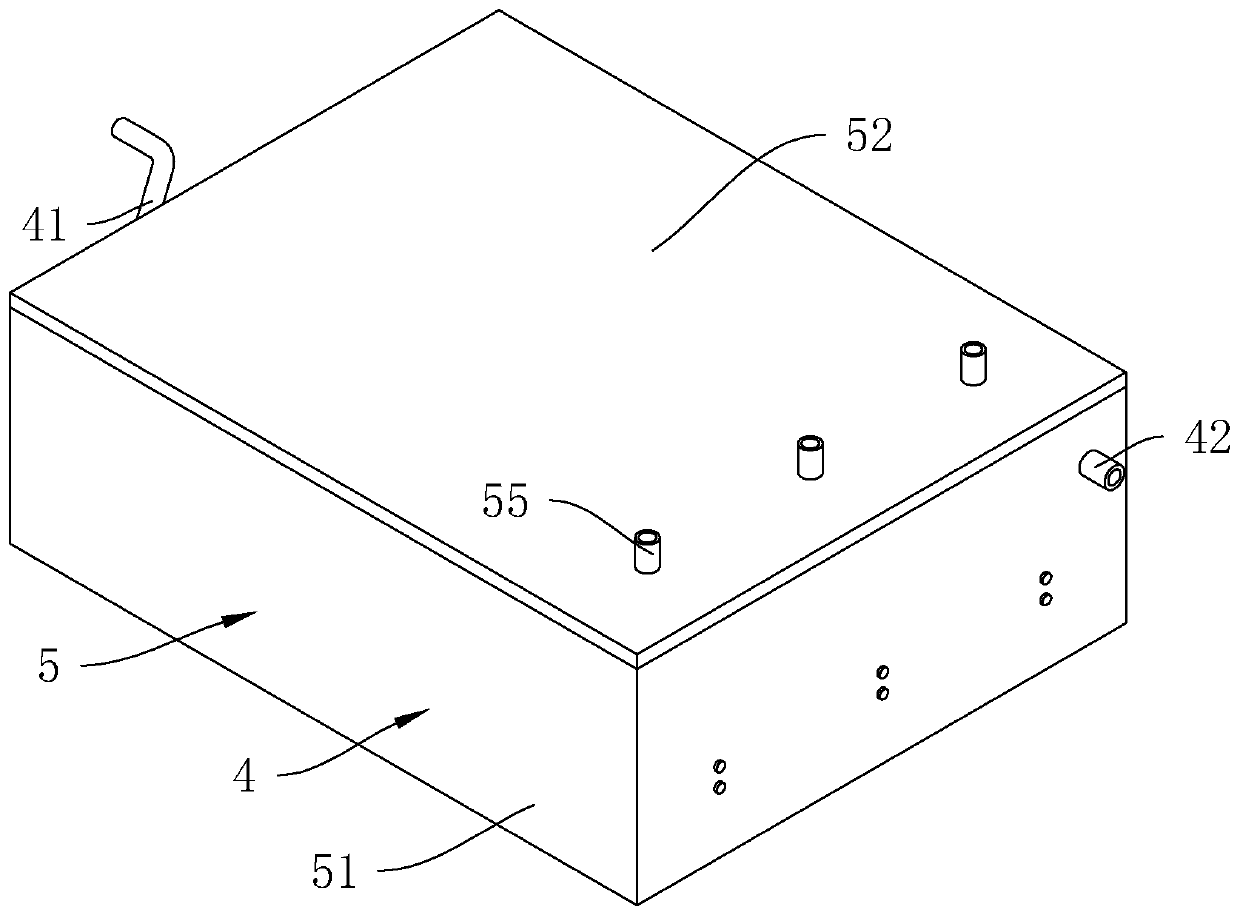
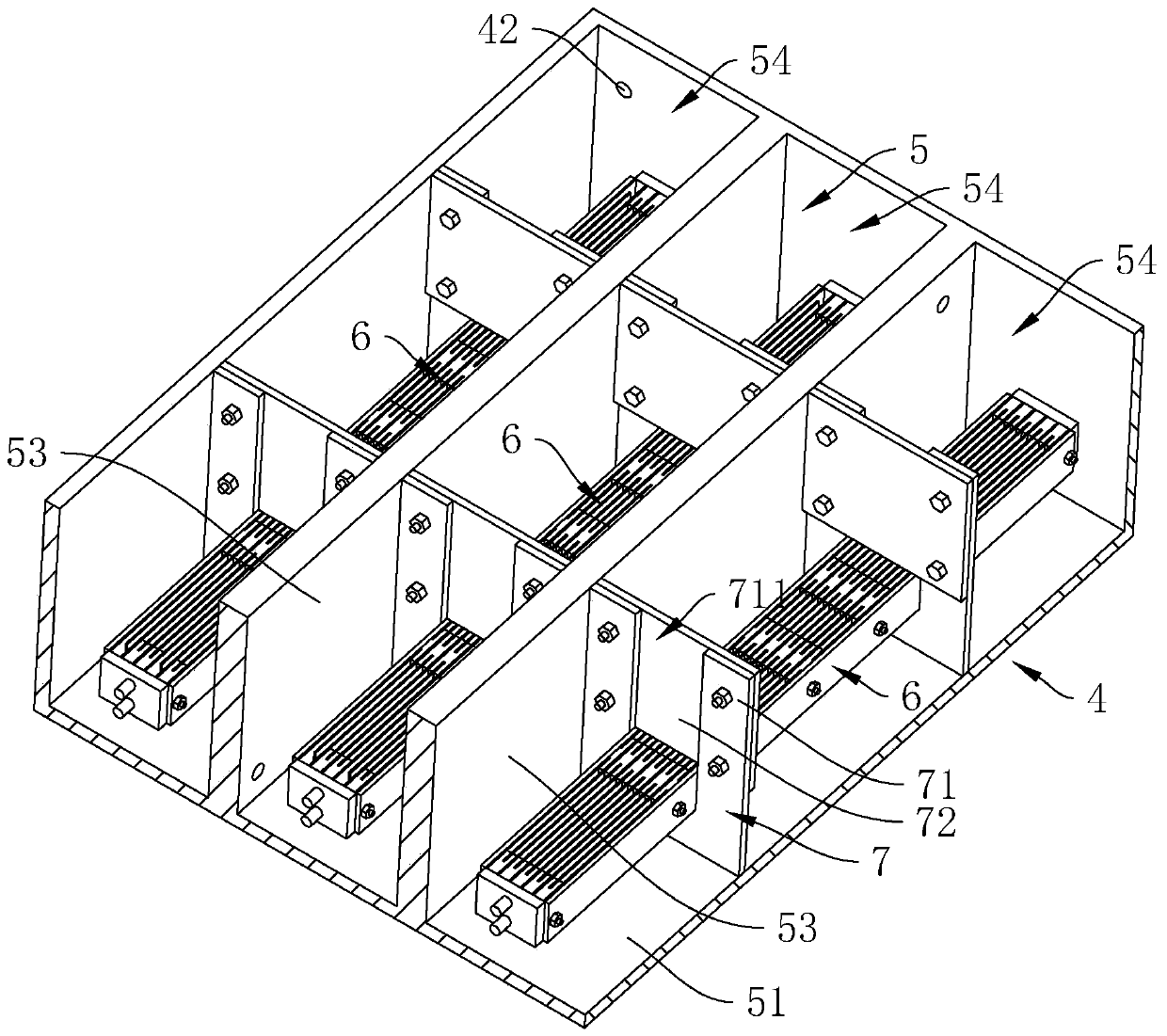
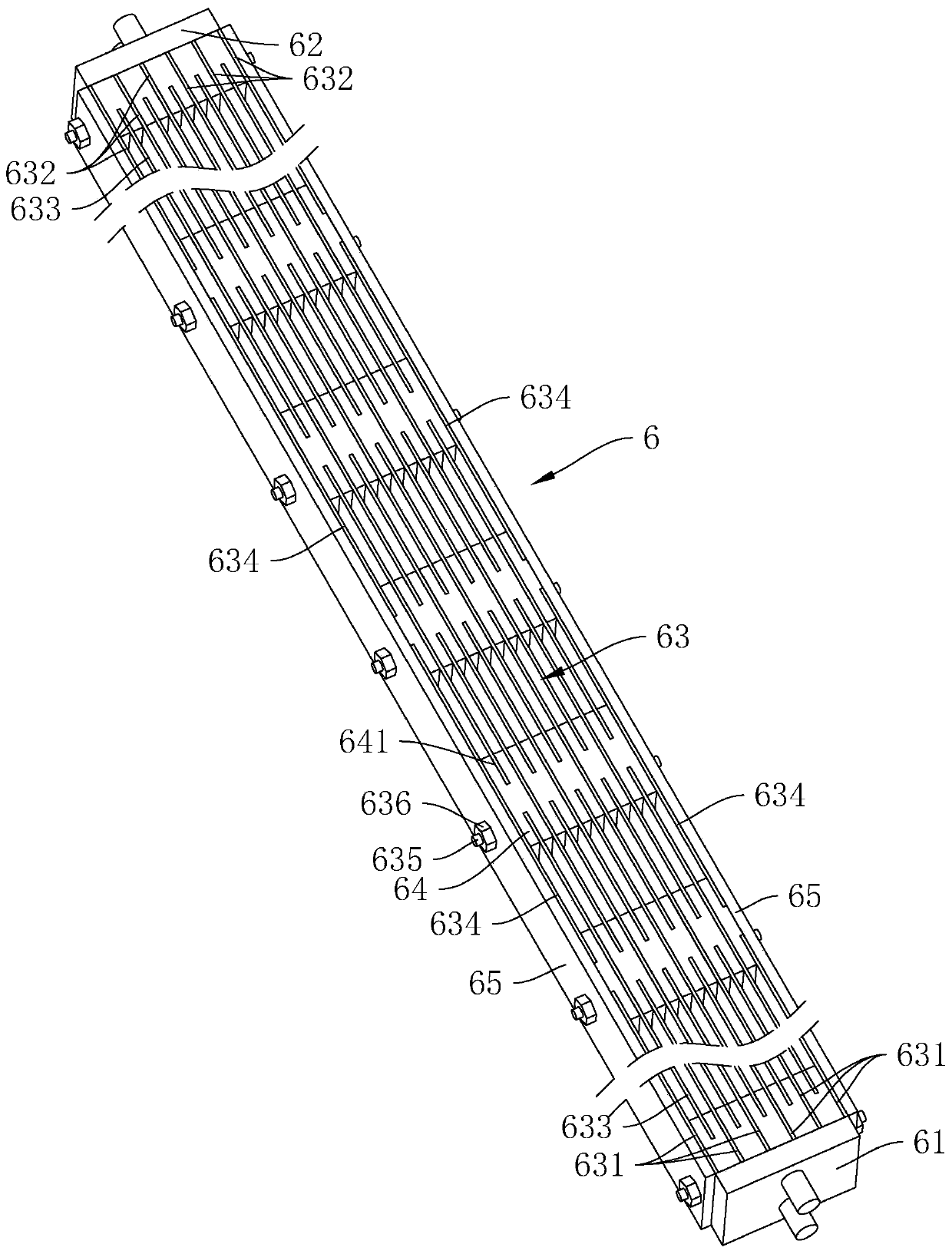
Treatment method of N-p-aminobenzoyl-L-glutamic acid medical intermediate wastewater
A technology for p-aminobenzoyl and wastewater treatment, which is used in neutralization water/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment, natural water treatment, etc. The effect of bonding and improving the contact area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1: a kind of N-p-aminobenzoyl-L-glutamic acid pharmaceutical intermediate waste water treatment method, comprises the following steps: 1: adjust pH: utilize lift pump to pass the former waste water into the waste water pool, multiple batches The raw pharmaceutical wastewater can be accumulated in the wastewater tank and stirred to make multiple batches of raw wastewater evenly mixed; the pH of the raw wastewater is adjusted to 2 with hydrochloric acid to obtain wastewater A.
[0052] Two: Fenton oxidation: Pass waste water A into the Fenton tank, measure the total COD amount in waste water A and the molar mass of ferrous ions, the mass-number ratio of hydrogen peroxide to COD is 1:0.05, and the calculated over Amount of hydrogen peroxide solution. When the molar mass ratio of ferrous ions in wastewater A to hydrogen peroxide is greater than 0.1:1, add aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution to wastewater A to obtain wastewater B and produce organic sediment sludge...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2: A method for treating wastewater of N-p-aminobenzoyl-L-glutamic acid pharmaceutical intermediates. The difference from Example 1 is that in one step, the pH of the raw wastewater is adjusted to 4.5.
[0065] In the second step, an aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution with a mass concentration of 22% is used; the mass-number ratio of hydrogen peroxide to COD is 1:0.2. In addition, when the molar mass ratio of ferrous ions and hydrogen peroxide in wastewater A is less than 0.1:1, water-soluble ferrous salt and hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution are added to obtain wastewater B, and ferrous ions and hydrogen peroxide in wastewater B The molar mass ratio is 0.5:1.
[0066] In the three steps, the pH of the supernatant of waste water B is adjusted to 8 by using an alkali-adjusting agent, and the alkali-adjusting agent adopts 5-25% sodium carbonate solution.
[0067] In the four steps, the second anode plate is a titanium plate coated with 50 μm ruthenium iridium; t...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3: A method for treating wastewater of N-p-aminobenzoyl-L-glutamic acid pharmaceutical intermediates. The difference from Example 1 is that the pH of the raw wastewater is adjusted to 6 in one step.
[0069]In the second step, an aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution with a mass concentration of 30% is used; the mass-number ratio of hydrogen peroxide to COD is 1:0.5. In addition, when the molar mass ratio of ferrous ions and hydrogen peroxide in wastewater A is less than 0.1:1, water-soluble ferrous salt and hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution are added to obtain wastewater B, and ferrous ions and hydrogen peroxide in wastewater B The molar mass ratio is 1:1.
[0070] In the three steps, the pH of the supernatant of waste water B is adjusted to 9 by using an alkali-adjusting agent, and the alkali-adjusting agent adopts 5-25% sodium bicarbonate solution.
[0071] In the four steps, the second anode plate is a titanium plate coated with 100 μm ruthenium iridium; the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com