Patents
Literature
683 results about "Molar mass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.
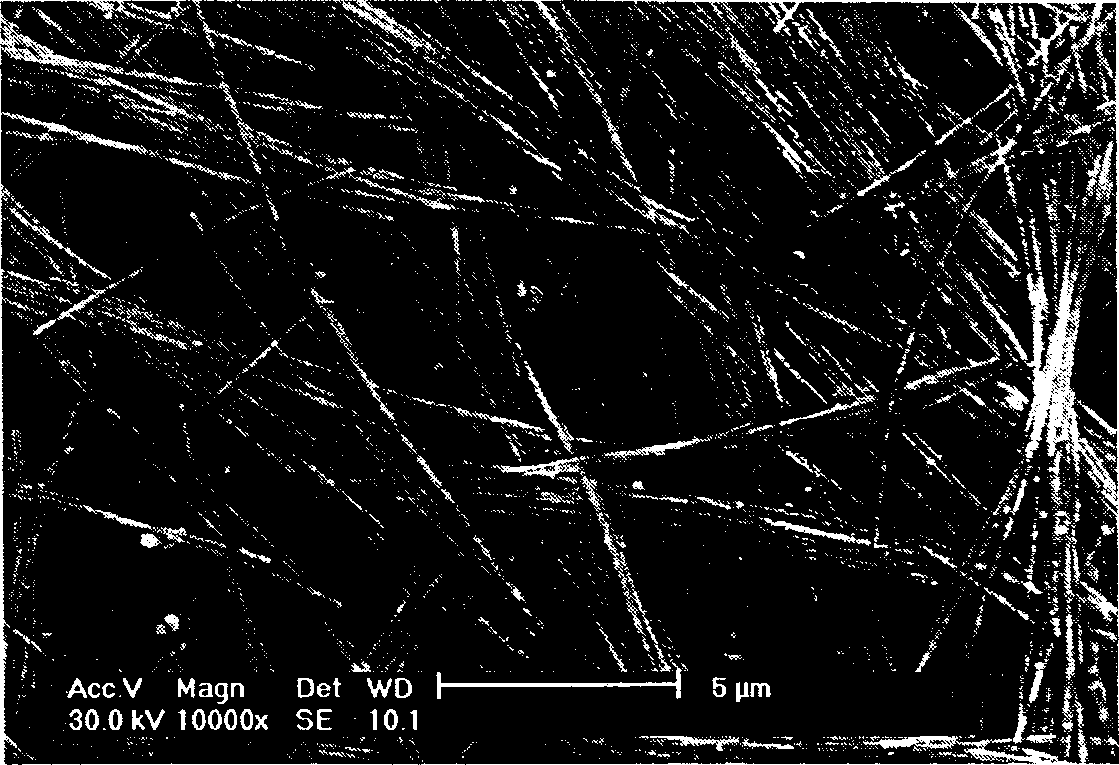
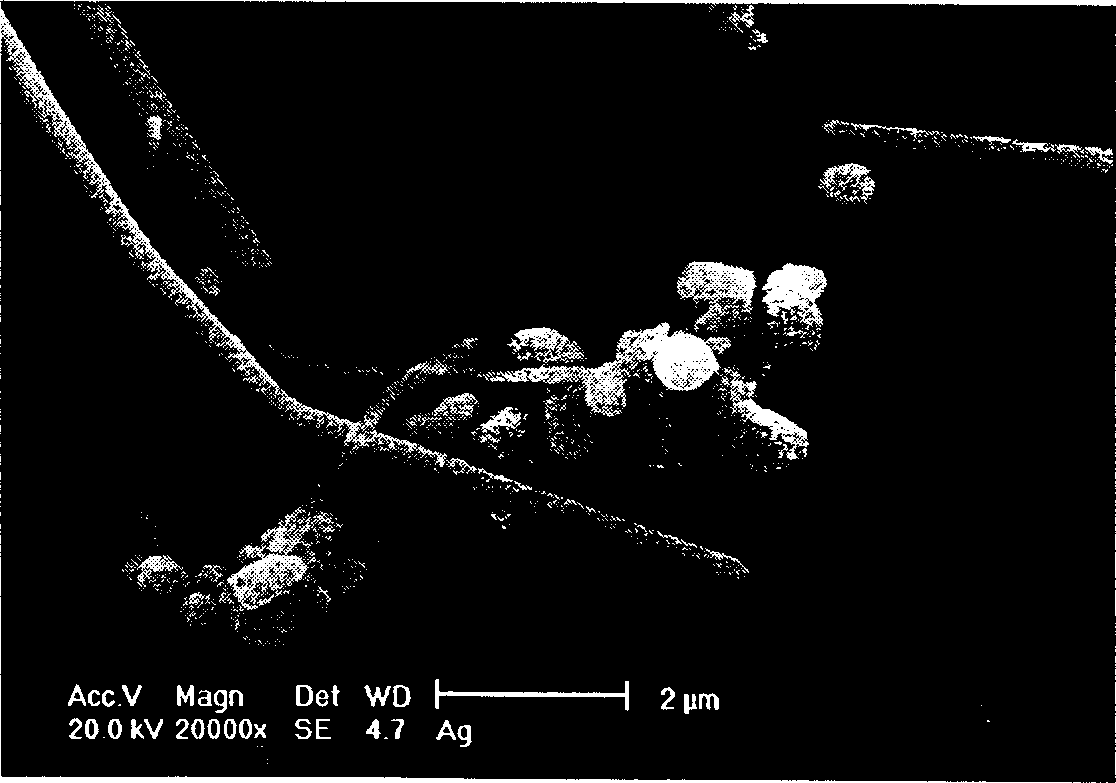
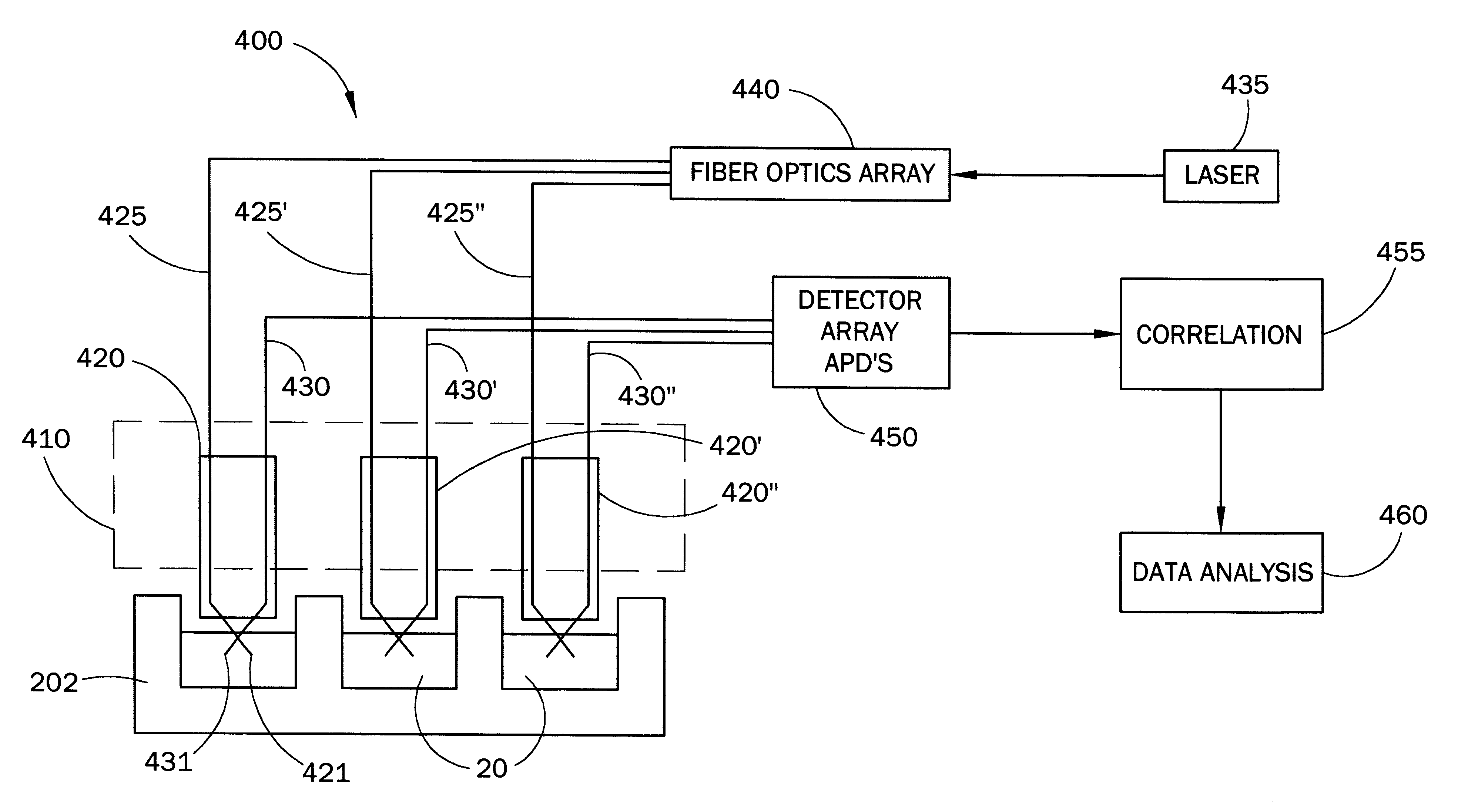
Fiber optic apparatus and use thereof in combinatorial material science
InactiveUS6519032B1Facilitate the discovery of commercially important polymericEffectively and efficiently characterizingSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationFiberHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
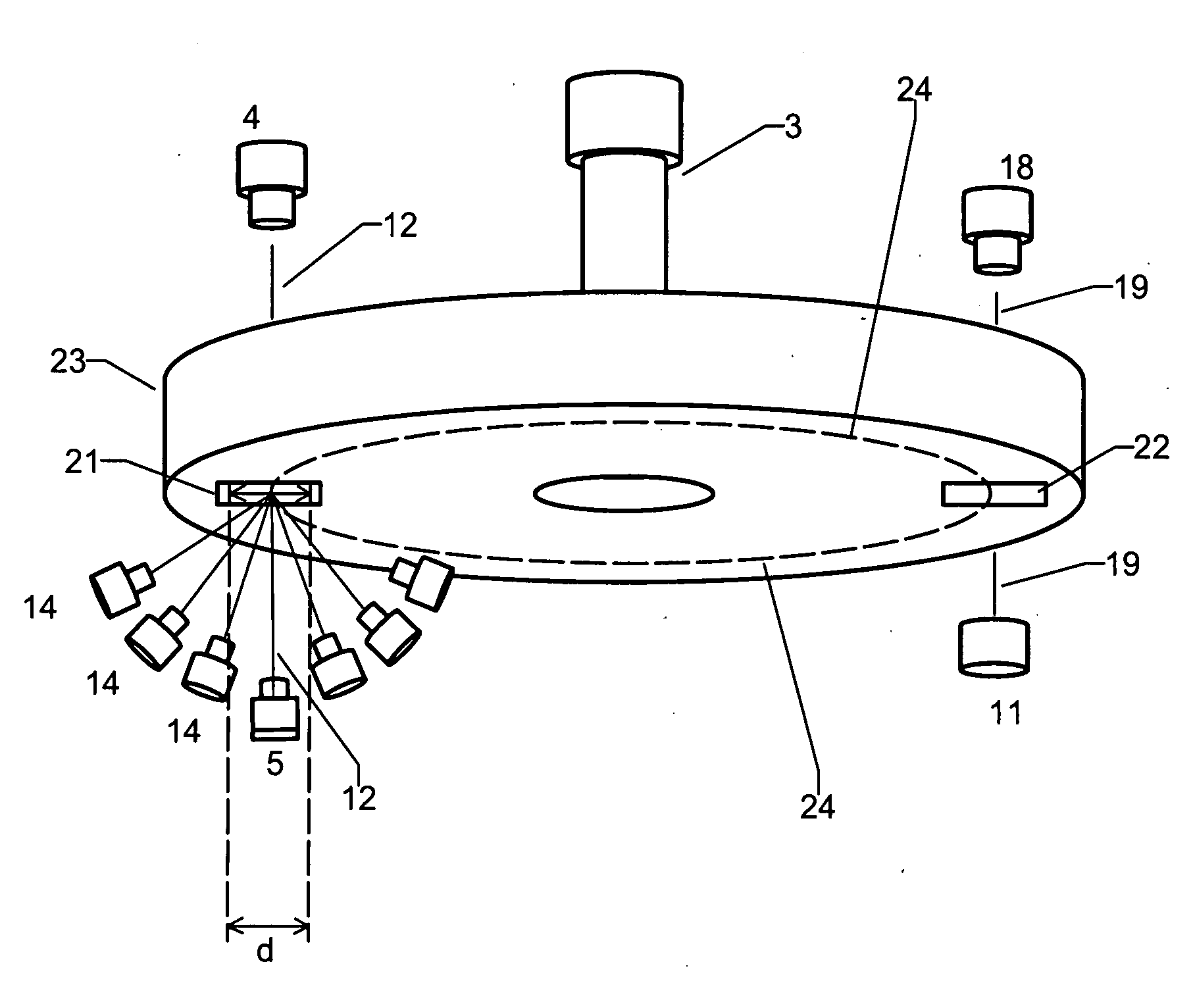
Methods, systems and devices are described for rapid characterization and screening of liquid samples to determine properties (e.g., particle size, particle size distribution, molar mass and / or molar mass distribution) thereof with static light scattering and / or dynamic light scattering. The liquid samples can be solutions, emulsions, suspensions or dispersions. One method, includes providing a vessel containing a liquid sample having an exposed surface that defines a gas-liquid sample interface, and analyzing the sample by light scattering methods that include transmitting light through the gas-liquid sample interface into the sample, and detecting light scattered from the sample or from a component thereof. Additional methods are directed to characterizing a plurality of liquid samples or components thereof. The methods, systems, and devices have applications in high-throughput screening, and particularly, in combinatorial materials research and in industrial process control.
Owner:WYATT TECH
High melt strength polypropylene
The present invention concerns a high melt strength propylene polymer or copolymer suitable for manufacturing foams and thermoformed product exhibiting a melt strength of at least 3 g and comprising a high molar mass portion and a low or medium molar mass portion. The polymers are produced by subjecting propylene and optionally other olefins to polymerization in a plurality of polymerization reactors connected in series, employing different amounts of hydrogen as a molar mass modifier in at least two of the reactors, and carrying out the polymerization reaction in the presence of a catalyst system capable of catalyzing the formation of a high molar mass polymerization product having a MFR2 of less than 0.1 g / l0 min and a low or medium molar mass polymerization product having a MFR2 of more than 0.5 g / 10 min.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH OY
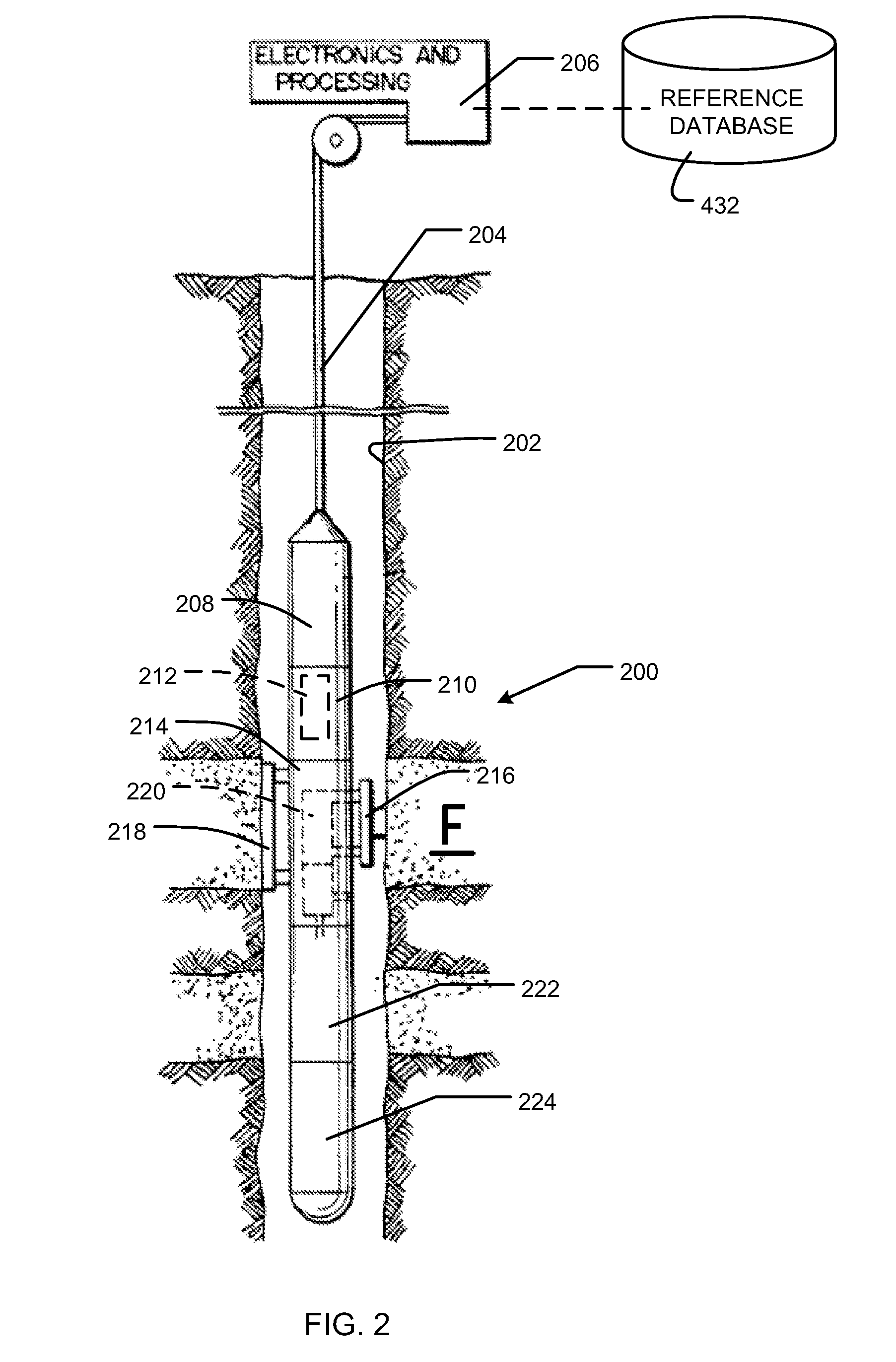
Method and apparatus for characterizing solutions of small particles
A method and apparatus is described by which means molecules in suspension may be characterized in terms of the size and mass distributions present. As a sample solution is separated by centrifugal means, it is illuminated at a particular radial distance from the axis of rotation by a fine, preferably monochromatic, light beam. Despite the high resolution of such devices, a key problem associated with most separators based upon use of centrifugal forces is the difficulty in deriving the absolute size and / or molar mass of the separating molecules. By integrating means to detect light scattered, over a range of scattering angles, from samples undergoing centrifugal separation, molecular sizes in the sub-micrometer range may be derived, even in the presence of diffusion. Adding a second light beam at a displaced rotational angle, preferably of an ultraviolet wavelength, that intersects the sample at the same radial region as the first beam permits determination of the molecular concentration at that region. Combining the light scattering data with the associated concentration permits the determination of the associated molar mass. In a preferred embodiment, the light beam and detectors may be controlled to scan synchronously the sample radially during separation.
Owner:WYATT TECH
Cationic mixed-oxide dispersion, coating pigment and ink-absorbing medium
InactiveUS7015270B2Avoid large quantitiesHigh glossCoatings with pigmentsInorganic pigment treatmentZeta potentialMixed oxide
A stable, aqueous dispersion, which includes:silicon dioxide mixed-oxide particles dispersed in at least one water-soluble cationic polymer having a mass average molar mass of less than 100,000 g / mol, said mixed-oxide including aluminum oxide or titanium dioxide,wherein said particles are produced by flame hydrolysis,wherein said particles have a BET specific surface area of 5 to 600 m2 / g and a negative zeta potential,and wherein the dispersion has a positive zeta potential.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Plastic body provided with a microstructured surface
InactiveUS20060121248A1Lamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticPoly methacrylate
The invention relates to a process for the production of a plastics article with a microstructured surface via production of a composite composed of a backing layer composed of a thermoplastic or thermoelastic with one or more structure layers, characterized in that the structure layer(s) is / are composed of from 1 to 100% by weight of a polymethacrylate moulding composition which comprises from 80 to 100% by weight of free-radical-polymerized methyl methacrylate units and from 0 to 20% by weight of other comonomers capable of free-radical polymerization, and which has an average (weight-average) molar mass Mw of from 30 000 g / mol to 70 000 g / mol and, where appropriate, is present in a. mixture with up to 99% by weight of a polymethacrylate moulding composition which is composed of from 80 to 100% by weight of free-radical-polymerized methyl methacrylate units and from 0 to 20% by weight of other comonomers capable of free-radical polymerization, and which has an average (weight-average) molar mass Mw of from 90 000 g / mol to 200 000 g / mol and the structure layer(s) obtain microstructuring via known structuring processes, after production of the composite. The invention further relates to the plastics articles themselves which are capable of production according to the invention, and also to their uses.
Owner:ROEHM GMBH & CO KG
Fiber optic apparatus and use thereof in combinatorial material science
InactiveUS20030142309A1Facilitate the discovery of commercially important polymericSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFiberHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Methods, systems and devices are described for rapid characterization and screening of liquid samples to determine properties (e.g., particle size, particle size distribution, molar mass and / or molar mass distribution) thereof with static light scattering and / or dynamic light scattering. The liquid samples can be solutions, emulsions, suspensions or dispersions. One method, includes providing a vessel containing a liquid sample having an exposed surface that defines a gas-liquid sample interface, and analyzing the sample by light scattering methods that include transmitting light through the gas-liquid sample interface into the sample, and detecting light scattered from the sample or from a component thereof. Additional methods are directed to characterizing a plurality of liquid samples or components thereof. The methods, systems, and devices have applications in high-throughput screening, and particularly, in combinatorial materials research and in industrial process control.
Owner:WYATT TECH
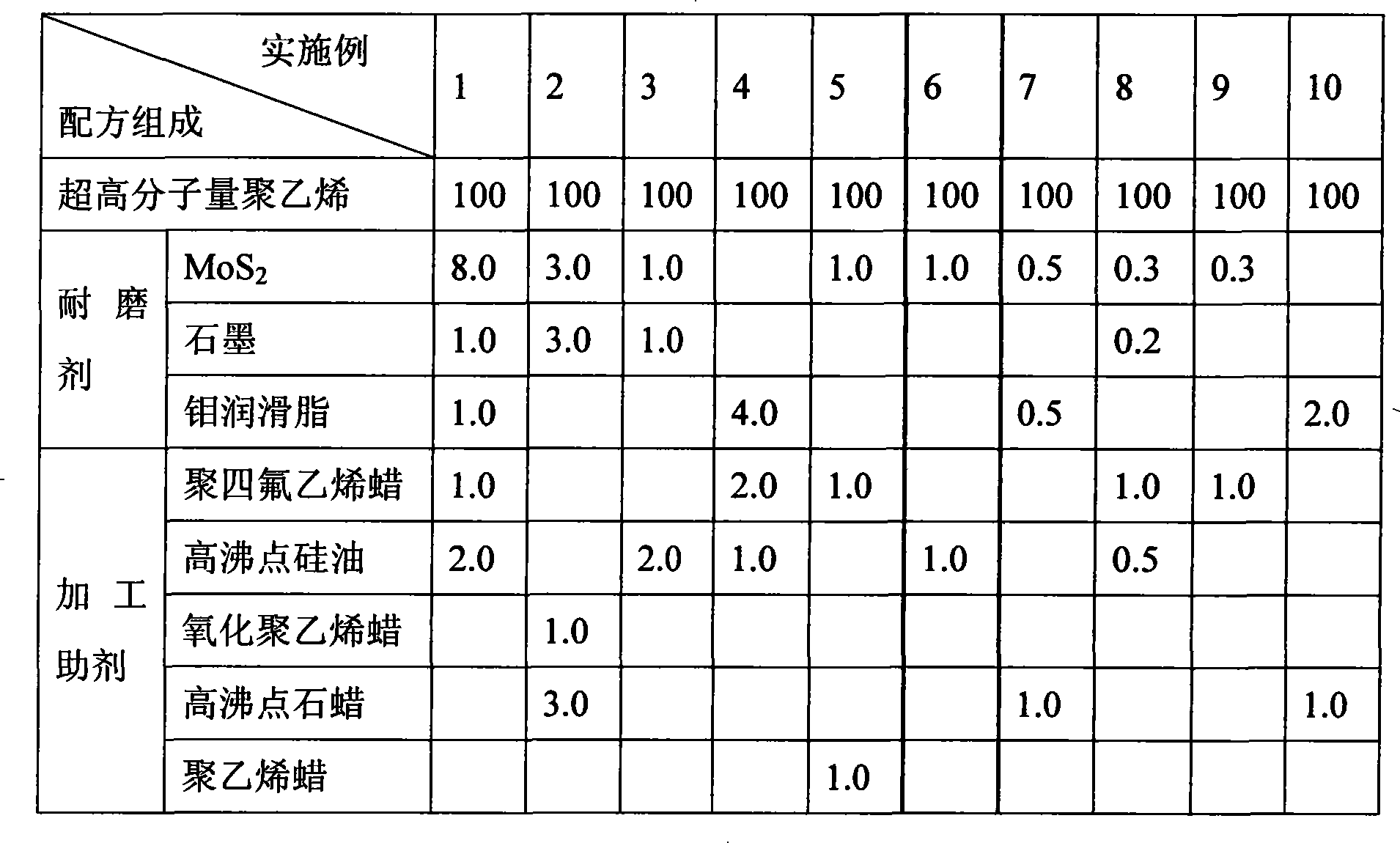
Super-high molecular weight polyethylene low frictional coefficient wearable composite material and its preparation and use
InactiveCN101240092AImprove performanceExcellent formulaBridge structural detailsParaffin waxProcedure Agents
Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene composite with low molar mass and high friction resistance, preparation and application thereof. Raw materials of 100 parts by weight of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene, 0.1-10 parts by weight of wear-resisting agent, 0.1-5.0 parts by weight of processing aid is prepared into highly friction resistant composite by mixing, chill-pressing, heating to melt, compression molding, cooling for shaping and cutting. The mentioned utra high molecular weight polyethylene has a matrix molecular weight of greater than 6 millionl. The mentioned wear-resisting agent is MoS2 surface treated by coupling agent, black lead, lubricating grease of molybdenum, copper powder, or mixture of more than two of them. The mentioned processing agent is organic silicon oil with high boiling point, polytetrafluroethylene, oxidized polyethylene wax, olefin or polyethylene wax with high boiling point, or mixture of more than two of them.
Owner:ZHUZHOU TIMES NEW MATERIALS TECH
Polylactic acid foaming material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a polylactic acid foaming material and a preparation method thereof. The polylactic acid foaming material is prepared from the following ingredients according to parts by weight: 45-93 parts of polylactic acid, 5-28 parts of toughener, 1-5 parts of nucleating agent and 1-10 parts of foaming agent. The polylactic acid is one of poly-L-lactic acid, poly-D-lactic acid and poly-DL-lactic acid or a mixture or a polymer thereof, and has the weight average molar mass of 0.8-3.5 million, molecular weight distribution of 1.2-2.5, and degree of crystallinity of 15-60 percent. The toughener is one of poly succinic acid butyl ester and poly adipate / butylene terephthalate or a mixture of two with random ratio. Other accessory ingredients can also be added. The preparation method comprises the following steps: evenly mixing the polylactic acid, the toughener, the nucleating agent, the foaming agent, the accessory ingredients and the like in a high mixing machine according to a certain proportion, then milling for 5-25 minutes at the temperature of 100-170 DEG C, and carrying out die pressing foaming on obtained materials at the temperature of 120-210 DEG C on a vulcanizing machine for 2-10 minutes to prepare the polylactic acid foaming material. The polylactic acid foaming material prepared by using the preparation method has the advantages of high resistance to shock, high elongation at break, high tensile strength and complete biodegradation after used.
Owner:南京冠创生物科技有限公司
Polymers for use in optical devices
InactiveUS6559256B2Improved shape stabilityQuality improvementElectroluminescent light sourcesConductive materialCross-linkPolymer science
Optical devices fabricated from solvent processible polymers suffer from susceptibility to solvents and morphological changes. A semiconductive polymer capable of luminescence in an optical device is provided. The polymer comprises a luminescent film-forming solvent processible polymer which contains cross-linking so as to increase its molar mass and to resist solvent dissolution, the cross-linking being such that the polymer retains semiconductive and luminescent properties.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for characterizing solutions of small particles
A method and apparatus is described by which means molecules in suspension may be characterized in terms of the size and mass distributions present. As a sample solution is separated by centrifugal means, it is illuminated at a particular radial distance from the axis of rotation by a fine, preferably monochromatic, light beam. Despite the high resolution of such devices, a key problem associated with most separators based upon use of centrifugal forces is the difficulty in deriving the absolute size and / or molar. mass of the separating molecules. By integrating means to detect light scattered, over a range of scattering angles, from samples undergoing centrifugal separation, molecular sizes in the sub-micrometer range may be derived, even in the presence of diffusion. Adding a second light beam at a displaced rotational angle, preferably of an ultraviolet wavelength, that intersects the sample at the same radial region as the first beam permits determination of the molecular concentration at that region. Combining the light scattering data with the associated concentration permits the determination of the associated molar mass. In a preferred embodiment, the light beam and detectors may be controlled to scan synchronously the sample radially during separation.
Owner:WYATT TECH
Low permanent compression deformation thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer
The invention discloses a low permanent compression deformation thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer, which is characterized in that: a certain amount of short-chain alcohol with the molar mass of 100-600g and the functionality of more than 2 is added into a chain extender; and due to the crosslinking of the short-chain alcohol, the elasticity, strength and permanent compression deformation resistance of a product are improved.
Owner:烟台美瑞化学材料有限公司
Method for increasing retention rate of calcium carbonate in paper-process reconstituted tobacco sheets
The invention relates to a method for increasing the retention rate of calcium carbonate in paper-process reconstituted tobacco sheets. The purpose of the invention is to solve the problems that: since the prior art directly adds calcium carbonate, the bonding force between the calcium carbonate and tobacco fibers is weak, as a result, loss is severe, the material utilization rate is low, the amount of waste water to be treated is large, and the treatment cost is high. The technical point is that: needed chemical constituents are extracted from tobacco material, residue is ground into pulp after extraction, and the concentration of the pulp is regulated between 3 percent and 25 percent; the solution of soluble carbonate accounting for 4 percent to 40 percent of the weight of dry fibers in the pulp is added into the pulp, and is fully stirred and uniformly mixed, and impregnation is then carried out for 20 to 150 minutes, so that the fibers of the pulp can be impregnated with the soluble carbonate; the solution of soluble calcium salt, the molar mass of which is approximately equal to the molar mass of the soluble carbonate, is added into the impregnated pulp, and is fully stirred and uniformly mixed, static reaction is then carried out for 30 to 180 minutes, and the reaction temperature is controlled at 5 DEG C to 50 DEG C; and after the static reaction, the pulp is made into reconstituted tobacco sheets by papermaking equipment.
Owner:GUANGDONG JINKE REFORGING TOBACCO LEAF CO LTD
Metallocene compounds, catalysts comprising them, process for producing an olefin polymer by use of the catalysts, and olefin homo-and copolymers
ActiveUS20100267907A1Desirable characteristicImprove productivityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPolypropyleneCopolymer
Certain metallocene compounds are provided that, when used as a component in a supported polymerization catalyst under industrially relevant polymerization conditions, afford high molar mass homo polymers or copolymers like polypropylene or propylene / ethylene copolymers without the need for any α-branched substituent in either of the two available 2-positions of the indenyl ligands. The substituent in the 2-position of one indenyl ligand can be any radical comprising hydrogen, methyl, or any other C2-C40 hydrocarbon which is not branched in the α-position, and the substituent in the 2-position of the other indenyl ligand can be any C4-C40 hydrocarbon radical with the proviso that this hydrocarbon radical is branched in the β-position. This metallocene topology affords high melting point, very high molar mass homo polypropylene and very high molar mass propylene-based copolymers. The activity / productivity levels of catalysts including the metallocenes of the present invention are exceptionally high.
Owner:LUMMUS NOVOLEN TECH
Metallocene compounds, catalysts comprising them, process for producing an olefin polymer by use of the catalysts, and olefin homo- and copolymers
InactiveUS20110230630A1High melting pointQuality improvementOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPolypropyleneCopolymer
Owner:LUMMUS NOVOLEN TECH
Transparent copolymers having polyamide blocks and polyether blocks
The present invention relates to copolymers having polyamide blocks and polyether blocks, in which: the polyether blocks essentially consist of PTMG having a number-average molar mass {overscore (M)}n of between 200 and 4000 g / mol; the polyamide blocks are formed from a linear (noncyclic, nonbranched) aliphatic predominantly semicrystalline monomer and from a sufficient amount of at least one comonomer to reduce their crystallinity, while remaining immiscible with the polyether amorphous blocks; and the shore D hardness is between 20 and 70. These copolymers are useful for manufacturing many articles and in particular sports shoes.
Owner:ATOFINA
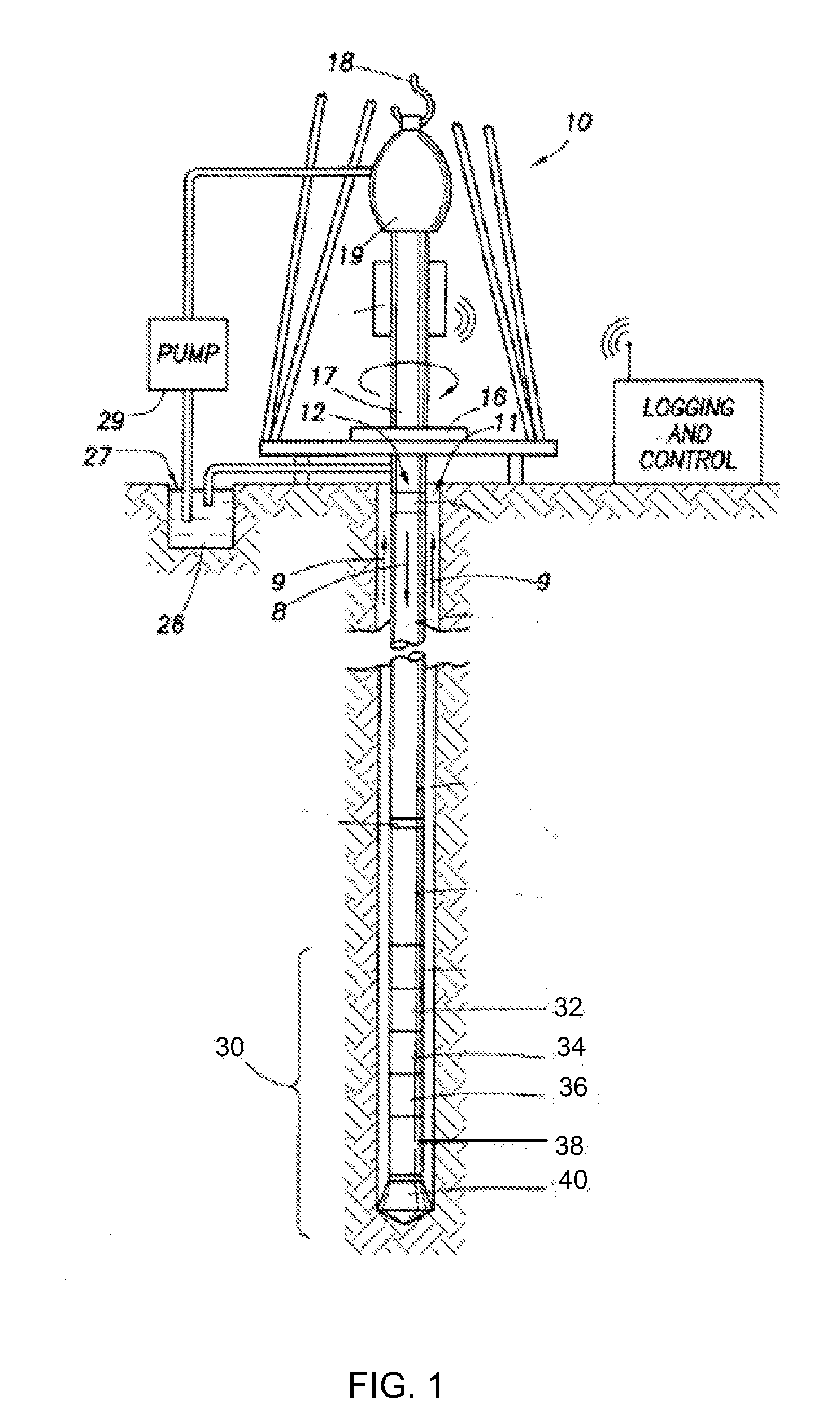
Apparatus and methods to analyze downhole fluids using ionized fluid samples
InactiveUS20090126928A1Reduce the total massSurveyMaterial analysis by optical meansEnvironmental geologyMolar mass
Apparatus and methods to analyze downhole fluids are described herein. A disclosed example method involves obtaining a sample of a downhole fluid. Additionally the example method involves ionizing at least a portion of the sample to decompose molecules having a relatively high molar mass into molecules having a relatively lower molar mass. Further, the example method involves analyzing the ionized portion of the sample to determine a parameter of the downhole fluid sample.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method of producing amorphous polyolefins with a wide mole weight distribution
The present invention relates to a process for producing a bimodal or multimodal mixture of amorphous polyolefins having a different molar mass, in which at least one amorphous polyolefin having a high molar mass is brought into contact and mixed with at least one amorphous polyolefin having a low molar mass in solution and the solvent is subsequently removed.
Owner:TICONA GMBH
Method for reduction preparation of silver nanowire by composite solvent
The invention relates to a method for using compound solvent reduction method to prepae silver nanometer wire, belonging to the technique of metallic powder preparation, with lower cost, environment protection and the application for industrial production. The method comprises: dissolving polyvinyl pyrrolidon in compound solvent whose volume ration is 1:0.1-1:1 between glycerin, and water, ethanol, isopropanol, glycol, or acetylacetone, to be heated; adding silver nitrate into the solution of glycerin and ion-exchange water whose volume is 1:2, to attain the Ag+ solution in 0.5-2.0M; using said solution to spray compound solvent and react 1 / 4-4 hours in 90-160Deg. C; collecting products; the mol percentage between the polyvinyl pyrrolidon and the Ag+ is 0.5-10; and the Ag+ solution sprays the regurgitated compound solvent in the speed of 3g / m2.s-10g / m2.s while the reaction time is 1-4 hours and the reaction temperature is 120-160Deg. C. The shape and size of particles are controlled by the ration of react matters and react condition, and said invention can attain the silver nanometer wires whose length is 5 mum-200 mum, diameter is 70-90nm, and reduced silver rate is 99%.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
High melt strength polypropylene
InactiveUS20050159564A1Improve melt strengthHigh viscosityChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPolymer scienceHydrogen
The present invention concerns a high melt strength propylene polymer or copolymer suitable for manufacturing foams and thermoformed product exhibiting a melt strength of at least 3 g and comprising a high molar mass portion and a low or medium molar mass portion. The polymers are produced by subjecting propylene and optionally other olefins to polymerization in a plurality of polymerization reactors connected in series, employing different amounts of hydrogen as a molar mass modifier in at least two of the reactors, and carrying out the polymerization reaction in the presence of a catalyst system capable of catalyzing the formation of a high molar mass polymerization product having a MFR2 of less than 0.1 g / 10 min and a low or medium molar mass polymerization product having a MFR2 of more than 0.5 g / 10 min.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH OY
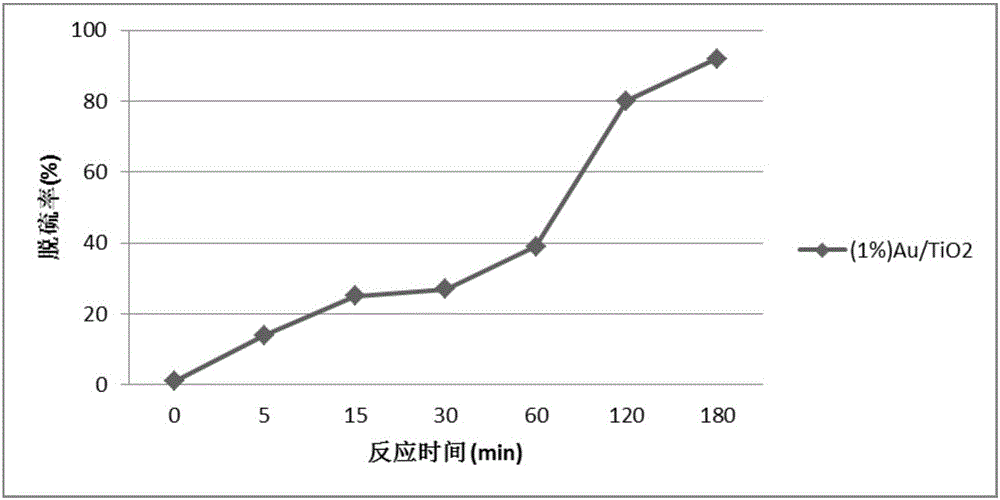
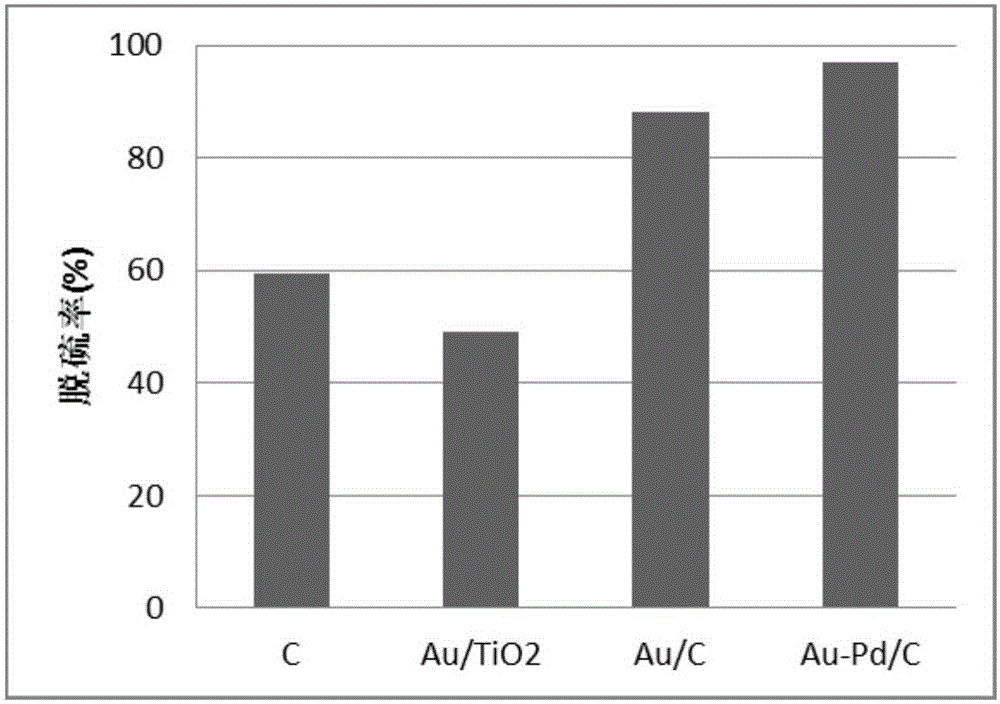
Method for low-temperature oxidation desulfurization of fuel oil
InactiveCN105112089AAvoid large-scale equipment investmentOvercome longevityRefining with oxygen compoundsFuel oilOxygen
The invention relates to a method for oxidation desulfurization of fuel oil. According to the method, (1) peroxide or a mixture of peroxide and oxygen (air) and (2) a heterogeneous catalyst which has catalytic action and contains Pd, Pt, Ru, Au and Ag are involved, and under the effect of the catalyst, the peroxide is decomposed to generate high-oxidbillity free radicals to be used for oxidized removal of sulphur-containing substances in the fuel oil. The molar mass of the catalyst on a metal basis is 1 / 5000-1 / 2 that of sulfide, and the molar mass of an oxidizing agent is 1 / 2-100 / 1 that of the sulfide. Compared with a conventional method, the method has the advantages of being high in desulfurization efficiency, moderate in reaction condition and simple in process and having easiness in separation.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
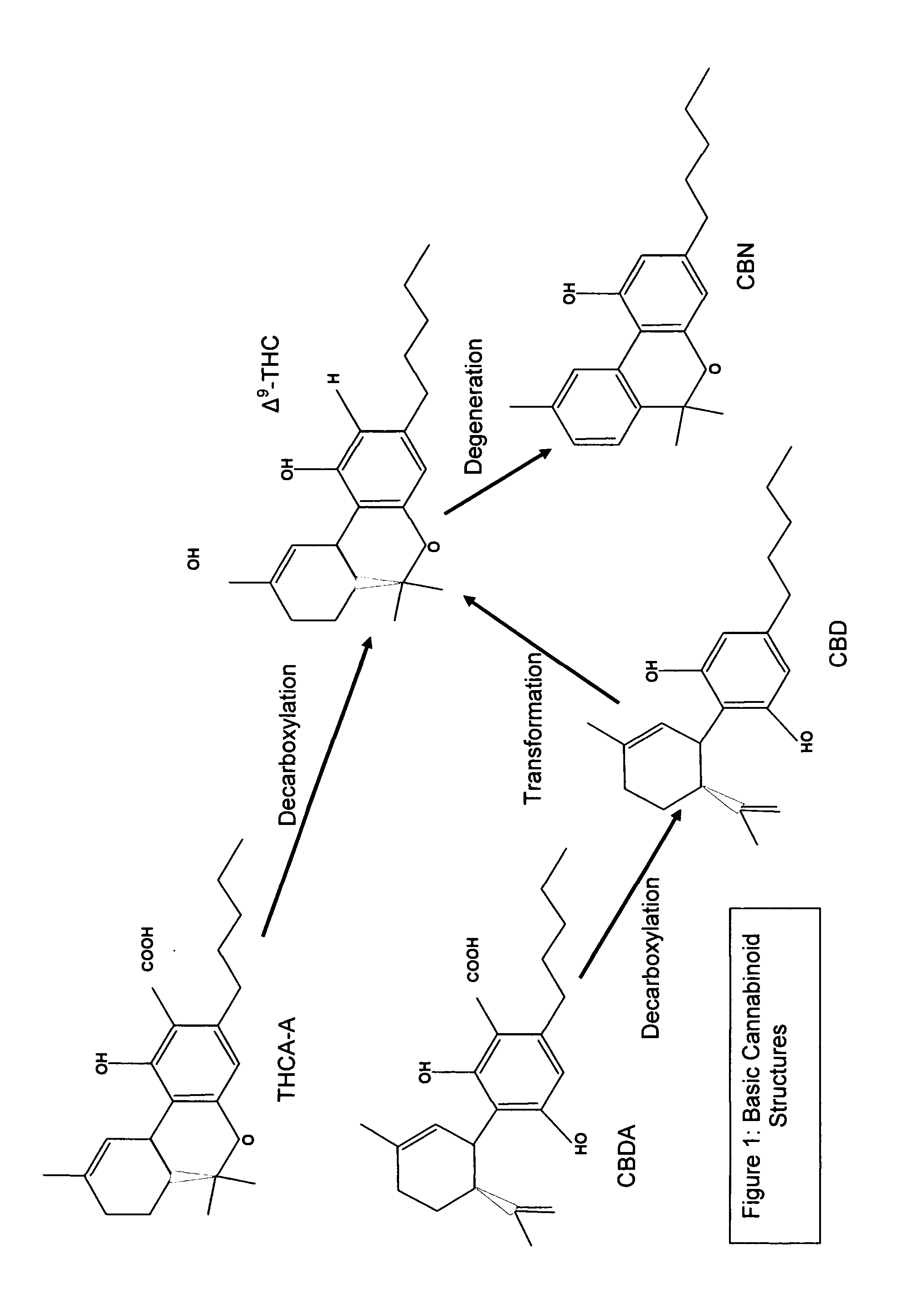
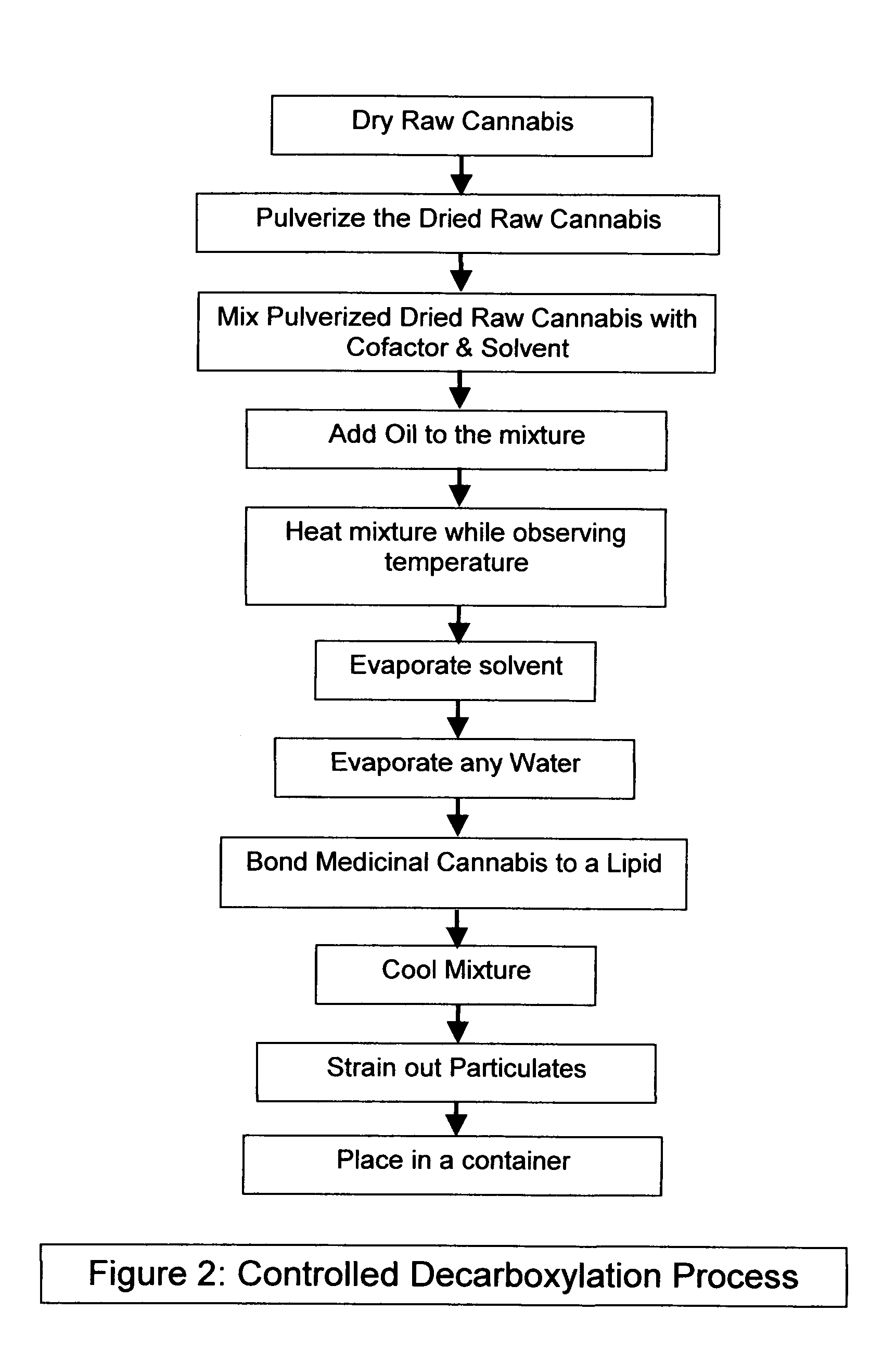
Controlled cannabis decarboxylation
The invention is a process for the controlled decarboxylation of cannabis wherein Medicinal Delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and other cannabinoid medicinal substances are decarboxylated through a chemical reaction facilitated by a cofactor. The amount of medicinal cannabis decarboxylated will be directly proportional to the amount of cofactor used. Use a small amount of the cofactor and only some of the medicinal cannabis contained in raw cannabis will be converted from an acidic form into a non-acidic form. Use a large amount of the cofactor and most or all of the medicinal cannabis will be decarboxylated. The reaction is proportional to the molar mass of cofactor.
Owner:HOSPODOR ANDREW DAVID
Polyurethane dispersion with high film hardness, process for preparing it, and its use
InactiveUS20020193507A1Wide scope for variationHigh film hardnessPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyurethane dispersionPolymer science
A description is given of a polyurethane (hybrid) dispersion with high film hardness, high flexibility and good emulsion stability which comprises the following reaction components: (A) from 3 to 25% by weight of a polyol component consisting of (i) from 2 to 20% by weight of a polymeric polyol having two or more polyisocyanate-reactive hydroxyl groups and a molar mass of from 500 to 4 000 daltons (ii) from 0.5 to 5% by weight of a low molecular mass polyol having two or more polyisocyanate-reactive hydroxyl groups and a molar mass of from 50 to 500 daltons (B) from 3 to 30% by weight of an anionically modifiable 1,2-polymethacrylatediol, (C) from 2 to 20% by weight of a polyisocyanate component, (D) from 0 to 6% by weight of a solvent component, (E) from 0.15 to 1.5% by weight of a neutralizing component composed of at least one organic or inorganic base, (F) from 0 to 1% by weight of a chain extender component composed of one or more polyamines having two or more polyisocyanate-reactive amino groups, and, optionally (G) from 5 to 40% by weight of a monomer component, (H) from 0.01 to 1.5% by weight of an initiator component, and water as the remainder.
Owner:TH GOLDSCHMIDT AG
Method for preparing Co3O4 nano material by hydrothermal method under magnetic field effect
InactiveCN101434418AGrain refinementEvenly dispersedCobalt oxides/hydroxidesReaction temperatureSolvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing Co3O4 nano material under the action of a magnetic field by a hydrothermal method, which belongs to the technical field of chemical material technology. The method of the invention adopts cobalt salt, a dispersant, a precipitator, a surfactant and a solvent as the raw material; the precipitator and the cobalt salt react in a reaction kettle for 4-36 hours under the conditions that the molar mass ratio between the precipitator and the cobalt salt is 1:1-6:1, the compactness is 50-85 percent, the magnetic field strength is 1-100 Tesla on the basis of the hydrothermal method, and the reaction temperature is 100-240 DEG C to obtain the reaction product, and then the product is dried in a vacuum drying chamber for 6-12 hours under 60-80 DEG C to obtain the powder material of Co3O4. The Co3O4 nano powder material prepared by the method of the invention has the advantages of finer crystal grain, uniform dispersion and extremely high purity without other impurities.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Moisture absorption humectant and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101225125AIncrease production costImprove moisture absorption and moisturizing performanceAcetic acidFiltration
The invention relates to a moisture absorbing humectant of polysaccharides and a preparation method, belonging to the fields of daily chemicals and medical industry; wherein, carboxymethyl hyaluronic acid is adopted for the moisture absorbing humectant; the preparation method comprises steps as follows: 1 to 5-hour reaction is carried out for the hyaluronic acid swollen in alkaline isopropyl alcohol solution and the chloroacetic acid with a molar mass ratio between 1 to 6 and 1 to 4 in the excessive alkaline isopropyl alcohol solution under temperatures between 35 and 75 DEG centigrade, and then pumping filtration and drying are carried out to acquire the moisture absorbing humectant. With the carboxymethyl hyaluronic acid acquired through effective synthesis, the production cost hardly increases, while the moisture absorption and maintaining performance is remarkably improved, so as to enhance the activity and indirectly reduce the production cost. By adopting the carboxymethyl hyaluronic acid with better moisture absorption and maintaining performance than that of the hyaluronic acid as the moisture absorbing humectant, the preparation method for moisture absorbing humectant of polysaccharides has the advantages of low cost and high yielding.
Owner:烟台大境生物科技有限公司
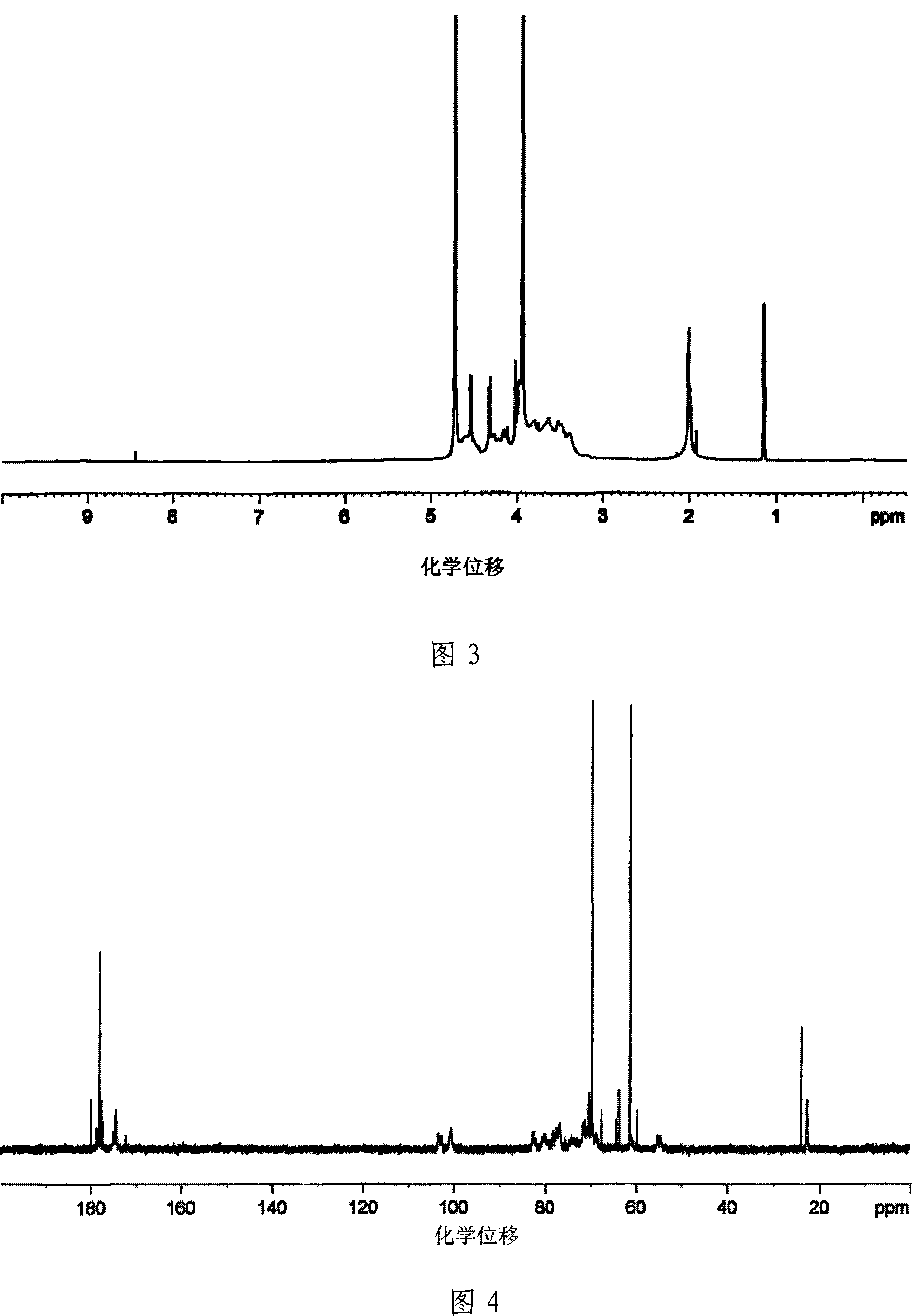
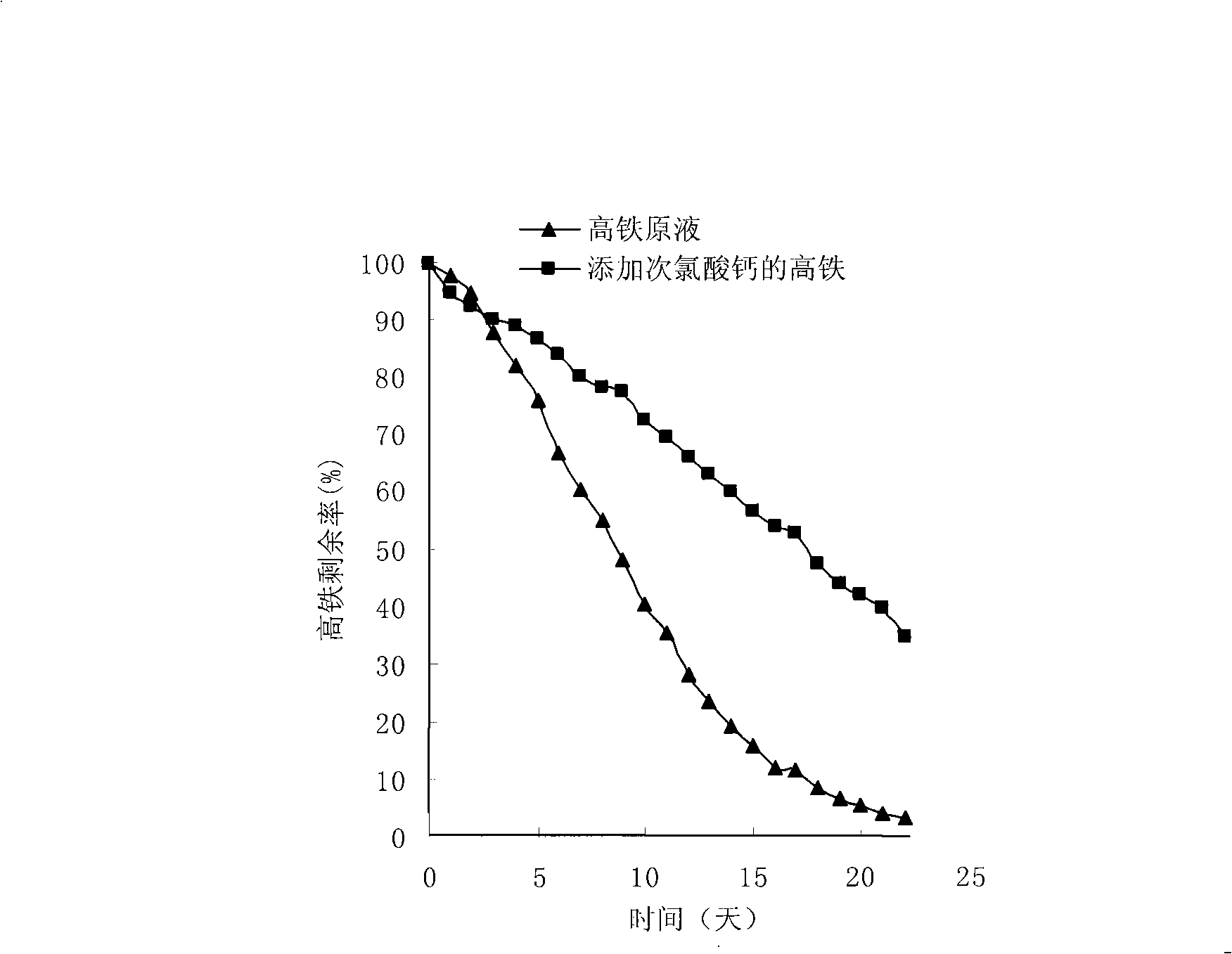
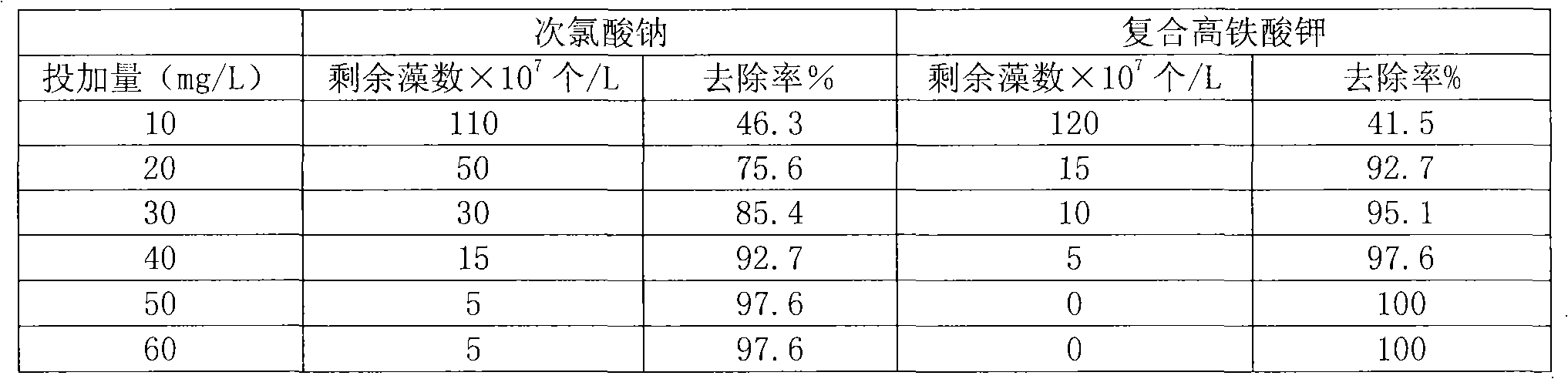
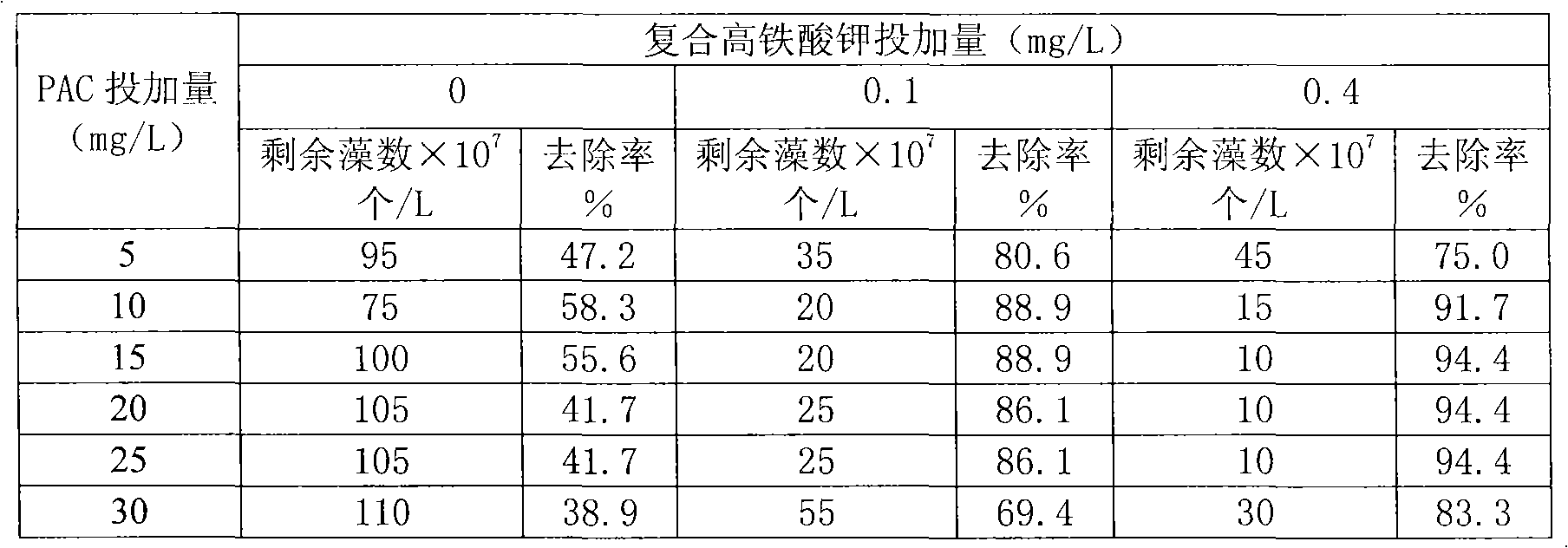
Method for preparing steady composite potassium ferrate solution
InactiveCN101318707AImprove stabilityLong storage timeIron compoundsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processChemical industryFiltration
The invention relates to a method for preparing a composite potassium ferrate solution, which belongs to the chemistry and chemical industry and water treatment agent preparation process technical field. The method comprises the following preparation processes that: firstly, a sodium hypochlorite solution reacts with sodium hydroxide, a white salt substance is generated first and is subject to pumping filtration, then ferric nitrate is added according to a molar mass ratio of sodium hypochlorite to ferric nitrate being equal to between 1.5 and 2.0 to 1, the reaction temperature is between 20 and 45 DEG C, and the pumping filtration is performed after 1.5 to 2.0 hours of reaction; and then a filtrate is added with a saturated potassium hydroxide solution to ensure that the filtrate is transformed into a potassium ferrate solution. Then 0.06 to 0.16mol / L of calcium hypochlorite is added, the reaction temperature is controlled to between 10 and 30 DEG C, the reaction time is between 10 and 30 minutes, and finally the composite potassium ferrate solution with good stability is produced. The composite potassium ferrate solution prepared by the method has good stability, long preservation time, difficult decrease of high iron content, and easiness for industrialized production. The product can be widely used for purification treatment of algae-laden water, city domestic sewage and so on.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation method for cement auxiliary-grinding strengthener of polyethylene glycol amine ester carboxylic acid system
The invention belongs to the technical field of cement auxiliary-grinding agents, and in particular to a preparation method for a cement auxiliary-grinding strengthener of a polyethylene glycol amine ester carboxylic acid system. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) performing esterification reaction on alcohol amines and unsaturated carboxylate in a molar mass ratio to obtain esterification monomers which contain polar groups, such as hydroxyl and carboxyl; (2) adding unsaturated large monomers and water into a reaction container, stirring, heating and dissolving, respectively adding an initiator, the esterification monomers and a chain transfer agent dropwise, preserving the heat after the reaction is performed for a certain period of time, and adjusting the pH of a solution to be neutral after the reaction is completed so as to prepare the cement auxiliary-grinding strengthener of the polyethylene glycol amine ester carboxylic acid system. The cement auxiliary-grinding strengthener fully plays the action mechanism of the polar functional groups, such as the hydroxyl and the carboxyl, on cement; when the using amount is 0.01 to 0.1 percent of the mass of the cement, the yield each grinding machine per hour is improved by 12 to 25 percent, the 3-day strength of the cement can be increased by 2 to 5 MPa, the 28-day strength of the cement can be increased by 4 to 8 MPa, and the aims of stable performance and remarkable effects of auxiliary grinding and strengthening are fulfilled.
Owner:KZJ NEW MATERIALS GROUP CO LTD
Method for Preserving Polypeptides Using a Sugar and Polyethyleneimine
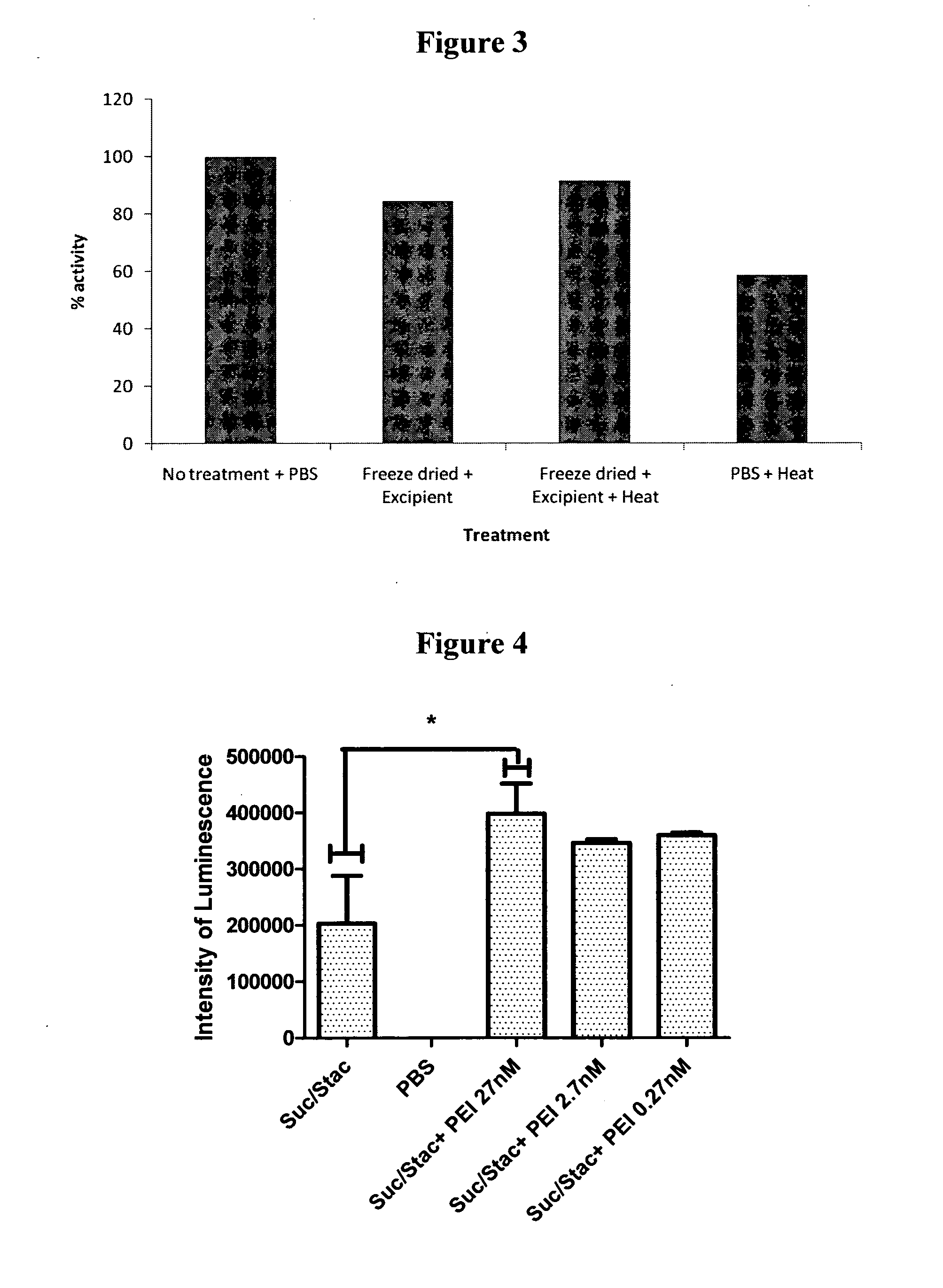
InactiveUS20110236412A1Reduce concentrationIncrease sugar concentrationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSugarAqueous solution
A method for preserving a polypeptide comprises (i) providing an aqueous solution of one or more sugars, a polyethyleneimine and said polypeptide wherein the concentration of polyethyleneimine is 25 μM or less based on the number-average molar mass (Mn) of the polyethyleneimine and the sugar concentration or, if more than one sugar is present, total sugar concentration is greater than 0.1 M; and (ii) drying the solution to form an amorphous solid matrix comprising said polypeptide.
Owner:STABILITECH
Hyperbranched Polymers
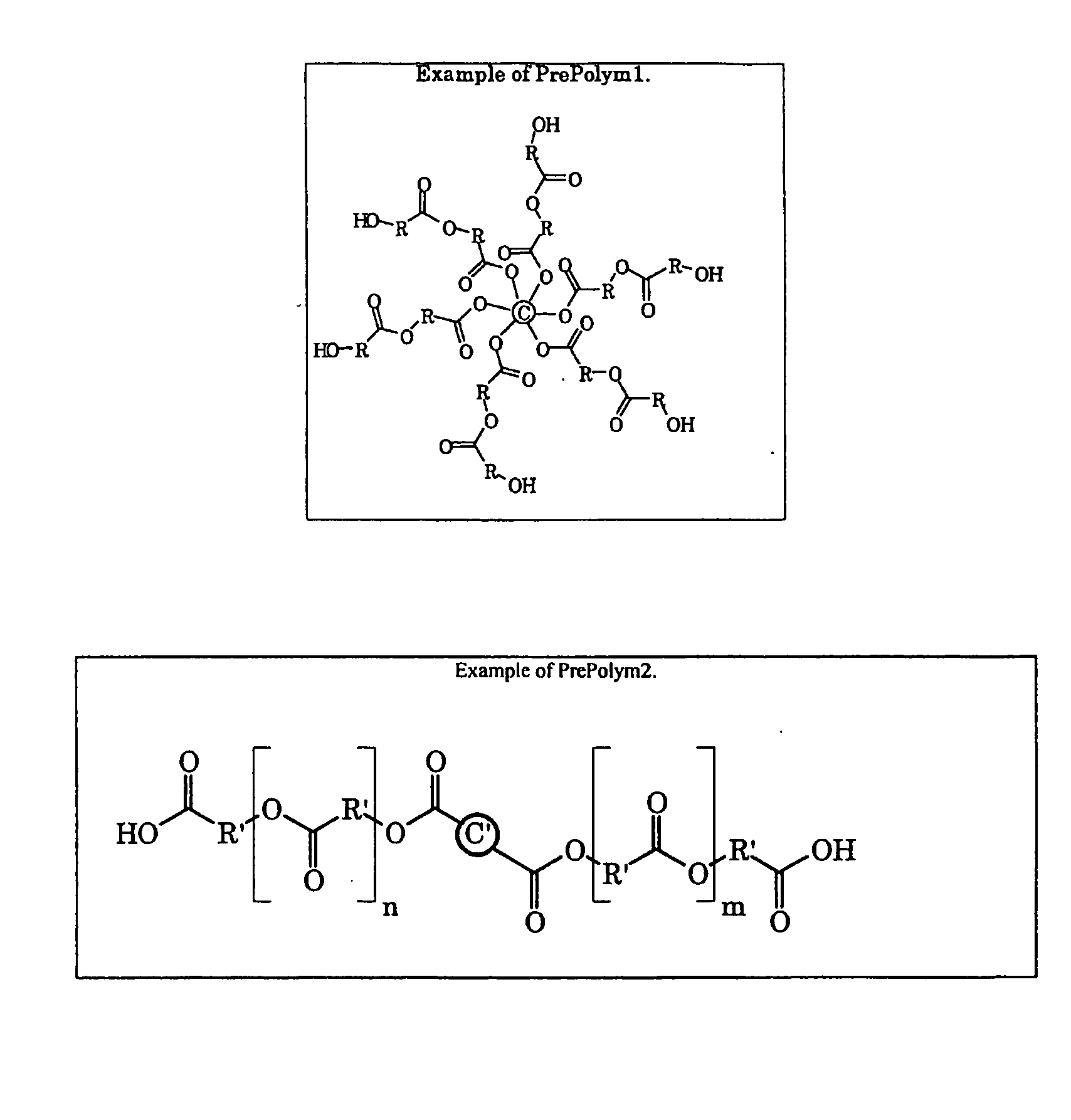
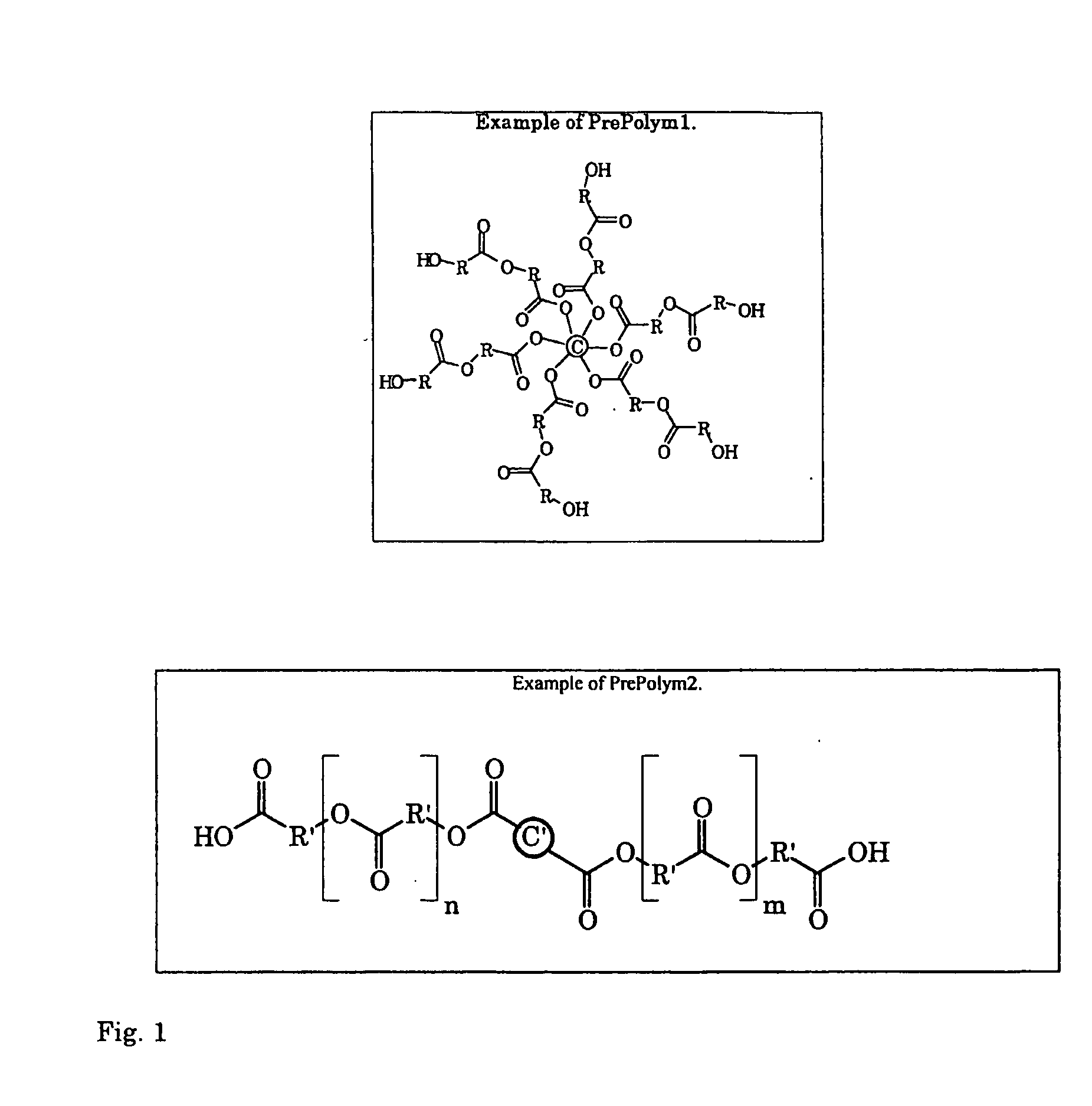
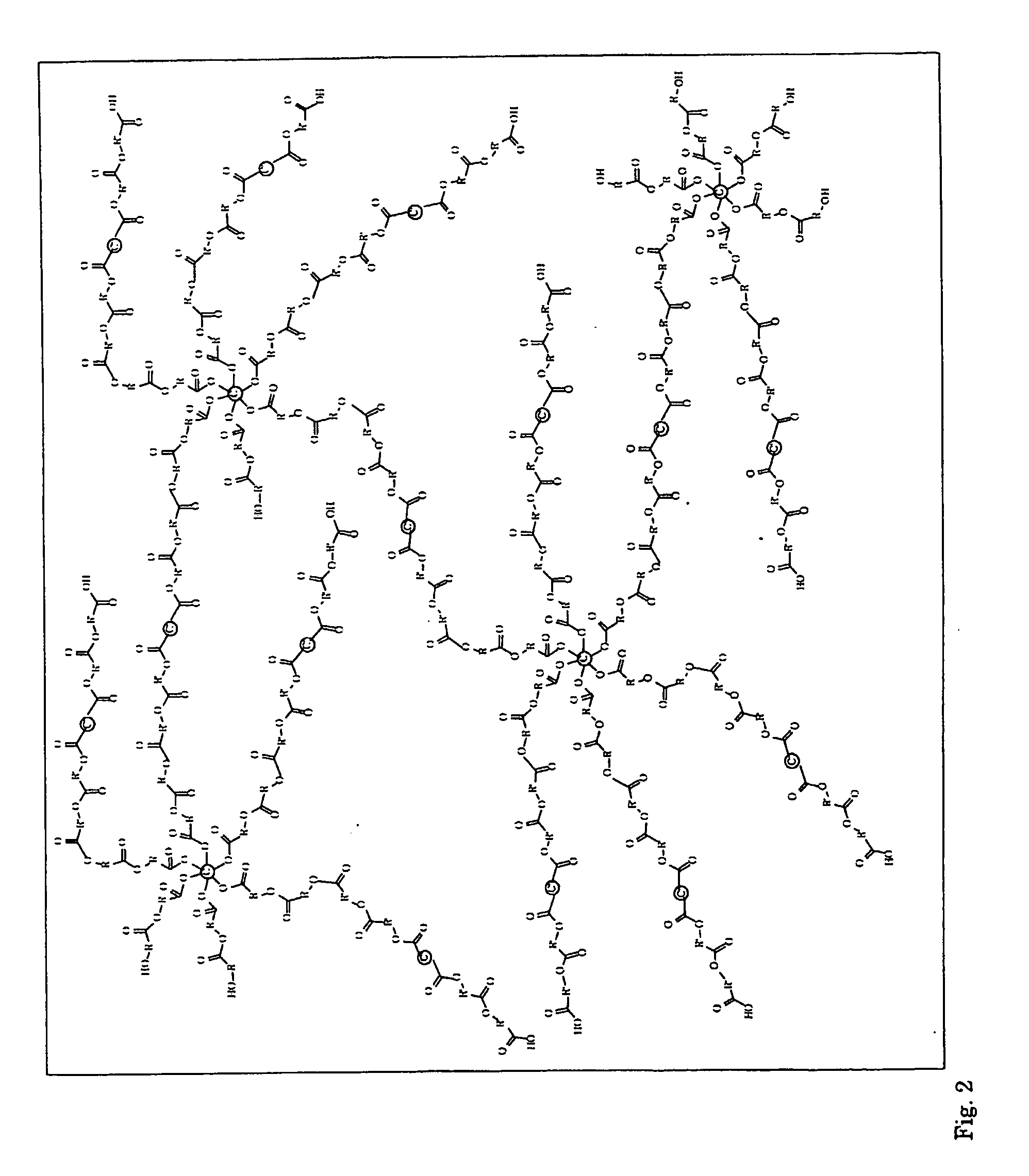
InactiveUS20080221265A1Easy to controlQuality improvementChewing gumAdhesivesOrganic solventChemical reaction
A process for preparing a hyperbranched polymer having a weight-average molar mass of at least 30,000, includes coupling a first prepolymer having at least three functional end groups with a second prepolymer having at least two functional end groups by a dehydration condensation reaction between the end groups in the prepolymers. The number of arms and / or molar mass of the functionalized prepolymers can accurately be adjusted, thus affecting the properties of the resulting hyperbranched polymer in a desired way. The polymer can be equipped e.g. with hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts. Also, the number of functional end groups, that optionally can be used for further chemical reactions, in the hyperbranched polymer can easily be adjusted to a desired level. The hyperbranched high molar mass polymer can be prepared in high yields without the use of organic solvents or linking compounds, which is advantageous from an environmental as well as an economical point of view.
Owner:TATA & LYLE TECH LTD (GB)
Transparent sunscreen gels
InactiveUS6045781AImprove actionLow refractive indexCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAlcoholPolyol
The invention relates to transparent sunscreen gels comprising (a) silicone oil (b) polyoxyalkylene-organpolysiloxanes of the general formula (I) where R is an alkyl radical or a hydrogen radical, n=10 to 200, m=1 to 25 and o=1 to 100 with the proviso that, in the average molecule, o> / =m and 3o<n, p=7 to 17, and the molar mass of the residue (C2H4O-)x-(C3H6O-)yR is from about 250 to about 2000, where x and y are chosen such that the weight ratio of oxyethylene groups to oxypropylene groups is from 100:0 to about 20:80, (c) water, (d) a component chosen from alcohols and / or polyols and (e) at least one UV absorber soluble in the aqueous or in the oily phase.
Owner:EVONIK GOLDSCHMIDT GMBH
Biologically active silicic acid
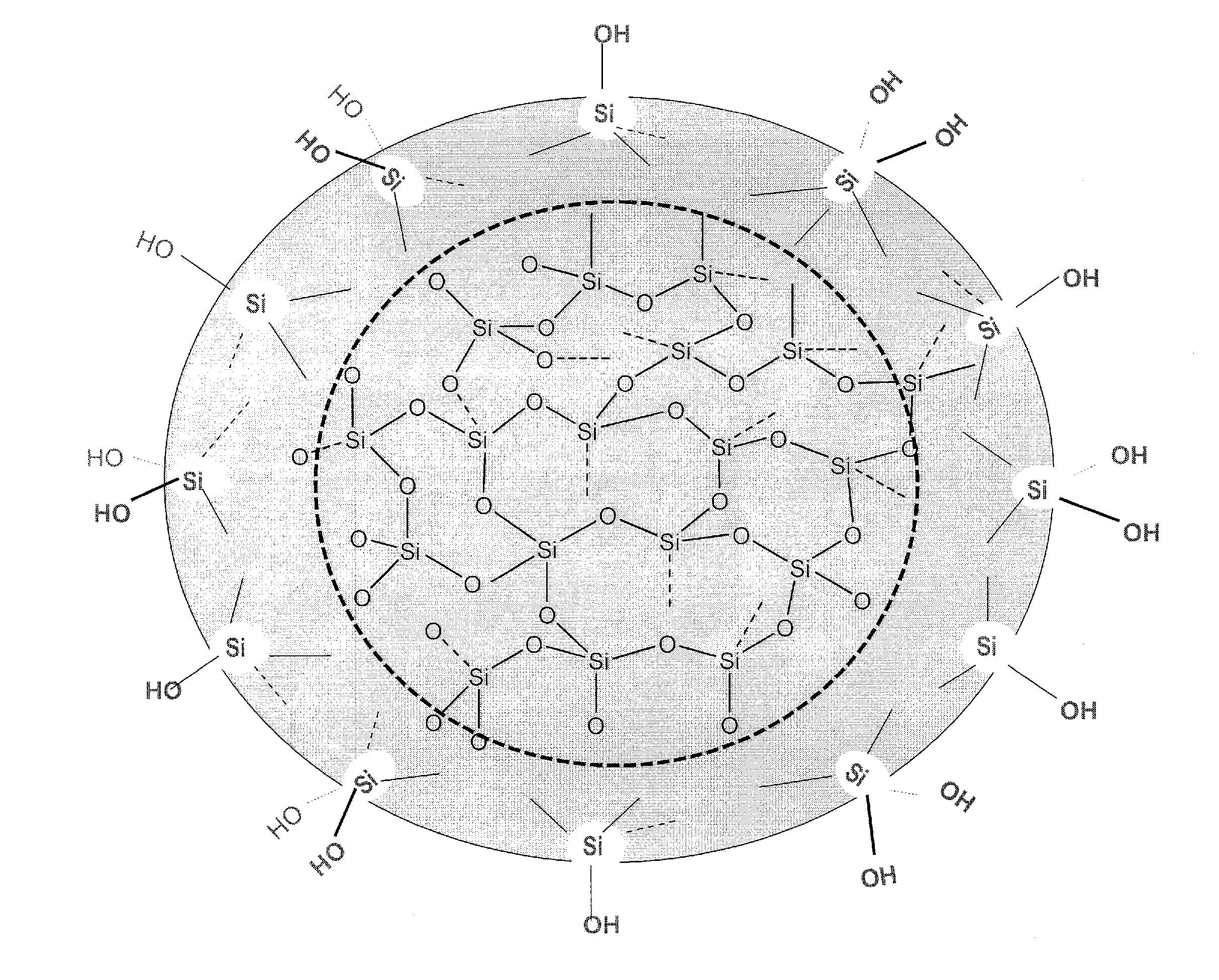
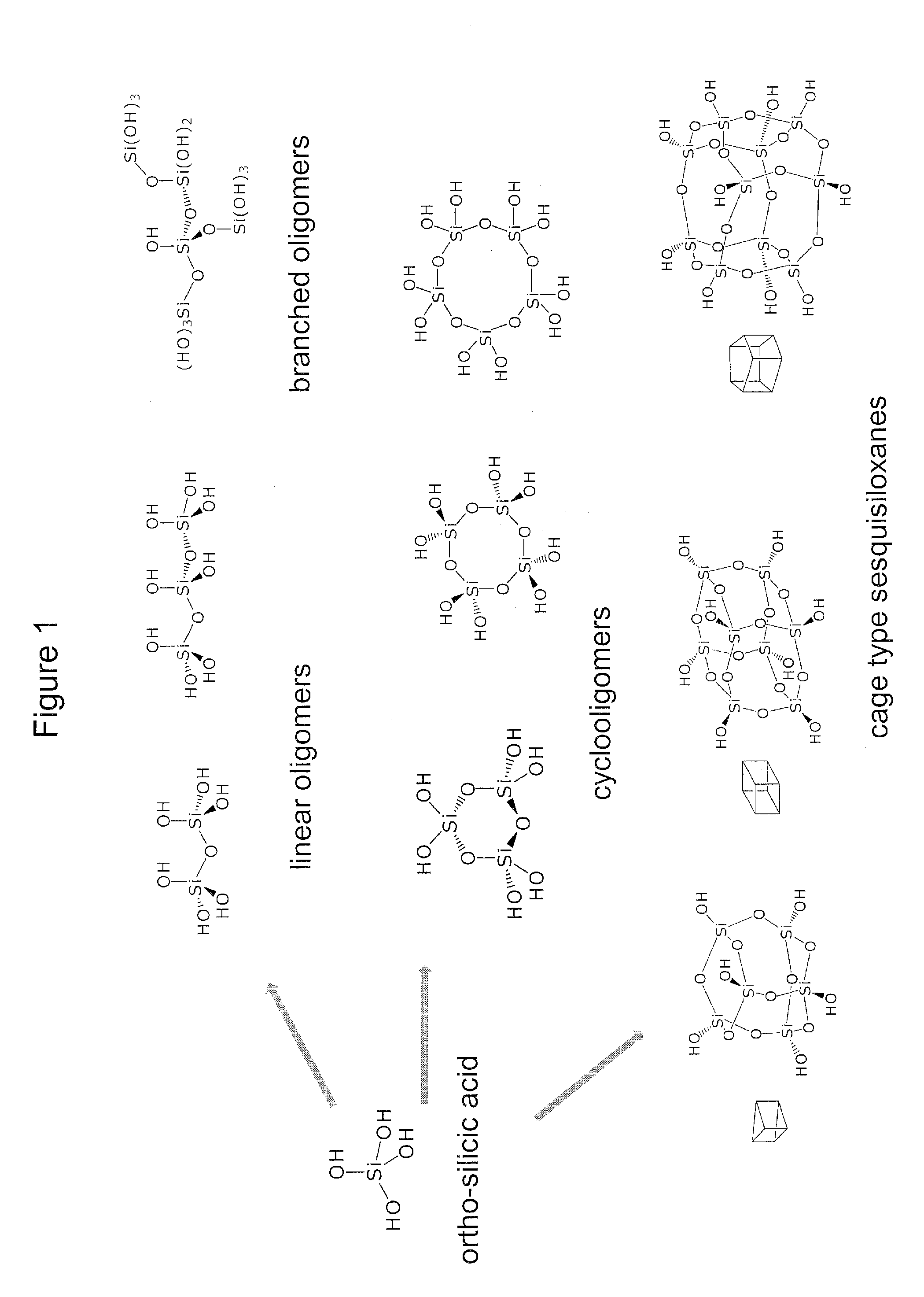
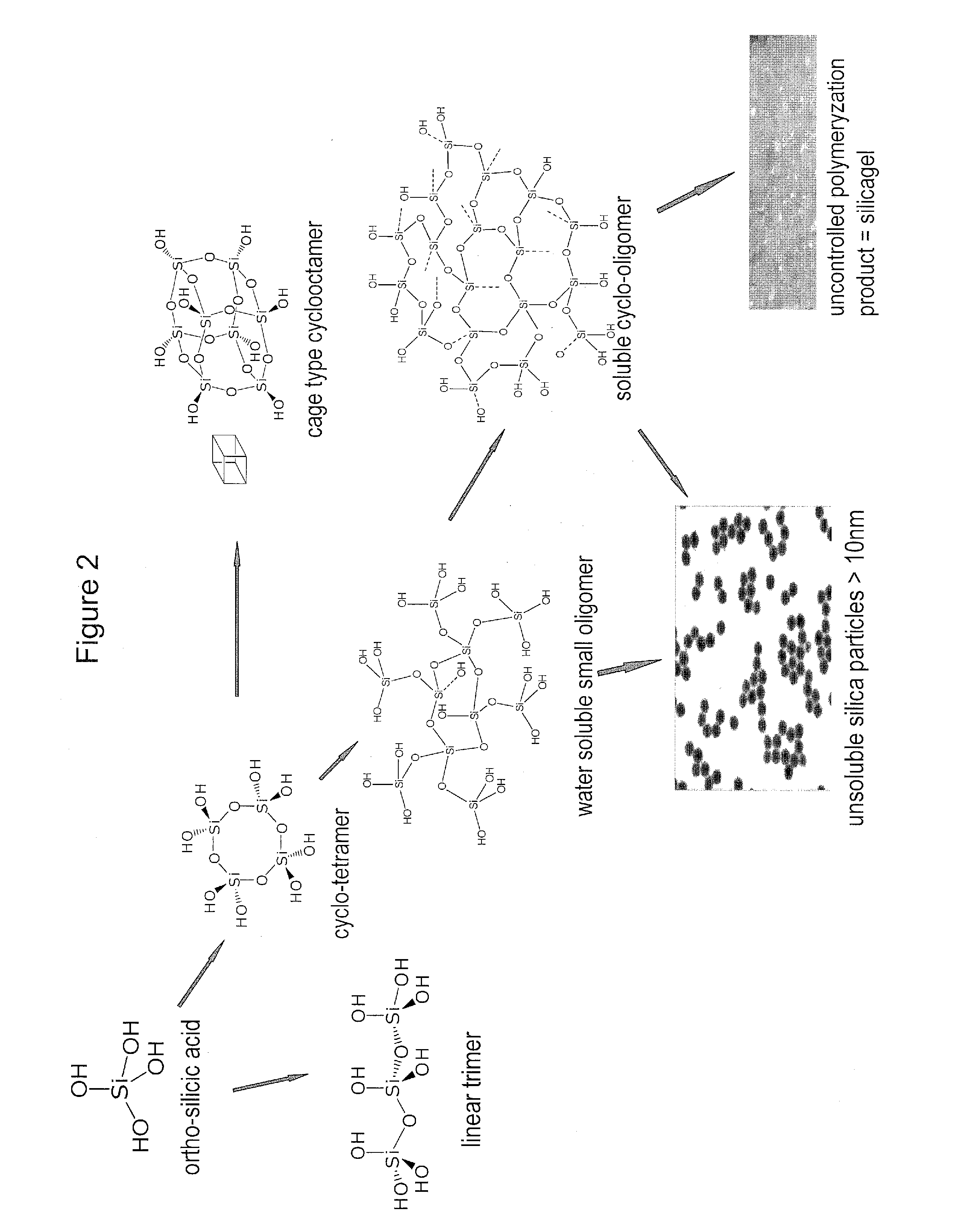
The present invention relates to low-molar mass condensed derivatives of silicic acid of sub-nano particle size characterised by particular structure and specific biological activities. Preparation methods and applications are presented for the here disclosed sub-nano silicic acid (SNSA) which interact with bio-molecules and modify significantly their structure and biological function. Preferred field of application of the inventive silicic acid derivatives is to modulate the structure and biological function of proteins particularly of those involved in reversible phosphorylation within biological signal transduction or membrane transport processes. Structure of the substances, methods for the preparation and stabilization, as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising the substances and methods of application in the prevention, diagnosis and therapy of diseases are disclosed.
Owner:SINATUR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com