In-situ construction method of tailing covering layer
A construction method and technology of covering layer, applied in the field of mineral processing and environmental protection, can solve the problems of unclear impact of steel slag life, pollution of groundwater and lakes, backward mineral processing technology, etc., to achieve strong adsorption capacity, maintain reactivity, energy and resources The effect of low demand
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
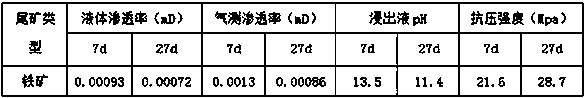
[0026] Samples of iron ore tailings, local red soil (silicon-aluminum ratio 2.2), kaolin, and corn stalk ash were taken and dried in a ventilated room at 25°C for 2 days and sieved separately with a mesh number of 120. The red soil, kaolin, and corn stalk ash Mix evenly, the mass ratio is 9:9:3, and the total mass is 85g. Grind the product, sieve 120 mesh and take 20g of mass, take a dry sample of iron tailings and sieve 120 mesh, weigh, take 20g of dry sample, mix the product and dry iron tailing sample evenly and place them in a petri dish to prepare a mixed material, and the compaction coefficient was measured to be 0.9. Stir the solid water glass, NaOH, and water according to the mass ratio of 5:6:35 until fully uniform to obtain lye, wherein the mass of lye is 20g, uniformly infiltrate the mixture with the prepared lye, let it stand at room temperature for 20 days, and again Add 20 g of aqueous solution to evenly wet the surface of the covering layer, and test after 7 da...
Embodiment 2
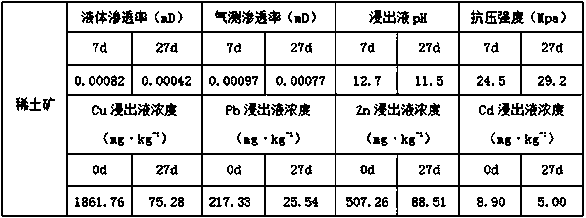
[0029] Take copper ore tailings samples, local red soil (silicon-aluminum ratio 2.2), micro-silica fume, and corn stalk ash in a ventilated room for 2 days at 25°C and sieve with a mesh number of 120. Air-dried red soil, micro-silica fume 1. Mix the corn stalk ash evenly, the mass ratio is 9:5:3, and the total mass is 85g. Grind the product, sieve 120 mesh and take 20g of mass, take a dry sample of copper tailings, sieve 120 mesh and weigh, take 20g of dry sample, mix the product and dry iron tailing sample evenly and place them in a petri dish to prepare a mixed material, and the compaction coefficient was measured to be 0.9. Solid water glass, NaCO 3 1. Stir the water according to the mass ratio of 5:5:35 until it is fully uniform to obtain lye, in which the mass of lye is 20g, soak the mixture evenly with the lye, let it stand at room temperature for 20 days, add 20g of aqueous solution again to wet it evenly Cover the surface of the layer and let it stand for 7 days at r...
Embodiment 3
[0032] An in-situ construction method for a tailings covering layer, comprising the following steps:
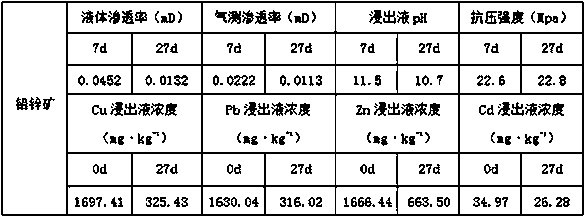
[0033] (1) Mix the compounding agent evenly according to the proportion of raw materials to obtain the precursor material of the tailings solidified covering layer, and set aside; the tailings are lead-zinc ore; the compounding agent includes the following raw materials in parts by weight: plant ash 2 9 parts of red soil, 5 parts of silica fume; the plant ash is coniferous tree ash; the silicon-aluminum ratio of the red soil is 2, and it is air-dried at 20°C until the water content is 10%; The particle size of the raw material is 200 mesh;
[0034] (2) Apply the overburden precursor material obtained in step (1) evenly to the tailings pond, turn over the soil and break the surface of the tailings. The depth of the overturning and crushing of the surface of the tailings is 0 cm, and then mix the precursor material and homogenize it. The mesh number of raw materials is more th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com