Synthesis method and application of diphenyl sulfone-based double-chromophore thermally activated delayed fluorescent materials
A delayed fluorescence, dual chromophore technology, applied in the field of organic electroluminescent materials, can solve the problem of width at half maximum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Synthesis of compound 3a
[0027] Compound 1 (5.0 g, 0.03 mol ), NaH (1.44 g, 0.06 mol ) and 100 mL of dry N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) were sequentially added into a 250 mL three-necked flask, and the mixture was placed in a nitrogen atmosphere at Stir at room temperature for 30 min; add compound 2 (7.62 g, 0.03 mol), then raise the temperature to 100°C and stir for 4 h. After the reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, it was poured into a large amount of water, and a white solid was precipitated. Suction filtration, the solid was washed successively with ethanol and diethyl ether, and dried, and the resulting white solid was further purified by column chromatography, and purified with petroleum ether / dichloromethane ( V / V ; 2:1) as the eluent to obtain white solid compound 3a (3.85 g, yield: 32%). 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 8.15 (dd, J= 11.0, 8.2 Hz, 2H), 8.07(dd, J= 8.8,5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.77 (d, J= 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.43 (q, J= 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.37-7.29 (m...
Embodiment 2
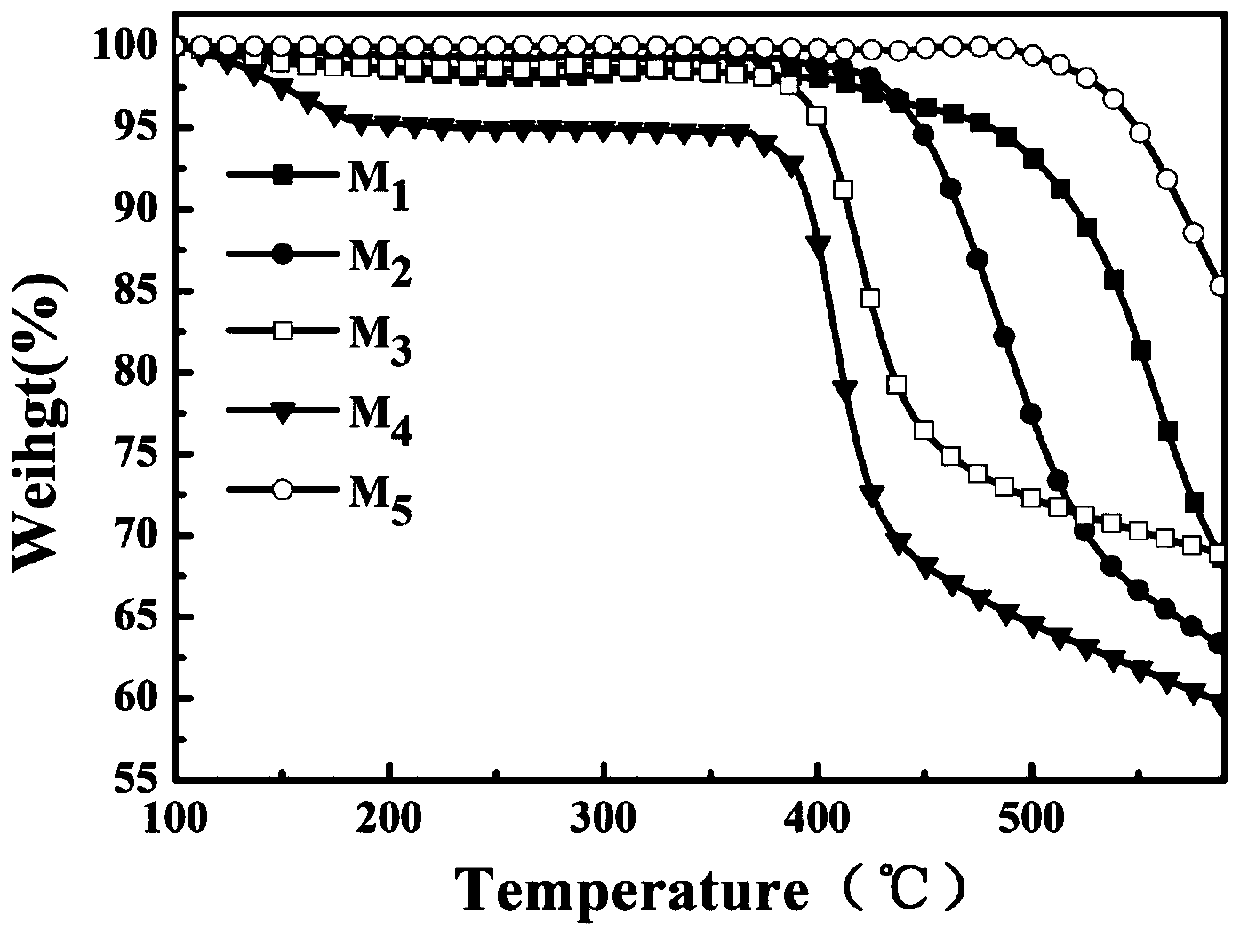
[0069] Compound M 1 -M 5 The thermogravimetric curves are shown in Figure 1, and their thermal decomposition temperatures are 480, 447, 402, 393, and 549°C, respectively. According to the corresponding molecular structure and the change trend of thermal decomposition temperature, the following conclusions can be drawn: the introduction of halogen atom bromine and the insertion of oxygen atom or alkoxy group all reduce the thermal decomposition temperature of the compound to a certain extent T d . Structurally, it can be explained that the carbon-bromine bond has a lower dissociation energy, so M 1 ~ M 4 The trend of thermal decomposition temperature change is M 2 1 ,M 4 3 ; Further with the insertion of oxygen atoms and alkoxy groups, the rigid structure of the molecule is reduced, so M 3 and M 4 of T d Average ratio M 1 and M 2 Low. m 5 It has the largest conjugated structure, so its thermal decomposition temperature is the highest at 549°C.
Embodiment 3
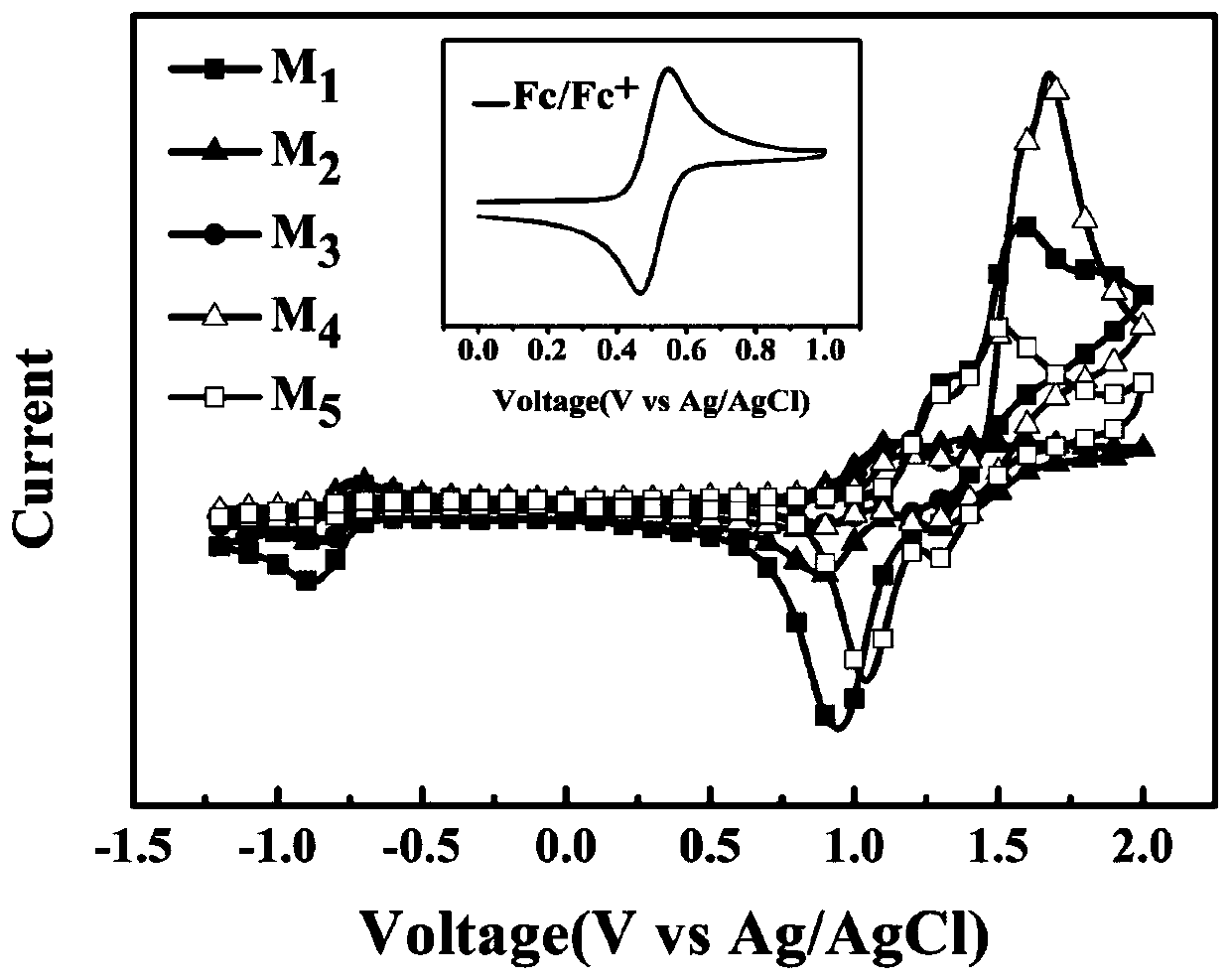
[0071] To study compound M 1 ~ M 5 The electrochemical performance of the compound was tested by cyclic voltammetry in chloroform solution. As shown in Figure 2 (inset is Fc / Fc + CV curve), compound M 1 ~ M 5 All exhibit irreversible oxidation-reduction potentials in the voltage range of -1.5 to 2.0V. According to the oxidation potential ( E ox ) and reduction potential ( E red ) value, by the formula E (HOMO) (eV)=-( E ox.vsFc / Fc+ +4.8) eV; E (LUMO) (eV)=-( E red.vsFc / Fc+ +4.8) eV; E ox.vsFc / Fc+ =( E ox -0.50) V and E red.vsFc / Fc+ =( E red -0.50) V (wherein the actual test process Fc / Fc + The potential relative to Ag / AgCl is 0.50V) to calculate M 1 ~ M 5 The HOMO energy levels are -5.4, -5.12, -5.15, -5.75, -5.4 eV; and the LUMO energy levels are -3.59, -3.62, -3.63, -3.62, -3.61 eV. The results showed that the introduction of bromine atoms and oxygen atoms or alkoxy groups mainly had a greater impact on the HOMO energy levels of the compounds; w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com