Method for performing ovulation at same period and performing semen deposition in timing manner
A technology of timed insemination and estrus cycle, applied in the field of animal husbandry, can solve the problems of long production cycle and low conception rate in cattle breeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 A method of synchronous ovulation timing insemination
[0028] A method for timing insemination during synchronous ovulation, which includes:
[0029] 1) Take healthy young Simmental cattle with moderate body condition (body condition score between 2.5-4.0), and check the basic condition of the ovaries by B-ultrasound at the beginning, and divide them into luteal phase (luteal body diameter > 0.3 cm), follicular phase ( Follicle diameter > 0.3 cm), resting phase (no corpus luteum and follicles), normal reproductive organs, no reproductive diseases;
[0030] 2) Determine any day of the estrus cycle as 0d, and inject melatonin subcutaneously on the 4th day (-4d) counting from 0d, and the injection dose is 12mg / 50kg cattle body weight;
[0031] 3) Inject GnRH (100µg) intramuscularly into the cattle on the 0th day, inject PG (0.25mg) intramuscularly into the cattle on the 7th day (+7d) counting from 0d, and inject GnRH (100µg) intramuscularly and subcutaneously i...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Beef cattle synchronous ovulation timing insemination experiment
[0033] 1. Experimental animals
[0034] A total of 86 young Simmental cattle aged over 18 months who were healthy and moderate in body condition (body condition score between 2.5 and 4.0) were selected. At the beginning of the experiment, the basic condition of the ovary was checked by B-ultrasound in all experimental cattle, and they were divided into luteal phase (luteal body diameter > 0.3 cm), follicular phase (follicle diameter > 0.3 cm), quiescent phase (without corpus luteum and follicles), normal reproductive organs, and no reproductive diseases.
[0035] 2. Grouping
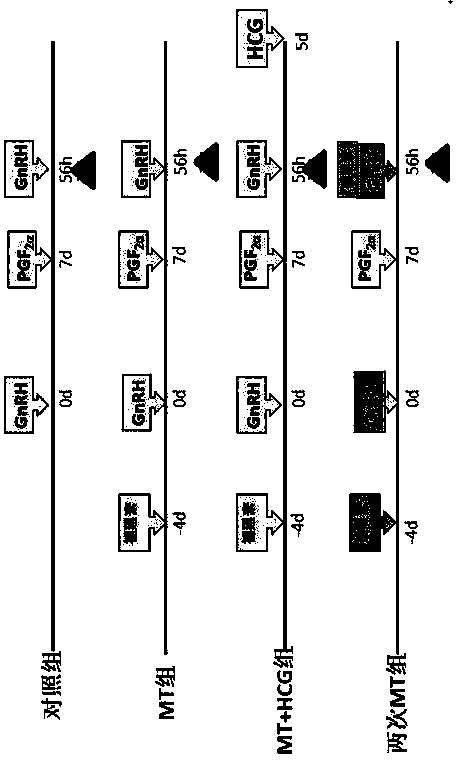
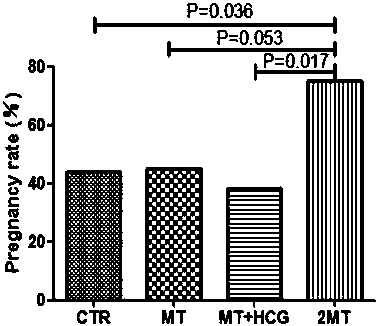
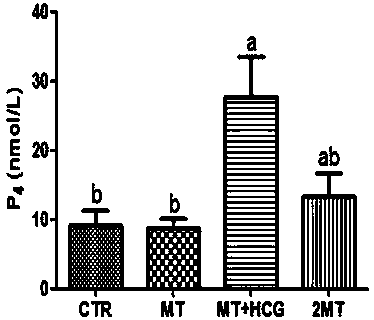
[0036] The selected 86 test cows were randomly divided into 4 groups: control group (CTR, n=25), melatonin group (MT, n=20), melatonin+HCG group (MT+HCG, n=21) , twice melatonin group (2MT, n=20) ( figure 1 );
[0037] 1) Control group: GnRH (100 µg) was injected intramuscularly for the first time on day 0, PG (0.25 m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com