Composite down material and preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and down technology, applied in the field of textile and chemical fiber, can solve the problems of low proportion of down, easy to generate static electricity, complicated process, etc., and achieve the effects of more air storage space, good antibacterial property, and low price.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
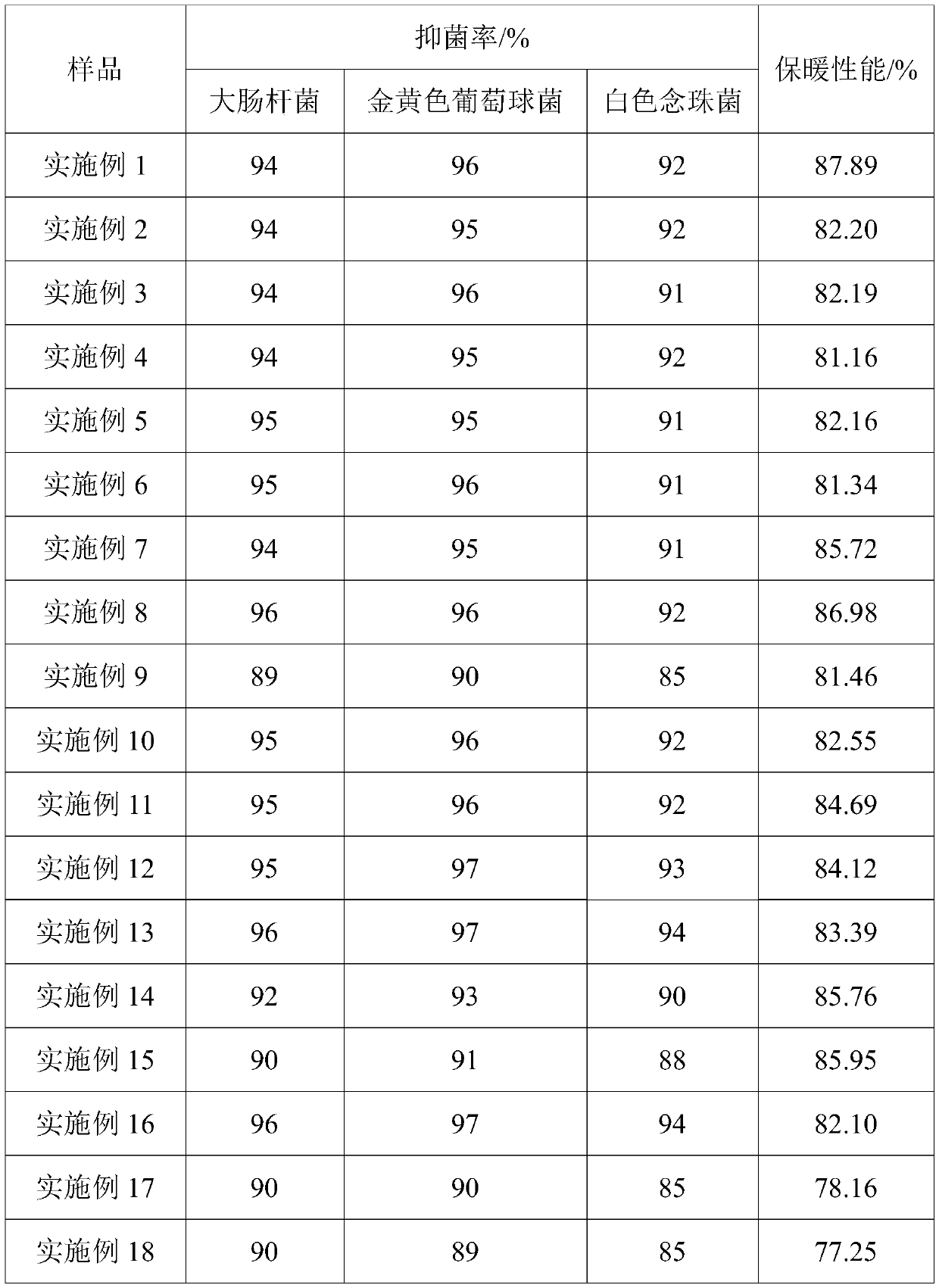
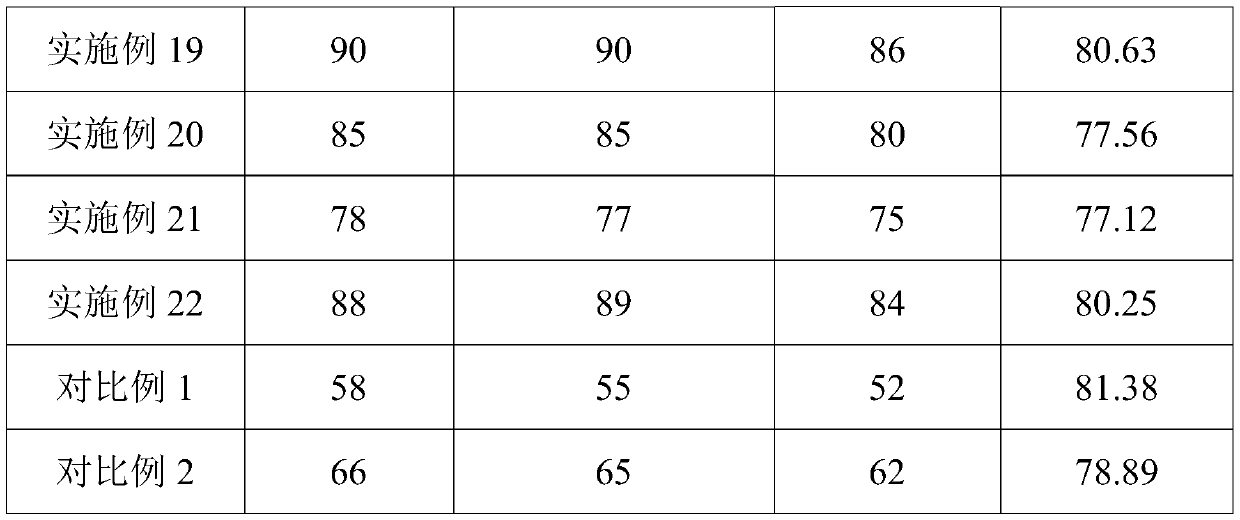
Examples
preparation example 1
[0056] A graphene material modified polyester staple fiber, wherein the graphene material is biomass graphene with a mass percentage of 1%; a linear density of 0.9D and a length of 9mm.
[0057] The preparation method is as follows:
[0058] (1) Mix 2 parts of dispersant, 10 parts of biomass graphene, and 88 parts of polyester chip powder together, use a powder mixer to fully stir and mix for 30 minutes, and then pass the mixed powder through a screw extruder Melt granulation to obtain biomass graphene modified polyester masterbatch.
[0059] (2) Take 10 parts of biomass graphene-modified polyester masterbatch and 90 parts of polyester slices and mix evenly, and spin through a melt spinning machine to obtain as-spun silk.
[0060] (3) The as-spun silk is bundled, drawn, shaped, oiled, cut, and packaged to prepare biomass graphene-modified polyester staple fibers.
preparation example 2
[0062] A graphene material modified acrylic staple fiber, wherein the graphene material is biomass graphene with a mass percentage of 1%; a linear density of 0.9D and a length of 9mm.
[0063] The preparation method is as follows:
[0064] Adopt the preparation method of the embodiment 1 that CN104862807A provides to prepare graphene modified acrylic staple fiber.
preparation example 3
[0066] A graphene material modified nylon staple fiber, wherein the graphene material is biomass graphene with a mass percentage of 1%; a linear density of 0.9D and a length of 9mm.
[0067] The preparation method is as follows:
[0068] (1) Mix 2 parts of dispersant, 10 parts of biomass graphene, and 88 parts of nylon chip powder together, use a powder mixer to fully stir and mix for 30 minutes, and then pass the mixed powder through a screw extruder Melt granulation to obtain biomass graphene modified nylon masterbatch.
[0069] (1) Get 10 parts of biomass graphene-modified nylon master batches and 90 parts of nylon slices and mix them evenly, and spin them through a melt spinning machine to obtain primary silk.
[0070] 3) The as-spun silk is bundled, drawn, shaped, oiled, cut, and packaged to prepare biomass graphene-modified nylon staple fibers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Linear density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Linear density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com