Micro-nano lignocellulose as well as preparation method and application thereof
A lignocellulose, micro-nano technology, applied in the directions of lignin derivatives, synthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paper, fiber raw material processing, etc., can solve the complicated preparation process, large environmental impact, and complicated steps. and other problems, to achieve the effect of weakening hydrogen bonding, destroying bonding and reducing hardness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
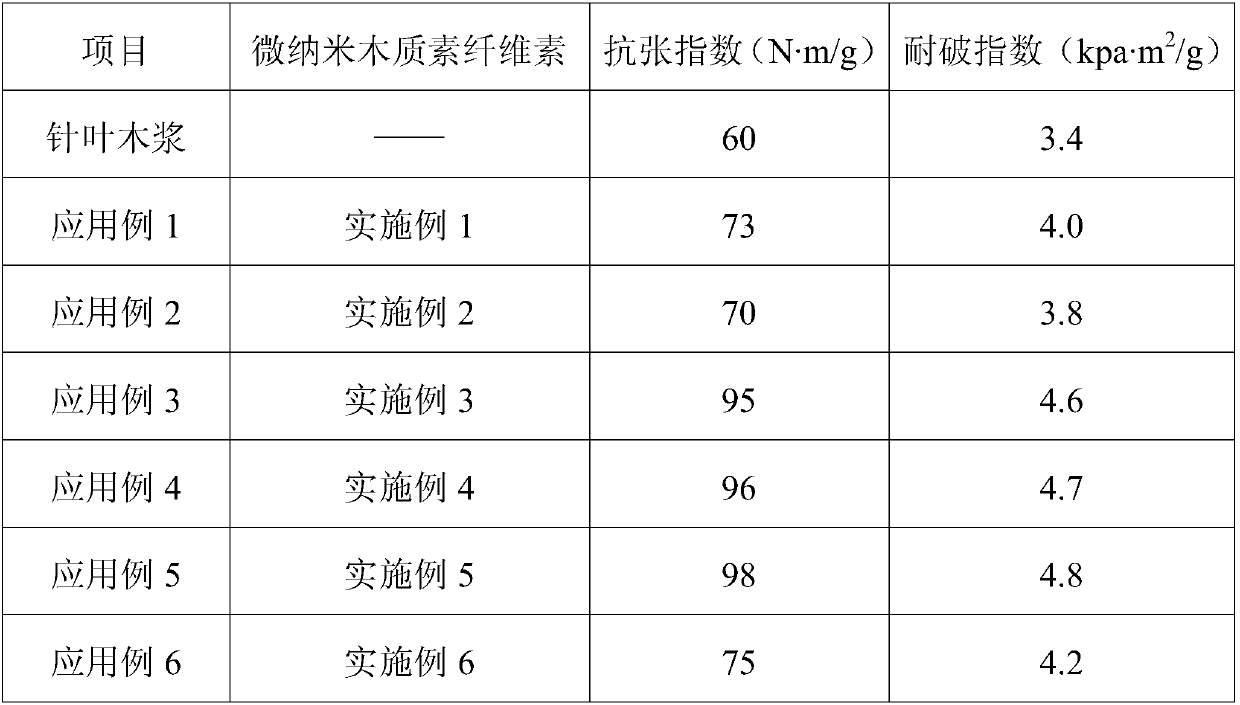
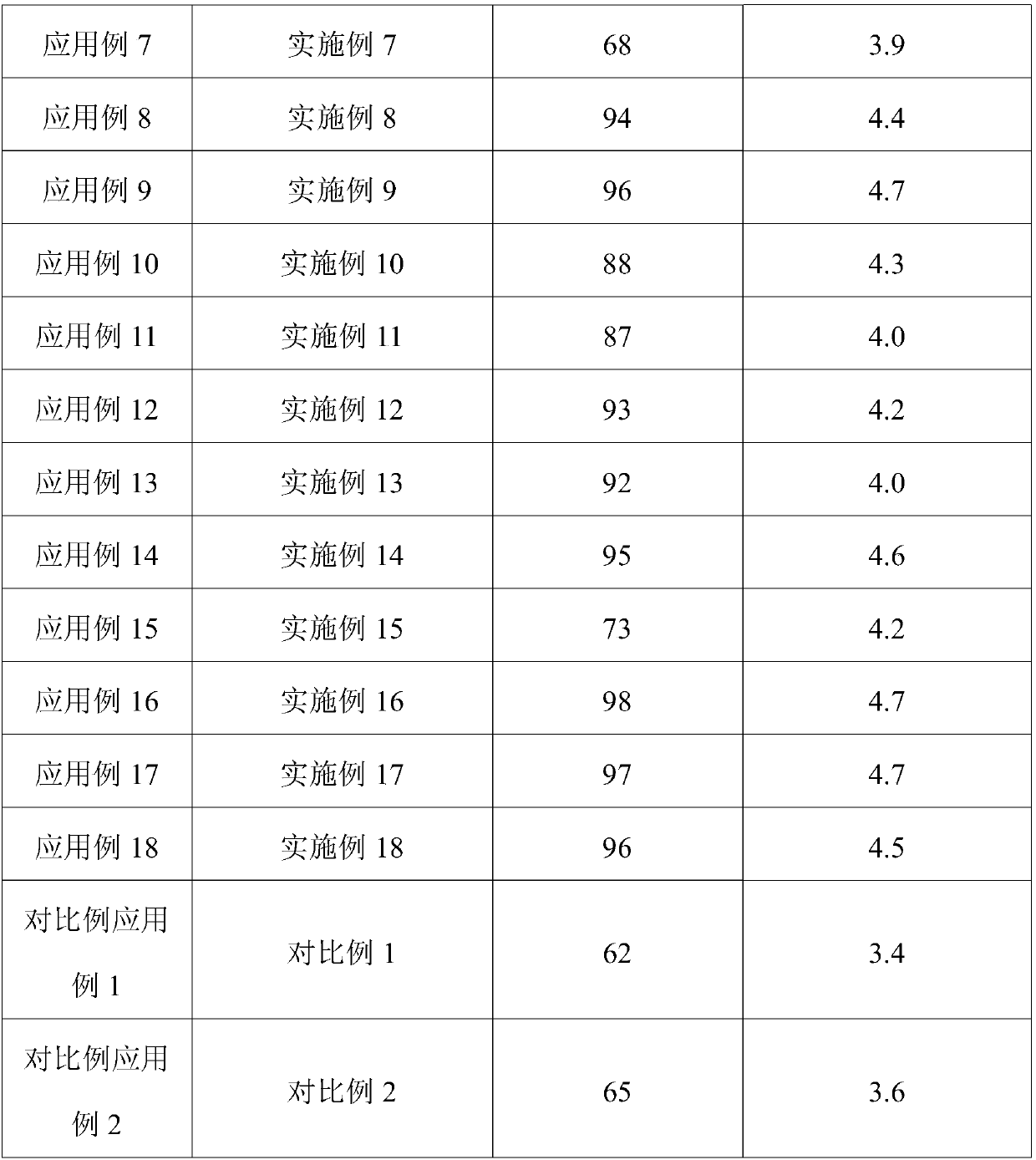
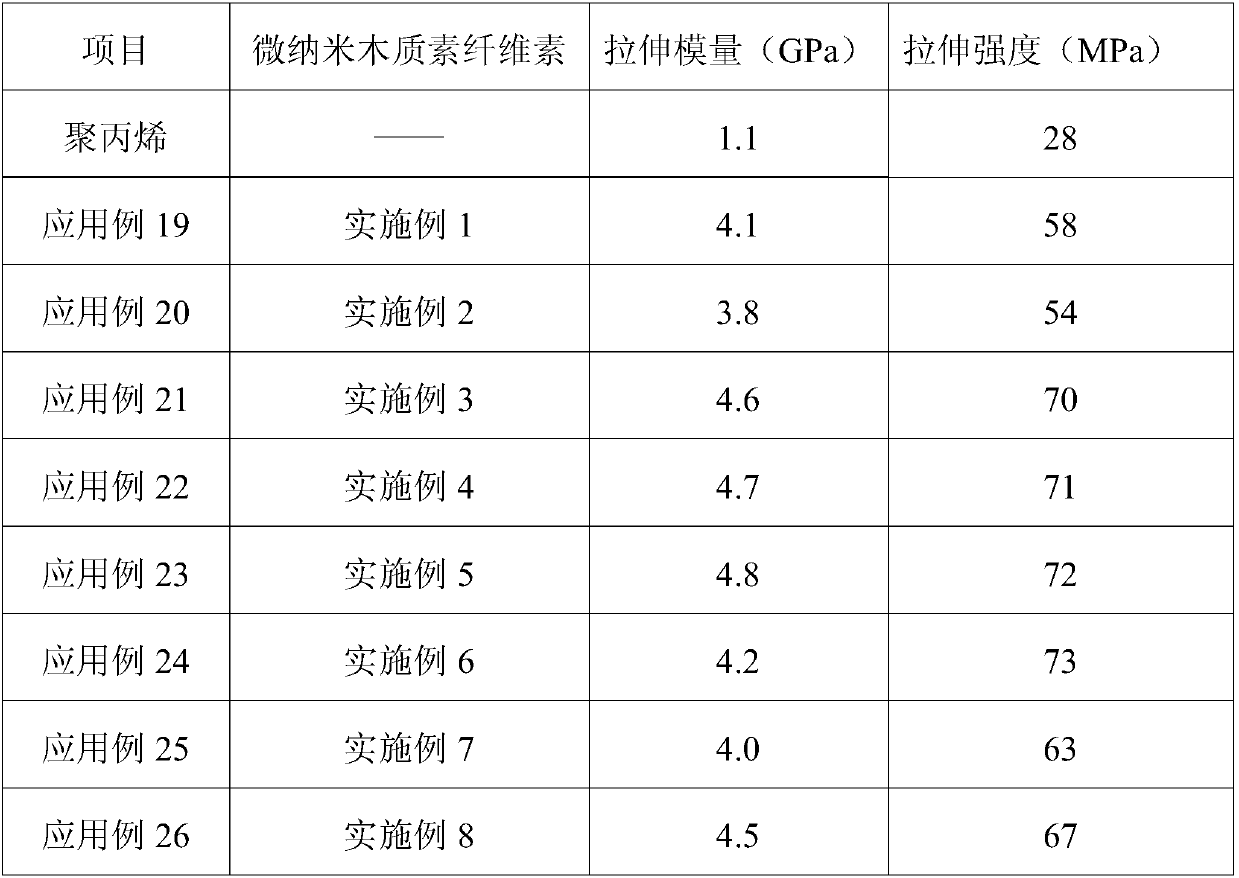
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A micro-nano lignocellulose prepared by the following method:
[0054] (1) Weigh 10g of xylose residue (containing 70wt% cellulose, 28wt% lignin and 2wt% hemicellulose) after extracting hemicellulose from corncobs, dissolve it in 490mL deionized water, and heat to 60°C Stir evenly to obtain a raw material dispersion (concentration 2wt%);
[0055] (2) Place the xylose residue raw material dispersion liquid obtained in step (1) in a sand mill, and keep the temperature of the raw material dispersion liquid at 60°C for 2 times of circular sand milling to obtain a stripped object with a diameter of about 400nm;
[0056] (3) Transfer the exfoliation prepared in step (2) to a high-pressure homogenizer, and under the pressure of 75MPa, while keeping the solution temperature at 60°C, high-pressure crushing 5 times to obtain a dispersion of micronano lignocellulose liquid.
[0057] The micro-nano lignocellulose has a diameter of 100-150 nm, an aspect ratio of 220-250, and a lig...
Embodiment 2~6
[0059] A kind of micro-nano lignocellulose, the only difference from Example 1 is that the stirring temperature in step (1) is 50°C (Example 2), 70°C (Example 3), 75°C (Example 4) , 80°C (Example 5), and 85°C (Example 6).
Embodiment 2
[0060] The micronano lignocellulose obtained in Example 2 has a diameter of 80-170 nm, an aspect ratio of 230-260, and a lignin content of 27 wt%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com