A method for removing and recovering copper in copper-containing molten iron
A technology for recovering copper, copper and iron, which is applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve problems such as difficulty in guaranteeing process continuity and stability, decline in decopper ability, high equipment requirements, etc., to achieve directional mass transfer and enrichment, equipment and environment The effect of low requirements and simple process operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
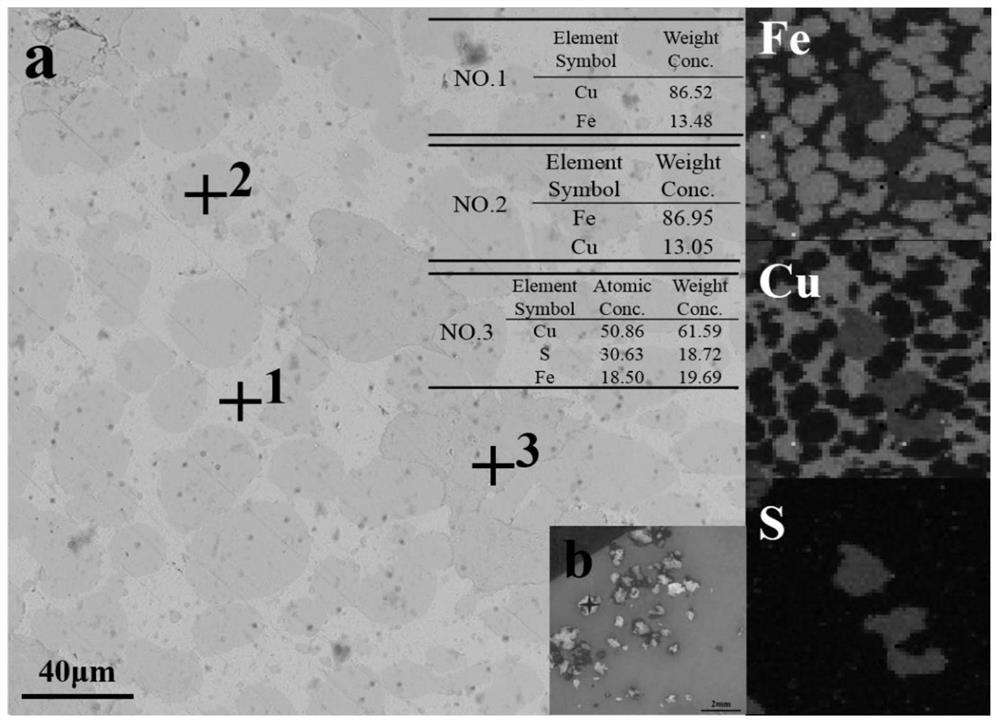
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
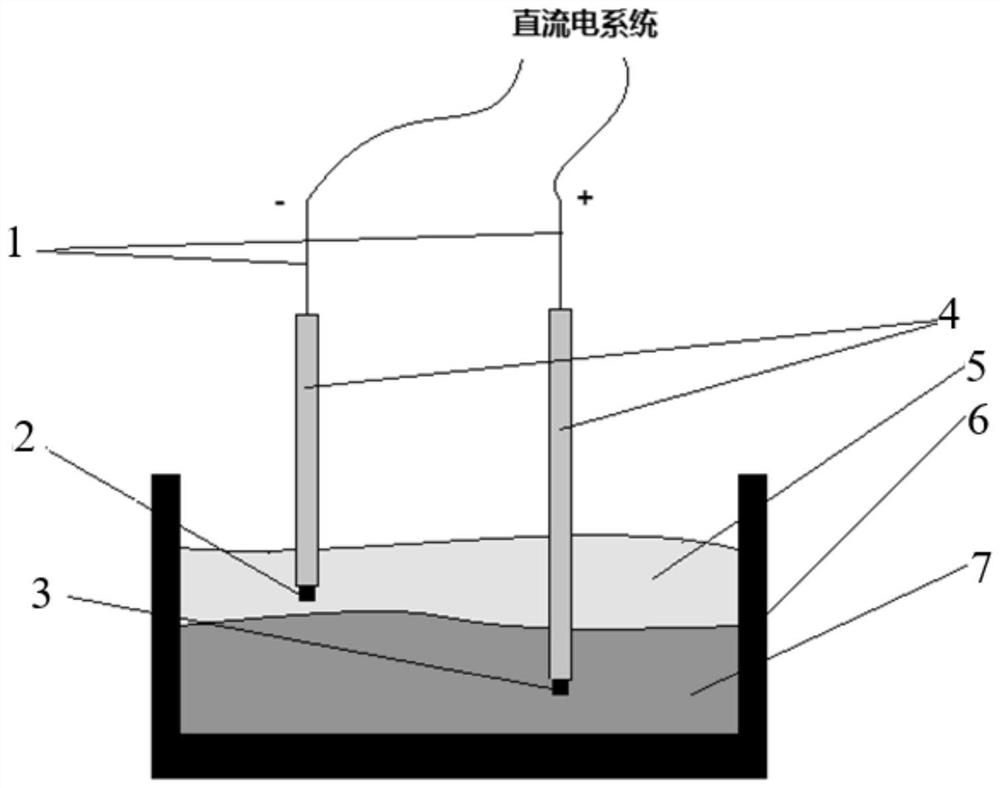
[0050] In this embodiment, the molten iron containing 5wt% Cu is subjected to the de-Cu treatment of the sulfide slag system and the DC electric field, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0051] (1) Preparation of copper removal slag system: for the molten iron environment, preparation of FeS-Na 2 S binary sulfide slag system, prepare 100g decopper slag system at a molar ratio of 2:8.
[0052] (2) Copper removal from sulfide slag: 380g of pig iron is crushed and mixed with 20g of pure copper particles, put into figure 1 The electrolytic cell 7 in the present invention does not limit the material structure and type of the electrolytic cell 7, as long as it meets the functions of insulation and holding slag iron at high temperature. In a heating furnace under the protection of an inert gas, raise the temperature of iron slag to 1300°C and melt it, then add the sulfide decopper slag system prepared in step (1). The type of inert gas is not limited, preferably argon.
[005...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com