Method for degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by using zero-valent iron activated persulfate
A technology for activating persulfate and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, applied in the application field of soil pollution control, can solve the problems of unfavorable pollutant reaction and degradation effect reduction, and achieve the effect of difficult removal, simple operation and wide pH application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Dissolve 10 mg of phenanthrene in 100 ml of acetone solution to prepare a phenanthrene mother solution with a concentration of 100 mg / L. Take 10ml of phenanthrene mother liquor in the reaction bottle, then add 10ml of ultrapure water, then add 6mg of nanometer zero-valent iron to the reaction system, and finally add 0.238g of sodium persulfate, and place the reaction bottle on a mixer for reaction . The molar ratio of nanometer zero-valent iron to sodium persulfate in the system is 0.1:1, and the reaction temperature is room temperature.
[0028] Sampling was carried out after 0min, 5min, 10min, 30min, and 60min of the reaction respectively. There were 8 sampling points in total. The percentage of the ratio of the concentration of phenanthrene in the sample at each time to the initial concentration.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the molar ratio of zero-valent iron to sodium persulfate dosage is 1:1.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Compared with Example 1, the only difference is that the molar ratio of zero-valent iron to sodium persulfate dosage is 0.5:1.
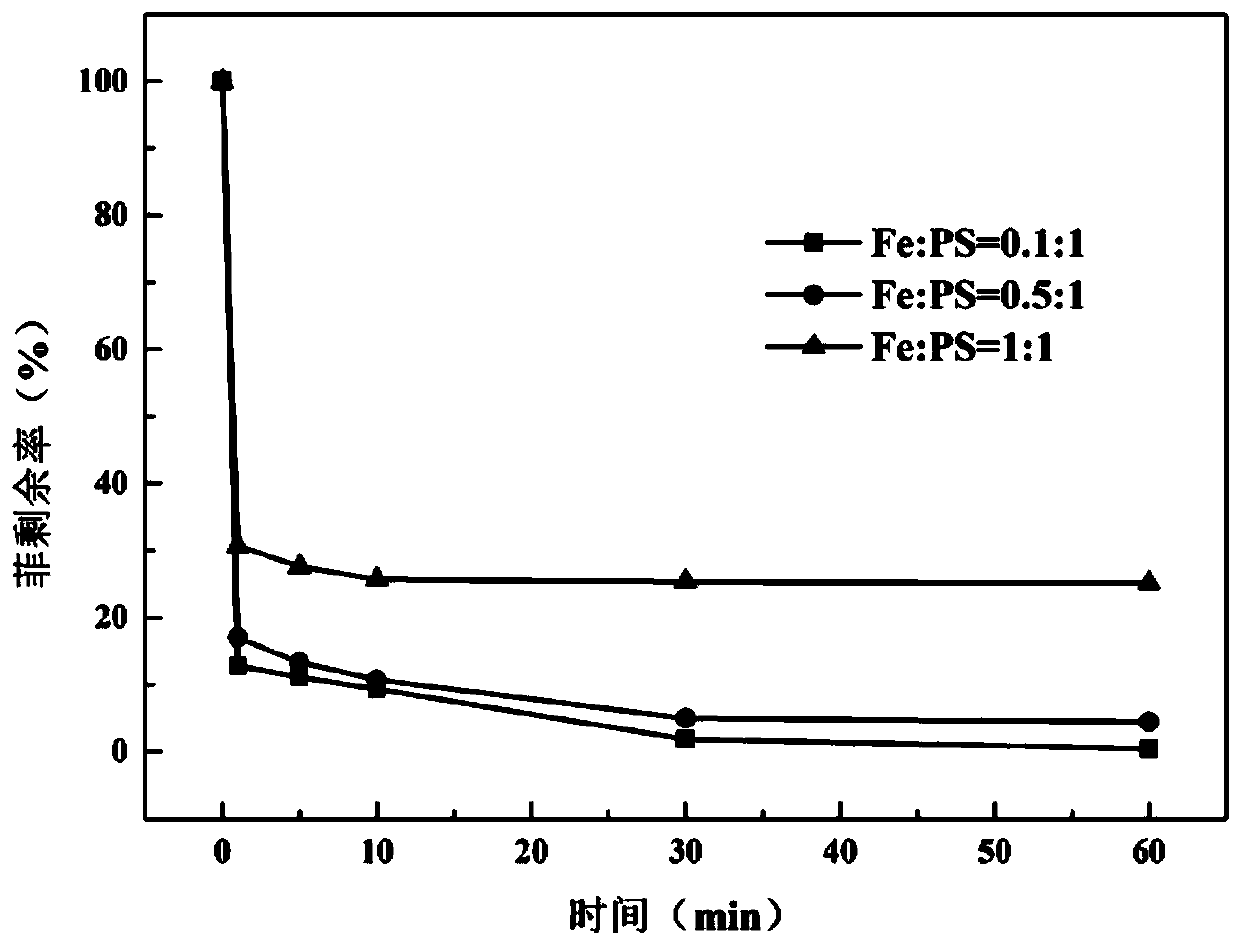
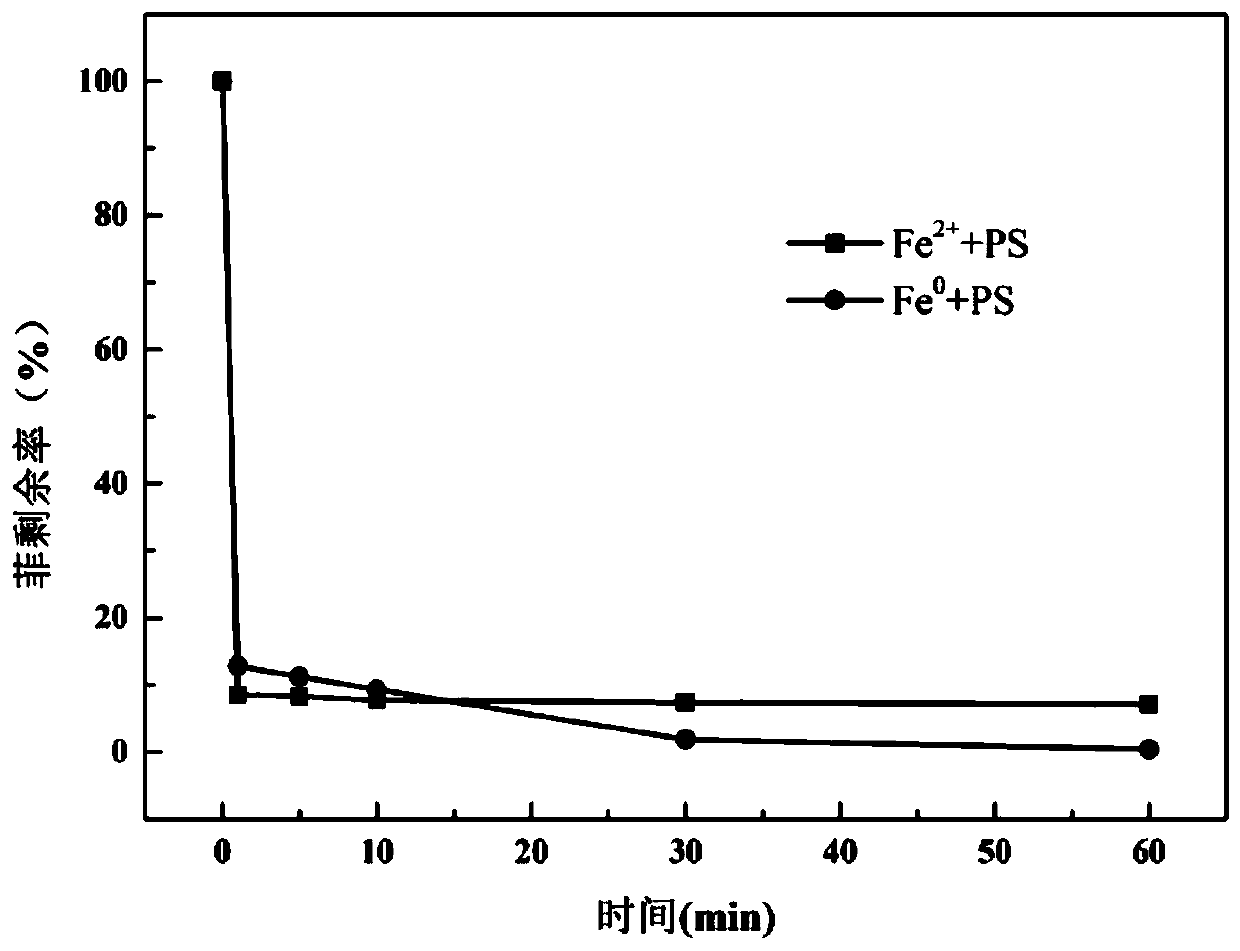
[0033] In embodiment 1~3, the remaining rate-time relationship figure of the obtained phenanthrene is as follows figure 2 As shown, the ordinate in the figure is the remaining rate of phenanthrene, and the abscissa is the reaction time. The degradation effect is reflected by the phenanthrene residual rate. The smaller the phenanthrene residual rate, the better the degradation effect. The phenanthrene residual rate is the percentage of the ratio of the concentration of phenanthrene in the sample to the initial concentration of phenanthrene at each moment. figure 2 It reflects the effect of different proportions of zero-valent iron and persulfate on the degradation effect.
[0034] Embodiments 1 to 3 utilize different ratios of zero-valent iron and persulfate to degrade phenanthrene, by figure 2 It can be seen that when the molar ratio of z...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com