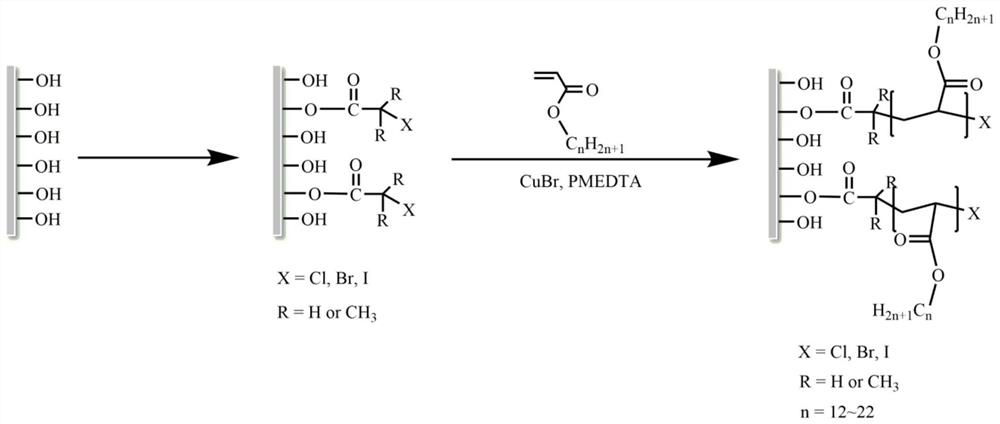
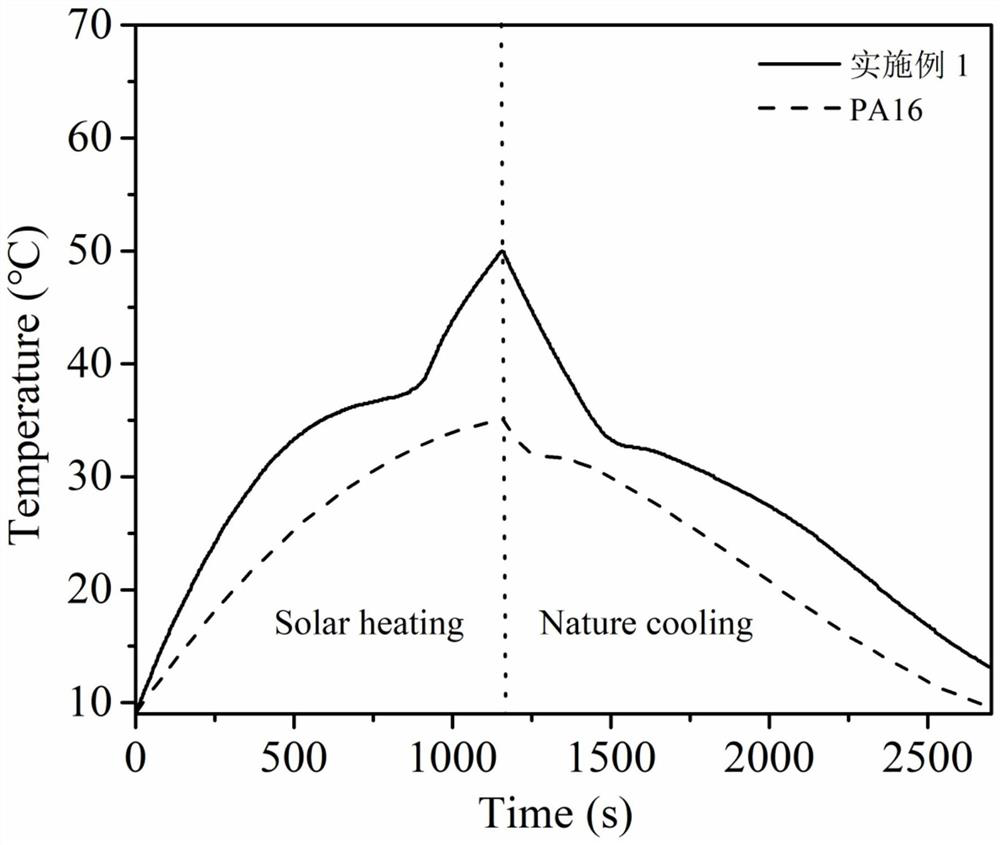
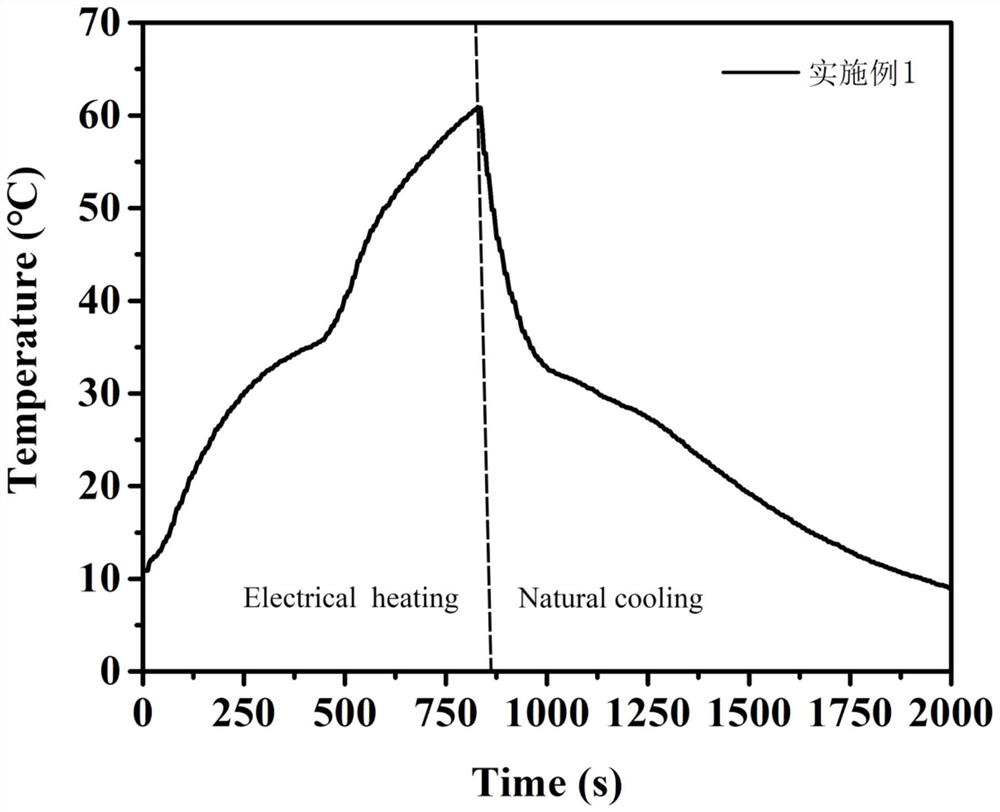
A method and application for preparing gn@cellulose-based solid-solid phase change fibers in different phases
A technology of cellulose fiber and phase change fiber, which is applied in plant fiber, fiber treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem that the flexibility of graphene-based phase change materials is not suitable for secondary processing and the heat conduction of cellulose polymer phase change materials Low stability, incapable of energy storage and diffusion, etc., to achieve excellent thermal cycle stability and structural controllability, narrow phase transition temperature range, and less defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] 1) Dry the cotton pulp in a vacuum drying oven at 60° C. for 12 hours; take the dried cotton pulp and disperse it in DMF at a temperature of 65° C. to obtain a cellulose fiber dispersion with a mass fraction of 8 wt %;
[0047] 2) The cellulose fiber dispersion is cooled to room temperature, and 2-bromopropionyl bromide is added dropwise to the cellulose fiber dispersion in an ice-water bath to react with cellulose, and the 2-bromopropionyl bromide and the cellulose unit ring The molar ratio of the hydroxyl groups is 3:1; after the dropwise addition is completed, the reaction is placed at room temperature for 3 hours; then heated to 50 °C for 2 hours; after the reaction is completed, the product is cooled to room temperature, and distilled water is added to remove unreacted raw materials and by-products, After suction filtration, rinsed repeatedly to obtain a white solid; then vacuum-dried at 50° C. to obtain a white solid product, cellulose bromopropionate, with a yield...
Embodiment 2
[0054] 1) drying the bamboo pulp in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for 12h; taking the dried bamboo pulp and dispersing it in DMSO at a temperature of 80°C to obtain a cellulose fiber dispersion with a mass fraction of 10wt%;
[0055] 2) The cellulose fiber dispersion is cooled to room temperature, and 2-iodopropionyl bromide is added dropwise to the cellulose fiber dispersion in an ice-water bath to react with cellulose, and the 2-iodopropionyl bromide and the cellulose unit ring. The molar ratio of the middle hydroxyl group is 5:1; after the dropwise addition, the reaction is placed at room temperature for 2 hours; then heated to 50 °C for 6 hours; after the reaction is completed, the product is cooled to room temperature, and distilled water is added to remove unreacted raw materials and by-products, After suction filtration, rinsed repeatedly to obtain a white solid; then vacuum-dried at 60° C. to obtain a white solid product, cellulose iodopropionate, with a yield of 93%;
...
Embodiment 3
[0061] 1) Dry the cotton linters in a vacuum drying oven at 90°C for 12 hours; take the dried cotton linters and stir and disperse them in DMAC at a temperature of 80°C to obtain a cellulose fiber dispersion with a mass fraction of 9 wt%;
[0062] 2) The cellulose fiber dispersion is cooled to room temperature, and in an ice-water bath, 2-chloropropionyl bromide is added dropwise to the cellulose fiber dispersion to react with cellulose, wherein 2-chloropropionyl bromide and cellulose units The molar ratio of hydroxyl groups in the ring is 6:1; when the dropwise addition is completed, the reaction mixture is placed at room temperature for 4 hours; then heated to 50°C for 3 hours; after the reaction is completed, the product is cooled to room temperature, and distilled water is added to remove unreacted raw materials and by-products, and repeatedly rinsed after suction filtration to obtain a white solid; the obtained product was vacuum-dried at 60 °C to obtain a white solid prod...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com