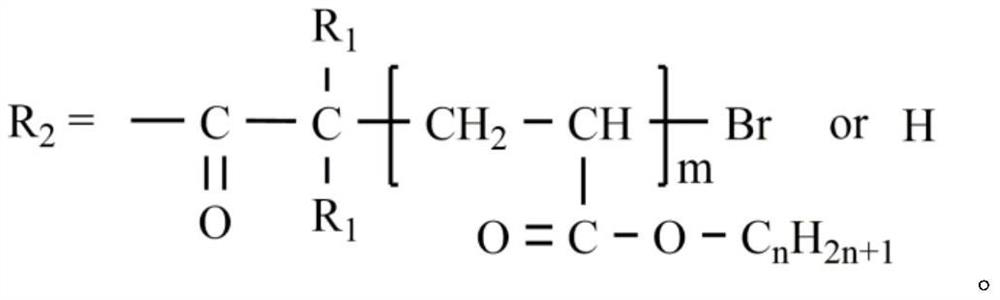A kind of gn@cellulose-based solid-solid phase change material and its preparation method and application
A phase change material, cellulose-based technology, applied in heat exchange materials, fiber chemical characteristics, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of low thermal conductivity of cellulose polymer phase change materials and flexibility of graphene-based phase change materials It is not suitable for secondary processing and molding, and achieves the effects of narrow phase transition temperature range, excellent thermal cycle stability, structural controllability, and fast heating rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
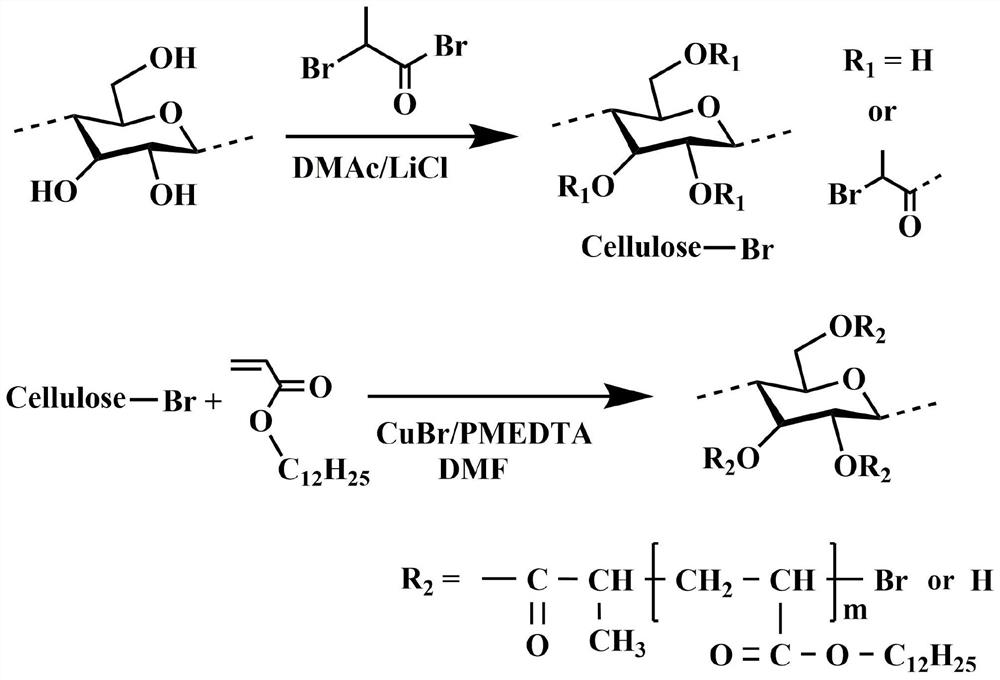
[0039] The present invention also provides a preparation method (method for short) of a GN@cellulose-based solid-solid phase change material, characterized in that the method comprises the following steps:
[0040] (1) Cellulose dissolution: the dried cellulose is stirred and dissolved in the solvent A at a temperature of 65 to 95° C. to obtain a cellulose solution with a mass fraction of 5 to 15 wt %;
[0041] In step 1), the cellulose is microcrystalline cellulose, cotton pulp, cotton linters, cotton, wood pulp, bamboo pulp, cellulose filter paper or absorbent cotton;
[0042] The solvent A is a solvent capable of dissolving cellulose, specifically a mixed solution of paraformaldehyde (PF) / dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a mixed solution of lithium chloride / N,N-dimethylformamide or Ionic liquid; in the mixed solution of paraformaldehyde and dimethyl sulfoxide, the mass ratio of paraformaldehyde and dimethyl sulfoxide is 1:(8~12); lithium chloride and N,N-dimethyl sulfoxide In th...
Embodiment 1
[0066] 1) Dry the microcrystalline cellulose in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for 12 hours; take the dried microcrystalline cellulose and dissolve it in dimethyl sulfoxide / paraformaldehyde (DMSO / PF) (the mass ratio of DMSO to PF is In 12:1), the concentration of microcrystalline cellulose is 8 wt.%, and mechanical stirring is performed at 95° C. until it becomes a homogeneous system to obtain a cellulose solution;
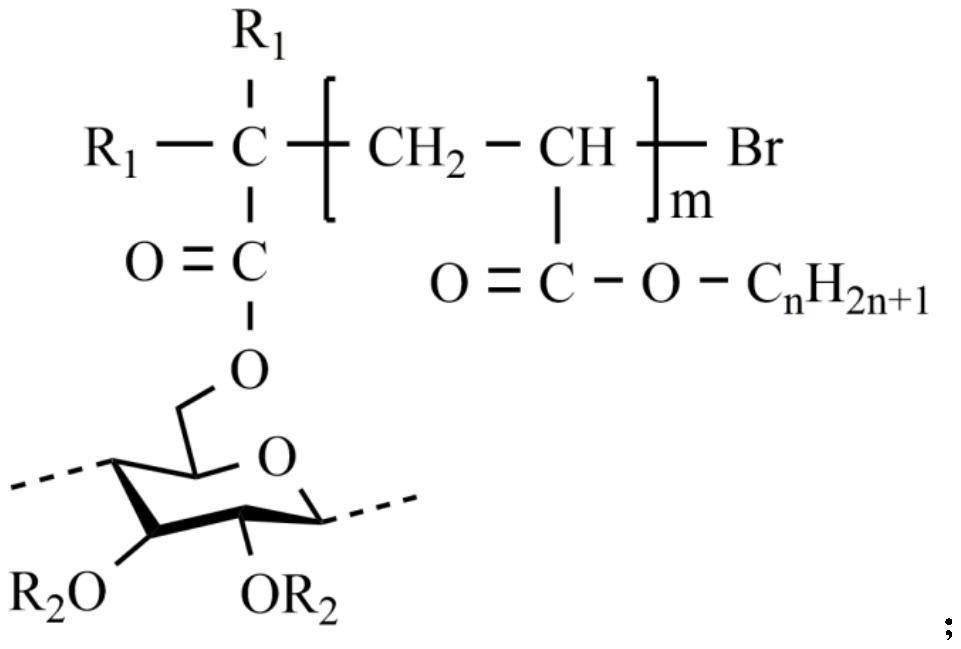
[0067] 2) The cellulose solution is cooled to room temperature, and in an ice-water bath, 2-bromopropionyl bromide is added dropwise to the cellulose solution to react, wherein the mol ratio of hydroxyl and 2-bromopropionyl bromide in the cellulose unit ring is 1:3; after the dropwise addition, it was placed at room temperature for 3 hours; then heated to 50°C for 2 hours; the product was cooled to room temperature, distilled water was added to remove unreacted raw materials and by-products, and the crude product was obtained by repeated rinsing and suction filtratio...
Embodiment 2
[0076] 1) Dry the cotton fiber in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for 12 h; take the dried cotton fiber and dissolve it in 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (AmimCl) solution, and the concentration of the cotton fiber is 9wt. %, mechanically stirred at 95°C until a homogeneous system was obtained to obtain a cellulose solution;
[0077] 2) The cellulose solution is cooled to room temperature, and 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide is added dropwise to the cellulose solution in an ice-water bath to react, wherein the mol ratio of hydroxyl and 2-bromoisobutyryl in the cellulose unit ring The ratio is 1:4; after the dropwise addition, the reaction is placed at room temperature for 3 hours; then heated to 50°C for 2 hours; the product is cooled to room temperature, distilled water is added to remove unreacted raw materials and by-products, and the crude product is obtained by repeated washing and suction filtration; The crude product was heated and dissolved in acetone, and distilled water...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com