Flocculating agent for microalgae capture and preparation method and application of flocculating agent
A flocculant and microalgae technology, applied in the field of microalgae capture, can solve the problems of poor flocculation performance, increase in flocculant dosage, consumption of large flocculant, etc., and achieve the effect of strong charge neutralization ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
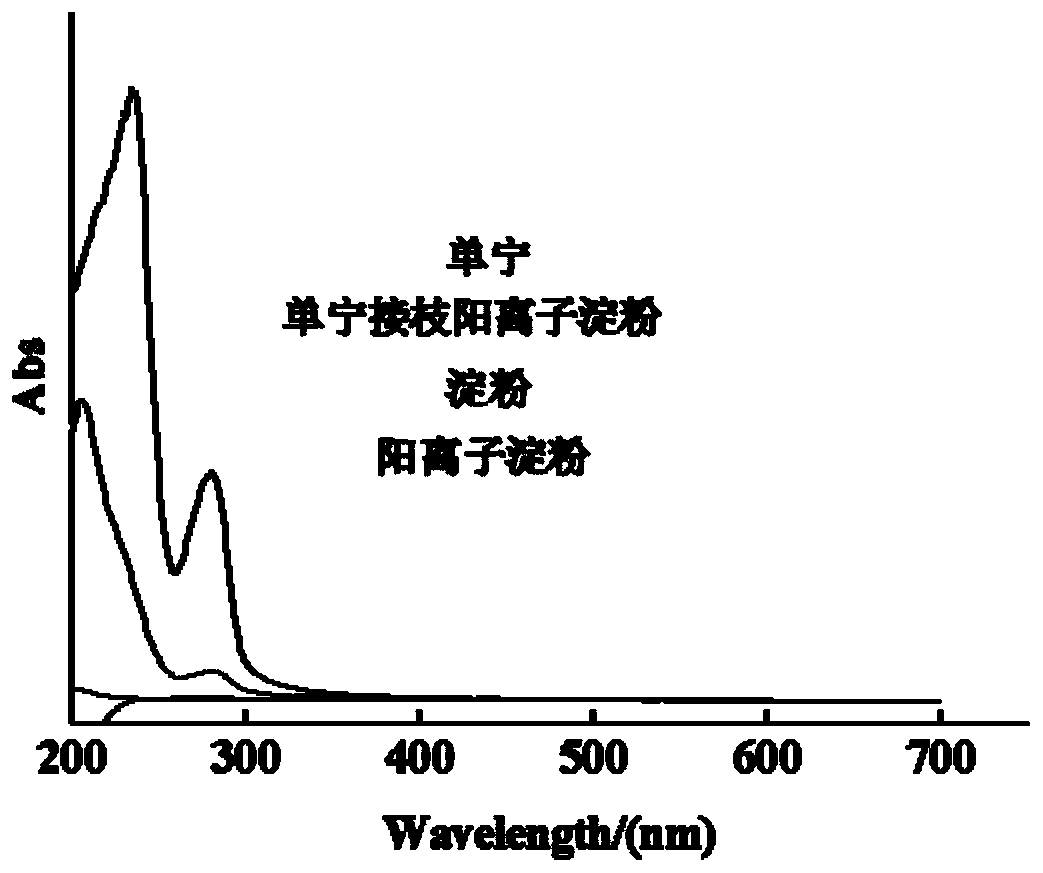
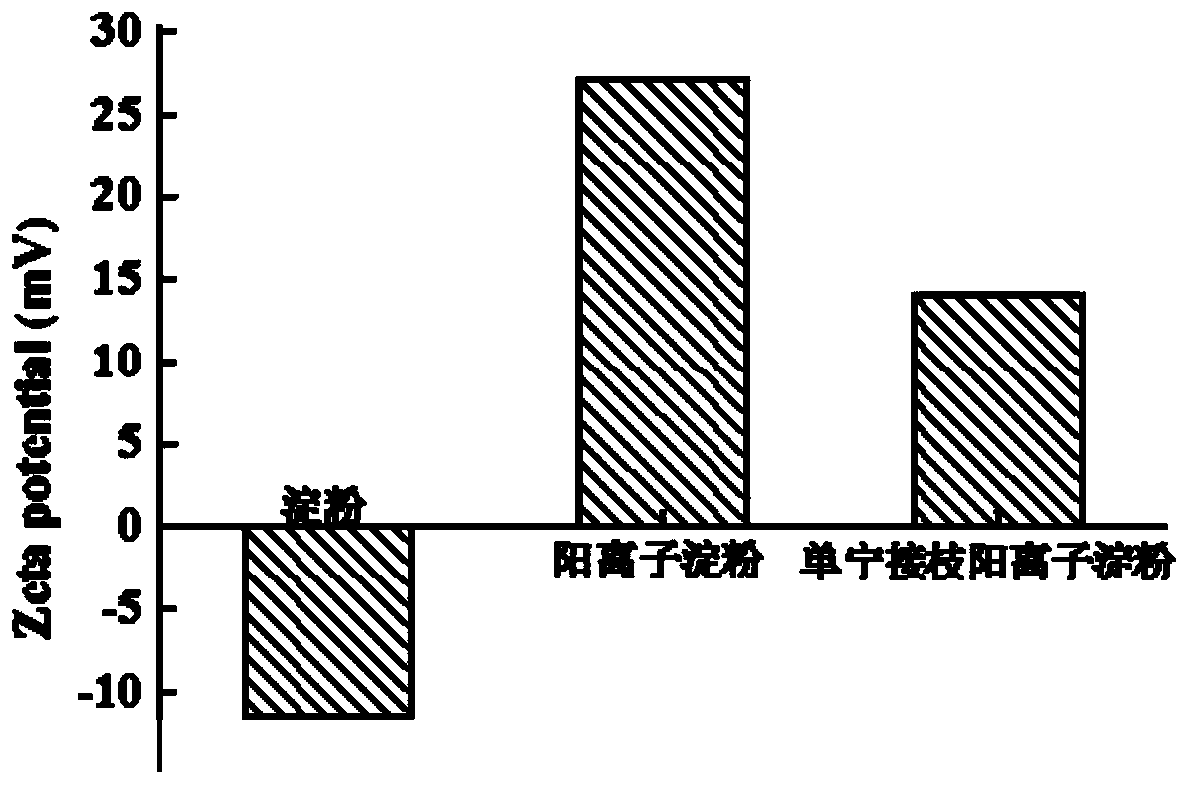
[0027] A flocculant for capturing microalgae, comprising a cationic starch substrate and tannic acid grafted on the substrate, the grafting degree of the tannic acid on the substrate is about 20%. The preparation steps of this flocculant are as follows:
[0028] S1: Spray 30g of 2% sodium hydroxide solution evenly into 100g of starch and stir evenly, then add 20g of 2,3-epoxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride, mix well and react at 65°C 6h; then wash the product with 80% ethanol solution, then dry and grind to obtain cationic starch; the degree of substitution of the obtained cationic starch is about 0.2;
[0029] S2: Dissolve 1g of cationic starch in 25g of distilled water to obtain a cationic starch suspension; add 0.05g of vitamin C and 1g of hydrogen peroxide (1mol / L) to the cationic starch suspension, stir and react at room temperature for 30min, and then add 10g of water ethanol, and dropwise added 25 g of 5% tannic acid aqueous solution, and reacted at room temperature f...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A flocculant for capturing microalgae, comprising a cationic starch base and gallic acid tannin grafted on the base, the grafting degree of the gallic acid tannin on the base is about 4%. The preparation steps of this flocculant are as follows:
[0033] S1: Spray 30g of 2% sodium hydroxide solution evenly into 100g of starch and stir evenly, then add 20g of 2,3-epoxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride, mix well and react at 70°C 5h; then wash the product with 80% ethanol solution, then dry and grind to obtain cationic starch; the degree of substitution of the obtained cationic starch is about 0.2;
[0034] S2: Dissolve 1 g of cationic starch in 30 g of distilled water to obtain a cationic starch suspension; add 0.08 g of vitamin C and 1 g of hydrogen peroxide (1 mol / L) to the cationic starch suspension, stir and react at room temperature for 35 minutes, and then add 10 g of water ethanol, and dropwise adding 25 g of a gallic acid tannin aqueous solution with a mass concen...
Embodiment 3
[0037] A flocculant for capturing microalgae, comprising a cationic starch substrate and tannic acid grafted on the substrate, the grafting degree of the tannic acid on the substrate is about 12%. The preparation steps of this flocculant are as follows:
[0038] S1: Spray 30g of 2% sodium hydroxide solution evenly into 100g of starch and stir evenly, then add 20g of 2,3-epoxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride, mix well and react at 65°C 8h; then wash the product with 80% ethanol solution, then dry and grind to obtain cationic starch; the degree of substitution of the obtained cationic starch is about 0.2;
[0039] S2: Dissolve 1g of cationic starch in 25g of distilled water to obtain a cationic starch suspension; add 0.1g of vitamin C and 1g of hydrogen peroxide (1mol / L) to the cationic starch suspension, stir and react at room temperature for 40min, and then add 10g of water ethanol, and dropwise added 25 g of a 2% tannic acid aqueous solution, and reacted at room temperature ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com