Method for rapidly obtaining bacterial drug resistance by detecting number of bacteria on gel
A technology of drug resistance and bacteria, which is applied in the field of quickly obtaining bacterial drug resistance by detecting the number of bacteria on the gel, can solve the problems of long time consumption, and achieve the effect of strong water absorption capacity and high water content of the gel
Active Publication Date: 2020-01-14
上海氘峰医疗科技有限公司
View PDF8 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Both methods require bacteria to grow for 16-24 hours to determine the MIC of antibacterial drugs, which takes a long time
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
[0033] Preparation of agarose gel glass slide with a mass fraction of 2%: prepare an agarose solution with a mass fraction of 2%, dissolve it by microwave heating, take 1-2mL of agarose gel, drop it on a glass slide, and cover it with a cover glass , press lightly to make the surface of the agarose gel flat, slide out the cover slip gently after solidification, and place it at room temperature for later use.
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
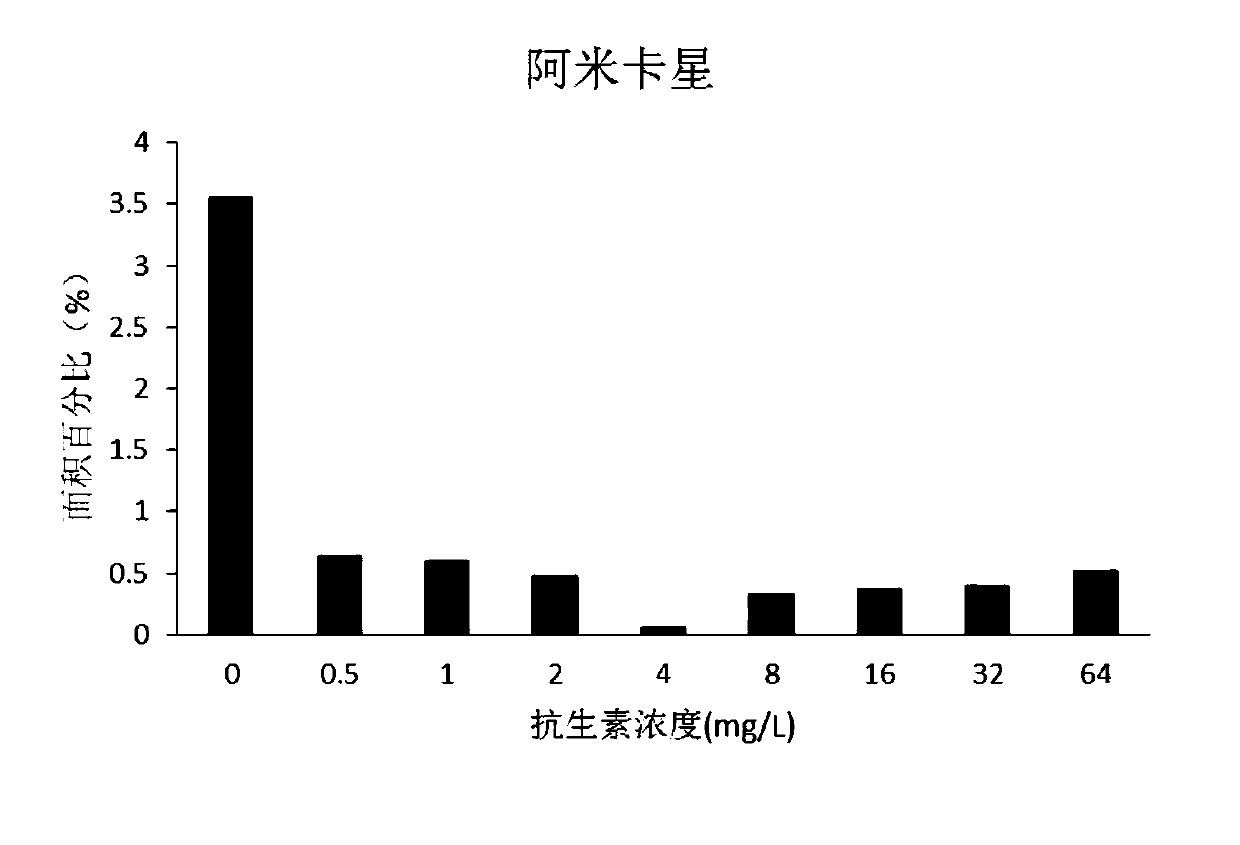
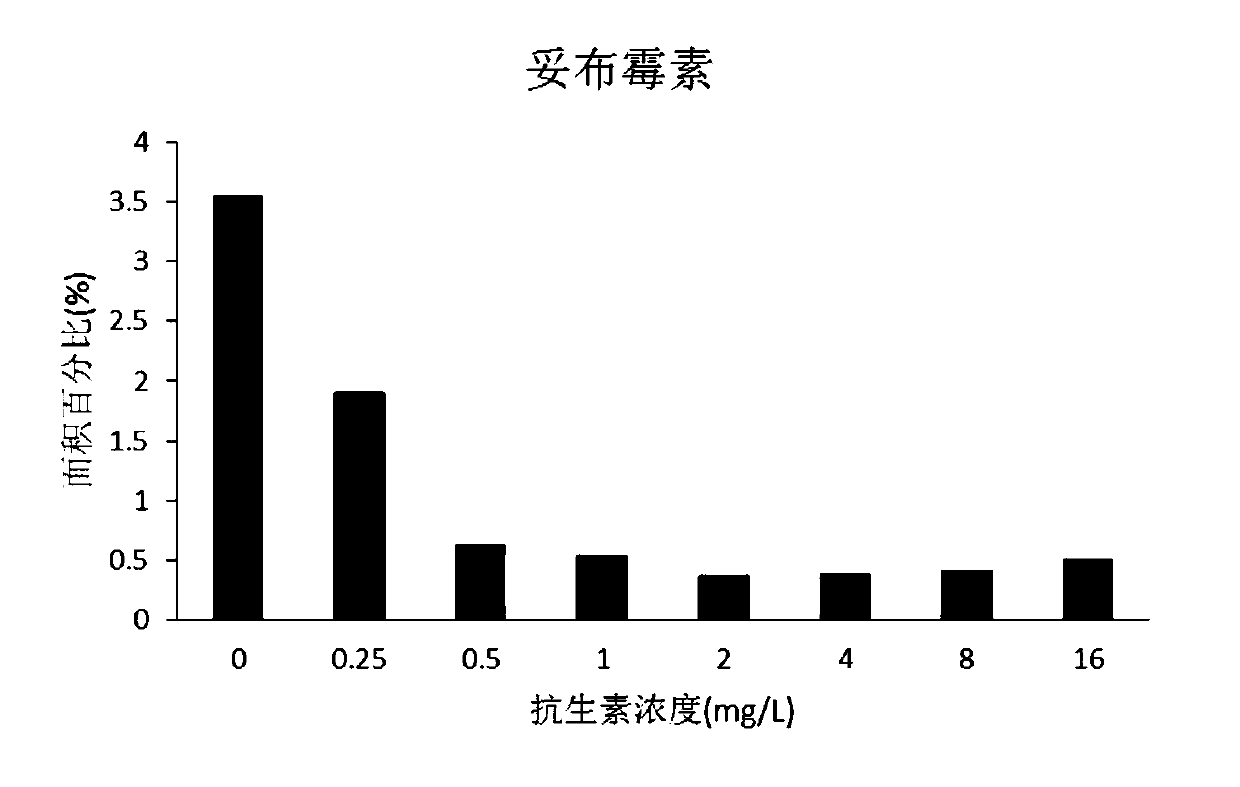
The invention relates to a method for rapidly obtaining bacterial drug resistance by detecting number of bacteria on a gel, and is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: bacterial liquid obtained after the action of a to-be-detected drug is subjected to dropwise adding onto the agarose gel; water, inorganic salt and small organic molecules in the bacterial liquid enter a net structure of the agarose gel, only bacteria are left on the surface of the gel, whether the selected bacteria have drug resistance to the drug to be detected or not is judged by detecting the number of the bacteria on the surface of the gel, and the minimum inhibitory concentration of the drug to be detected to the selected bacteria is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the MIC can be quickly judged by observing the number of bacteria within 2-3 hours without culturing and incubating for 16-24 hours, and medication guidance is given. The MIC obtained by the method disclosed by the invention is in a range which is one time higher than or equal to the MIC obtained by a trace broth dilution method, and according to clinical standards, the drug resistance result obtained by the method disclosed by the invention is completely consistent with that obtained by a clinical gold standard trace broth dilution method.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to a method for detecting bacterial drug resistance, in particular to a method for quickly obtaining bacterial drug resistance by detecting the number of bacteria on a gel. Background technique [0002] The significance of antimicrobial drug sensitivity test is to predict the effect of antibacterial treatment, guide the clinical application of antibacterial drugs, discover or suggest the existence of bacterial drug resistance mechanism, help clinicians choose appropriate drugs, avoid or aggravate bacterial drug resistance, detect bacterial Drug resistance and analysis of changes in drug resistance (Clinical Microbiology Testing Technology. Liu Yunde, Lou Yongliang). At present, the traditional drug susceptibility methods mainly include disk diffusion method and micro broth dilution method. In the disk method, the size of the inhibition zone of antibacterial drugs can be read only after the bacterial colonies are covered with the c...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): C12Q1/18C12Q1/14C12Q1/10C12Q1/06C12Q1/04C12R1/19C12R1/385C12R1/445C12R1/01
CPCC12Q1/18C12Q1/14C12Q1/10C12Q1/06C12Q1/045G01N2333/245G01N2333/21G01N2333/31G01N2333/315Y02A50/30
Inventor 罗艳君衣晓飞彭迪
Owner 上海氘峰医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com