Method for removing bacterial contamination in fungi
A bacterial contamination and fungus technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of large restrictions on antibiotics and insignificant bacteriostatic effect, and achieve the effect of excellent bacterial removal effect, avoiding the use of antibiotics, and short experimental period.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Test materials:
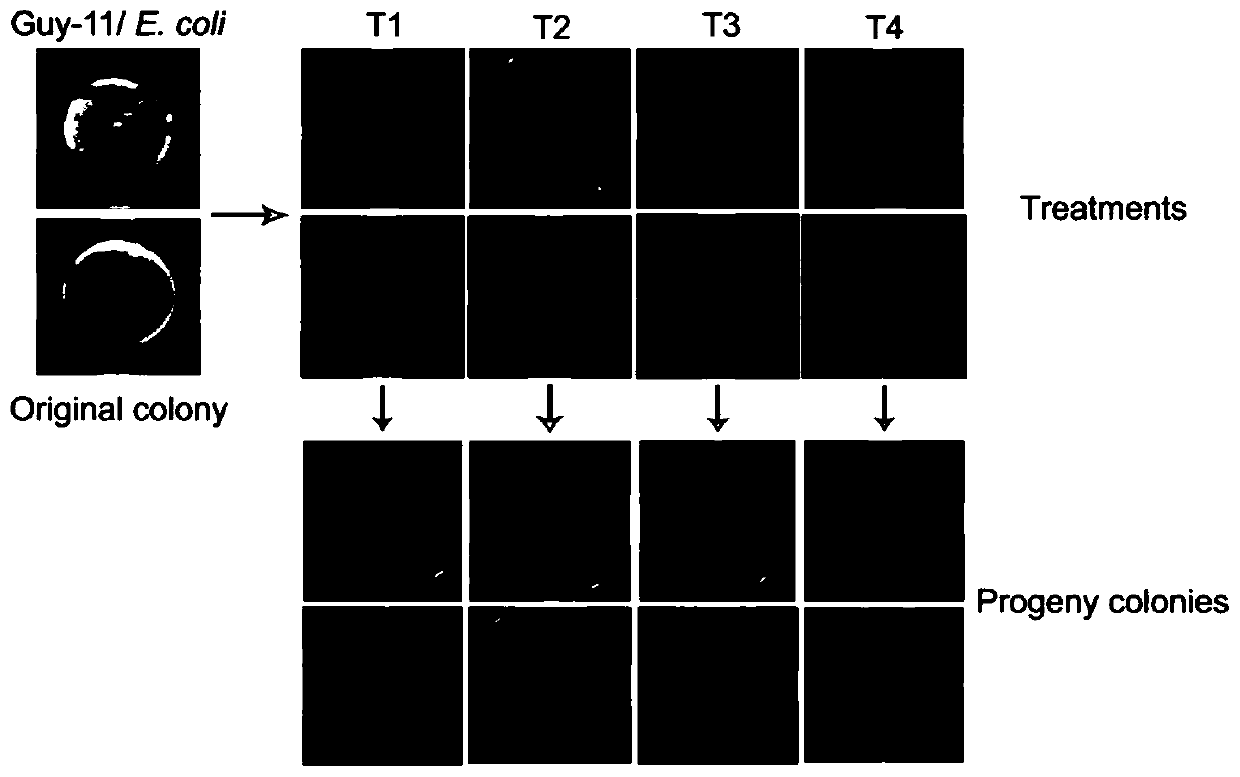
[0038] Rice blast pathogen: Magnaporthe oryzae Guy-11 was used as a strain of Magnaporthe oryzae, which was preserved by the Fungal Disease Room of the Institute of Plant Protection and Microbiology, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences. In this example, Magnaporthe oryzae Guy-11 was contaminated by Escherichia coli (E. coli for short).
[0039] Specifically follow the steps below:
[0040] (1) Preparation of medium: According to the growth rate of Magnaporthe grisea in the medium suitable for fungal culture, the CM medium used to remove bacterial contamination in fungi was screened. Among them, the medium (CM) for plate culture: 10g glucose, 2g peptone, 1g yeast extract, 1g casamino acid, 50mL nitrogen salt (20×Nitrate salts; trace elements; vitamins), 18g agar, ddH2O constant volume to 1000mL, 1M NaOH solution to adjust the pH to 6.5, sterilized by high pressure steam at 121℃ for 15min.
[0041] (2) Pre-treatment of the culture medium: Cut ou...
Embodiment 2
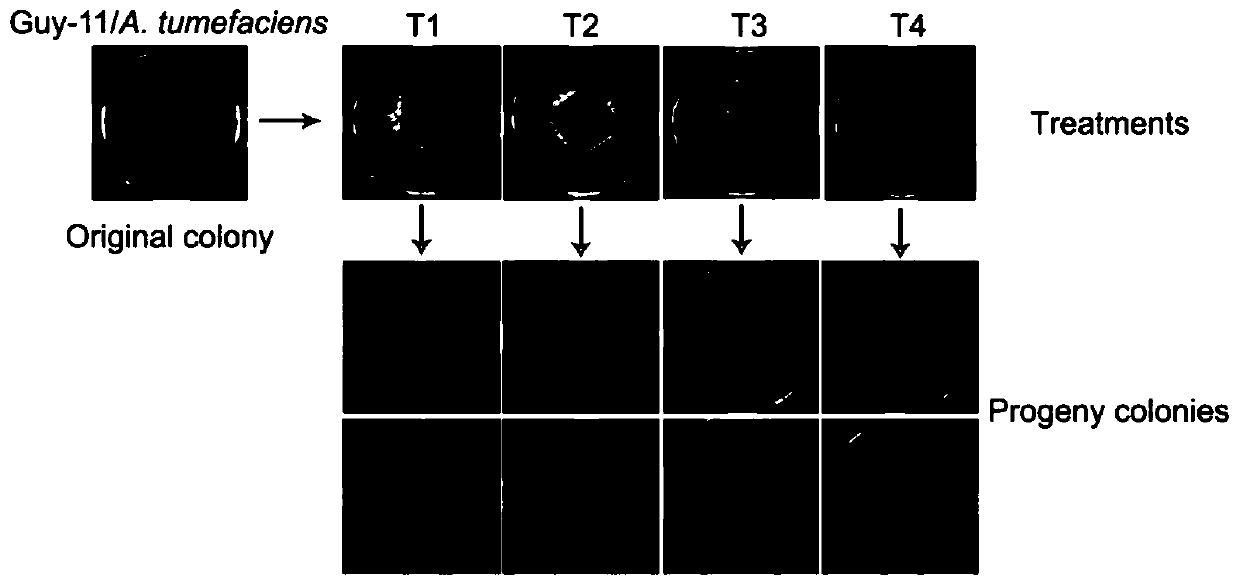
[0048] Select the rice blast fungus Guy-11 polluted by agrobacterium as object, and other are with embodiment 1, carry out agrobacterium removal experiment to blast fungus Guy-11 bacterial strain, experimental result is as follows figure 2 As shown, there is no difference in effect between T1 and T2. The blast fungus Guy-11 was purified after treatment, and its growth rate on the medium, colony behavior, sporulation and other traits were all restored and improved. T1 saves the use of antibiotics relative to T2. After T3 treatment, there was some improvement, but the fungal colonies could not be completely purified. After T4 treatment, the bacterial contamination and culture traits of Magnaporthe grisea Guy-11 strain were not improved, so it could no longer be used for scientific research and teaching. Genomic DNA was extracted from strains T1, T2, T3, and T4, and PCR detection was performed using Agrobacterium-specific primers. The results showed that fragments of Agrobacte...
Embodiment 3
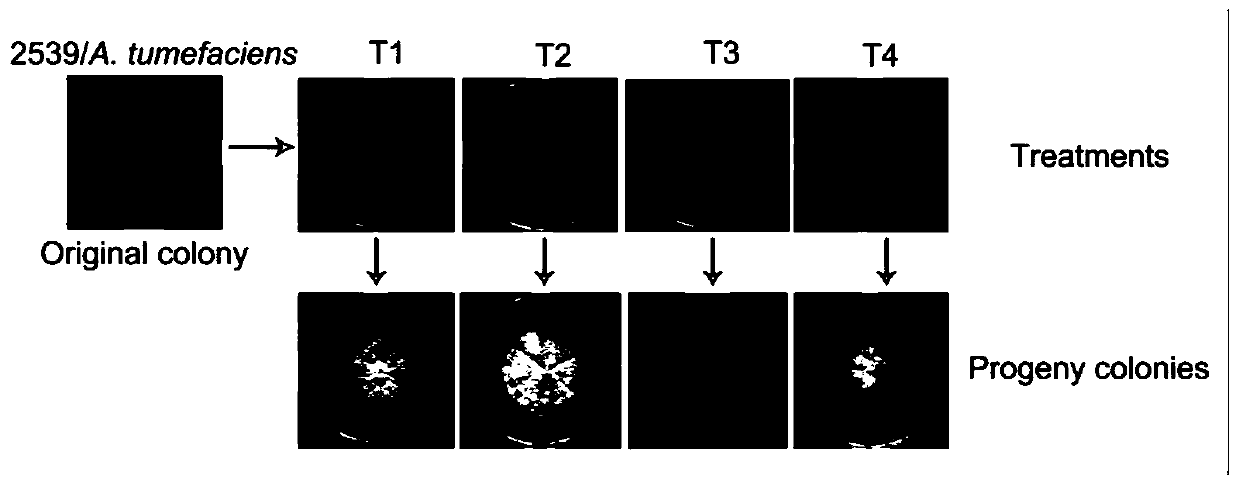
[0050] The Magnaporthe grisea 2539 bacterial strain contaminated by Agrobacterium was selected as the object, and the others were the same as in Example 1, and the Agrobacterium removal experiment was carried out on the Magnaporthe oryzae 2539 bacterial strain. Experimental results such as image 3 As shown, there is no difference in effect between T1 and T2, and the treated Magnaporthe grisea 2539 strain grows well on the medium, the colony is purified, and the traits such as sporulation are restored. After T3 treatment, the strains were partially improved, but the fungal colonies could not be completely purified. After T4 treatment, the bacterial contamination and culture traits of Magnaporthe grisea 2539 strain were not improved, so it could no longer be used for scientific research and teaching. Genomic DNA was extracted from strains T1, T2, T3, and T4, and PCR detection was performed using Agrobacterium-specific primers. The results showed that fragments of Agrobacteriu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com