Polyolefin carbonization method
A polyolefin and thermoplastic polyolefin technology, applied in the field of carbonization of waste polymers, can solve the problems of a large number of catalysts, high energy consumption, complex process, etc., achieve great industrialization potential, simplify the preparation process, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] A carbonization method for polyolefins, comprising the steps of:
[0043] (1) Weigh 0.5g LLDPE (produced by Sinopec Maoming Petrochemical Co., Ltd., molecular weight is 141000g / mol) and 1g starch (produced by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.), put them into a ball mill, stir and mix at a speed of 70r / min 5min, a homogeneous mixture of the two was obtained.
[0044] (2) Transfer the mixture to a crucible, put the crucible into a muffle furnace, set the muffle furnace at a heating rate of 5°C / min to the carbonization temperature of 340°C, and keep it at this temperature for 30min.
[0045] (3) After natural cooling in the muffle furnace, the carbonized product was obtained, and the mass was weighed, and the yield was 35 wt%.
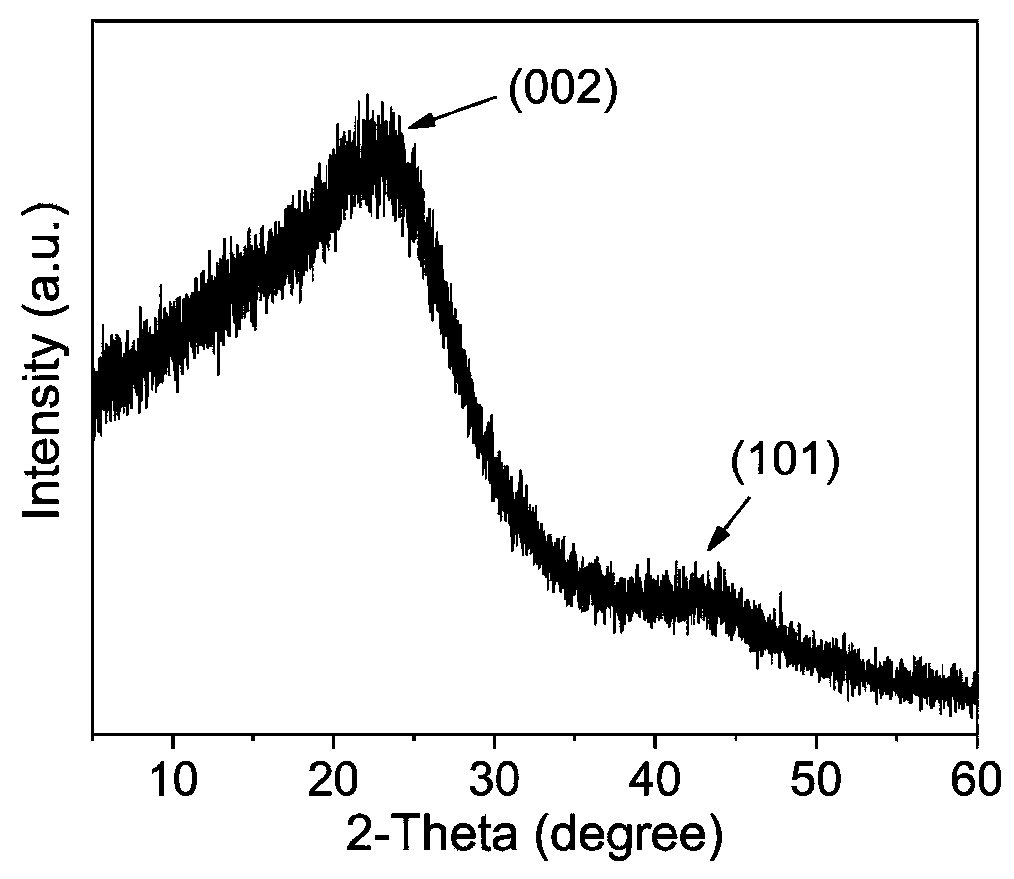
[0046] The prepared carbonized products such as figure 1 In the content (a) shown. The product is completely carbon black, indicating that the mixture of LLDPE and starch has been carbonized at 340 ° C, figure 2 The X-ray diffraction patter...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The biomass used in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is changed from starch to sodium lignosulfonate (produced by Shandong Haobo Chemical Co., Ltd., molecular weight is 52000g / mol), and other steps are unchanged to obtain the joint carbonization product of LLDPE and sodium lignosulfonate, The yield was 56 wt%.
[0049] The prepared carbonized products such as figure 1 In the content (b) shown. The product is completely carbon black, indicating that the mixture of LLDPE and sodium lignosulfonate has been carbonized at 340°C.
[0050] Figure 4 The infrared comparison spectrum shows that heating LLDPE at 340°C will generate a large number of oxygen-containing functional groups such as aldehyde groups, and sodium lignosulfonate will also generate a large number of oxygen-containing functional groups such as hydroxyl groups. After the two are co-carbonized, the obtained carbon material has a large amount of C-O Functional groups, indicating that the aldehyde group of LLD...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The biomass used in the above Example 1 was changed from starch to cellulose (produced by Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.), and other steps were kept unchanged to obtain a co-carbonized product of LLDPE and cellulose with a yield of 45 wt%.
[0053] The prepared carbonized products such as figure 1 In the content (c) shown. The product is completely carbon black, indicating that the mixture of LLDPE and cellulose has been carbonized at 320°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com