Wild edible fungus tissue separation method
A technology for tissue separation and fungus, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and separation of microorganisms, can solve the problems of lack of standardized operation of fungus and efficient drying methods, high pollution rate, etc., to save time and reduce pollution efficiency, efficient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Embodiment 1 A kind of wild fungus tissue separation method
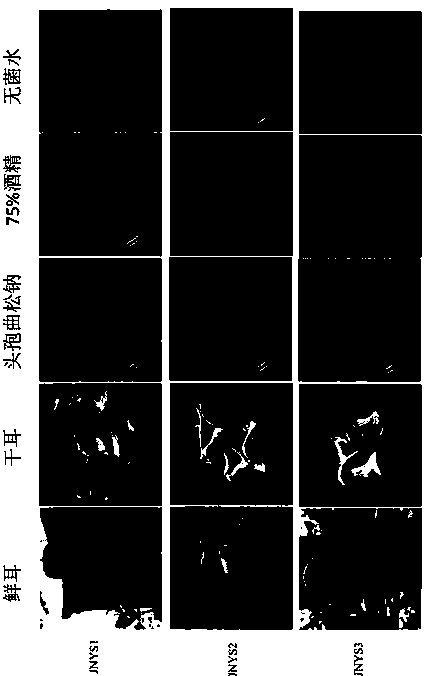
[0018] 1) Collect dried ears: Collect complete, mildew-free, and insect-free fungus, gently wipe off surface debris, put them in a hot air drying box for drying, set the drying temperature at 65°C, and collect dry ears after drying for 4-8 hours. Ear;
[0019] 2) Tissue separation: Use sterile forceps to remove the thinner tissue on the edge of the dry ear, and then take 0.3-0.6cm 2 Small and large tissues, placed in the prepared ceftriaxone sodium alcohol solution, soaked for 3-5min, taken out with tweezers, quickly passed through the flame twice, and transferred to a plate culture dish filled with PDA medium;
[0020] 3) Separation culture: place the petri dish in a constant temperature incubator at 25°C and incubate in the dark until the mycelium grows to the medium, pick the tip of the mycelium and inoculate it on the PDA medium, and the strain can be preserved after it is full;
[0021] Described ceftr...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2 Tissue Separation Example of Fresh Fruiting Body of Auricularia auriculae
[0024] 1. Collection and drying of fungus
[0025] Record the habitat and tree species of 3 fresh fungus collected in Jilin Agricultural University, and select complete, mildew-free, and insect-free fungus to gently wipe off the surface debris. They are numbered JNYS1, JNYS2, and JNYS3 respectively. After recording, put it into a ziplock bag; put the collected specimens into a hot air drying box for drying, set the drying temperature at 60°C, and collect them after drying for 5 hours;
[0026] 2. Preparation of disinfectant
[0027] Take out 5ml of sterile water, pour it into the ceftriaxone sodium medicine bottle, beat it repeatedly until it is completely dissolved, take out 3ml of the medicine solution and pour it into a sterile glass plate filled with 75% alcohol and set the volume to 40ml, and prepare the ceftriaxone sodium alcohol solution. Beat and mix repeatedly so that the co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com