Yeast hydrolysate with high free nucleotide and preparation method and application of yeast hydrolysate
A yeast hydrolyzate, nucleotide technology, applied in the application, animal feed, animal feed and other directions, can solve the problem of low free nucleotide content, increase the breeding efficiency, the preparation method is simple, and ease the use of feed nucleotides. The effect of scarcity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0060] The invention provides a kind of preparation method of yeast hydrolyzate, it comprises the following steps:
[0061] (1) Fermentation culture: fermenting and culturing the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to obtain the first yeast milk;
[0062] (2) Autolysis and enzymolysis: heat-shock treatment is performed on the yeast milk that accounts for 60-80% by weight of step (1), preferably 65-70% by weight of the first yeast milk, to perform autolysis, and then add papain Enzymolysis to obtain the second yeast milk;
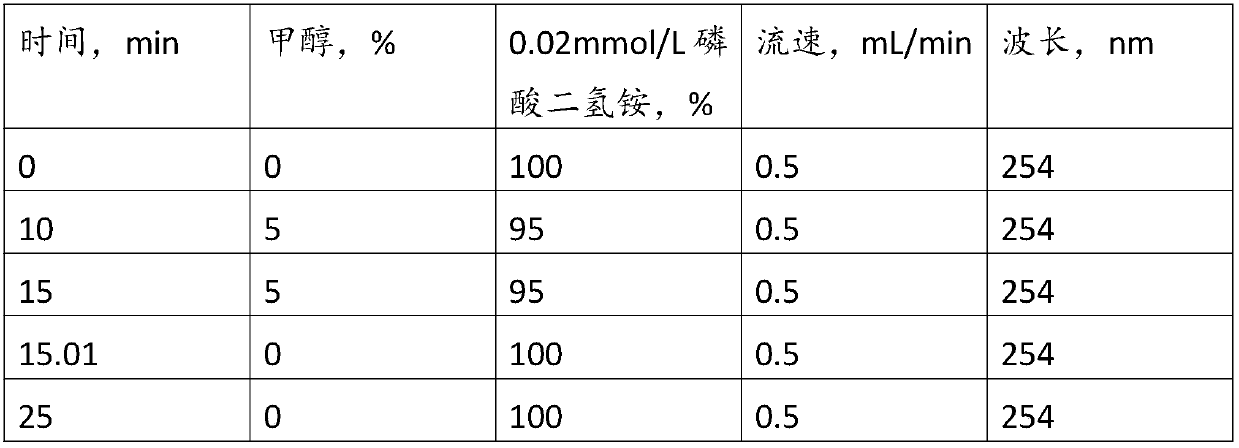
[0063] (3) Nucleotidation: adding yeast RNA and nuclease to the second yeast milk obtained in step (2) for enzymolysis to obtain the third yeast milk, preferably adding yeast RNA first, and then adding nuclease for enzymolysis;
[0064] (4) Nucleotide enhancement: adding nucleotide disodium salt to the third yeast milk obtained in step (3) to obtain high free nucleotide yeast hydrolyzate.
[0065] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, wherein, in...
Embodiment 1
[0090] Example 1 Preparation of Yeast Hydrolyzate
[0091] (1) Yeast fermentation culture
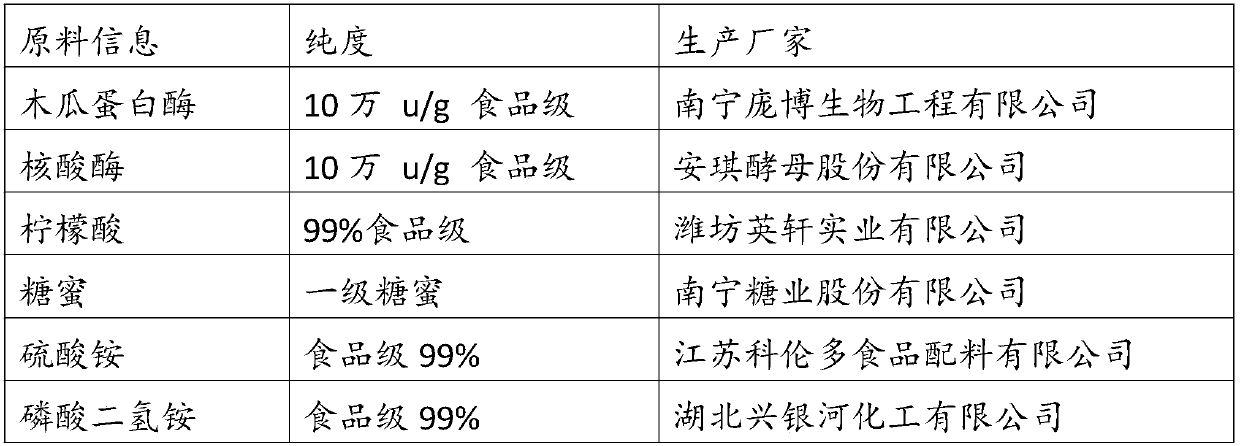
[0092] The culture solution contains carbon source, nitrogen source and phosphorus source, wherein the carbon source is 7500g of 35% molasses, the nitrogen source is 450g of ammonium sulfate, and the phosphorus source is 420g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate. Sterilize the culture solution at 121°C for 10 minutes, feed it into the tank, inoculate yeast to carry out fermentation culture, the fermentation temperature is 29°C, the fermentation time is 14 hours, the fermentation pH is 4.5, and the pure culture liquid is fermented to obtain the first yeast milk (wherein nitrogen The mass is 144.9g, and the amount of phosphorus is 113.4g).
[0093] (2) Yeast autolysis and enzymolysis
[0094] Heat-shock the yeast milk that accounts for 60% by weight of the first yeast milk in step (1) at a temperature of 85° C. for 55 seconds, control the temperature at 45° C., add citric acid accounting fo...
Embodiment 2
[0113] (1) Yeast fermentation culture
[0114] The culture solution contains carbon source, nitrogen source and phosphorus source, wherein the carbon source is 8000g of 35% molasses, the nitrogen source is 400g of ammonium sulfate, and the phosphorus source is 450g of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate. Sterilize the culture solution at 121°C for 10 minutes, feed it into the tank, inoculate yeast to carry out fermentation culture, the fermentation temperature is 30°C, the fermentation time is 15 hours, and the fermentation pH is 5.0 to obtain the first fermented yeast milk of pure culture liquid (wherein nitrogen The mass is 138g, and the amount of phosphorus is 121.5g).
[0115] (2) Yeast autolysis and enzymolysis
[0116] Heat-shock the yeast milk that accounts for 65% by weight of the first yeast milk in step (1) at a temperature of 88°C for 60s, then control the temperature at 50°C, add citric acid accounting for 4‰ of the added weight of the dry matter of the yeast milk, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com