An engineering strain and method for preparing farnesene from cellulose
A technology for engineering strains and cellulose, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as low yield, and achieve the effects of increasing yield and improving stress resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis solution.
[0041] Weigh 100 g of corn stover with a particle size of 20-80 mesh, add 1.5 L of formic acid solution (containing 88 wt % formic acid and 1 wt % HCl), and place it in a treatment tank. After reacting in a constant temperature water bath at 65°C for 3 h, the reaction slurry was separated into solid and liquid. The solid components were then treated with ammonia water, and the treatment conditions were: ammonia concentration 15wt%, volume of ammonia water used per kilogram of solid components was 8 liters, treatment temperature was 60°C and reaction time was 16h. After the reaction, the material is separated from solid and liquid, and the solid component is washed with distilled water to pH 6-7, and dried to obtain a pretreated solid material.
[0042] The pretreated solid material is subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis, and the enzymatic hydrolysis conditions include: the te...
Embodiment 2
[0044] This example is used to illustrate the sequence structure of the plasmid. Commercially available vectors used in this example include the pet-22b vector, pBAD33 vector, pACYDCDuet-1 vector, pBBR1MCS-4 vector, and pet-28a vector for knock-in of the acetate kinase ack (gene) into the E. coli genome .
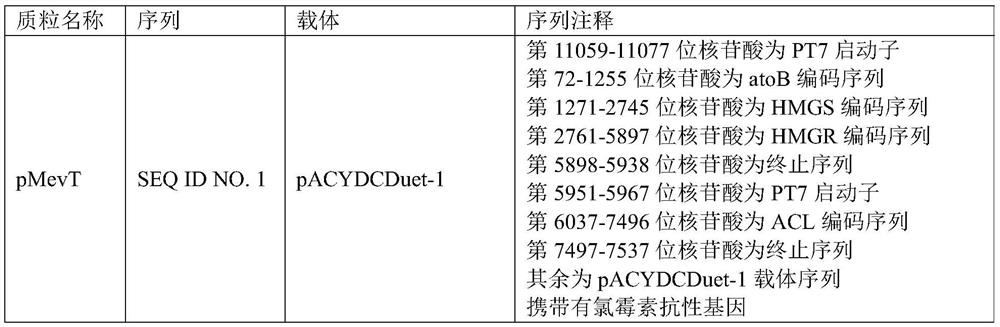
[0045] According to the instructions for use of the above-mentioned vectors, molecular biology operations such as PCR cloning, whole gene synthesis, restriction endonuclease digestion and ligation were used to construct a set of plasmids for the MVA metabolic pathway, specifically including pMevT plasmid, pMBIS plasmid and pFII plasmid, and then One plasmid was constructed to replace the pFII plasmid, that is, the pFG plasmid, and then two plasmids were constructed to replace the pMevT plasmid, namely pMevT-1 and pMevT-2. The sequence information of the above plasmids is specifically shown in Table 2.
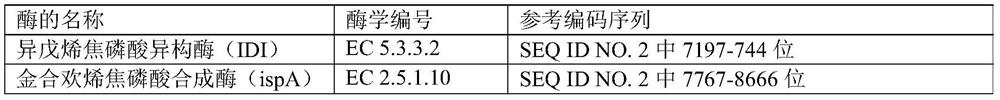
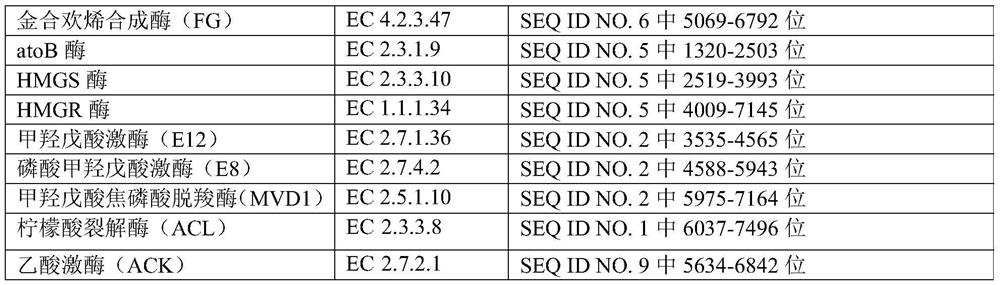
[0046] Table 2
[0047]
[0048]
[0049]
Embodiment 3
[0051] This example is used to illustrate the construction process of the engineered strain.
[0052] Construction of engineering strain F1 in the experimental group: Escherichia coli BL21 was selected as the host cell, and acetate kinase (ack) was knocked in according to the following method to obtain a strain overexpressing acetate kinase (ack) after knock-in.
[0053] The first step to prepare competent cells: after the plasmid pREDKI (shown in SEQ ID NO. 10) was transferred into Escherichia coli BL21, it was inoculated into LB liquid medium (kana resistance), and placed on a shaker at 30°C for overnight cultivation. The next day, it was transferred to fresh LB liquid medium (kana resistant) at a volume ratio of 1:100, cultured at 30°C to an OD600 of 0.2 to 0.3, and induced by adding L-arabinose with a final concentration of 10 mmol / L. After induction for 1-1.5 hours, take out the ice bath from the shaker at 30 °C for more than 10 min, centrifuge at 3500 rpm / min and 4 °C fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com