Application of Nrf2-based cyclovirobuxinum D in diabetic cardiomyopathy
A technology of diabetic cardiomyopathy and Cyclovir buxicine is applied in the field of medical inventions to achieve the effects of increased cardiac dysfunction, reduced ejection fraction, and improved cardiac function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
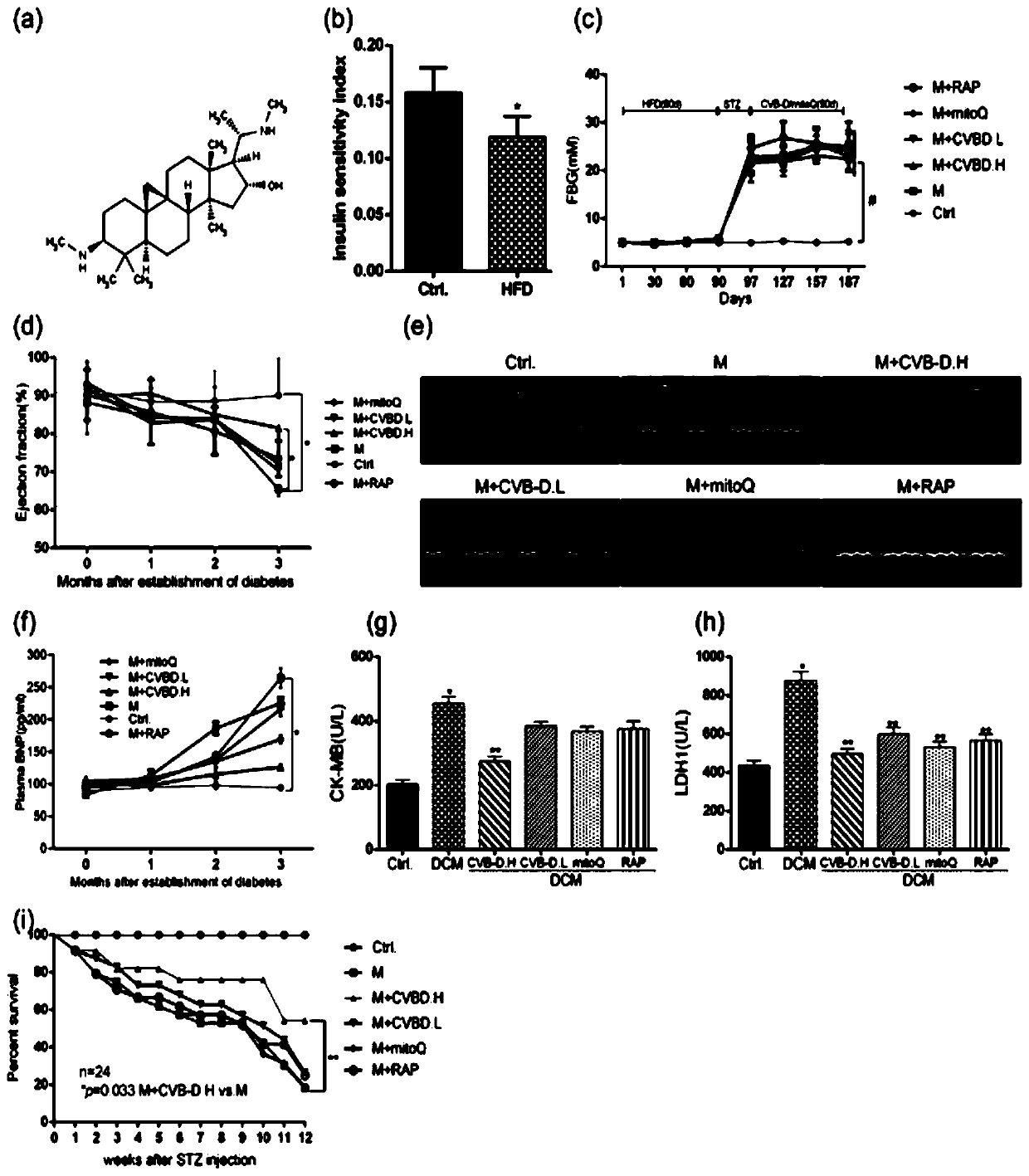
[0050] Effects of CVB-D on Cardiac Function and Survival Rate of DCM Rats
[0051] The establishment of DCM rat model: high-fat diet (18% of animal fat, 20% of sucrose, 2% of cholesterol, 0.2% of bile salt, 59.8% of basal feed) fed 2-month-old SD rats for 3 months, and blood was taken from the tail for determination Serum fasting insulin and blood sugar concentration, evaluate insulin resistance by 1 / fasting insulin * fasting blood sugar, intraperitoneally inject 25 mg / kg STZ to insulin resistant rats, inject the same volume of sodium citrate buffer solution in the control group, and measure random blood sugar with a blood glucose meter after 72 hours , ≧ 11.1mM for T2DM model success. After establishing the T2DM model, the experiment was divided into: normal control group, model group, M+CVB-D high-dose group (2mg / kg / d, intragastric administration), M+CVB-D low-dose group (1mg / kg / d , intragastric administration), the positive drug rapamycin group (2mg / kg, once every other da...
Embodiment 2
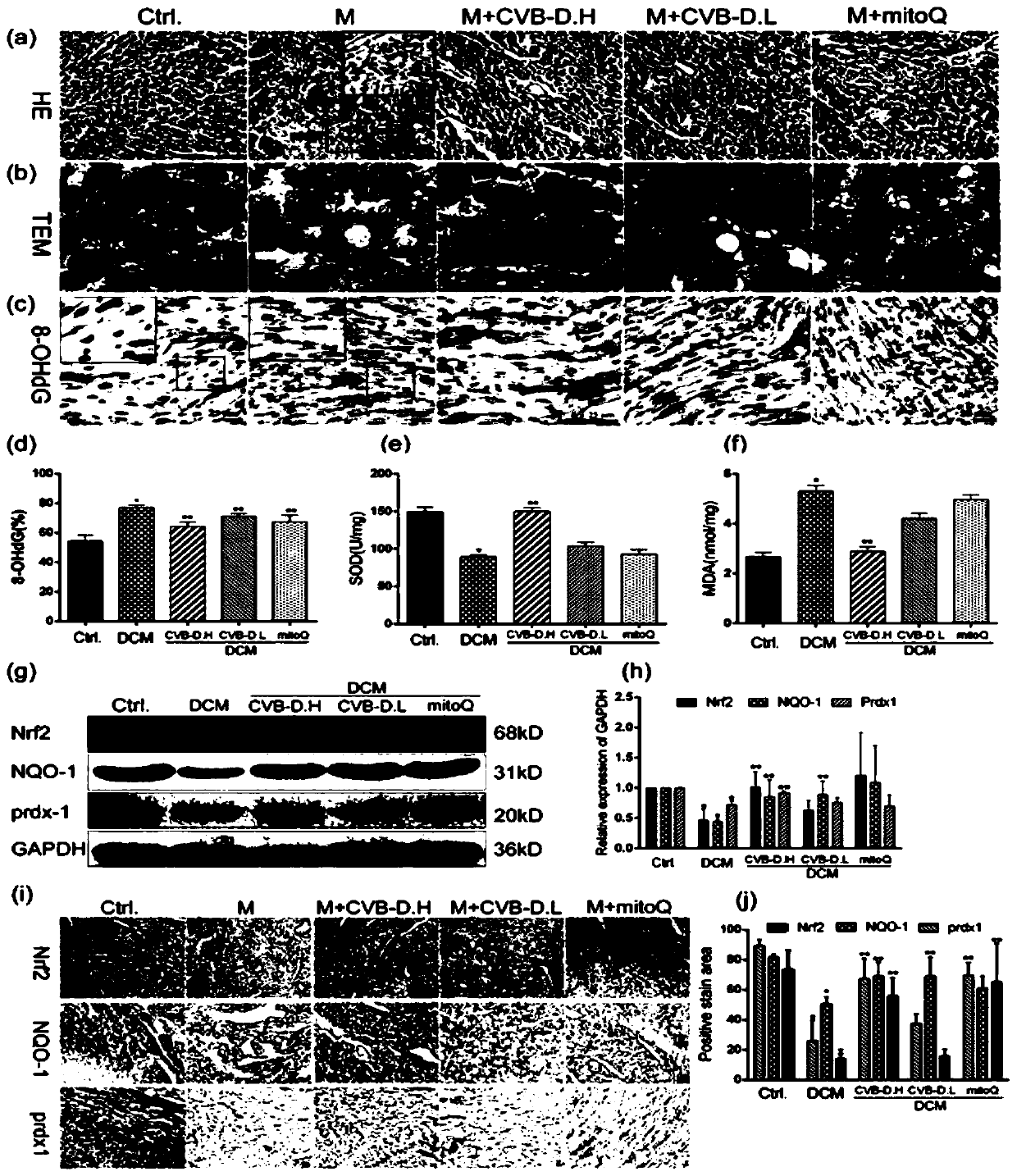
[0054] Effects of CVB-D on cardiac oxidative stress in DCM rats
[0055] The left ventricle was taken to detect SOD and MDA levels; HE staining was used to observe pathological changes; transmission electron microscopy was used to observe the morphology of cardiac mitochondria; Western blot was used to detect the expression of Nrf2, NQO-1, prdx1; expression;
[0056] Results: HE staining of heart tissue showed inflammatory cell infiltration in the heart of DCM rats (Fig. 2-a), and TEM indicated mitochondrial cristae damage ( figure 2 -b); DNA oxidative damage marker 8-OHdG immunohistochemical staining showed that the positive rate of the model group was significantly higher than that of the normal control group ( figure 2 -c, d); ELISA kit detection found that the peripheral blood SOD level of the model group decreased ( figure 2 -e), MDA level increased ( figure 2 -f), the above results suggest that the heart oxidative stress injury of DCM rats, after the intervention ...
Embodiment 3
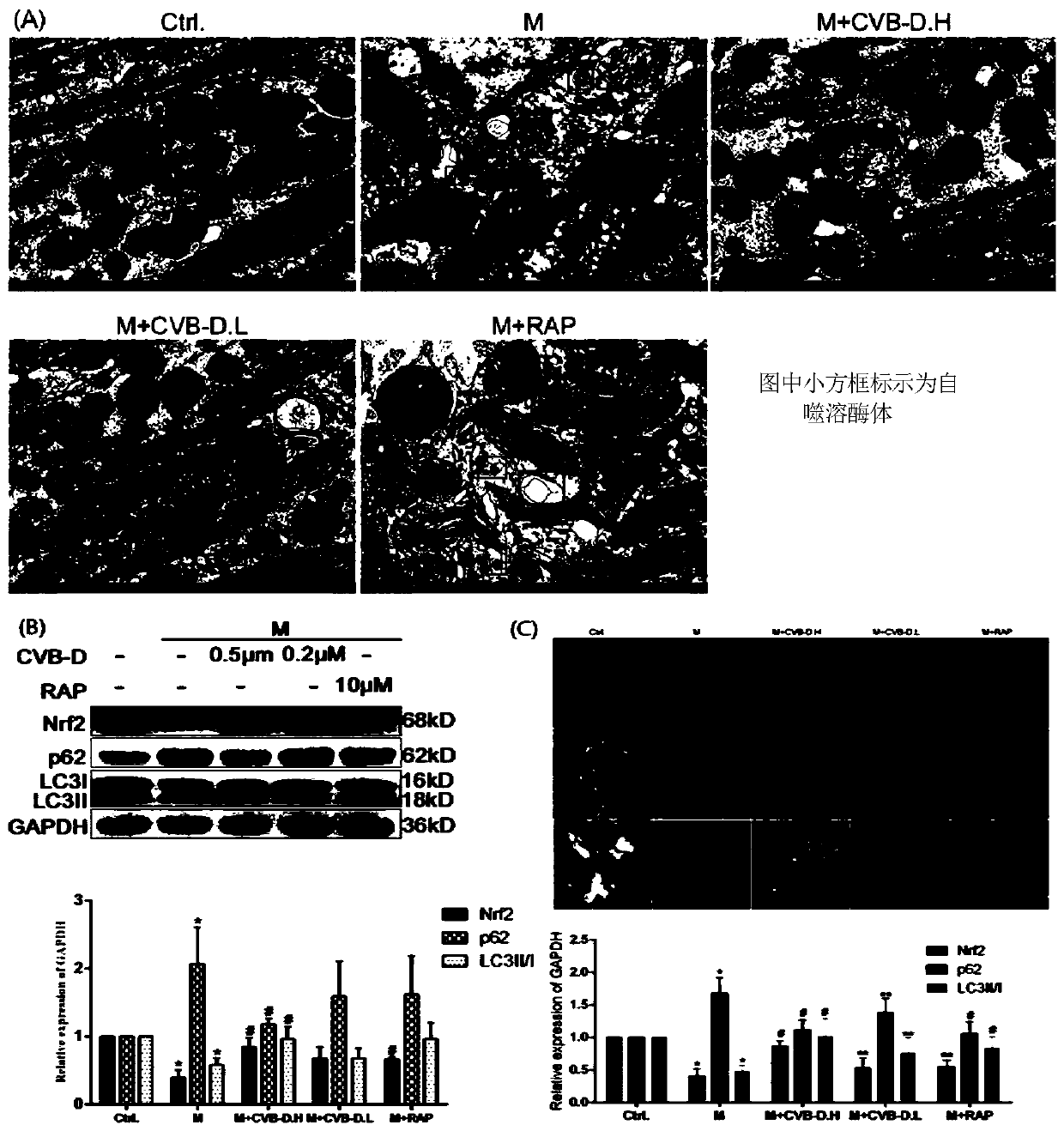
[0058] Effects of CVB-D on cardiac autophagy in DCM rats
[0059] The expressions of Nrf2, p62 and LC3 in heart tissue of rats in each group were detected by western blotting and immunofluorescence, and the number of cardiac autophagosomes was observed by transmission electron microscope.
[0060] Results: Transmission electron microscopy showed that the number of autophagic lysosomes in the heart of rats in the model group decreased (Fig. image 3 -B); Immunofluorescence results were similar, and suggested that Nrf2, LC3 and p62 co-localized ( image 3 -C). Values are represented by mean ± SD, each group n=3, by t test, *P<0.05vs. control group; #P<0.05vs. model group.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com