Physical specimen 3D printing method
A 3D printing and specimen technology, applied in the field of specimen 3D printing, can solve problems such as the limitation of the production of plasticized specimens, and achieve the effect of complete shape and structure, convenient teaching, and solving inconvenience.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] A kind of physical specimen 3D printing method, comprises the following steps:
[0044] (1) Antiseptic treatment: select a complete, non-trauma-free, and disease-free human specimen, and perform antiseptic treatment on the specimen.
[0045] Perfuse the specimen with formalin with a volume concentration of 15%, infiltrate the formalin into various parts of the specimen through the large blood vessels (femoral artery, common carotid artery), and finally put the formalin with a volume concentration of 10%. Soak in liquid for 3 months.
[0046] (2) Anatomical preparation, making the required specimens according to the anatomical atlas.
[0047] (2-1) Collect materials, cut the abdominal wall along the midaxillary line, cut off the inferior vena cava, hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery, common bile duct, and diaphragm with scissors, and take out the liver;
[0048] (2-2) Make, remove the superficial fascia on the liver and blood vessel wall, trim it neatly, keep 1 cm at ...
Embodiment 2
[0080] A kind of physical specimen 3D printing method, comprises the following steps:
[0081] (1) Antiseptic treatment: select human specimens that are complete, free from trauma, fractures, and lesions, and carry out antiseptic treatment on the human specimens.
[0082] Perfuse the specimen with formalin with a volume concentration of 20%, penetrate the formalin into various parts of the specimen through the large blood vessels (femoral artery, common carotid artery), and finally put the formalin with a volume concentration of 10%. Soak in liquid for 3 months.
[0083] (2) Anatomical preparation, making the required specimens according to the anatomical atlas.
[0084] (2-1) Collect materials, cut the abdominal wall along the midaxillary line, cut off the inferior vena cava, hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery, common bile duct, and diaphragm with scissors, and take out the liver;
[0085] (2-2) Make, remove the superficial fascia on the liver and blood vessel wall, trim i...
Embodiment 3
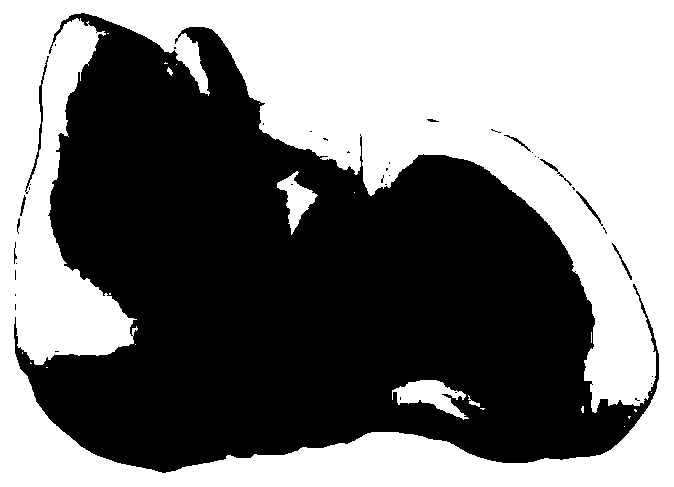
[0106] A method for 3D printing of physical specimens, the difference from Embodiment 1 is only in step (2). In this embodiment, human heart specimens are selected.
[0107] Anatomical fabrication includes:
[0108] (2-1) Material collection: Along the midline of the clavicles on both sides, use a rongeur to bite open the ribs, use a scalpel to incise the intercostal muscles to open the chest wall, open the pericardium, and use scissors to bluntly separate the pulmonary veins, pulmonary arteries, superior vena cava, and inferior vena cava. After the vena cava, brachiocephalic trunk, left subclavian artery, and left common carotid artery are separated, the blood vessels are cut off with a scalpel, and the heart is taken out;
[0109] (2-2) Production: Remove the superficial fascia on the heart and blood vessels, retain the myocardium and left coronary artery, right coronary artery, pulmonary vein, pulmonary artery, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, brachiocephalic trunk, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com