Application of fluorescence in-situ hybridization on bone marrow smears in multiple myeloma
A technique of fluorescence in situ hybridization and multiple myeloma, which is applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low false negative rate, increased cost, and low proportion of plasma cells, and achieve simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
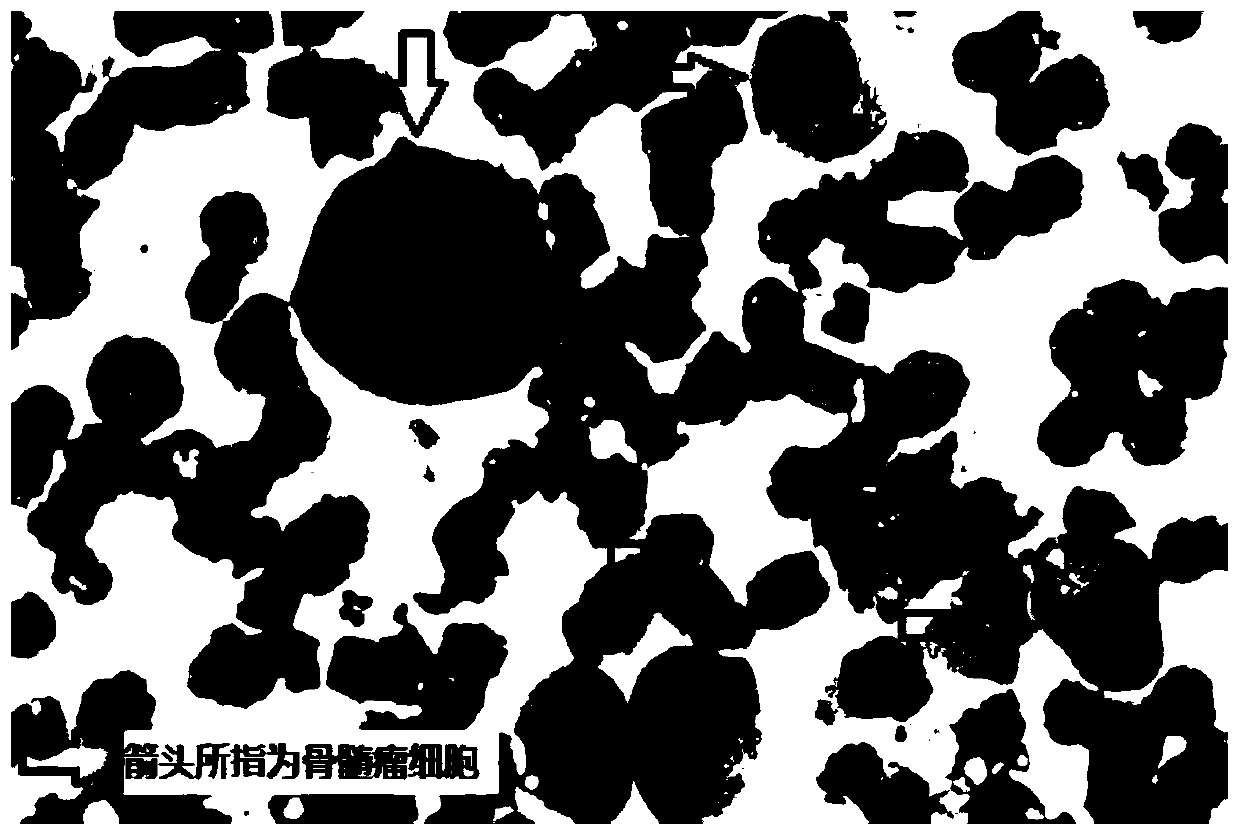
[0032] In a patient with multiple myeloma, the ilium bone marrow smear cell morphology of myeloma cells was 57%, the cell body size was different, the cytoplasm was increased, the nucleus was enlarged, the cytoplasm was light blue, and the nucleus was round or oval , visible giant, dual / multinucleated tumor cells (eg figure 1 shown). At the same time, the first tube of heparin-anticoagulated bone marrow aspirated at the same time was detected by flow cytometry, and only a group of abnormal monoclonal plasma cells accounted for 3.7% of bone marrow nucleated cells were found. The proportion of myeloma cells in the subsequently aspirated heparin-anticoagulated bone marrow was even lower. CD138 magnetic bead sorting requires more than 20 mL of bone marrow to obtain a sufficient amount of myeloma cells for FISH detection. In this embodiment, a bone marrow smear of less than 0.2 mL is selected for fluorescence in situ hybridization detection, and the specific operations are as foll...
Embodiment 2
[0058] In a patient with multiple myeloma, myeloma cells accounted for 10% of the iliac bone marrow smear cells, with large cell bodies, increased cytoplasm, enlarged nuclei, blue cytoplasm, round and oval nuclei (such as Figure 4 shown). At the same time, the first tube of heparin-anticoagulated bone marrow aspirated at the same time was detected by flow cytometry immunotype, only a group of monoclonal abnormal plasma cells accounted for 2.3% of bone marrow nucleated cells, and the proportion of myeloma cells in the subsequently aspirated heparin-anticoagulated bone marrow was even lower. CD138 magnetic bead sorting and aspirating more than 20mL of bone marrow still cannot obtain enough myeloma cells for FISH detection. In this embodiment, a bone marrow smear of less than 0.2 mL is selected for fluorescence in situ hybridization detection, and the specific operations are as follows:
[0059] 1. Preparation of Bone Marrow Smear
[0060] 1.1 Preparation of slides: quickly pl...
Embodiment 3
[0084] In a patient with multiple myeloma, myeloma cells accounted for only 3% of the iliac bone marrow smear cells, with small cell bodies, varying amounts of cytoplasm, light blue cytoplasm, and round or oval nuclei (such as Figure 8 shown). At the same time, the first tube of heparin-anticoagulated bone marrow aspirated at the same time was detected by flow cytometry immunotype, only a group of monoclonal abnormal plasma cells accounted for 0.2% of bone marrow nucleated cells, and the proportion of myeloma cells in the subsequent heparin-anticoagulated bone marrow was even lower. Sorting with CD138 magnetic beads cannot obtain enough myeloma cells for FISH detection. In this embodiment, bone marrow smear fluorescent in situ hybridization technology is selected for detection, and the specific operations are as follows:
[0085] 1. Preparation of Bone Marrow Smear
[0086] 1.1 Preparation of slides: quickly place 0.2mL of bone marrow fluid aspirated for the first time on a c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com