Dyeing and finishing process for reducing strength reduction of PLA-PHBV, Tencel and cotton interwoven fabrics during dyeing
A PLA-PHBV, interwoven fabric technology, applied in the direction of dyeing, enzyme/microorganism biochemical treatment, plant fibers, etc., can solve the problem of limiting the application of PLA-PHBV fibers, damage to the strength of PLA-PHBV fibers, and difficulty in dyeing and finishing. problem, to achieve the effect of bright color, suitable color depth, color depth and uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Embodiment 1: The dyeing and finishing process that reduces the strength of PLA-PHBV, Tencel, and cotton interwoven fabrics during dyeing, including the following steps:
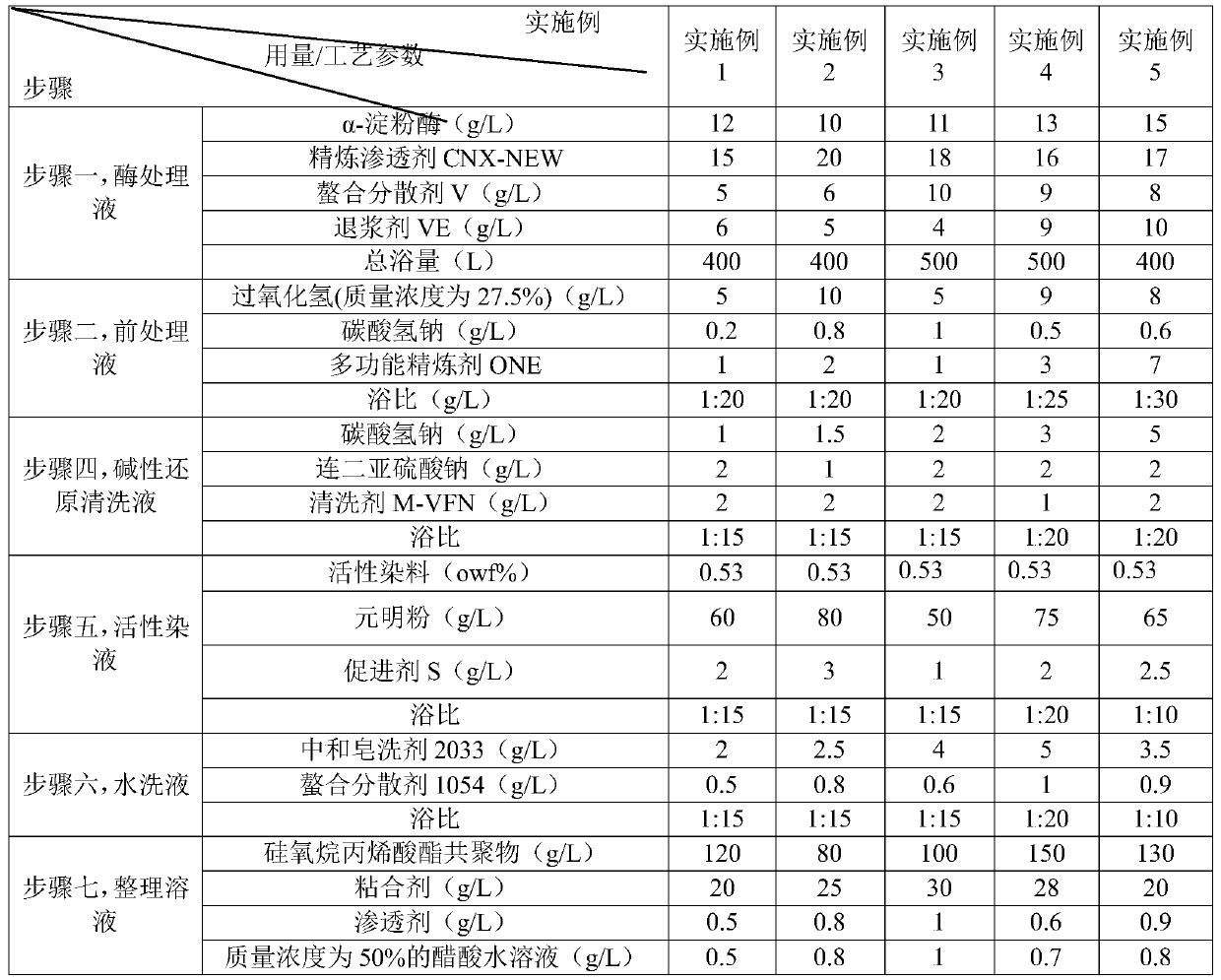
[0066] Step 1, enzyme treatment: Calculate according to the total bath volume 400L (the initial fabric can be fully immersed), according to the consumption in Table 1, α-amylase, refining penetrant CNX-NEW, chelating dispersant V, The desizing agent VE is thoroughly mixed, and the initial fabric (ie, PLA-PHBV, Tencel, and cotton interwoven fabric) is subjected to enzyme treatment. The fabrics were refrigerated for 24h after passing through the enzyme treatment solution on a paddle.
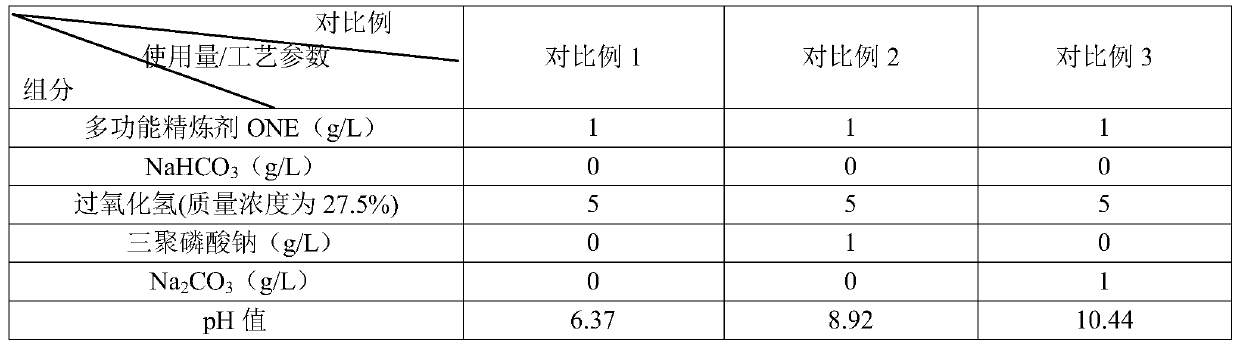
[0067] Step 2: Pretreatment: According to the dosage in Table 1, hydrogen peroxide (mass concentration is 27.5%), sodium bicarbonate, multifunctional refining agent ONE and water are prepared into a pretreatment solution, and the fabric after enzyme treatment is mixed with the The bath ratio of the pretreatment solution ...
Embodiment 2-5
[0074] Example 2-5: The dyeing and finishing process that reduces the strength of PLA-PHBV, Tencel, and cotton interwoven fabrics in dyeing is different from Example 1 in that the components used in each step and their corresponding consumption are as shown in Table 1 and Table 1. shown in Table 2.
[0075]The components involved in each step in the embodiment 1-5 of table 1 and their corresponding consumption and process parameters
[0076]
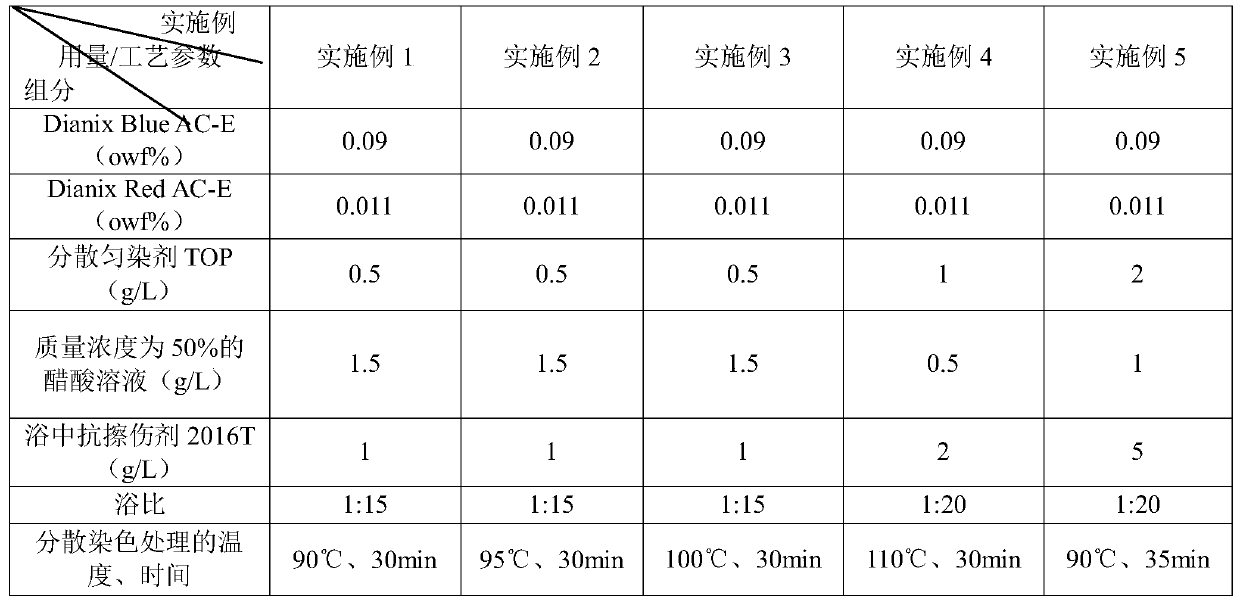
[0077] In the embodiment 1-5 of table 2, the composition of the disperse dye liquor of step 3 and its corresponding consumption, the technological parameter of disperse dyeing
[0078]
Embodiment 6
[0079] Example 6: Dyeing and finishing process for reducing the strength reduction of PLA-PHBV, Tencel, and cotton interwoven fabrics during dyeing. The difference from Example 1 is that in step 1, the temperature for enzymatic treatment is 55°C, and the time for enzymatic treatment is 5s, when the time is up, the fabric is subjected to the enzyme treatment solution on a paddle and then refrigerated for 12h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com