Mutant site of glufosinate-ammonium resisting Eleusine indica species, primer, detection method and application
A mutation site and detection method technology, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve time-consuming and labor-intensive problems, and achieve high detection accuracy, high detection efficiency, and specificity strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
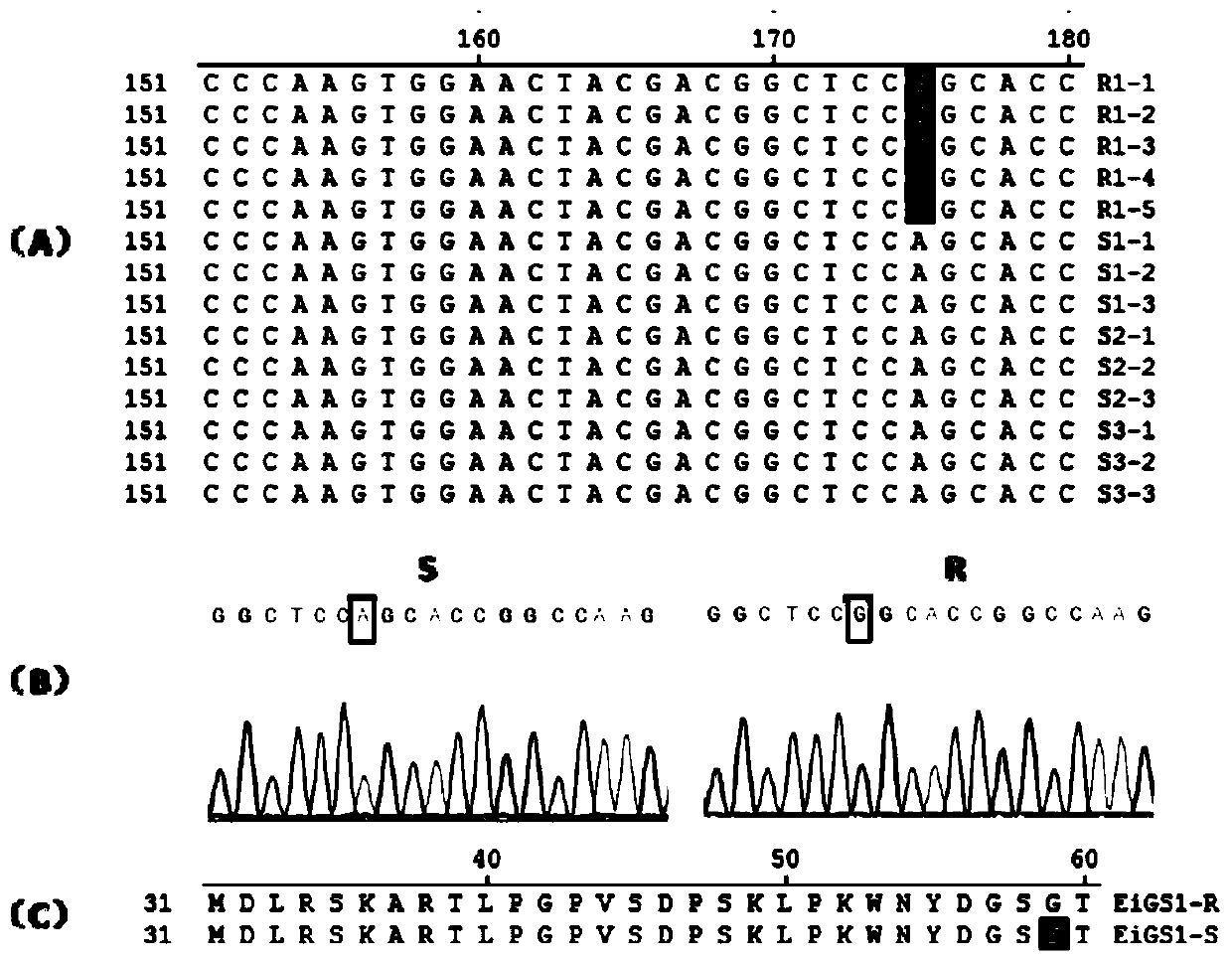
[0053] The glufosinate-ammonium-resistant and sensitive goosegrass glutamine synthetase gene EiGS1-R and EiGS1-S clones provided in this example and the steps for finding the A-175-G mutation characteristics of the EiGS1-R gene are as follows:
[0054] (1.1) RNA extraction of goosegrass, take 3 glufosinate-sensitive goosegrass populations (10 years ago, collected in the farmland where glufosinate has never been applied, multiplied and preserved in this laboratory, available to the public issued for the verification test.) and 1 glufosinate-resistant goosegrass population (collected and screened from the farmland where glufosinate has been applied for a long time, and stored in this laboratory, and can be distributed to the public for verification test) leaf material (3 plants were taken from each glufosinate-ammonium sensitive goosegrass material, a total of 9 plants, and glufosinate-ammonium-ammonium-resistant goosegrass population materials were taken from 6 plants), RNA was ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The dCAPs primer design for detecting the A-175-G gene mutation site of the glufosinate-resistant goosegrass population is as follows:
[0067] (2.1) Get glufosinate-ammonium-ammonium-resistant type and sensitive type goosegrass blade, adopt CTAB plant genome extraction method, obtain glufosinate-ammonium-ammonium-ammonium-resistant type and sensitive type goosegrass genomic DNA (gDNA) respectively;
[0068] (2.2) Using upstream primer GS1-F (shown in SEQ ID NO: 5) and downstream primer GS1-R (shown in SEQ ID NO: 6), using goosegrass gDNA as a template, clone EiGS1-R and EiGS1-S The genome sequence of the gene (respectively shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 1); the PCR reaction system is as follows: 2×PCR Buffer 12.5 μL, 10 μM GS1-F (10 μM) and GS1-R (10 μM) primers Each 1 μL, goosegrass gDNA 2 μL (about 100ng), add 8.5 μL sterile distilled water until the reaction system is 25 μL.
[0069] The PCR program is as follows: 40 cycles at 95°C for 4 minutes, 94°C for 30s...
Embodiment 3
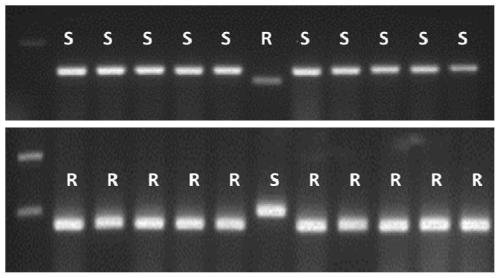
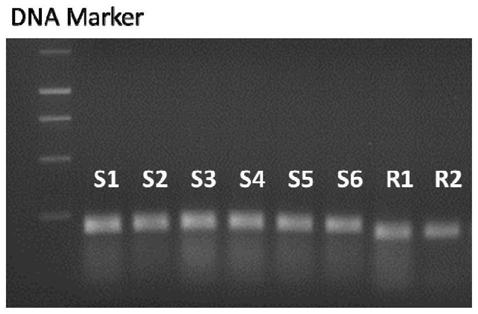
[0076] The detection method of the glufosinate-resistant goosegrass population provided by the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0077] (3.1) extract the genomic DNA (gDNA) of the leaves of glufosinate-ammonium-sensitive and resistant goosegrass (10 samples each);
[0078] (3.2) Using the primers dCaps-GS1-F and dCaps-GS1-R designed in Example 2, carry out PCR amplification with the gDNA of (3.1); PCR reaction system and its conditions: 2×PCR Buffer 12.5μL, 10μM 1 μL each of dCaps-GS1-F (10 μM) and dCaps-GS1-R (10 μM) primers, 2 μL (about 100 ng) of goosegrass gDNA, and 8.5 μL of sterile distilled water were added to make the reaction system 25 μL.
[0079] The PCR program is as follows: 40 cycles at 95°C for 4 minutes, 94°C for 30s, 58°C for 30s, and 72°C for 30s, and finally extended at 72°C for 7 minutes.
[0080] (3.3) Digest the PCR product of (3.2) and cut it with KpnⅠ-HF. The reaction system is as follows: 10×NEB. CustmerBuffer 3 μL, KpnⅠ-HF 1 μL, step ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com