Method for regulating and controlling body immunoreaction through regulation of skin DCs (dendritic cells)/ LCs (Epidermal Langerhans cells) by electric signal to be presented to T cell, and purpose of method
A technology for electrical signal regulation and body immunity, applied in the field of immunity, can solve the problems that antigen adsorption is easily affected by physical and chemical properties, the mechanism of action has not been clarified, and the effect of adjuvant immunity varies greatly, so as to enhance antigen absorption and biological immunity. Utilization rate, improved vaccine safety, low cost effect of electric field stimulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
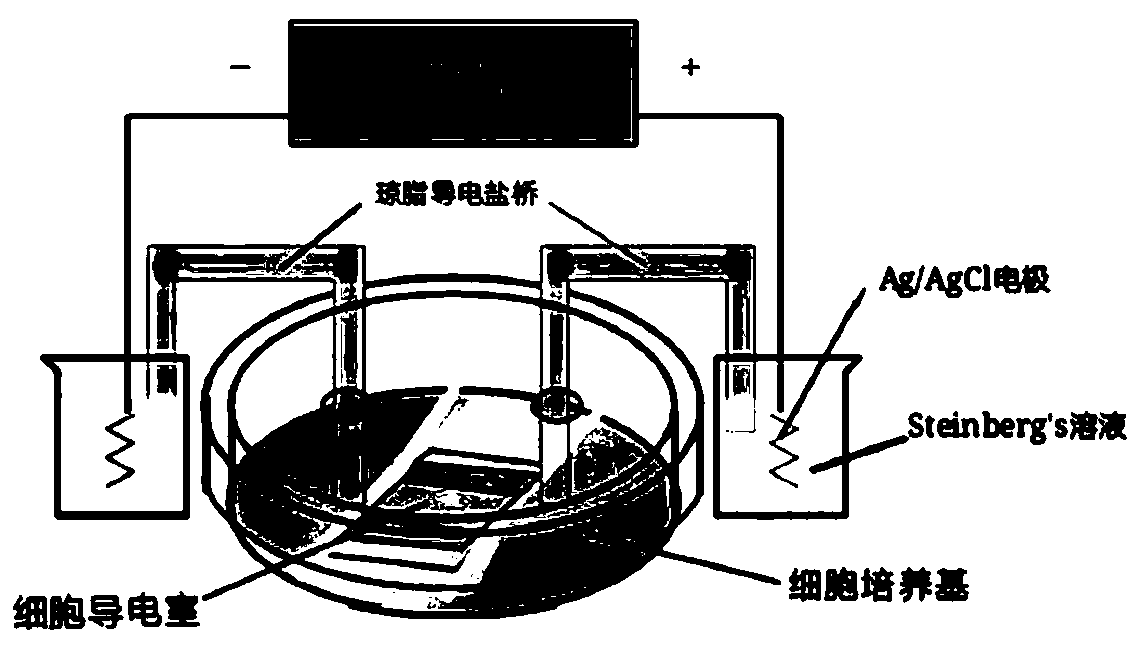
[0058] Example 1 In vitro cell powering experiment
[0059] Since it is difficult to isolate and maintain a sensitive homogeneous population of human DCs, several cell lines have been established to facilitate the study of DCs, one of which was used in this example: KG-1 cells (a cytokine-responsive CD34+ myelomonocytic cell line).
[0060] (1) Reagents and consumables required for in vitro cell powering:
[0061] ① Conductive solution Steinberg's solution preparation: dH2O 500ml, NaCl 3.4g, KCl0.05g, Ca(NO3).4H2O 0.08g, MgSO4.7H2O 0.205g, Trisasorb of buffer 0.56g, mix and dissolve according to the above ratio, add HCl to adjust the pH to 7.4
[0062] ②Preparation of conductive glass salt bridge: Heating and bending the glass tube of Zhongtong to make the shape required for power-on
[0063] ③Conductive electrode: put Ag wire or AgCl wire into Steinberg’s solution conductive liquid
[0064] ④ Preparation of agar conductive salt bridge gel: 100ml Steinberg’s solution, 2g A...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2 Mice in vivo electrification experiment one
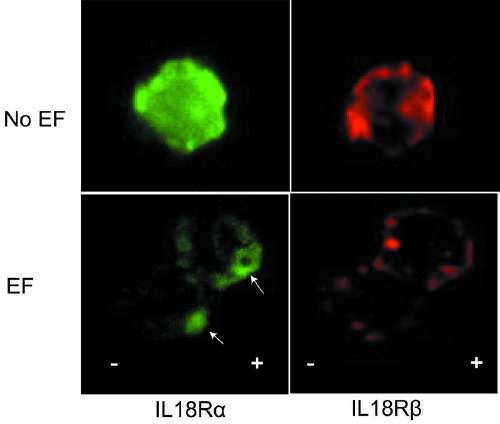
[0077] Based on the research results of in vitro cell electrification experiments, we believe that local electrical stimulation of mouse skin can eliminate some interfering factors in the in vitro experiments and provide a clear answer for the effect of EFs. At the same time, transgenic mice are of great significance for supporting and verifying hypotheses, so further confirmation of IL-18 and IL-18R gene knockout mice will significantly improve the reliability of this study.
[0078] (1) Selection of research objects: C57BL / 6 mice (wild type, WT), gene knockout IL-18 KO and IL-18RKO mice
[0079] (2) Consumables required for in vivo power-on of mice:
[0080] ① Skin conductive electrode patch: The skin conductive electrode patch selects medical conductive materials that can directly contact the skin, such as a disposable button-type ECG electrode patch, and trims it according to the electrified part so that the e...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Example 3 Mice in vivo electrification experiment two
[0099] In order to more intuitively detect the effect of EFs on the migration of LCs in the epidermis, we applied electricity to the ear skin of mice, and used fluorescent labeling to display the distribution and quantity of LCs in the ear epidermis, and analyzed the changes of LCs before and after electrification.
[0100] (1) Selection of research objects: C57BL / 6 mice (wild type, WT), gene knockout IL-18 KO and IL-18RKO mice
[0101] (2) Consumables required for in vivo power-on of mice:
[0102] ①Ear skin conductive electrode patches: also select medical conductive materials that can directly contact the skin, such as disposable button-type ECG electrode patches, and trim them to an appropriate size according to the mouse's ears, and weld the positive and negative electrodes. Placed on the ear of the mouse with an ear clip structure
[0103] ② Preparation of power supply device: specific DC or AC power genera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com