Methods of regulating grain structure and improving properties of zk60 wrought magnesium alloy
A technology for deforming magnesium alloys and grains, applied in the field of deformed magnesium alloys, can solve problems such as increasing the manufacturing cost of materials, increasing the size of magnesium alloy profiles, and difficult to solve core problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The method for preparing ZK60 wrought magnesium alloy comprises the following steps:
[0037] 1) Melting: heating pure magnesium, pure zinc and Mg-Zr master alloy to 700-750°C for 20-30 minutes. After the alloy is completely dissolved, stir fully to make the raw material fraction uniform, then keep it for 20-30 minutes, and then cast it into an ingot to obtain ZK60, wherein the content of the main elements in the alloy is: 5.8wt% Zn, 0.5wt% %Zr, the balance is Mg
[0038] 2) Machining: sawing the ingot, machining the wagon to a suitable size.
[0039] 3) Solution treatment: heat the ZK60 magnesium alloy of appropriate size in step 2) at 400° C. for 10 hours, and then quench to room temperature.
[0040] 4) Pre-aging treatment: The solution-treated ZK60 magnesium alloy is subjected to a stepwise pre-aging process. The process is divided into three stages: aging at 120°C for 60 minutes, aging at 180°C for 30 minutes and aging at 240°C for 15 minutes.
[0041] 5) Extrus...
Embodiment 2
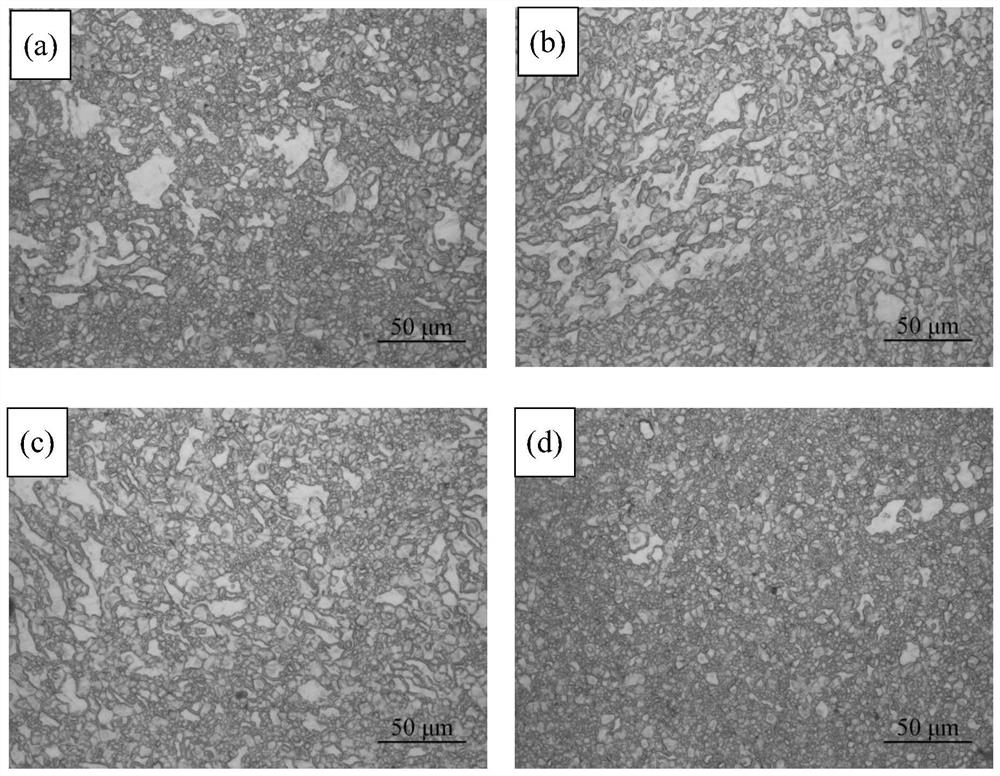
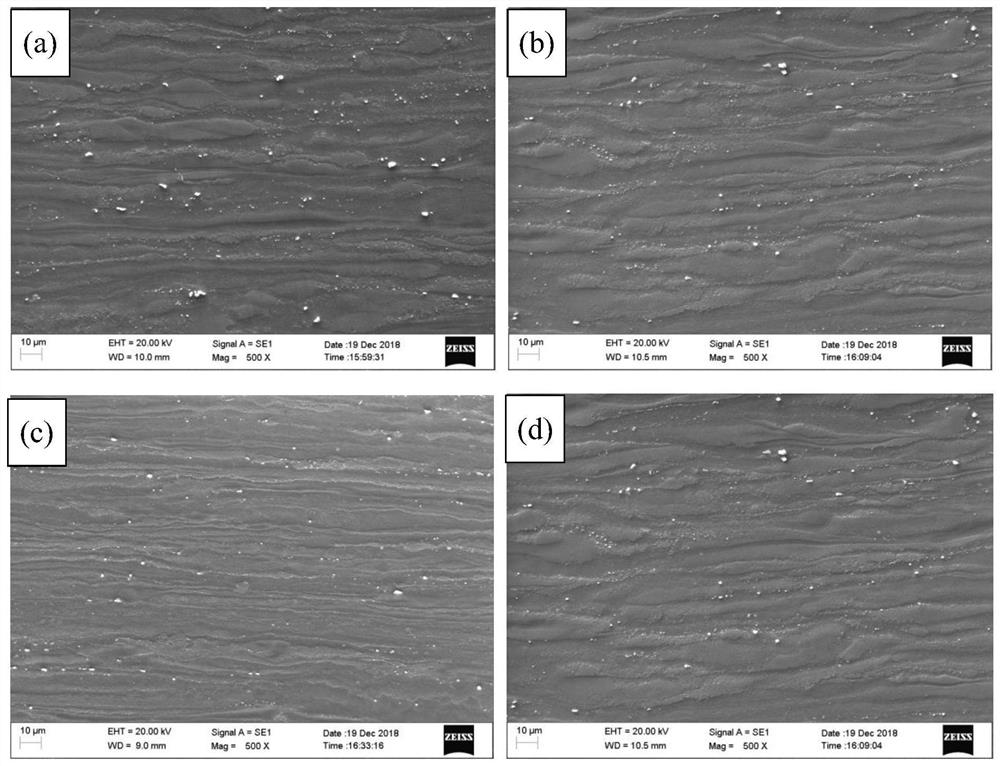
[0044] In this embodiment, the difference between the preparation method of the ZK60 deformed magnesium alloy and the embodiment 1 is that in step 3) the pre-aging treatment is not performed after the solution treatment, and the extrusion treatment is directly performed. The metallographic microstructure of the prepared ZK60 wrought magnesium alloy is as follows: figure 1 As shown in b, its SEM structure is as figure 2 As shown in b, the test results of its mechanical properties are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0046] In this example, the difference between the preparation method of the ZK60 wrought magnesium alloy and Example 1 is that a one-stage pre-aging treatment is performed after the solution treatment in step 3), and the pre-aging treatment process is: aging at 240°C for 15 minutes, and then extrusion pressure treatment. The metallographic microstructure of the prepared ZK60 wrought magnesium alloy is as follows: figure 1 As shown in c, its SEM structure is as figure 2 As shown in c, the test results of its mechanical properties are shown in Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com