Method for detecting content of aldehyde groups contained in biological tissue
A technology for the content of biological tissue and aldehyde groups, applied in the detection field, can solve the problems of inability to detect products, affect the content of free aldehyde groups, and many reaction steps, and achieve the effects of rapid detection, high detection accuracy and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] (1) Establish a standard curve
[0046] A 0.1 mmol / L DNPH solution was precisely prepared, wherein the pH of the DNPH solution was adjusted to 6.0 with acetic acid.
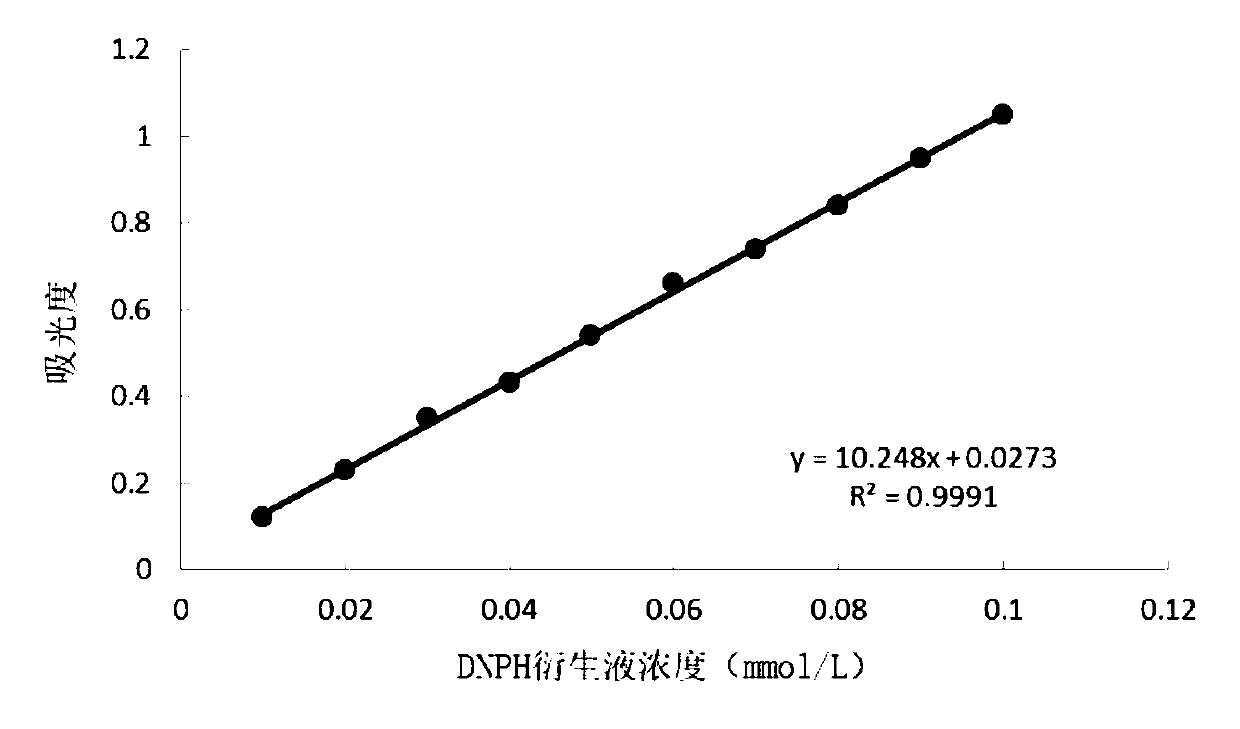
[0047] Select respectively 1ml, 2ml, 3ml, 4ml, 5ml, 6ml, 7ml, 8ml, 9ml, 10ml of DNPH solutions with a concentration of 0.1mmol / L, dilute to 10ml with purified water, and use a UV spectrophotometer to measure its concentration at 218nm. Absorbance value, with the concentration of DNPH solution as the abscissa and the absorbance value as the ordinate, draw a standard curve. The obtained standard curve is as figure 1 As shown, the regression equation of the curve is: y=10.248x+0.0273, R2=0.9991, wherein x represents the concentration of DNPH solution in mmol / L, and y represents the absorbance value.
[0048] (2) Detection of aldehyde content contained in biological tissue
[0049] Get the DNPH solution of 5ml 0.1mmol / L and use the ultraviolet spectrophotometer to test its absorbance value A1 at 218nm place...
Embodiment 2
[0054] (1) Establish a standard curve
[0055] Precisely prepare 0.3mmol / L DNPH solution, wherein phosphoric acid is used to adjust the pH of DNPH solution to 2.0.
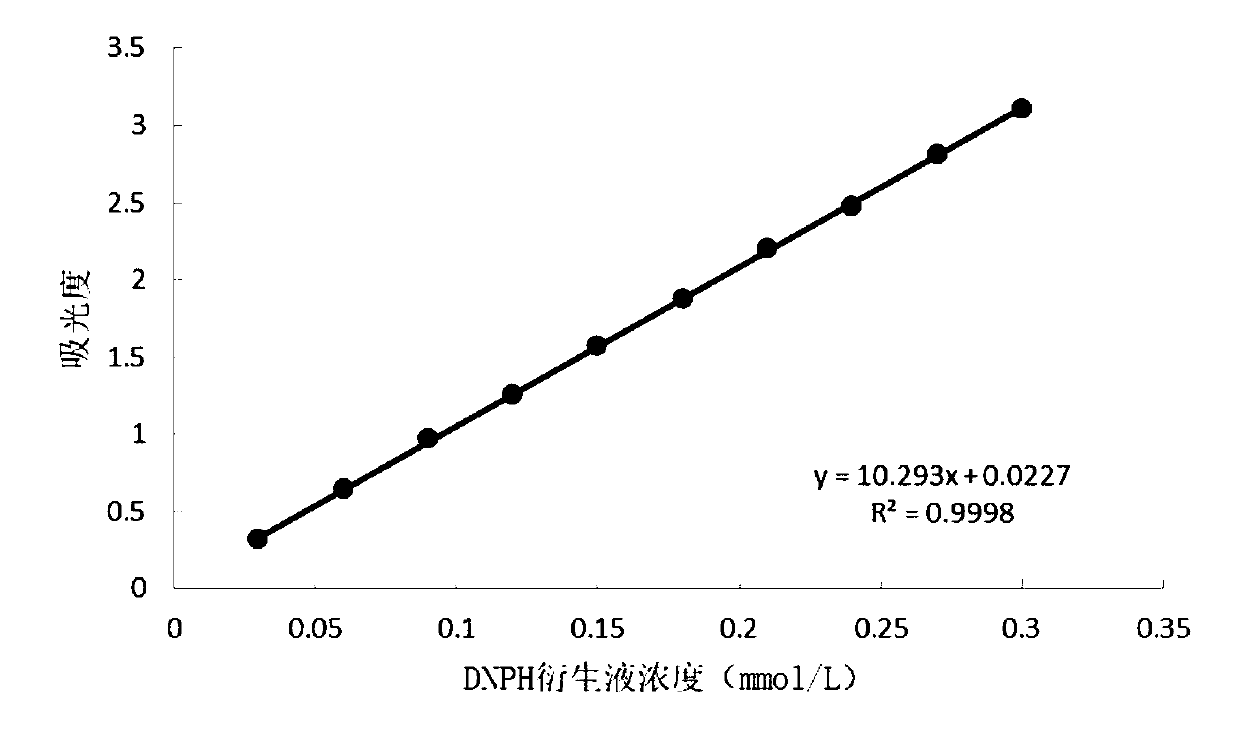
[0056] Select respectively 1ml, 2ml, 3ml, 4ml, 5ml, 6ml, 7ml, 8ml, 9ml, 10ml of DNPH solutions with a concentration of 0.1mmol / L, dilute to 10ml with purified water, and use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer to measure its concentration at 264nm. Absorbance value, with the concentration of DNPH solution as the abscissa and the absorbance value as the ordinate, draw a standard curve. The obtained standard curve is as figure 1 As shown, the regression equation of the curve is: y=10.293x+0.0227, R 2 =0.9998, wherein x represents the concentration of DNPH solution in mmol / L, and y represents the absorbance value.
[0057] (2) Detection of aldehyde content contained in biological tissue
[0058] Get 10ml of 0.3mmol / L DNPH solution and dilute to 20ml, as DNPH reaction solution, use ultraviolet spectrophotometer to te...
Embodiment 3
[0065] (1) Establish a standard curve
[0066] A 1.0 mmol / L DNPH solution was precisely prepared, and the pH of the DNPH solution was adjusted to 4.0 with perchloric acid.
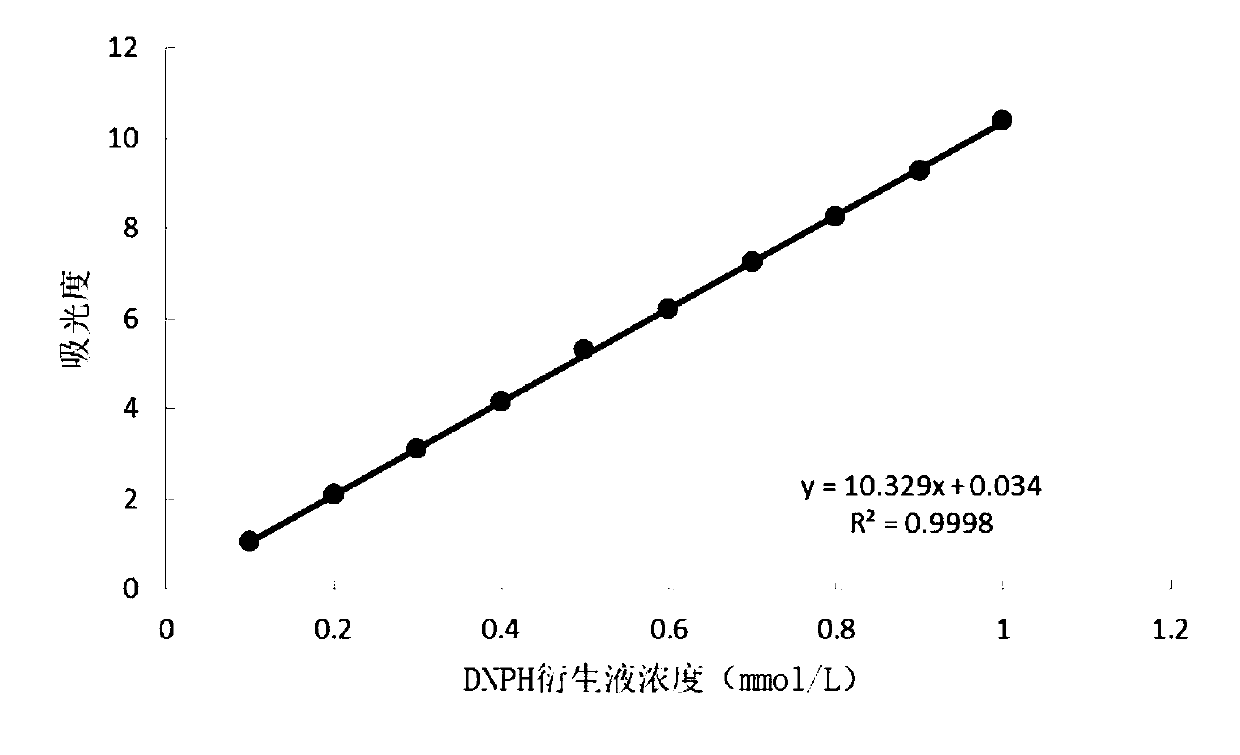
[0067] Select respectively 1ml, 2ml, 3ml, 4ml, 5ml, 6ml, 7ml, 8ml, 9ml, 10ml of DNPH solution with a concentration of 1.0mmol / L, dilute to 10ml with purified water, and measure its concentration at 323nm using a UV spectrophotometer. Absorbance value, with the concentration of DNPH solution as the abscissa and the absorbance value as the ordinate, draw a standard curve. The obtained standard curve is as figure 1 As shown, the regression equation of the curve is: y=10.329x+0.034, R2=0.9998, wherein x represents the concentration of DNPH solution in mmol / L, and y represents the absorbance value.
[0068] (2) Detection of aldehyde content contained in biological tissue
[0069] Take 1ml of 1.0mmol / L DNPH solution and dilute it to 10ml, and use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer to test its absorbance value A...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com