Enrichment method of electroactive biofilms for antibiotic wastewater treatment
A technology of antibiotic wastewater and biofilm, applied in biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, electrochemical biological combination treatment, etc., can solve the problems of poor tolerance and long domestication cycle of electrode biofilm, and achieve Solve the difficulty of domestication, shorten the domestication cycle, and improve the effect of activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
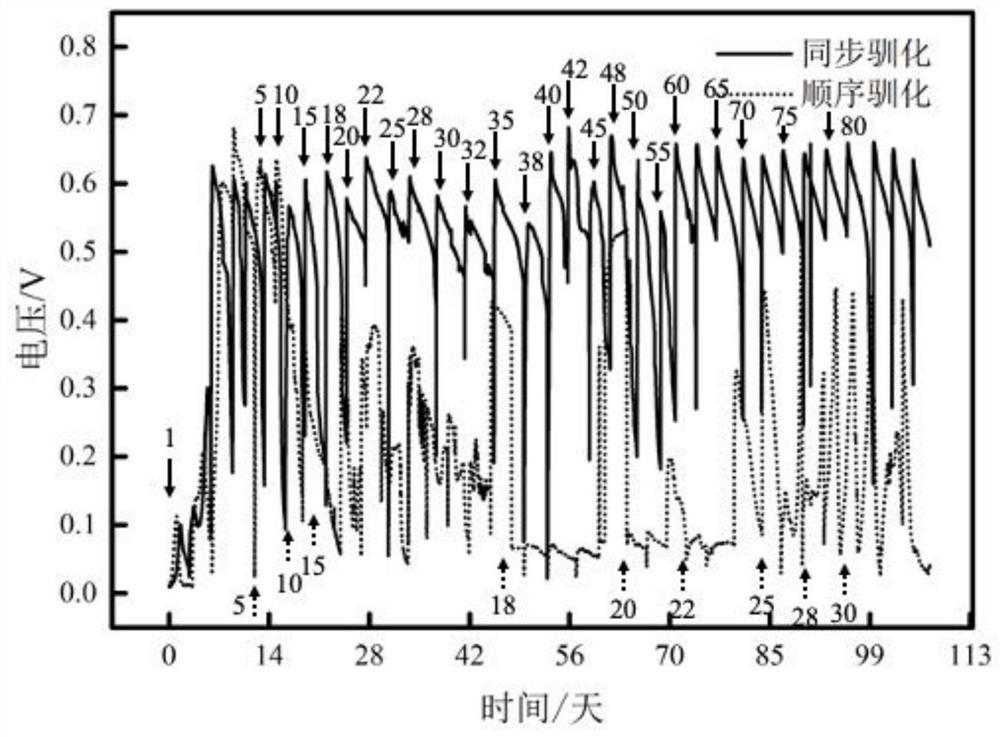
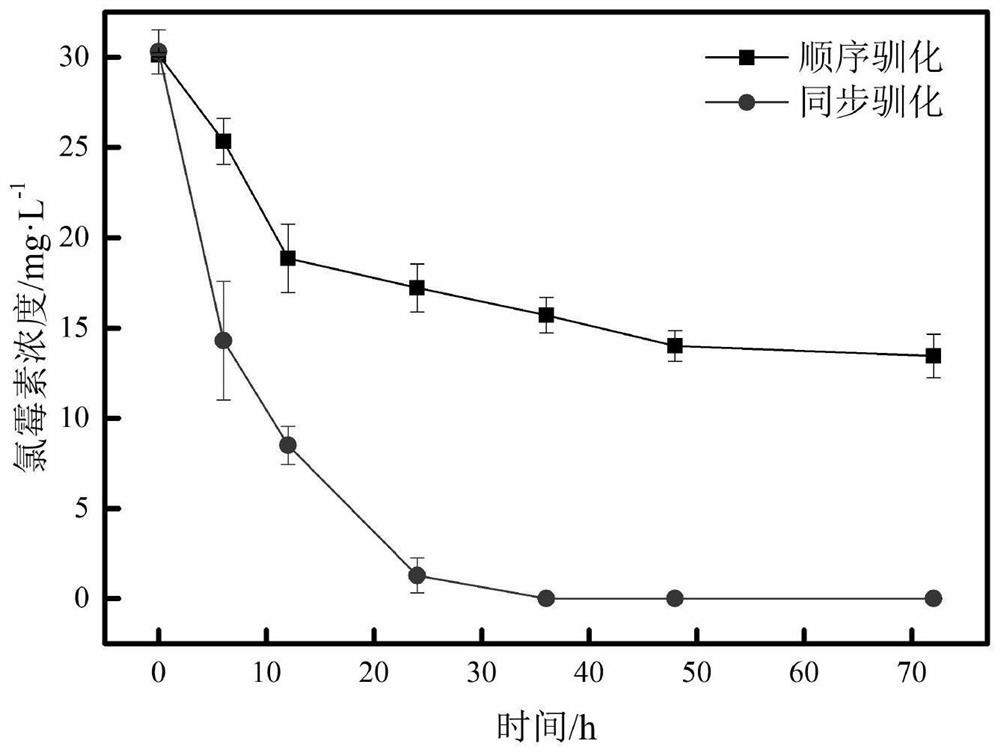
[0043] This example illustrates the influence of the synchronous domestication and the traditional sequential domestication method adopted in the present invention when using the MFC anode to domesticate the electroactive biofilm degraded by chloramphenicol:
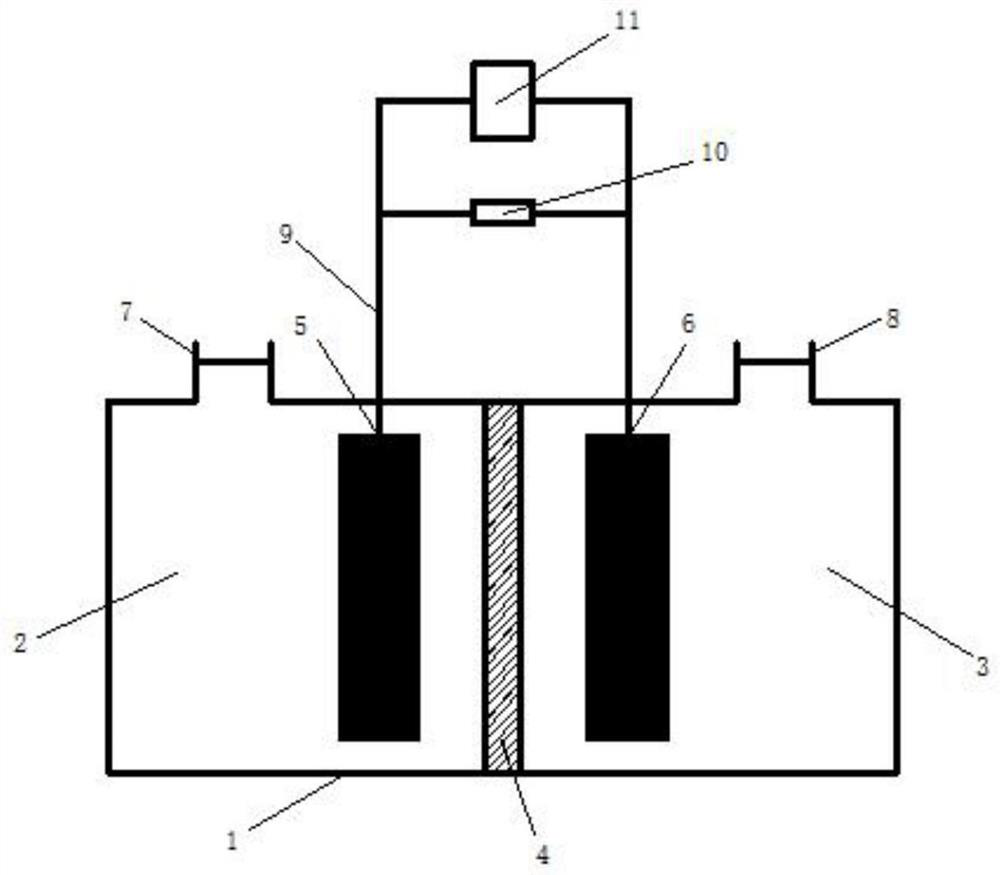
[0044] build as figure 1 In the dual-chamber MFC shown, a proton exchange membrane is arranged between the anode compartment and the cathode compartment, and an anode electrode and a cathode electrode are respectively arranged, the anode electrode and the cathode electrode are connected by an external circuit, and the cathode or anode material is a carbon-based material.
[0045] MFC anode uses anaerobic activated sludge (taken from Nanjing Jiangxinzhou Sewage Treatment Plant, hereinafter referred to as sludge) as the source of inoculated bacteria, the inoculation ratio is 1:2 (sludge: anolyte), and the anolyte is COD=1000mg / L The glucose simulated organic wastewater (0.31g / LNH 4 Cl; 2.452g / LNaH 2 PO 4 ·H 2 O; 4.576g...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This example illustrates that when the electroactive biofilm degraded by chloramphenicol is acclimated at the anode of the MFC using a new synchronous acclimation method, the sludge, sludge leaching solution, and sterilized sludge will be further investigated after the MFC has stabilized electricity production. Influence of leaching solution and sterilized sludge:
[0050] build as figure 1 The dual-chamber MFC shown, the new synchronous domestication method is as described in Example 1, and chloramphenicol is added to the anode gradient at the beginning, and the anolyte and sludge are regularly replaced every 3 days. When the dosing concentration was 5 mg / L, the battery produced electricity for 2 consecutive cycles and tended to be stable. In the later stage, different experimental groups were added with sludge, sludge extract, sterilized sludge extract, and sterilized sludge, respectively. The added concentration of chloramphenicol was still increasing gradually, and...
Embodiment 3
[0053] This example illustrates the acclimation of electroactive biofilms of different antibiotic wastewaters in MFC anodes using simultaneous acclimation and traditional sequential acclimation:
[0054] build as figure 1 The two-chamber MFC shown, the novel simultaneous acclimation versus the traditional sequential acclimation approach is as described in Example 1. Antibiotics were selected as typical representatives of 6 classes of antibiotics: chloramphenicol, tetracycline, sulfamethoxazole, penicillin, metronidazole, and nitrofurazone. As shown in Table 1, after 30 days of MFC operation in all experimental groups, the degradation of the target antibiotics was measured every 72 hours of operation. The tolerance concentration of chloramphenicol was only 15mg / L, and the degradation rate was 89.2%. Under the synchronous acclimation mode, the tolerated concentration of tetracycline can reach 20 mg / L, and the degradation rate is 100%; under the sequential acclimation method, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tolerance concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tolerance concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tolerance concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com