Patents
Literature
50results about How to "High tolerance concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
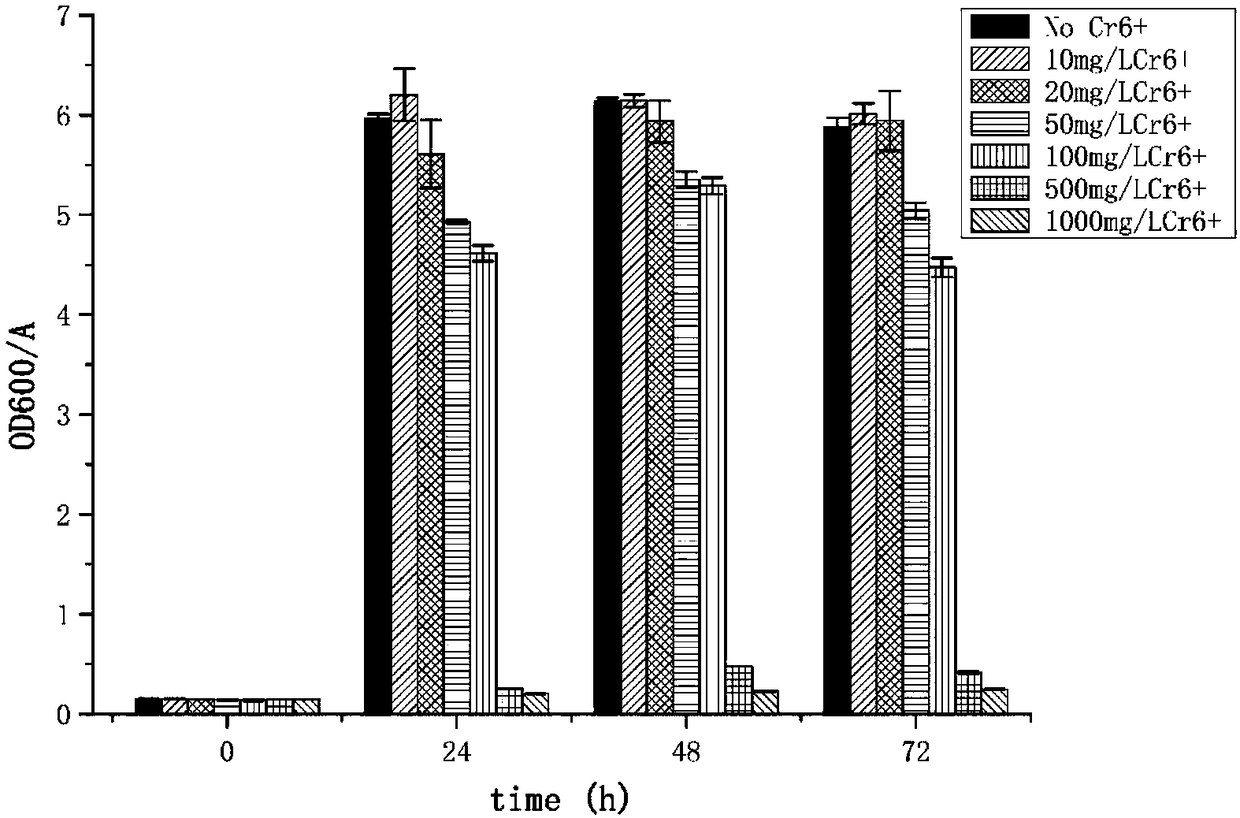
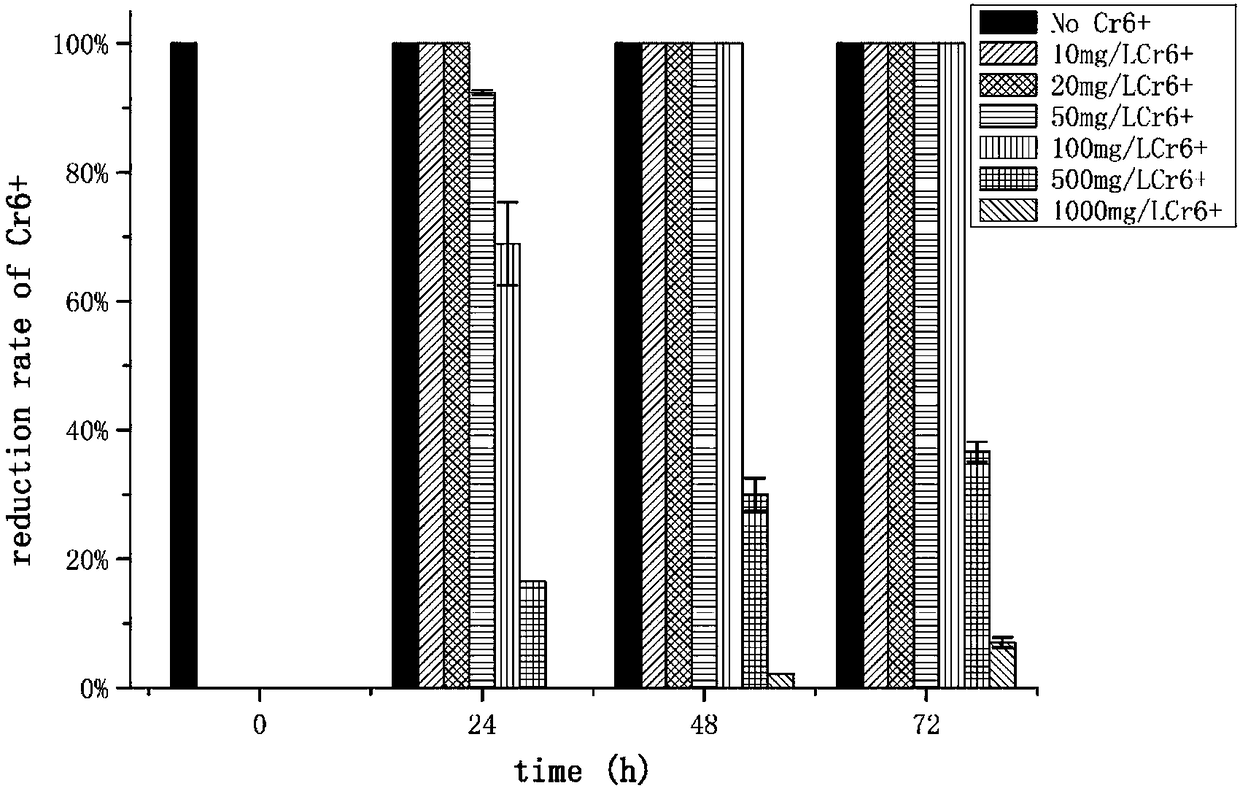
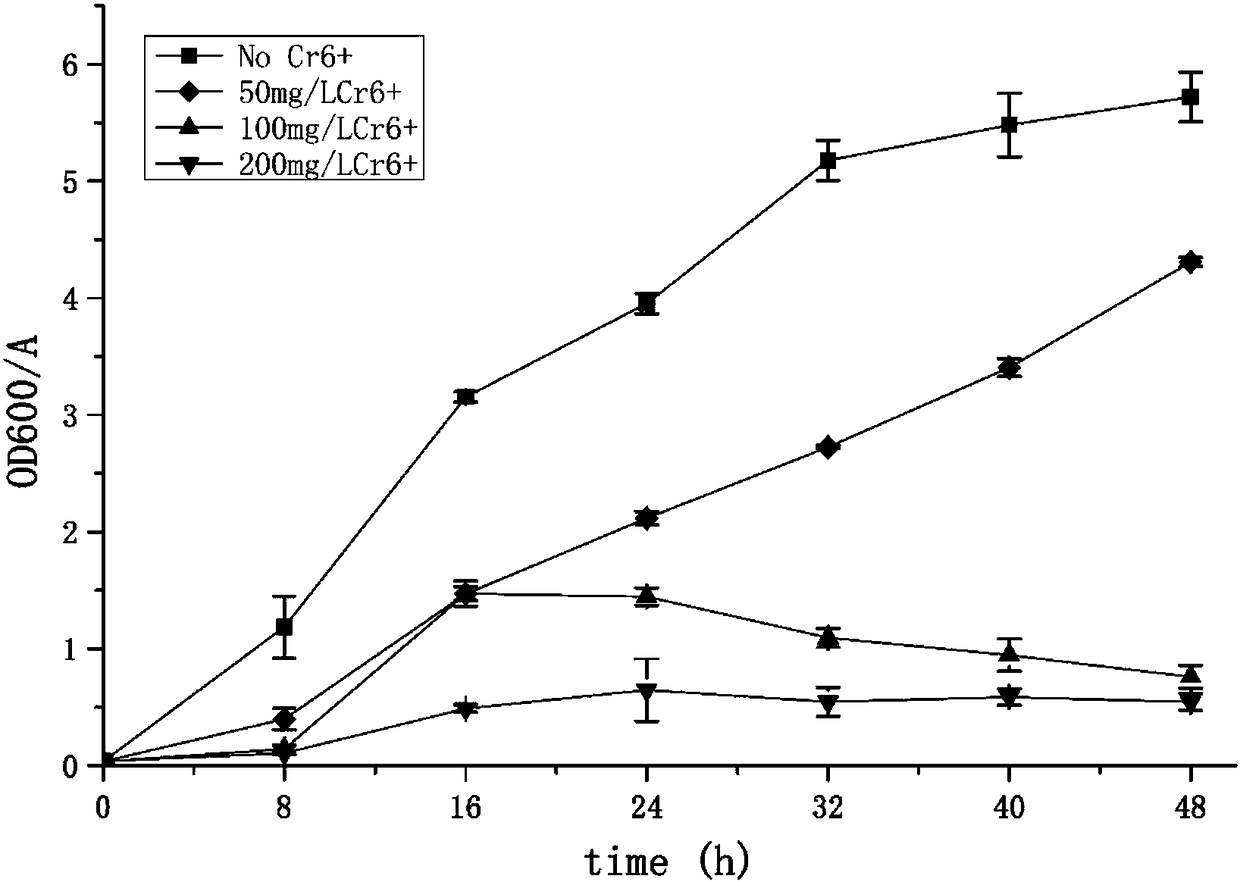
Application of Stenotrophomonas rhizophila DSM14405 in reduction of hexavalent chromium
ActiveCN108251327ALow toxicityReduce contentBacteriaWater contaminantsReduction rateStenotrophomonas rhizophila
The invention discloses application of Stenotrophomonas rhizophila DSM14405 in reduction of hexavalent chromium. The Stenotrophomonas rhizophila DSM14405 survives in an alkaline environment for reducing the hexavalent chromium to trivalent chromium, and the trivalent chromium is bonded with hydroxide to produce a chromium hydroxide precipitate. The Stenotrophomonas rhizophila DSM14405 has a fasterreduction rate of the hexavalent chromium, the reduction rate of the hexavalent chromium of 50 mg / L is up to 100% within 32 h, and the concentration tolerance to the hexavalent chromium is high. Whenthe concentration of the hexavalent chromium reaches 200 mg / L, thallus can also grow, and the reduction rate reaches 47.6% within 48 hours.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bacillus subtilis multifunctional bacterial strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104031864AHigh tolerance concentrationPromote growthBacteriaWater contaminantsCelluloseBroad spectrum
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis capable of degrading lignin, cellulose and broad-spectrum dye and capable of degrading chlorpyrifos. The bacterial can still well grows in 5% chlorpyrifos, has an excellent degrading capability to chlorpyrifos in soil and water, can form a stable community relationship with indigenous strains to synergetically degrade chlorpyrifos.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
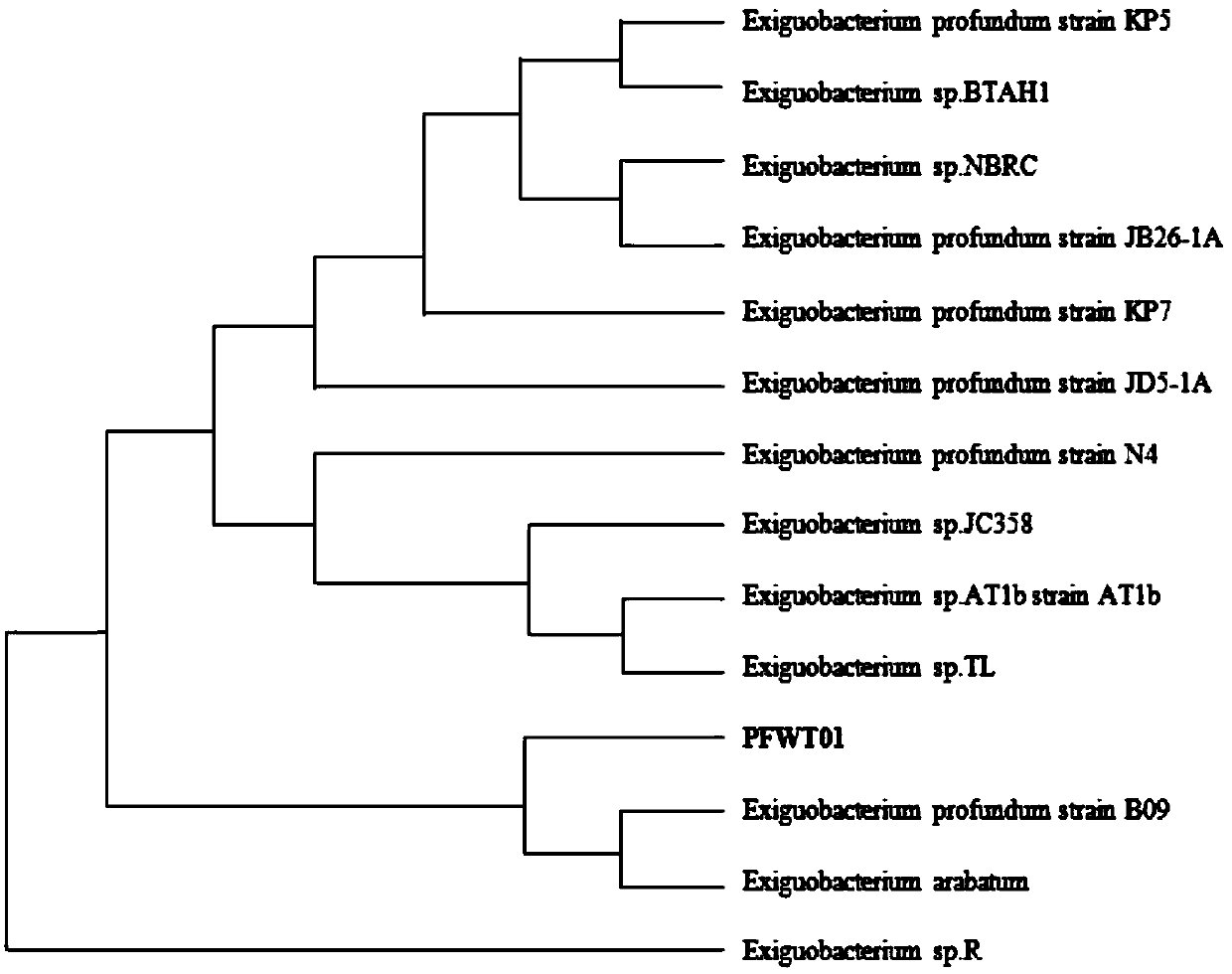
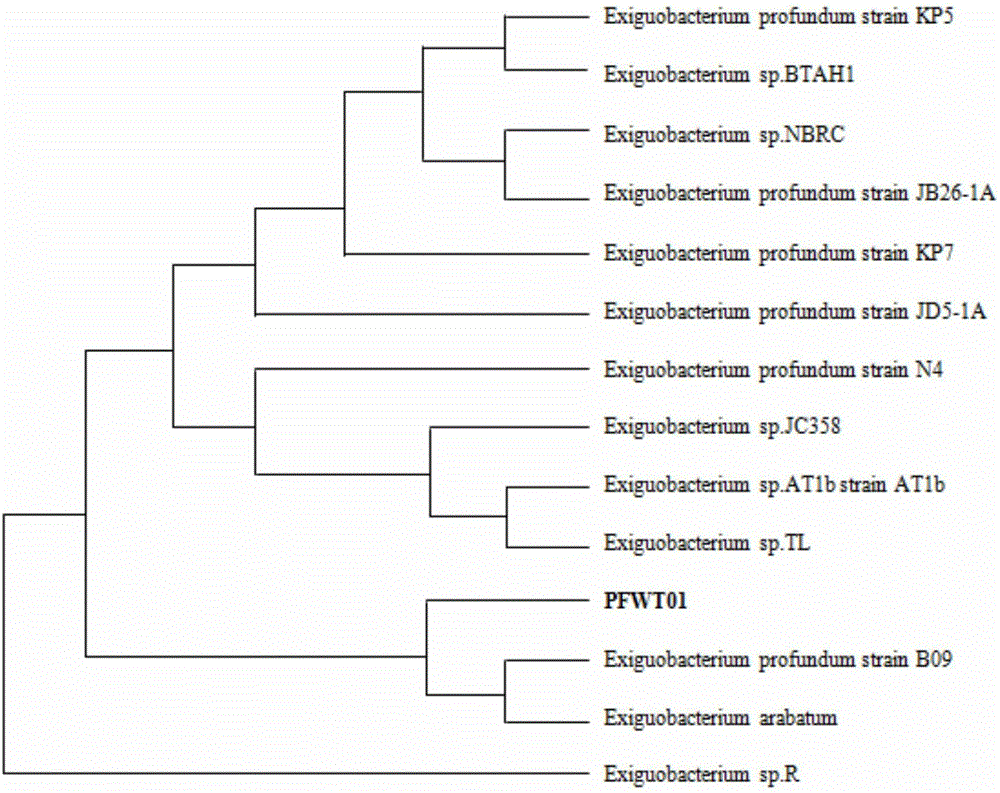
Exiguobacterium profundum having tolerance to vadaium and application of deep-sea exiguobacterium
ActiveCN106148239AImprove toleranceHigh tolerance concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismExiguobacterium
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, particularly relates to exiguobacterium profundum having tolerance to vanadium and application of exiguobacterium profundum and aims to provide a technical scheme for bioremediation of environment polluted by heavy metals. The collection number of exiguobacterium profundum PFWT01 is CCTCC NO:M2016175. Exiguobacterium profundum is highly tolerant to vanadium and has tolerance to heavy metals like Cr, Pb, Cu, Ni and Co, and tolerance to vanadium is up to 2000mg / L. Exiguobacterium profundum has capability of reducing pentavalent vanadium to tetravalent vanadium in a basic culture medium, conversion rate is up to 54.33%, toxicity of high-valence vanadium in a solution can be lowered, and exiguobacterium profundum can be applied to removing vanadium toxicity high-vanadium-toxicity liquid environment containing other heavy metal pollution especially, and has good application prospect in bioremediation of environment polluted by the heavy metals.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
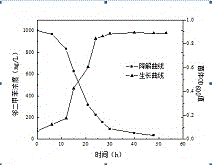
Method for synthesizing caproic acid by catalyzing lactic acid through microorganisms
ActiveCN104357496AHigh substrate selectivityMature methodMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismMetabolite
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing caproic acid by catalyzing lactic acid through microorganisms. According to the method, specific functional florae are adopted to biologically synthesize caproic acid from lactic acid in a culture liquid or wastewater. By adopting the method that lactic acid is adopted as the electron donor for producing caproic acid, the efficiency is increased by more than 20% when being compared with that of a conventional method that ethanol is adopted as an electron donor for producing caproic acid, the toxicity resistance concentration of the caproic acid functional bacterium to metabolites (caproic acid) is increased by more than 2 times when being compared with that of reported caproic acid bacteria, and the caproic acid functional bacterium has the characteristics of high conversion rate and high stress resistance. When the lactic acid as a non-fuel substance which is easy to obtain is converted into caproic acid, the conversion efficiency is high, and the high industrial practicability is achieved.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
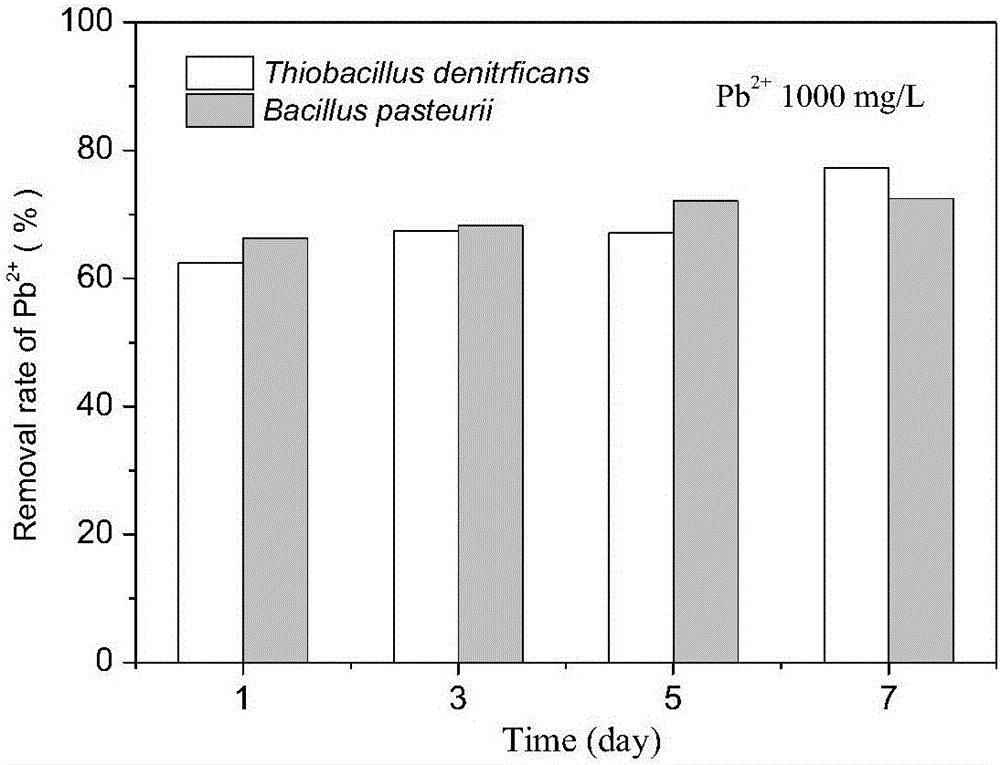
Method for joint treatment of lead ion pollution by using carbonate-mineralization microbe-thiobacillus denitrificans
ActiveCN106269850ATo achieve the purpose of removing heavy metalsImprove removal efficiencyWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationThiobacillusAmmonia
The invention discloses a method for joint treatment of lead ion pollution by using carbonate-mineralization microbe-thiobacillus denitrificans. The method includes the steps that nutritional ingredients like fertilizer containing urea and ammonia thiosulfate are applied to soil or a water body; the prepared carbonate-mineralization microbe (0.5*10<8>-5.0*10<8> cfu / mL) is added into the soil or the water body polluted by heavy metal according to the proportion of the soil (0.5-5.0L / m<2>) to the water body being 1:10-1:100; after the carbonate-mineralization microbe is cultivated for 1-5d, the prepared thiobacillus denitrificans with the bacterium concentration being 0.5*10<8>-5.0*10<8> cfu / mL is added according to the volume ratio of the soil (0.5-5.0L / m<2>) to the water body being 1:10-1:100 to be evenly stirred and mixed, and cultivation lasts for 3-15d; and the removal rate of heavy metal Pb2 reaches 83%-99%. The method is low in cost, high in efficiency, easy to implement and broad in application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
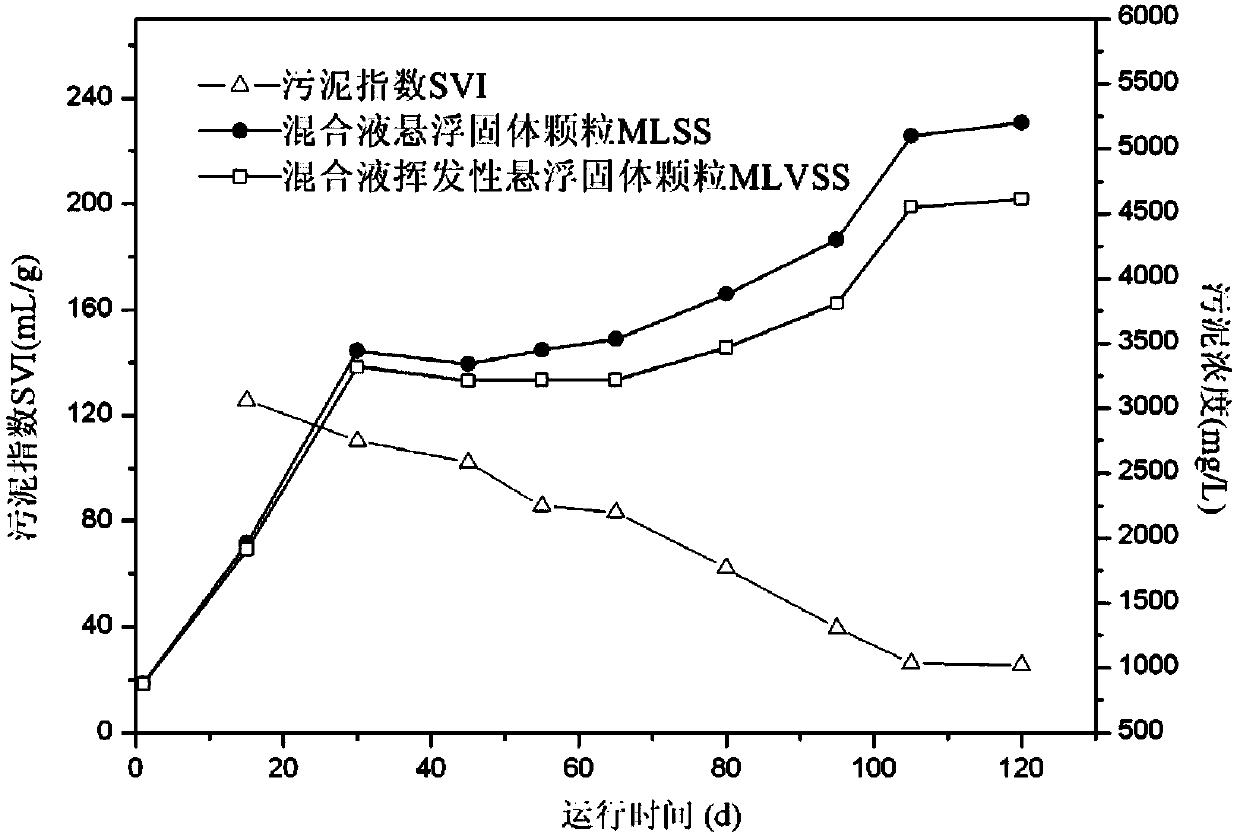
Aerobic granular sludge with pyridine degradation function as well as cultivation and application thereof
ActiveCN103626287ARegular shapeIncrease concentrationWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentFlocculationSequencing batch reactor
The invention discloses aerobic granular sludge with a pyridine degradation function as well as cultivation and application thereof. The sludge is obtained from a single strain (Rhizobiumsp.) NJUST18 with self-flocculation characteristics in a cultivation manner. A pyridine specific degradation strain (Rhizobiumsp.) NJUST18 is adopted as inoculum, a reactor form of a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is adopted, and formation of pyridine degradation particle sludge is facilitated by using the self-flocculation characteristic of the (Rhizobiumsp.) NJUST18 and controlling the parameters such as operation cycle, sedimentation time and organic load of an SBR system. The aerobic granular sludge with the pyridine degradation function can take pyridine as a sole carbon source and nitrogen source to grow. The aerobic granular sludge is regular in particle shape, good in settling property (the sludge index (SVI) value just is 25.6mL / g), high in sludge concentration of the reaction system (the concentration of mixed liquor volatile suspended solid (MLVSS) can be up to 4610mg / L), and high in degradation efficiency (the maximal degradation rate Vmax can be up to 1867.4mgl<-1>h<-1>). Complete degradation of 4200mg / L of pyridine can be achieved within 7.5 hours in the SBR system after the granular sludge is matured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
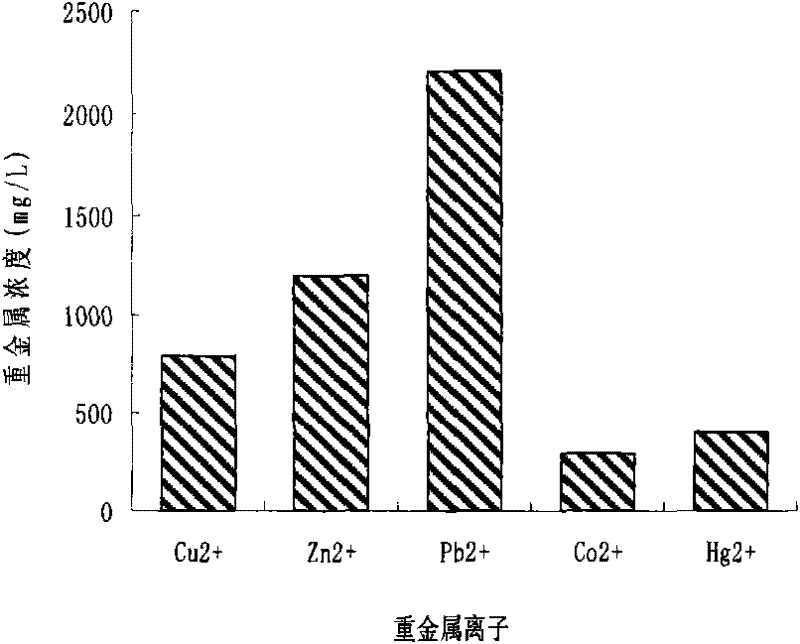
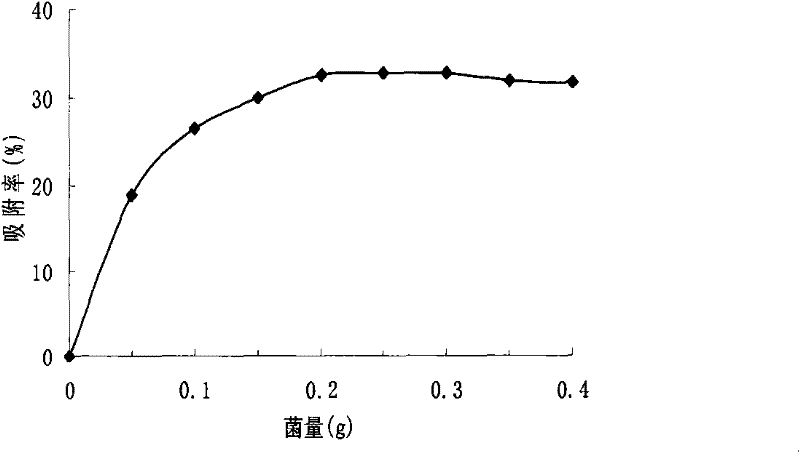
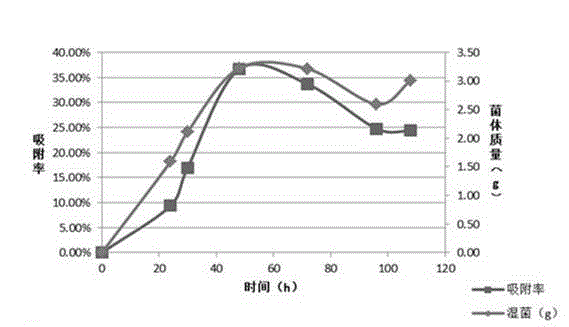
Acinetobacter and application thereof to biological treatment of heavy metal ions
InactiveCN101974448AHave tolerance propertiesHigh tolerance concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsAcinetobacter baumanniiIon
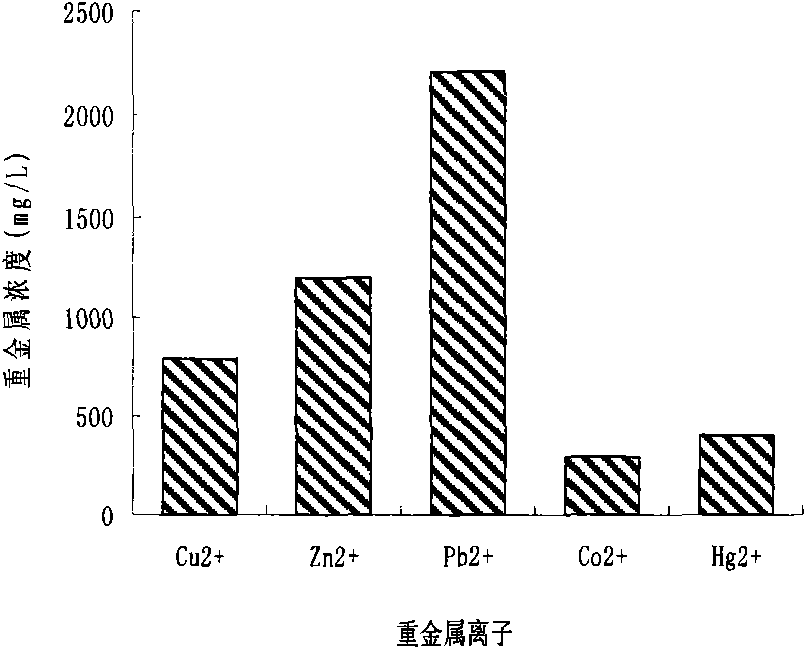
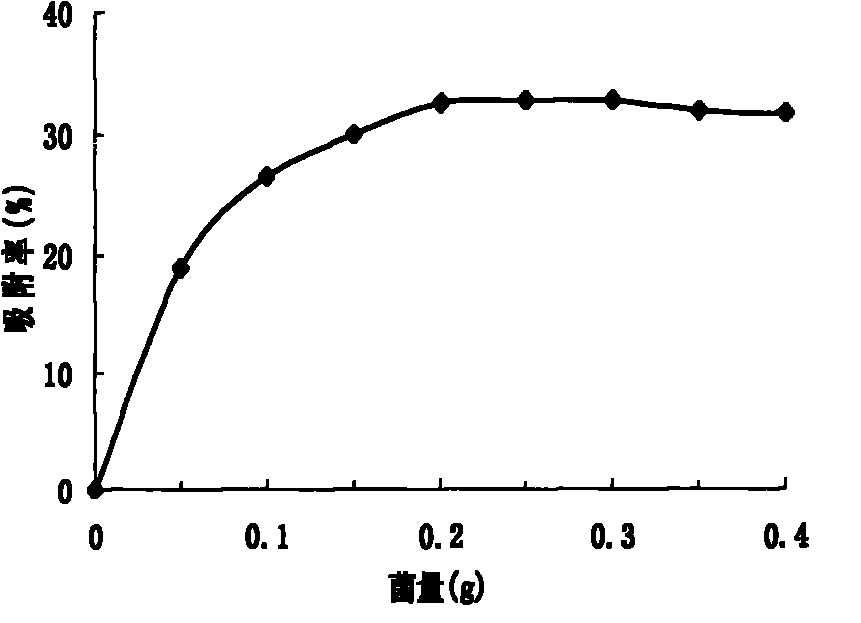
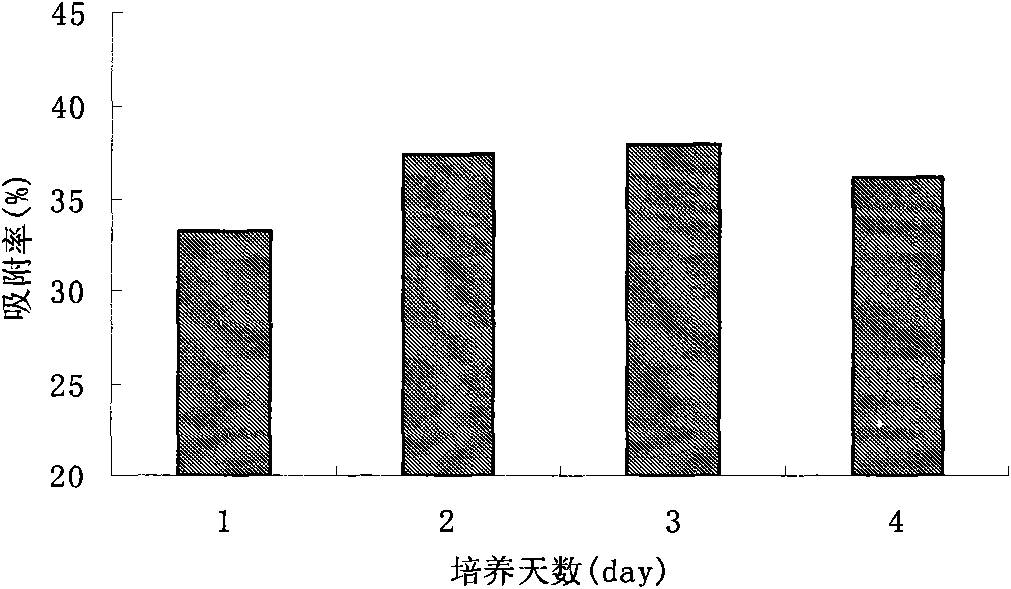
The invention discloses acinetobacter baumannii R9 CGMCC No.3947 and application thereof to the adsorption of heavy metal ions. The acinetobacter baumannii is tolerant to five types of ions, namely, Hg<2+>, Cu<2+>, Co<2+>, Pb<2+> and Zn<2+>, wherein the tolerance concentrations to Pb<2+> and Zn<2+> are highest and are up to 2,200 mg / L and 1,500 mg / L respectively; the tolerances to Cu<2+> and Hg<2+> are up to 800 mg / L and 400 mg / L respectively; and the tolerance to Co<2+> is 300 mg / L. Through the method, lead ions are adsorbed by the growth of thalli and can be directly adsorbed by using wet thalli of which the maximum adsorption capacity is up to 39.56 mg / g. The acinetobacter has good adsorption effect in the application of the heavy metal ions and good application prospect.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Cultivation method of high-selenium coprinus comatus
InactiveCN102763561AHigh fruiting body selenium contentIncrease selenium contentHorticultureFertilizer mixturesAnimal scienceAreal distribution
The invention method provides a cultivation method of high-selenium coprinus comatus. The cultivation method is achieved by configuring cultivation matrix composed of a basic cultivation material and selenium-rich cultivation material additive. The selenium-rich cultivation material additive occupies 1-10% of the total weight of a cultivation dry material, selenium amount of the selenium-rich cultivation material is 10-500mg / kg, particle size of particles in the selenium-rich cultivation material additive is in the range of 0.05-5.0mm, and the particles are in multi-particle-size areal distribution. The selenium-rich cultivation material additive comprises by weight, 100 parts of corncob powder or straw powder of other crops and 0.5-20 parts of organic selenium yeast. The coprinus comatus cultivated by the method has strong utilization ability of selenium, fruiting body selenium content is high, enrichment factor of a fruiting body to the selenium is high, the proportion of organic selenium in the fruiting body of the coprinus comatus accounting for the total selenium reaches up to above 90%, and the selenium shape is safe. The cultivation method of the high-selenium coprinus comatus is simple to operate and strong in practicability.
Owner:SUZHOU SETEK
Radiation-proof Fusarium sp. and application thereof to cesium adsorption biotreatment
InactiveCN104403951AHigh tolerance concentrationHave tolerance propertiesFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCesium adsorption
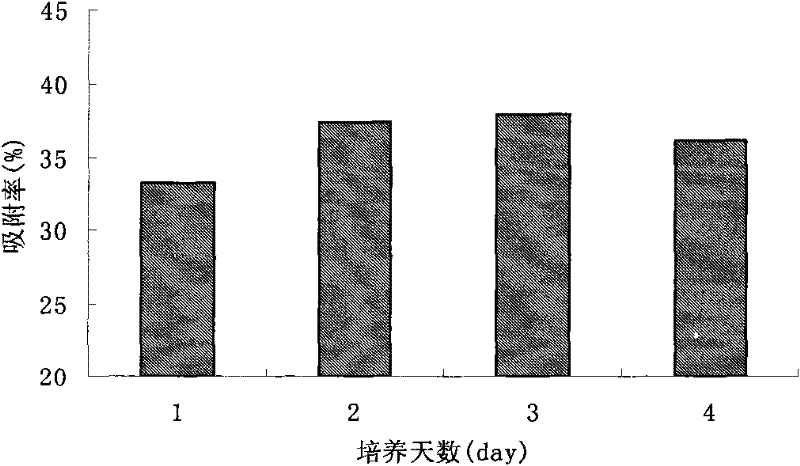
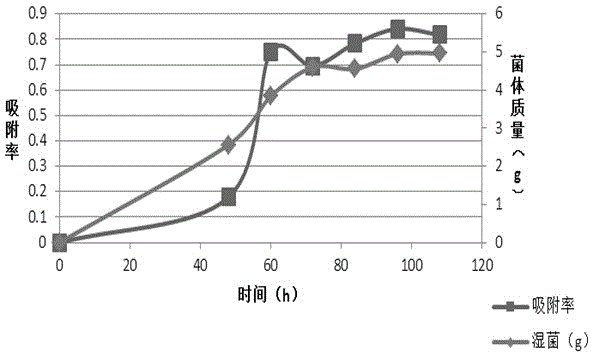
The invention discloses radiation-proof Fusarium sp. and application thereof to cesium adsorption biotreatment. Through providing of the self-screening radiation-proof Fusarium sp. F54 CGMCC No. 8359 and application thereof, tests show that the Fusarium sp. F54 CGMCC No. 8359 has tolerance to various metals, and has the maximal tolerance concentrations to Pb <2+>, Zn <2+> and Ni <2+>, which can respectively reach 1000 mg / L, 500 mg / L and 500 mg / L, and the tolerance to Co <2+>, Cr<2+> and Hg<2+> take second place and can reach 200 mg / L. When the radiation-proof Fusarium sp. strain is applied to cesium adsorption, remarkably obvious technical effects are achieved, and accordingly, a favorable application prospect of the radiation-proof Fusarium sp. in cesium adsorption biotreatment is testified.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Radiation-resistant Aspergillus sp. and application thereof in cesium 137 adsorption biological treatment
InactiveCN104087519AImprove adsorption capacityHave tolerance propertiesFungiOther chemical processesThallusBiologic treatment
The invention discloses a radiation-resistant Aspergillus sp. and application thereof in cesium 137 adsorption biological treatment. Sampling in a certain region, screening, separation, screening and physiologic and biochemical identification are performed to obtain the Aspergillus sp. F77 CGMCC No.8382. By utilizing the application of the Aspergillus sp. in cesium 137 adsorption biological treatment, the Aspergillus sp. has the maximal resistance concentrations for Pb<2+>, Zn<2+> and Ni<+>, which can respectively reach 1000 mg / L, 500 mg / L and 500 mg / L; and the resistance concentrations for Co<2+>, Cr<2+> and Hg<2+> take second place, and can respectively reach 200 mg / L. According to the method, the growing thallus can adsorb caesium ions and radiocesium, or the dry thallus can be directly used for adsorption, wherein the maximal adsorption capacity can reach 44.5 mg / g dry thallus. The application of the strain has actual value and functions in Cs 137 adsorption biological treatment.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Application of radiation resistant bacteria in biological treatment of heavy metal ions
InactiveCN102229896AHave tolerance propertiesHigh tolerance concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsRadiation resistantDeinococcus
The invention discloses an application of a radiation resistant bacteria Deinococcus wushiensis CGMCC No. 1.8884 in the biological treatment of heavy metal ions. The invention is characterized by: inoculating the bacterial strain Deinococcus wushiensis CGMCC No. 1.8884 to a liquid medium filled with 5ml TGY for cultivation at the temperature of 30 DEG C, carrying out a 200rpm shake cultivation for 36h, then cultivating according to an inoculation amount of 2%. The bacterial strain used in the invention has tolerance to Hg2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Pb2+ and Cr2+, wherein, the tolerance to Pb2+ and Cr2+ can reach to 150mg / L and 100mg / L respectively, and the tolerance to Cu2+ and Co2+ can reach to 80mg / L. The invention can be widely used in the field of environmental protection treatment of heavy metal waste liquor.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
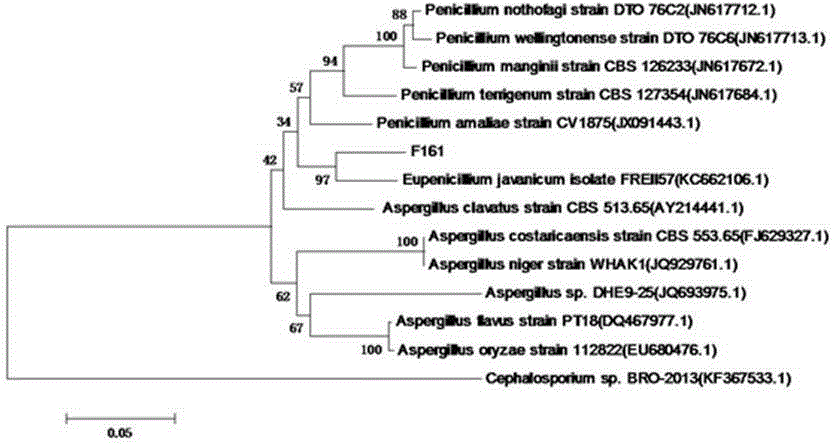
Radiation-resistant penicillium sp. and application to biological treatment of absorbing radioactive strontium 90
ActiveCN104152358AHigh tolerance concentrationFungiMicroorganism based processesStrontiumEupenicillium molle
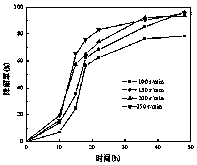
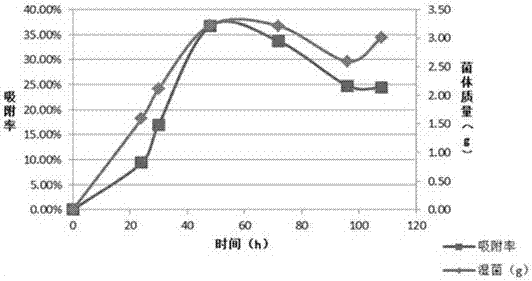
The invention discloses radiation-resistant penicillium sp. and application to the biological treatment of absorbing radioactive strontium 90. Penicillium sp. F161CGMCCNo.8381 is obtained by sampling, screening, separation, screening and physiological and biochemical identification. When being applied to the biological treatment of absorbing a radioactive substance, the Penicillium sp. F161CGMCCNo.8381 is tolerant to 16 heavy metals such as Pb<2+>, Zn<2+>, Ni<+>, Co<2+>, Cr<2+> and Hg<2+>, and the tolerated concentration can reach 200 mg / L; remarkable and obvious technical effects are achieved particularly when the Penicillium sp. F161CGMCCNo.8381 is applied to the absorption of the radionuclide strontium 90, so that the Penicillium sp. F161CGMCCNo.8381 is proven to have a broad application prospect in the biological treatment of absorbing strontium.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
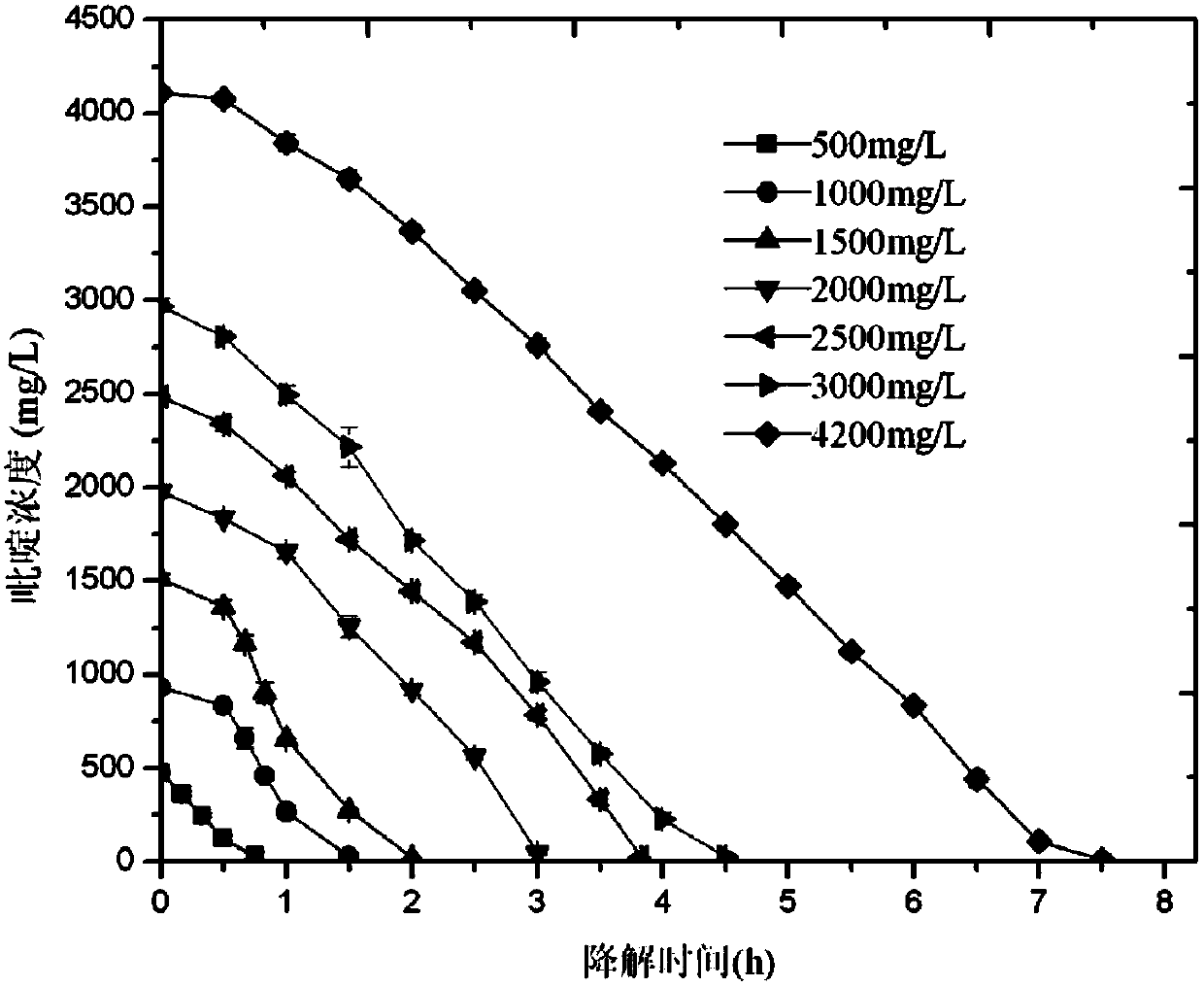
O-xylene degradation bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN105087429AFast degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsChemical oxygen demandPseudomonas stutzeri
The invention discloses an o-xylene degradation bacterium and application thereof. The o-xylene degradation bacterium OX5 provided by the invention belongs to pseudomonas sp., which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on June 29, 2015 with preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2015415. The bacterium is a Gram-negative bacterium that colony is round, slightly convex, milk white in space around while yellow in middle and is smooth and wet in surface. The bacterium can grow and reproduce by taking O-xylene as a unique carbon source; during pure culture, the degradation rate on 1500mg / L of O-xylene reaches up to 98% at 48th hour, and tolerance concentration to the O-xylene is 2500mg / L. The bacterium not only can degrade O-xylene and other benzene series in coking wastewater but also can reduce COD (chemical oxygen demand) in discharged coking biochemical water; and the bacterium is applicable to the biological enhancement treatment of cooking wastewater and is extensive in application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Trichoderma viridea LW-1 capable of degrading ethyl acetate and application of trichoderma viridea LW-1
ActiveCN104560728APromote degradationHigh tolerance concentrationFungiGas treatmentAcetic acidBenzene
The invention relates to trichoderma viridea LW-1 capable of degrading ethyl acetate and application of the trichoderma viridea LW-1 in degrading ethyl acetate, benzene, toluene, chlorobenzene, alpha-pinene or dichloromethane. The accession number of trichoderma viridea LW-1 is CCTCC NO: M2014176. The trichoderma viridea LW-1 provided by the invention can efficiently degrade target contaminants and is strong in endurance capability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
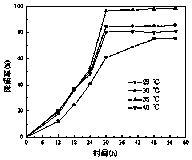
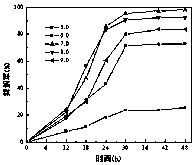
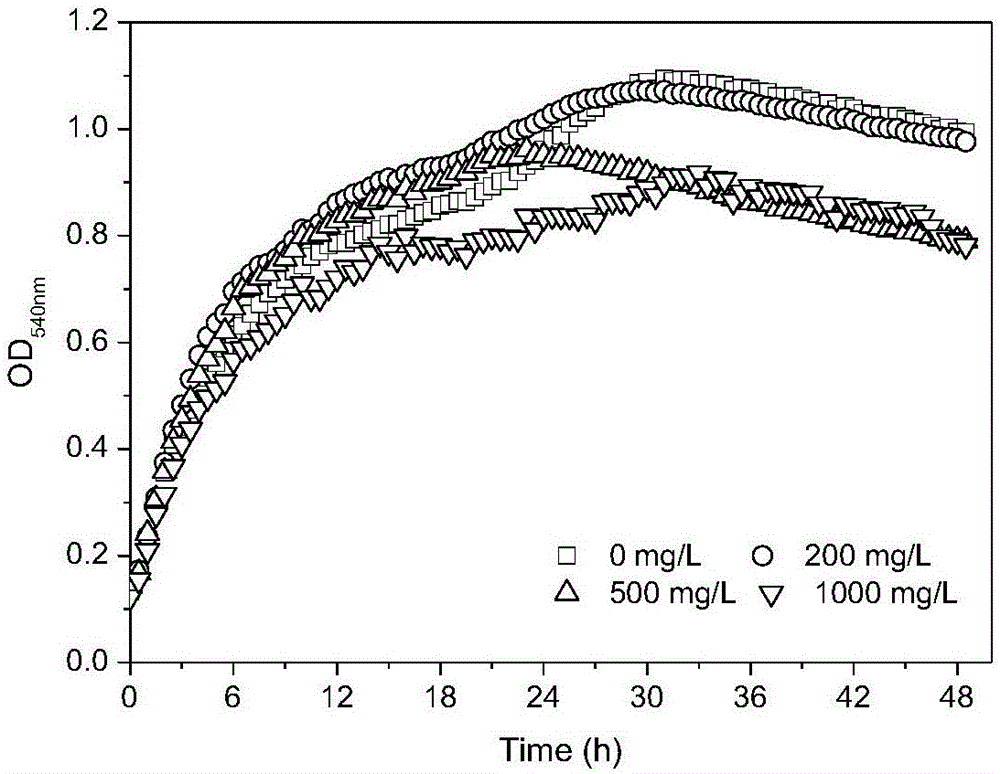
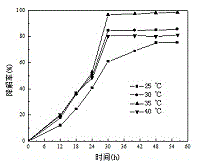
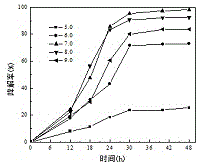
7[beta] hydroxy cholesterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
PendingCN112029740AHigh tolerance concentrationImprove toleranceOxidoreductasesFermentationKetoneMutant
The invention relates to a 7[beta] hydroxy cholesterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. Through mutant library construction and ahigh throughput screening method, an amino acid sequence disclosed by SEQ ID NO: 2 is obtained. Through error-prone PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), a key amino acid which affects the activity of 7[beta]-HSDH (hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) is determined, and the tolerated concentration of a 7[beta]-HSDH substrate is improved. The endurance capacity of the mutated 7[beta]-HSDH substrate is obviously enhanced than original 7[beta]-HSDH, and the mutated 7[beta]-HSDH substrate can endure 200 mmol / L of 7-ketone-lithocholic acid (7-KLCA (Ketolithocholic acid)) substrate concentration. The recombinant escherichia coli, which is constructed by the invention, of which the 7[beta]-HSDH secretion capacity is enhanced can improve 7[beta]-HSDH enzyme activity by 2.47 times than an original strain. The enzyme production ability of an improved genetically engineered bacterium is obviously improved, the genetically engineered bacterium is more suitable for industrial application, production cost isimproved, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGXI BONTAC GREEN BIOCATALYSIS ECOIND PARK CO LTD
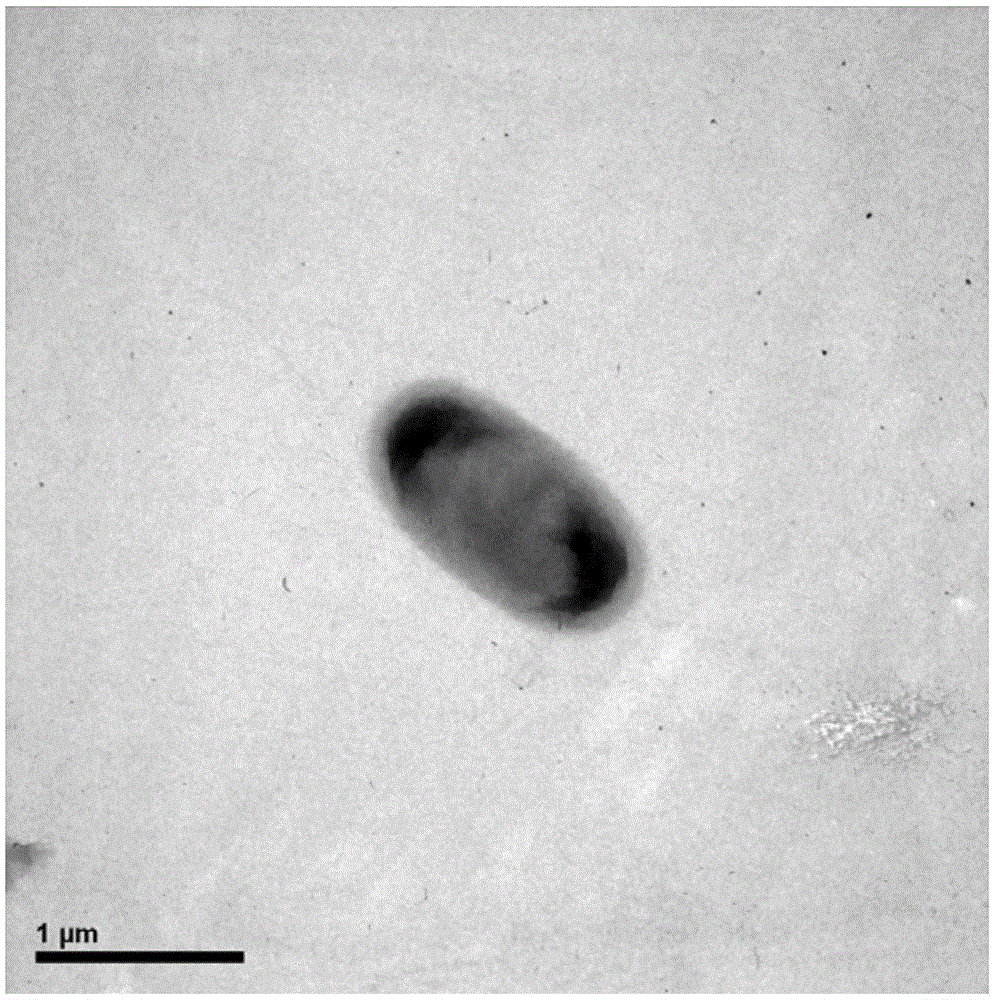
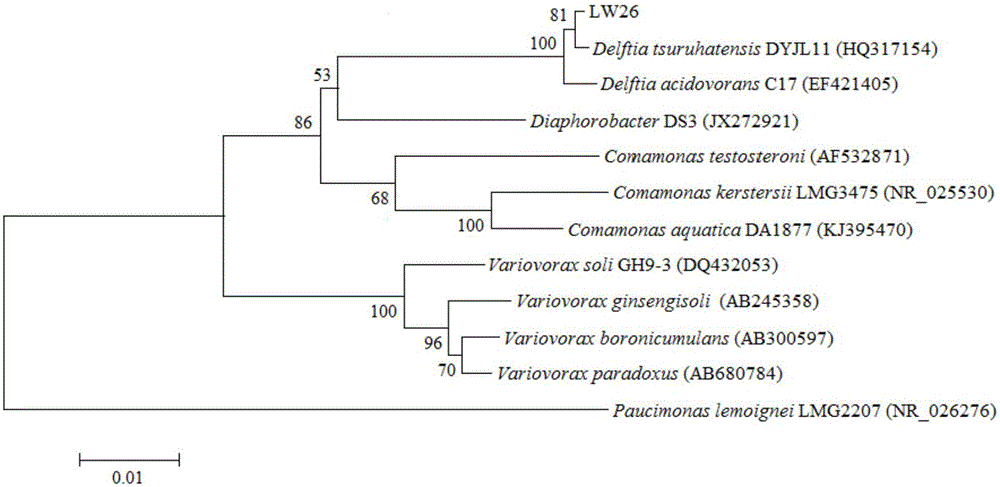
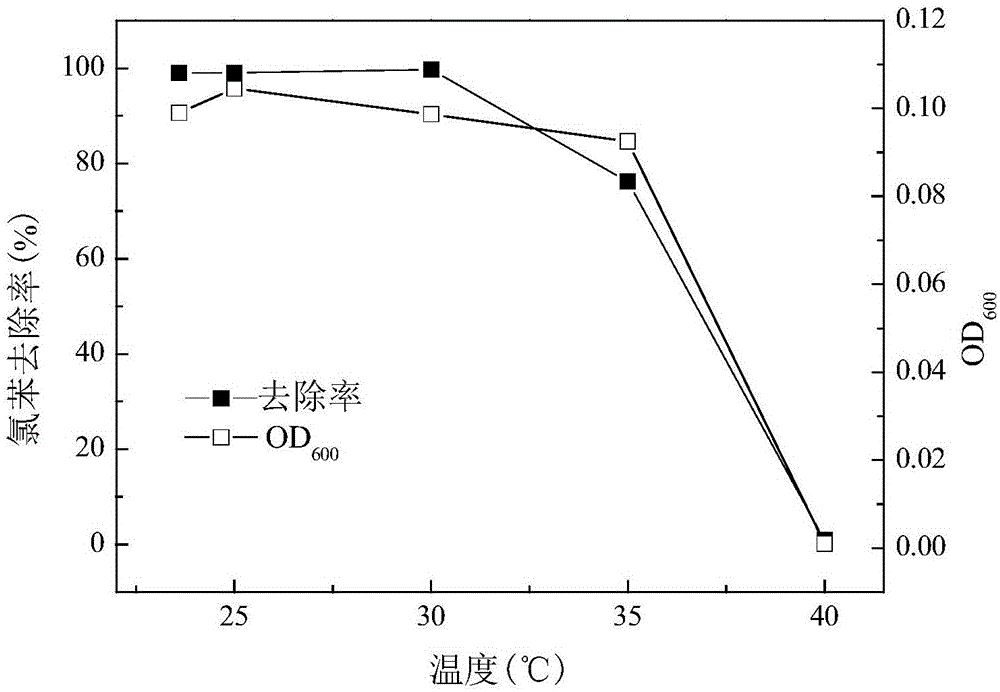
Delftia tsuruhatensis LW26 and application thereof in chlorobenzene degradation
ActiveCN105039222AHigh tolerance concentrationFast degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismChlorobenzene
The invention provides a strain Delftia tsuruhatensis LW26 which is capable of efficiently degrading chlorobenzene and application thereof in microbial decomposition and treatment of chlorobenzene. The Delftia tsuruhatensis LW26 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC): Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 430072, the preservation date is March 15, 2015 and a preservation number is CCTCC NO. M2015113. The chlorobenzene degradation bacteria provided by the invention can use chlorobenzene as a unique carbon source and energy for propagation and completely mineralize the chlorobenzene into CO2 and H2O; the strain can effectively degrade chlorobenzene in an environment of 23-30 DEG C and pH of 6.0-9.0; the strain has higher environment suitability and can play an important role in practice of waste gas and waste water treatment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A method for synthesizing hexanoic acid from lactic acid by microorganisms
ActiveCN104357496BHigh substrate selectivityMature methodMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismMetabolite
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing caproic acid from lactic acid by microorganisms. The method uses specific functional bacteria to biosynthesize caproic acid from lactic acid contained in culture fluid or waste water. The method uses lactic acid as an electron donor to produce caproic acid Compared with ethanol as the electron donor, the production efficiency of caproic acid is improved by more than 20%, and the toxicity tolerance concentration of the caproic acid functional bacteria of the present invention to metabolites (caproic acid) is more than 2 times higher than that of the reported caproic acid producing bacteria , has the characteristics of high conversion efficiency and strong stress resistance. Converting lactic acid, an easily available non-fuel substance, into caproic acid has high conversion efficiency and industrial applicability.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Assimilated nitrate nitrogen strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102220267AIncrease profitCause harmAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaMicroorganismBacillus megaterium
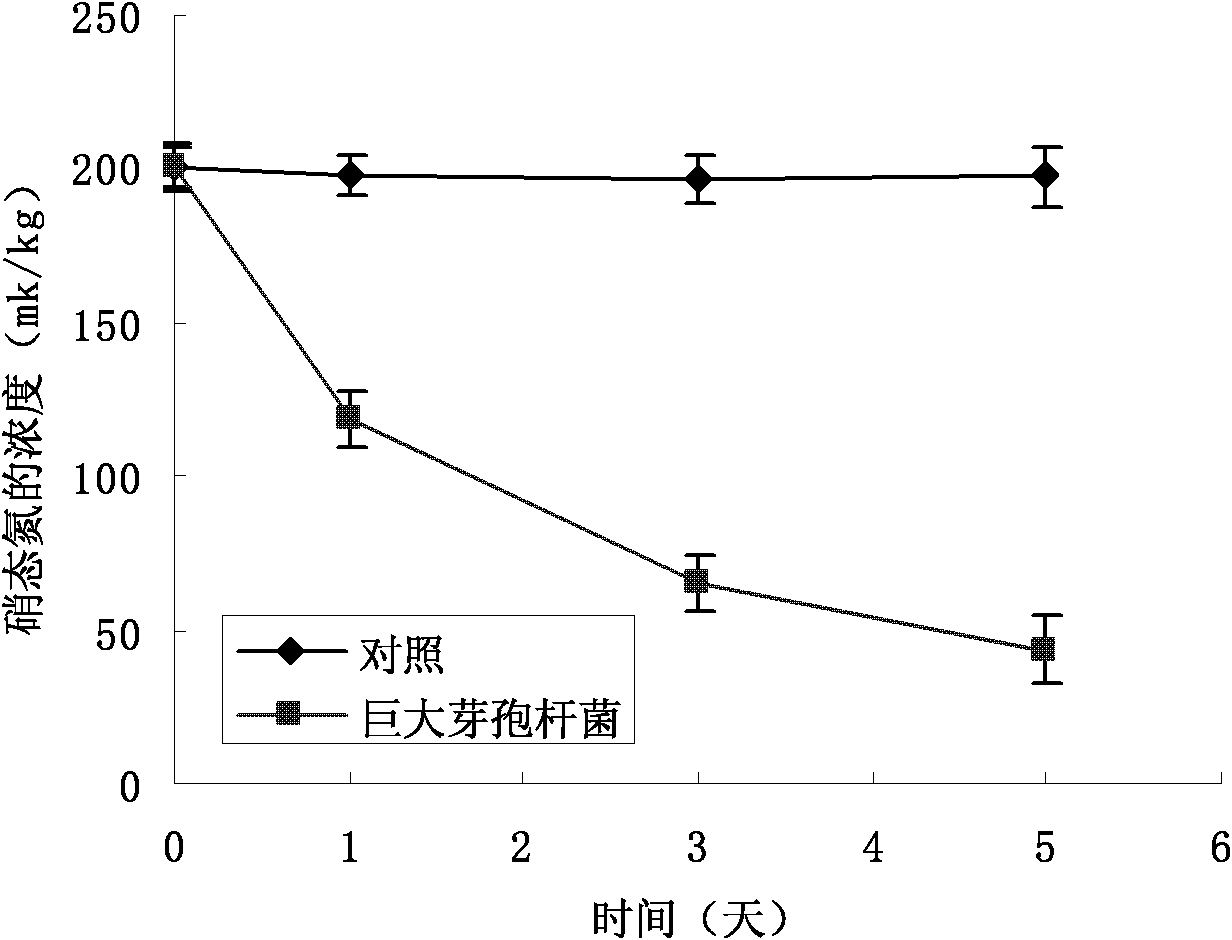
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganism soil processing, in particular to an assimilated nitrate nitrogen strain and application thereof. The strain is NCT-2 assimilated nitrate nitrogen strain, the classification name is Bacillus megaterium, the strain is preserved in the Chinese General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation date is March 21, 2011, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.4698. The invention can effectively assimilate the microorganisms of excessive nitrate nitrogen in facility cultivation soil.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Enterobacter bacteria for efficiently degrading organophosphorus pesticides and culturing method thereof
InactiveCN101818122AHigh tolerance concentrationImprove toleranceBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacteroidesSucrose
The invention provides enterobacter bacteria for efficiently degrading organophosphorus pesticides and a culturing method thereof. The enterobacter bacteria are characterized in that the main biological property of the enterobacter bacteria is Gram-negative, thalli are in a short-rod shape without spores, and the size is 0.6-1.1*1.2-2.5 mum; and the enterobacter bacteria have single-end overgrowing flagella and are aerobic bacteria, the optimum growing temperature is 30-37 DEG C, the optimum pH value is 7-8, the enterobacter bacteria form a bacterial colony with the diameter of 1-2 mm after being cultured on a blood agar medium for 48 h, and the bacterial colony is circular in shape and yellow in color, has no transparence, knurls, trim edge and moist and glossy surface. The Genbank login number of the bacterial strain 16SrDNA is GQ380575. The tolerance concentration of the bacterial strain on parathion-methyl and Dursban can reach 5000 mg / L in an inorganic salt medium containing 1% of cane sugar, the tolerance concentration on dimethoate reaches 10000 mg / L, the tolerance capacity of the bacterial strain is furthest higher than that of agricultural dose used in agricultural production, the degradation rate for the organophosphorus pesticides in soil reaches above 90%, and the enterobacter bacteria solve the problem that pesticide residues in the agricultural production exceed the standard, and can be used for producing green and nuisanceless agricultural products.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
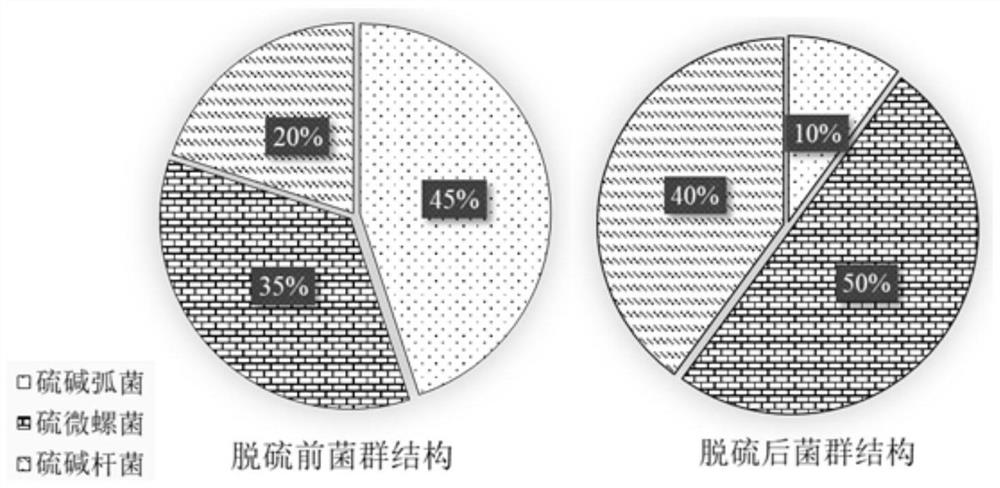
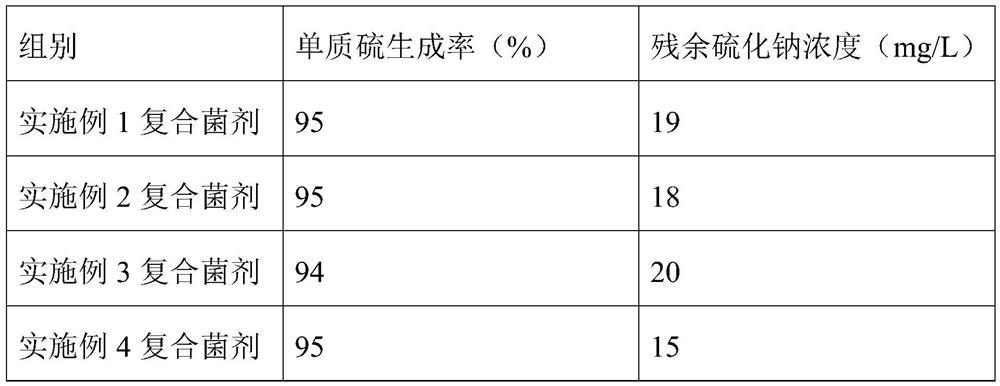
Halophilic and basophilic sulfur oxidation complex microbial inoculant as well as preparation method and application thereof in biological desulfurization
ActiveCN111996134AHigh tolerance concentrationStrong toleranceBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyThiobacillus
The invention relates to a halophilic and basophilic sulfur oxidation complex microbial inoculant as well as a preparation method and application thereof in biological desulfurization. The halophilicand basophilic sulfur oxidation complex microbial inoculant comprises vibrio thioalkaligenes, thiobacillus thiospirillum and thiobacillus thiooxidans. The halophilic and basophilic sulfur oxidation complex microbial inoculant has the capacity of oxidizing sulfide to generate elemental sulfur, the yield of the elemental sulfur can reach 85% or above, and the removal rate of the sulfide reaches 99%or above; and the halophilic and basophilic sulfur oxidation complex microbial inoculant can better meet the requirements of industrial desulfurization, the indexes such as the elemental sulfur generation rate and the sulfide removal rate of the halophilic and basophilic sulfur oxidation complex microbial inoculant reach or exceed those of a single strain, the application range of a biological desulfurization technology can be expanded, the capacity of coping with complex working conditions is enhanced, the system stability is improved, and the desulfurization effect is enhanced.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
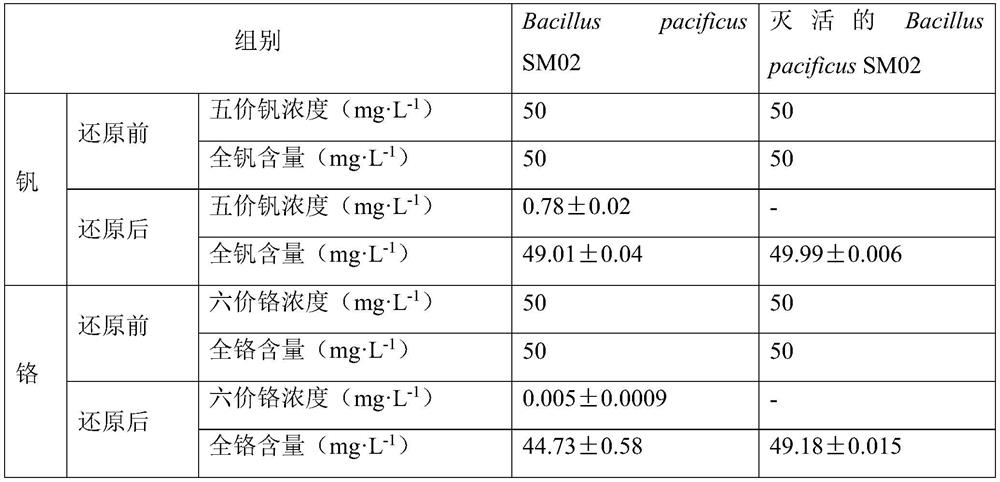
Bacillus separated from soil and application thereof
ActiveCN114292792AImprove toleranceHigh tolerance concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismChromium contamination
The invention relates to bacillus separated from soil and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The first technical problem solved by the invention is to provide the bacillus separated from the soil. The bacterium is bacillus pacificus SM02 separated from soil, and is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on August 16, 2021, and the preservation number of the bacterium is CCTCC NO: M 20211039. The Bacillus pacificus SM02 has high tolerance to vanadium and chromium in the environment, the tolerance concentration of the Bacillus pacificus SM02 to vanadium and chromium reaches up to 1200 mg.L <-1 > and 1000 mg.L <-1 >, the Bacillus pacificus SM02 can adapt to the survival condition of a high background pollution area, the bacterium can completely reduce hexavalent chromium, the reduction rate of 98.43 + / -0.42% to pentavalent vanadium is achieved, the reduction rate is high, the operation process is simple, convenient and efficient, and the method is suitable for industrial production. And a foundation is laid for a vanadium and chromium pollution bioremediation technology.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
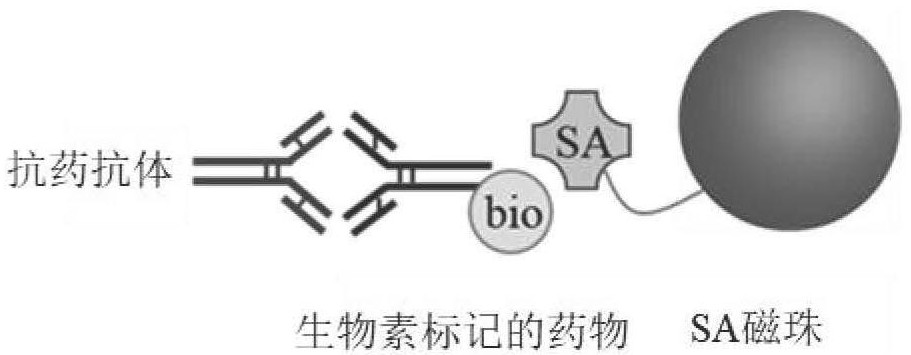
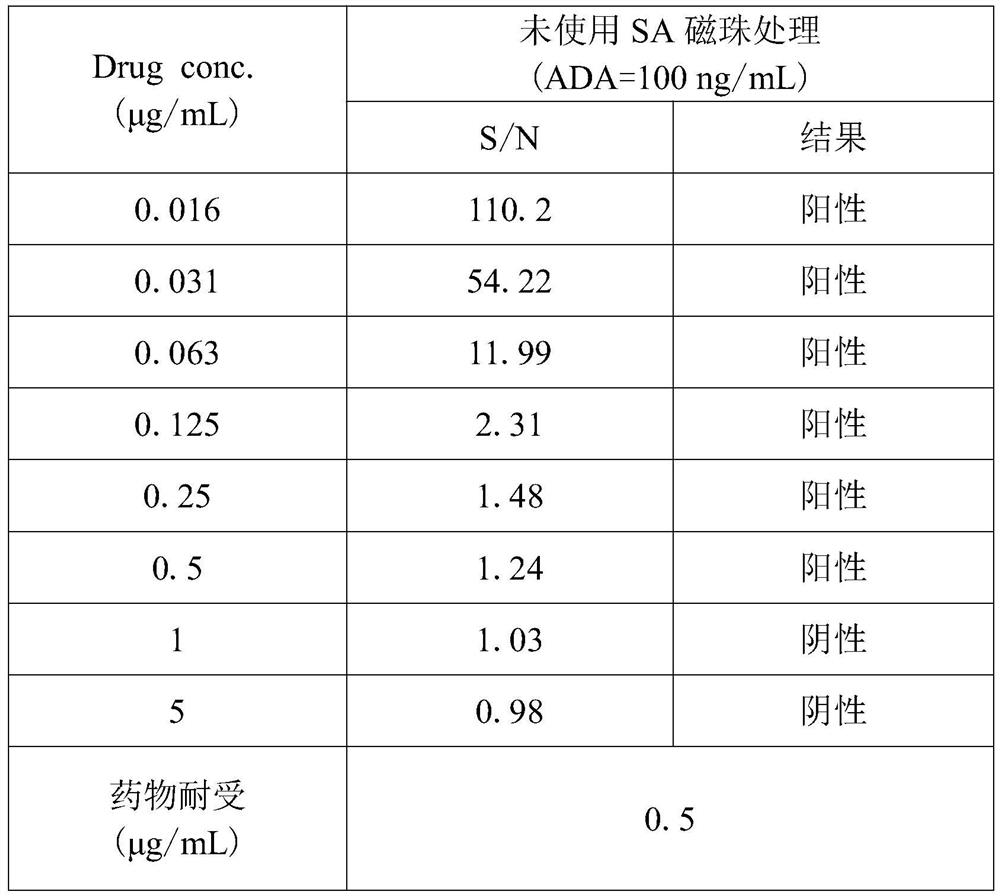
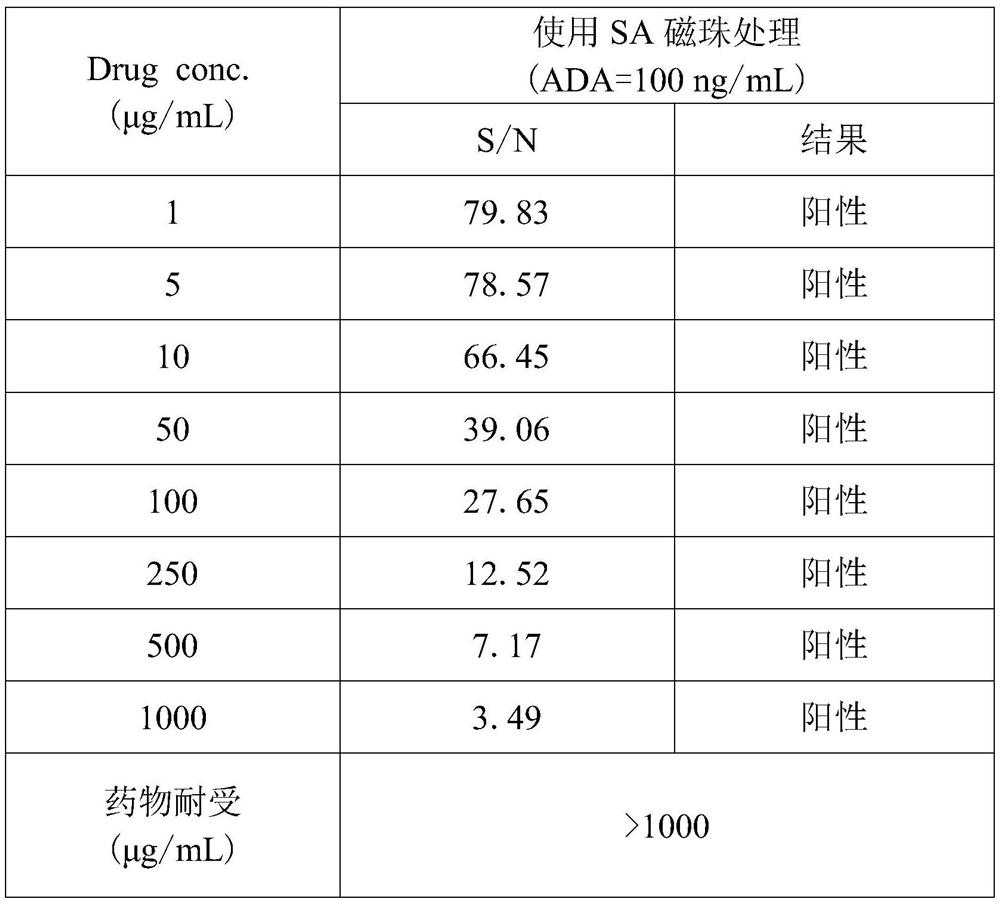
Operation method for improving drug tolerance in drug-resistant antibody analysis
PendingCN113607520AHigh tolerance concentrationHigh detection sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses an operation method for improving drug tolerance in drug-resistant antibody analysis. The operation method comprises the following specific steps: acidifying a sample; carrying out SA magnetic bead cleaning and sealing; incubating the biotin labeled medicine; enriching the magnetic beads; acidifying the magnetic beads; and neutralizing and incubating. According to the operation method for improving drug tolerance in drug-resistant antibody analysis, the sample is treated through magnetic bead enrichment, the grabbing and enrichment efficiency of ADA is greatly improved, therapeutic protein products in the sample are effectively removed, the therapeutic protein products are prevented from being combined with ADA again, and the complexity of later detection is reduced. The ADA enriched by the magnetic beads can be dissociated through acidolysis and then can be subjected to later detection. Compared with a traditional method, the drug tolerance concentration of the method is improved by more than thousands of times.
Owner:湖州中科湖兴生物科技有限公司
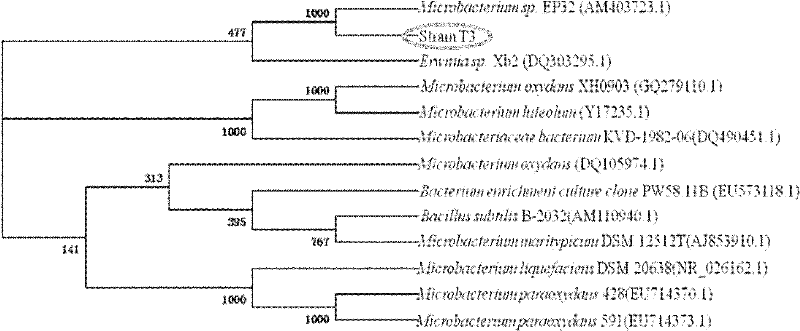
Microbacterium sp.T3 with tolerance on heavy metals and application thereof
ActiveCN102127516BImprove toleranceHigh tolerance concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyMicrobiology
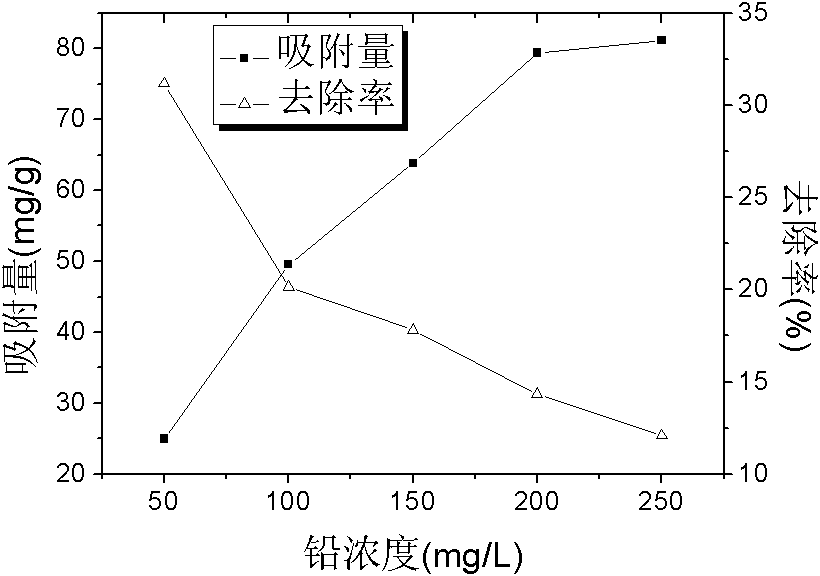
The invention discloses a Microbacterium sp.T3 with tolerance on heavy metals and application thereof. The Microbacterium sp.T3 is preserved with the number of CGMCCNo.4282. The bacterium can tolerate a plurality of heavy metals such as Pb<2+>, Cr<6+>, Mn<2+>, Zn<2+>, Cu<2+>, Ni<2+>, Cd<2+>, Co<2+>, Ag<+>, Hg<2+>, and the like, particularly has the tolerance concentration on the Pb<2+> and the Mn<2+> respectively reaching 2000mg / L and 1000mg / L. Strains are activated, cultured, collected, cleaned and dried to prepare an adsorbent in which heavy metals are removed. The maximum adsorption capacity on Pb<2+> as one of the heavy metals can reach 87.49mg / L.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Heavy metal-tolerant bacterial strain and application thereof
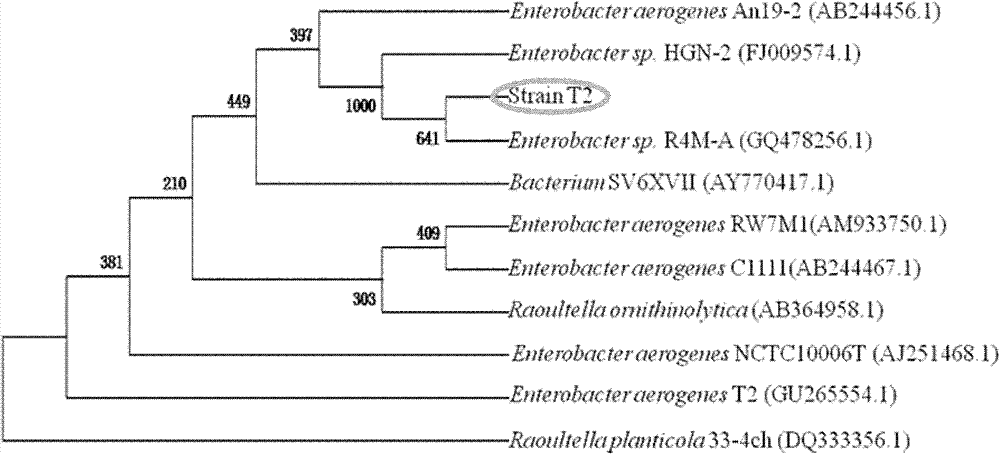
ActiveCN102191191BImprove toleranceHigh tolerance concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsEnterobacter spMicrobiology
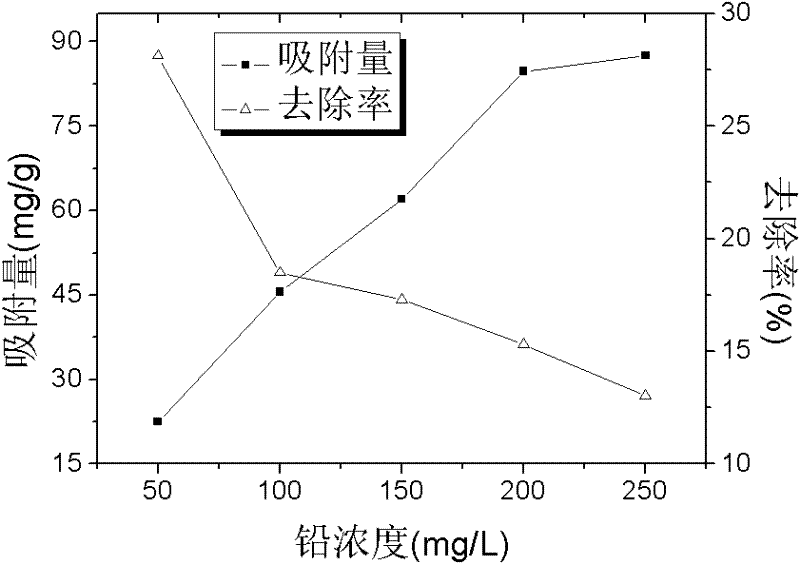
The invention discloses a heavy metal-tolerant bacterial strain Enterobacter sp.T2 and application thereof. The collection number of the heavy metal-tolerant bacterial strain Enterobacter sp.T2 is CGMCCNo.4281. The heavy metal-tolerant bacterial strain Enterobacter sp.T2 can tolerate various heavy metals such as Pb<2+>, Cr<6+>, Mn<2+>, Zn<2+>, Cu<2+>, Ni<2+>, Cd<2+>, Co<2+>, Ag<+>, Hg<2+> and thelike, in particular, the Pb<2+> tolerance concentration and the Mn<2+> tolerance concentration are more than 2,000 mg / L and 1,000 mg / L respectively. A heave metal-removed adsorbent is prepared by activating, culturing, collecting, washing and drying the bacterial strains and the maximum adsorption quantity of the heavy metal Pb<2+> can reach 81.22 mg / g.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
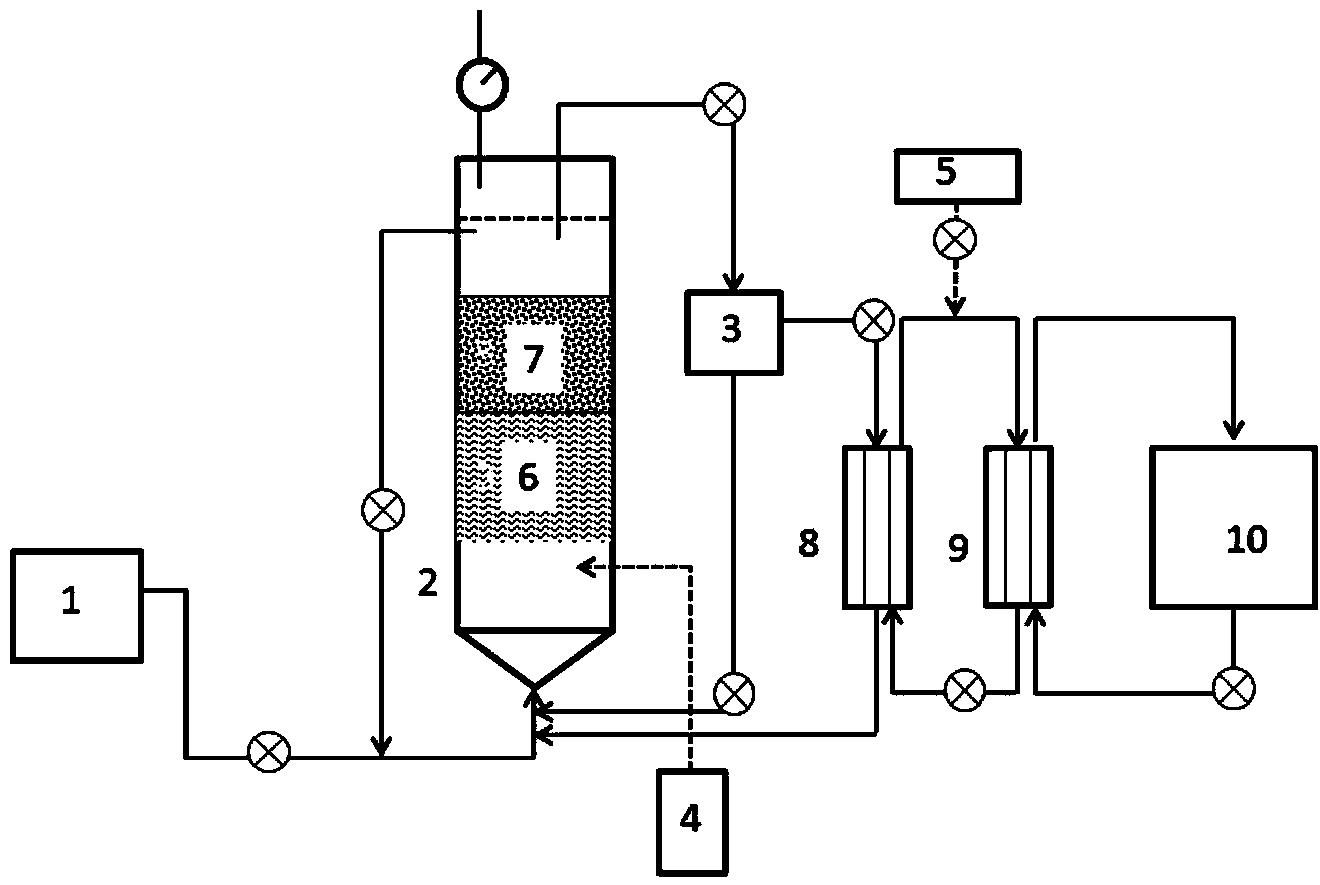
Membrane filter
InactiveCN100342956CImproved pollution resistanceExtended service lifeReverse osmosisAeration systemControl system
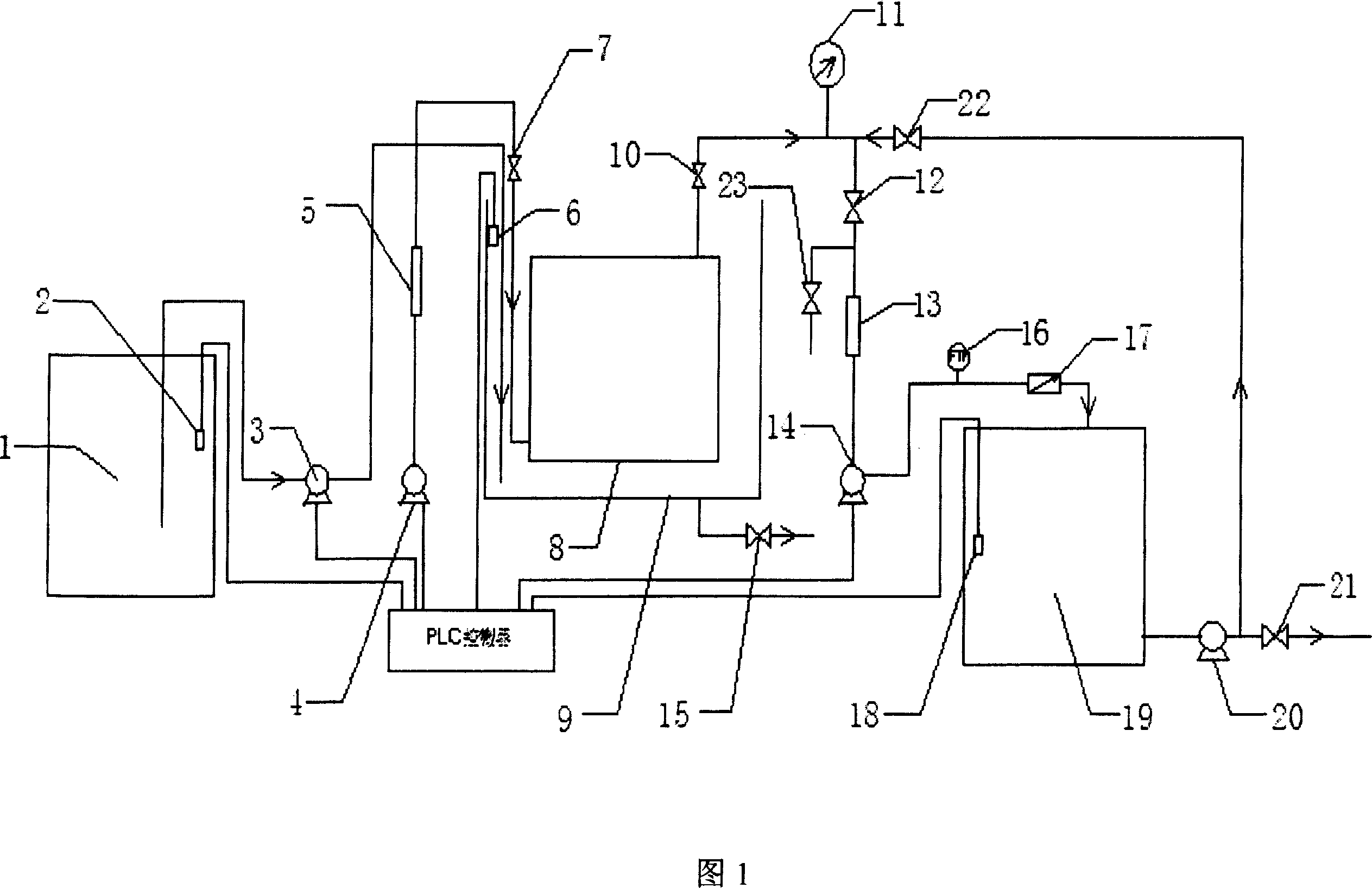
The membrane filter apparatus includes a water inlet system, a membrane filter system, a water producing system, an aeration system and a control system. The membrane filter system includes membrane filter tank and inside immersed modules, which has gas inlet pipe connected via the aeration system to the control system, water outlet port connected to the water producing system via valve and pressure meter and 2-10 membrane assemblies comprising curtain type membrane and connected to the aeration system via pipeline. The aeration system includes blower, gas flow meter, aeration regulating valve and aeration pipe connected successively via pipes and connected to the control system. The control system has PLC controller and corresponding software. The membrane filter apparatus is used in pre-treatment of sea water and the unique aeration mode results in raised antifouling capacity and long service life of the membrane and stable water output quality and amount.
Owner:TIANJIN MOTIAN MEMBRANE ENG & TECH
A Strain of Ortho-Xylene Degrading Bacteria and Its Application
ActiveCN105087429BFast degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsCoking wastewaterPure culture
The present invention disclosed a neighboring germinated bacteria and its application.The neighboring vitamin degradation OX5 provided by the present invention belongs to Pseudomonas SP. It is located in a typical cultivation center in China. The storage date is June 29, 2015, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2015415.The bacteria is the Gram -negative bacteria. The colonies are round and slightly convex. The colonies are milky white, yellow in the middle, and the surface is moist and smooth.The bacteria can use neighbors as the only carbon source for growth and reproduction. When pure cultivation, the degradation rate of 48H to 1500mg / L neighboring t atr is as high as 98%, and the tolerance concentration of neighboring toluene reaches 2500mg / L.This bacteria can not only degrade the neighboring dysfamer and other benzene in the coking wastewater, but also reduce the COD in the coking biochemical water, which is used for biological reinforcement treatment of coking wastewater and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A radiation-resistant Penicillium and its application in biological treatment of adsorbed radioactive strontium 90
ActiveCN104152358BHigh tolerance concentrationFungiMicroorganism based processesRadiation resistantMedicine
The invention discloses radiation-resistant penicillium sp. and application to the biological treatment of absorbing radioactive strontium 90. Penicillium sp. F161CGMCCNo.8381 is obtained by sampling, screening, separation, screening and physiological and biochemical identification. When being applied to the biological treatment of absorbing a radioactive substance, the Penicillium sp. F161CGMCCNo.8381 is tolerant to 16 heavy metals such as Pb<2+>, Zn<2+>, Ni<+>, Co<2+>, Cr<2+> and Hg<2+>, and the tolerated concentration can reach 200 mg / L; remarkable and obvious technical effects are achieved particularly when the Penicillium sp. F161CGMCCNo.8381 is applied to the absorption of the radionuclide strontium 90, so that the Penicillium sp. F161CGMCCNo.8381 is proven to have a broad application prospect in the biological treatment of absorbing strontium.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Deep-sea microbacterium with tolerance to vanadium and use thereof
ActiveCN106148239BImprove toleranceHigh tolerance concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismEnvironmental engineering
The invention belongs to the field of microbes, and in particular relates to a deep-sea microbacterium resistant to vanadium and its application. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide a technical solution for the bioremediation of the environment polluted by heavy metals. The technical solution of the present invention to solve the technical problem is to provide a deep-sea microbacterium Exiguobacterium profundum PFWT01, and its preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2016175. In addition to being highly resistant to vanadium, the bacterium has tolerance to heavy metals such as Cr, Pb, Cu, Ni, Co, etc., and its tolerance to vanadium is as high as 2000mg / L; The ability to reduce to tetravalent vanadium, with a conversion rate of 54.33%, can reduce the toxicity of high-valent vanadium in the solution, especially for the removal of vanadium toxicity in high-vanadium-toxic liquid environments polluted by other heavy metals. It has a good application prospect in restoration.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Acinetobacter and application thereof in biological treatment of heavy metal ions
InactiveCN101974448BHave tolerance propertiesHigh tolerance concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsAcinetobacter baumanniiAdsorption effect
The invention discloses acinetobacter baumannii R9 CGMCC No.3947 and application thereof to the adsorption of heavy metal ions. The acinetobacter baumannii is tolerant to five types of ions, namely, Hg<2+>, Cu<2+>, Co<2+>, Pb<2+> and Zn<2+>, wherein the tolerance concentrations to Pb<2+> and Zn<2+> are highest and are up to 2,200 mg / L and 1,500 mg / L respectively; the tolerances to Cu<2+> and Hg<2+> are up to 800 mg / L and 400 mg / L respectively; and the tolerance to Co<2+> is 300 mg / L. Through the method, lead ions are adsorbed by the growth of thalli and can be directly adsorbed by using wet thalli of which the maximum adsorption capacity is up to 39.56 mg / g. The acinetobacter has good adsorption effect in the application of the heavy metal ions and good application prospect.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A radiation-resistant Fusarium fungus and its application in biological treatment of adsorbed cesium
InactiveCN104403951BHigh tolerance concentrationHave tolerance propertiesFungiMicroorganism based processesRadiation resistantCesium adsorption
The invention discloses a radiation-resistant Fusarium sp. and its application in the adsorption of radionuclide cesium. By providing a self-screening radiation-resistant Fusarium sp. (Fusarium sp.) F54 CGMCC No.8359 and its application, the test passed It is proved that the radiation-resistant Fusarium sp. F54 CGMCC No.8359 strain is tolerant to various metals, among which the tolerance concentration to Pb2+, Zn 2+ and Ni+ is the highest, which can reach 1000 mg / L respectively , 500 mg / L and 500 mg / L; the tolerance to Co2+, Cr2+, Hg2+ is next, all up to 200 mg / L. At the same time, the application of the strain in the adsorption of radionuclide cesium has achieved remarkable and obvious technical effects, which proves that the strain has a good application prospect in the biological treatment of cesium adsorption.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![7[beta] hydroxy cholesterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof 7[beta] hydroxy cholesterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e693f613-306d-42fe-ac68-99f71a7b6d67/RE-HDA0002724945270000011.png)
![7[beta] hydroxy cholesterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof 7[beta] hydroxy cholesterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e693f613-306d-42fe-ac68-99f71a7b6d67/RE-HDA0002724945270000012.png)
![7[beta] hydroxy cholesterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof 7[beta] hydroxy cholesterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e693f613-306d-42fe-ac68-99f71a7b6d67/BDA0002683023040000051.png)